Economics 102: Macroeconomics Ch 8. Macroeconomic Equilibrium
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Inflation
the rate at which prices increase
the rate at which money loses its value
Nominal
valued in current market prices
Real
adjusted for price fluctuations
GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
the total value of all goods and services produced
is reported by quarter or by year, and by country
Inflation Rate
the weighted average prices increase of a predetermined basket of goods and services
Real Output
the total value of production as measured by inflation-adjusted dollars
the total value of all output as measured in today’s dollars
Real GDP
the gross domestic product as measured by inflation-adjusted dollars
How do increases in the price level impact GDP?
As price levels decrease, GDP increases, and vice-versa.
Because GDP is measured in currency terms, increases in price levels increase GDP, even if output stays the same.
Price levels and GDP are not directly correlated.
Increases in price levels increase GDP, since this implies increased economic output.
Because GDP is measured in currency terms, increases in price levels increase GDP, even if output stays the same.
What is the equation for the GDP deflator?
1 + inflation rate
1 / (1 + Inflation Rate)
1 * (Inflation Rate)
1 / (Inflation Rate)
1 + inflation rate
If nominal GDP is $10 billion and the inflation rate is 5%, then what is real GDP?
Just over $10 billion
$10.5 billion
About $9 billion
About $9.5 billion
About $9.5 billion
How do real GDP and nominal GDP differ?
Nominal GDP removes the effect of price levels on real GDP.
Nominal GDP includes the dollar value of services, while real GDP only includes the dollar value of tangible products.
Real GDP removes the effect of price levels on nominal GDP.
Real GDP includes the dollar value of services, while nominal GDP only includes the dollar value of tangible products.
Real GDP removes the effect of price levels on nominal GDP.
Which of the following BEST defines inflation?
The rate at which GDP increases.
The rate at which prices increase.
The difference between nominal GDP and real GDP.
The rate at which output increases or decreases.
The rate at which prices increase.
Full Employment GDP
a term used to describe an economy that is operating at an ideal level of employment, where economic output is at its highest potential
Potential Output
the highest level of real GDP that an economy can sustain over time
Frictional Unemployment
unemployment that occurs during this time is when workers are in between jobs
Which of the following statements regarding full employment GDP is FALSE?
Aggregate supply equals aggregate demand
Savings equals investment
Unemployment is at zero percent
Inflation is not accelerating
Unemployment is at zero percent
What is full employment GDP?
When unemployment is higher than GDP
An equilibrium where aggregate supply is equal to aggregate demand in the short term and the long term
When unemployment is equal to 0%
An equilibrium where the supply of money is equal to the demand for money
An equilibrium where aggregate supply is equal to aggregate demand in the short term and the long term
What is the non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment?
When the economy is above the full employment level and prices are rising rapidly
When the economy is at full employment and prices are stable
When inflation is negative
When the economy is in recession and therefore not accelerating
When the economy is at full employment and prices are stable
Why is unemployment not equal to zero at the full employment level of output?
There is cyclical unemployment, driven entirely by the economic cycle.
There is always a shortage of workers.
There is frictional unemployment, when some workers are in between jobs.
It does not account for government employees.
There is frictional unemployment, when some workers are in between jobs.
Classical economists also refer to full employment as _____.
recessionary gap
aggregate demand
zero unemployment
potential output
potential output
Expansion
economic output is at its potential
real GDP is positive, and inflation and unemployment are low
Peak
actual output is above potential output
at the peak of a business cycle, real GDP is growing quickly, inflation is higher, and unemployment is very low
Recession/Contraction
actual output is below potential output
in a recession, real GDP shrinks for at least six months in a row, prices are falling, and unemployment is higher
Trough
actual output is way below potential output
real GDP has been shrinking but has reached the bottom and is about to grow again. inflation is very low, and unemployment may stay high for a while
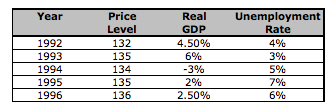
According to this chart, what was the unemployment rate during the peak of the business cycle?
3%
6%
5%
4%
7%
3%
What happens to real GDP, prices and unemployment at the peak of a business cycle?
Real GDP grows, prices fall, and unemployment is high.
Real GDP shrinks, prices rise, and unemployment is low.
Real GDP grows, prices fall, and unemployment is low.
Real GDP grows, prices rise, and unemployment is low.
Real GDP shrinks, prices fall, and unemployment is low.
Real GDP grows, prices rise, and unemployment is low.
Which of the following are the two phases and the two turning points of the business cycle?
Expansion and recession, intermediate 1 and intermediate 2
Recession and advance, peak and trough
Expansion and recession, peak and trough
Expansion and reversal, peak and prosperity
Growth and contraction, market top and market bottom
Expansion and recession, peak and trough
What happens to economic output as measured by GDP during a recession?
It contracts for at least three years in a row.
It falls more than the stock market does.
It contracts for at least two years.
It contracts for at least six months.
It contracts for one month.
It contracts for at least six months.
Economists recognize that the economy doesn't grow smoothly, but in regular patterns. Which of these terms best describes this?
The Classical Model
The circular flow of economic activity
A recession
The Keynesian Cycle
The Business Cycle
The Business Cycle
Recession
the contraction phase of the business cycle. it begins after the economy reaches a peak of activity and ends as the economy reaches its trough
Depression
prolonged period of economic recession marked by a significant decline in income and employment
caused by the same factors that lead to a recession
What's a depression?
A prolonged period of economic recession marked by significant declines in income and population
A brief period of economic recession marked by significant declines in income and employment
A brief period of economic recession marked by significant declines in income and population
A prolonged period of economic recession marked by significant declines in income and employment
A prolonged period of economic recession marked by significant declines in income and employment
Which of the following statements about the Great Recession is TRUE?
Unemployment reached 25% and median household wealth declined by around 50%.
Unemployment reached 10% and median household wealth declined by around 50%.
Unemployment reached 25% and median household wealth declined by around 40%.
Unemployment reached 10% and median household wealth declined by around 40%.
Unemployment reached 10% and median household wealth declined by around 40%.
What common rule of thumb do economists use to define a recession?
A decline of 10% in GDP
Two quarters (six months) of negative GDP growth
One quarter of negative GDP growth
A decline of 5% in GDP
Two quarters (six months) of negative GDP growth
Which of the following statements regarding recessions is FALSE?
They are the contraction phase of the business cycle.
They are very rare.
They begin after the economy reaches a peak of activity and end with a trough.
They last at least six months.
They are very rare.
How do the effects of the Great Depression and the Great Recession compare to each other?
Unemployment was higher and household values fell by more in the Great Depression.
Unemployment was higher in the Great Recession, but household values fell by more in the Great Depression.
Unemployment was higher and household values fell by more in the Great Recession.
Unemployment was higher in the Great Depression, but household values fell by more in the Great Recession.
Unemployment was higher in the Great Depression, but household values fell by more in the Great Recession.