Test: We the People - Unit 1
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All the terms from "We the People" Unit 1.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

60 Terms
Sugar Act of 1764
An act that raised tax revenue in the colonies for the British monarchy. It also increased the tax on foreign sugar imported to the Americas.

Colonies
Lands that are controlled by another nation
Patriot
An American colonist who favored American independence.

George Washington
1st President of the United States and commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution.

Marquis de Lafayette
French aristocrat and soldier who served under George Washington in the American Revolution.

Mutiny
Open rebellion against authority.

Loyalist
American colonists who remained loyal to Britain and opposed the war for independence.

Aristocrat
A member of a rich and powerful family.

Treaties
Formal agreements between nations.

Treaty of Paris
Agreement signed by British and American leaders that stated the United States of America was a free and independent country.

Charles Cornwallis
British general who surrendered at Yorktown ending the American Revolution.

King George III
King of England during the American Revolution.

Taxes
Required payments to a government.

Tyranny
Cruel and oppressive government rule.

Boycott
A refusal to buy or use goods and services.

Boston Massacre
An incident in 1770 in which British troops fired on and killed American colonists.

Patrick Henry
An American leader from Virginia who spoke out against British rule of the American colonies; coined the phrase "Give me liberty or give me death."
Thomas Jefferson
An American Patriot from Virginia and the author of the Declaration of Independence.

Colony
A group of people in one place who are ruled by a parent country elsewhere.
Diverse
Anything that has a great deal of variety, like ideas or people.

Founders
The people who were involved in establishing the United States via the Declaration of Independence.

Indentured Servants
Colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a specific number of years.

Plantation
A large estate farmed by many workers, typically in the American south.

Self-sufficient
Being able to produce enough for one's own needs.

Subject
Someone who owes allegiance to a government or ruler.

Slave
A person who is the legal property of another person and is forced to obey them against their will.

Natural Rights
The idea that all humans are born with rights, which include the right to life, liberty, and property.

Consent to be Governed
The idea that government derives its authority from the people it governs.

Social Contract
An agreement between the people and their government signifying their consent to be governed.

Civic Virtue
Willingness on the part of citizens to sacrifice their self-interests for the public good.

Common Good
The good of the community as a whole.

Direct Democracy
A form of government in which citizens rule directly and participate in all aspects of government.

Representative Democracy
A system of government in which citizens elect representatives to make decisions and laws for all people.

Constitution
A set of rules and laws that explain how a government is organized and how it will run.

Limited Government
The idea that certain restrictions should be placed on government to protect the natural rights of citizens.

Right to Life
The right to live without fear of being injured or killed.

Right to Property
The right to own things such as land and ideas.

Right to Liberty
The right to be free.

Consent
Giving permission to do something.

State of Nature
A condition in which no governments or laws existed at all; anarchy.

Interests
A specified common concern of a person or group of people.

Constitutional Government
A government whose power is defined and limited by law.
Dictatorial Government
Government in which the rulers have unlimited power.

Roman Republic
Government of Rome from 509 BCE to 27 BCE. Thought to be one of the first true representative democracies.

Represent
To be appointed to act or speak for someone else, especially in an official capacity.

Representatives
A person chosen or appointed to act or speak for another person or a community.

Limit
A point beyond which something cannot go.

Republican Government
Another name for a representative democracy; citizens elect representatives to rule on their behalf.

American Revolution
A war from 1775 - 1783 between Britain and the American colonies.
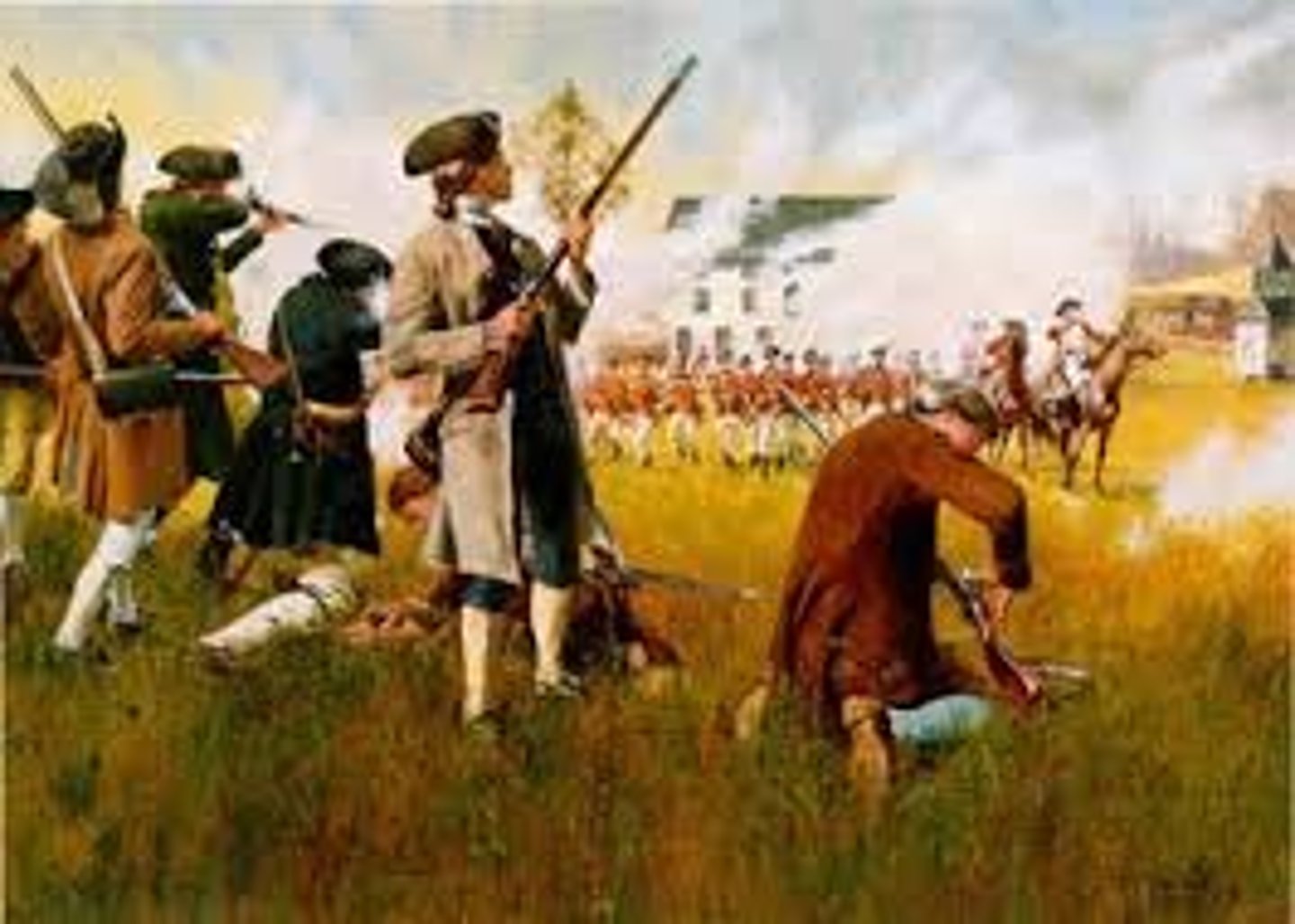

First Continental Congress
A 1774 meeting in Philadelphia where 12 of the 13 colonies attempted to get the British to change unfair laws that were affecting them.
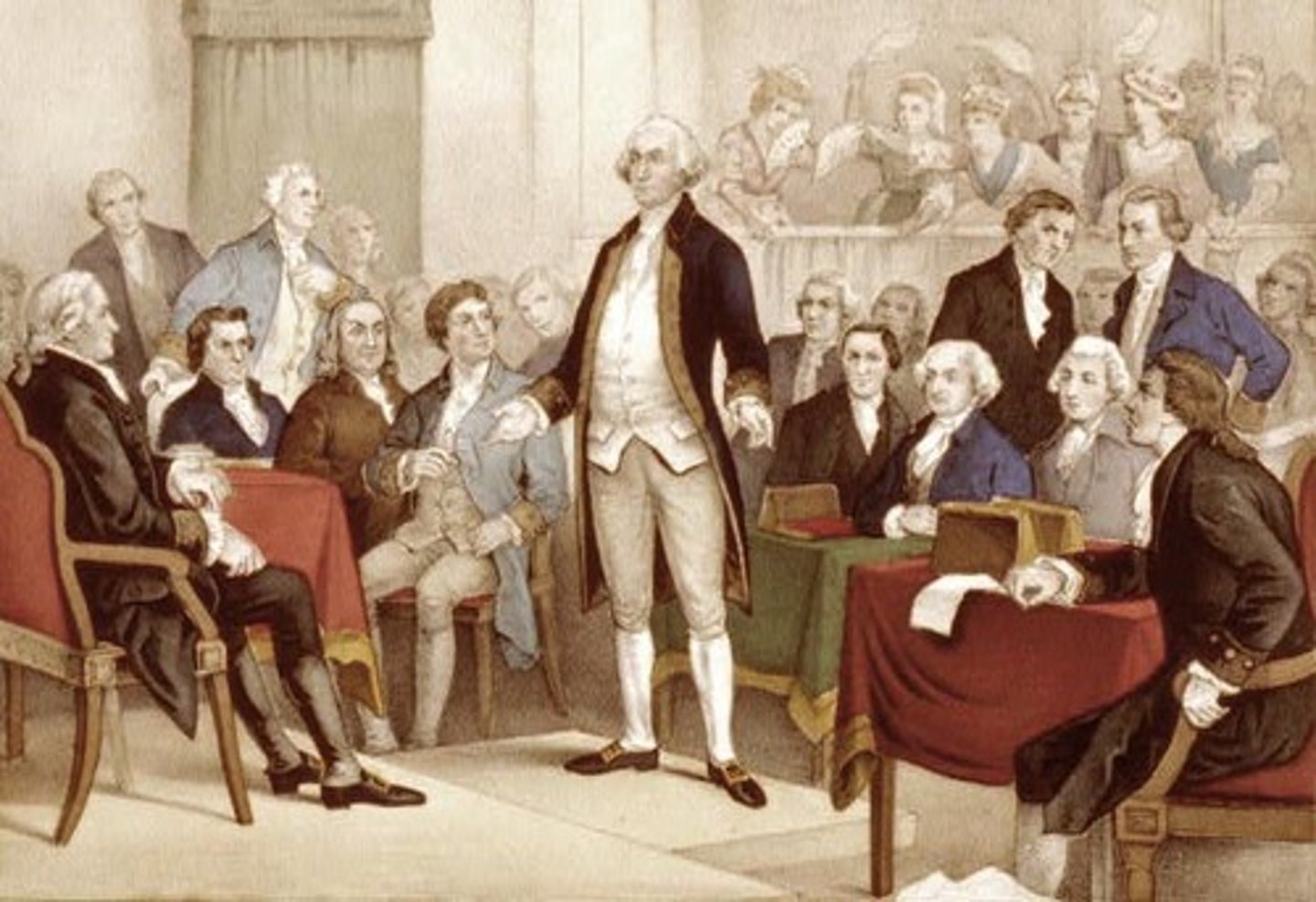

Second Continental Congress
A 1776 meeting in Philadelphia to conduct the war against Britain. Eventually led to the creation of the Declaration of Independence.
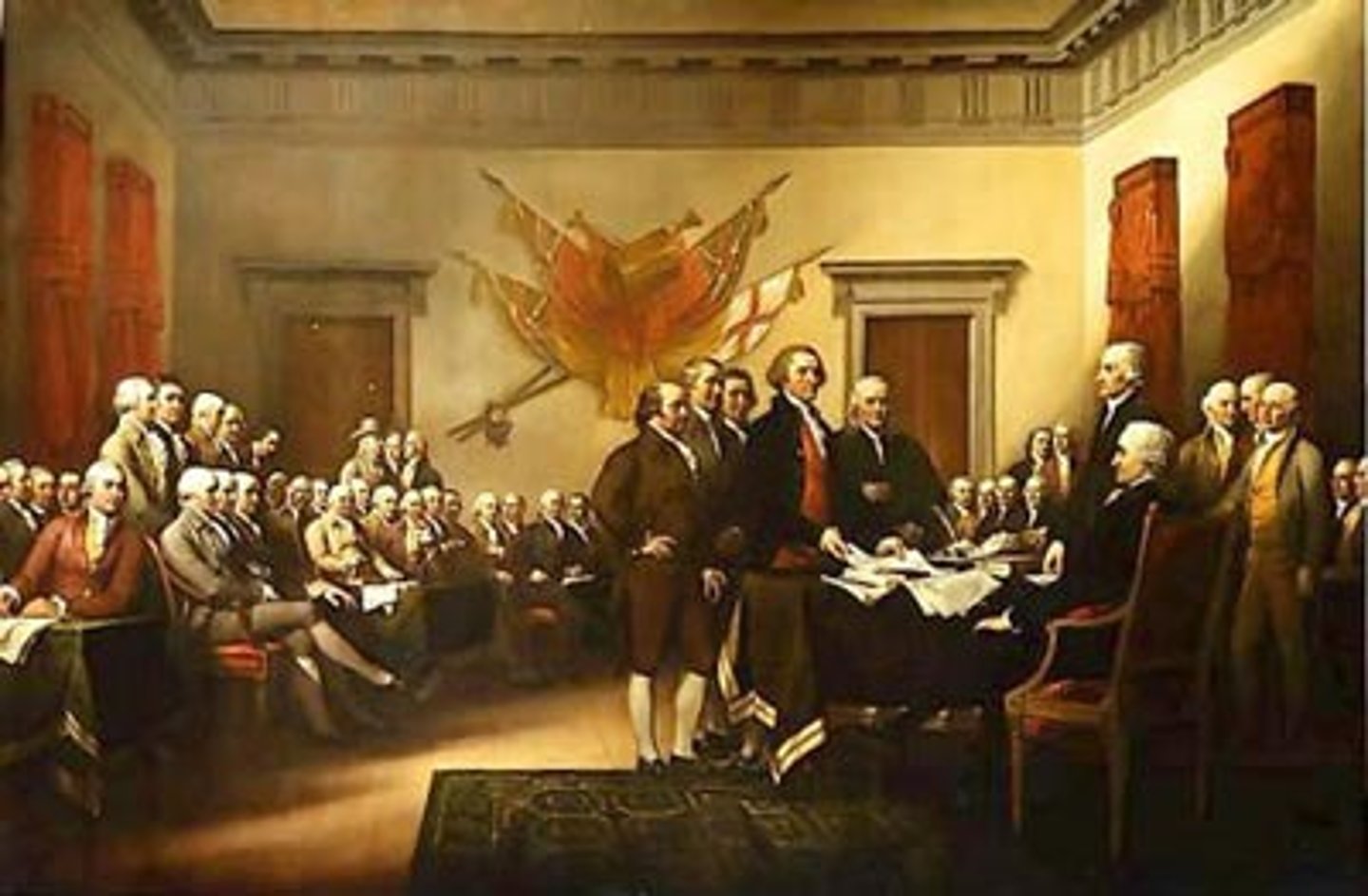

Declaration of Independence
A document that described the basic principles of the United States and all of the complaints the colonies had against King George III.

Principles
Rules or beliefs about how to behave.

Bill of Rights
A list of the rights of citizens for a state or nation.

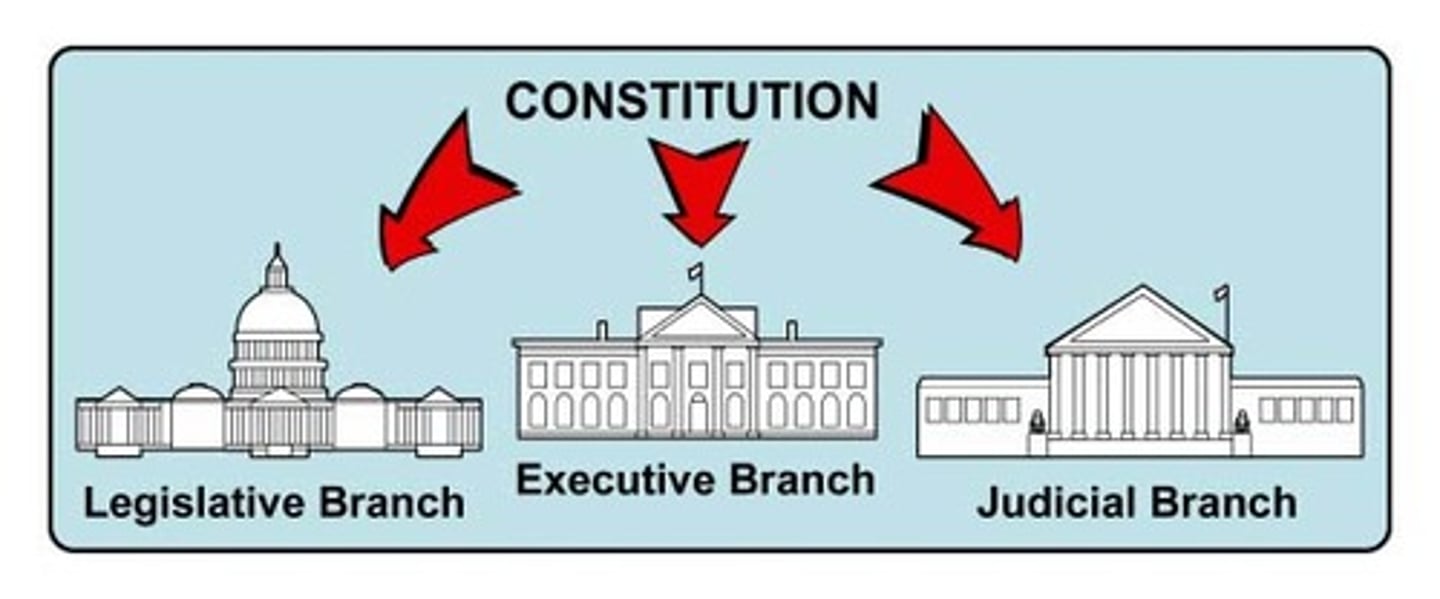
Checks and Balances
A system by which each of the three branches of government stops the others from getting too much power.

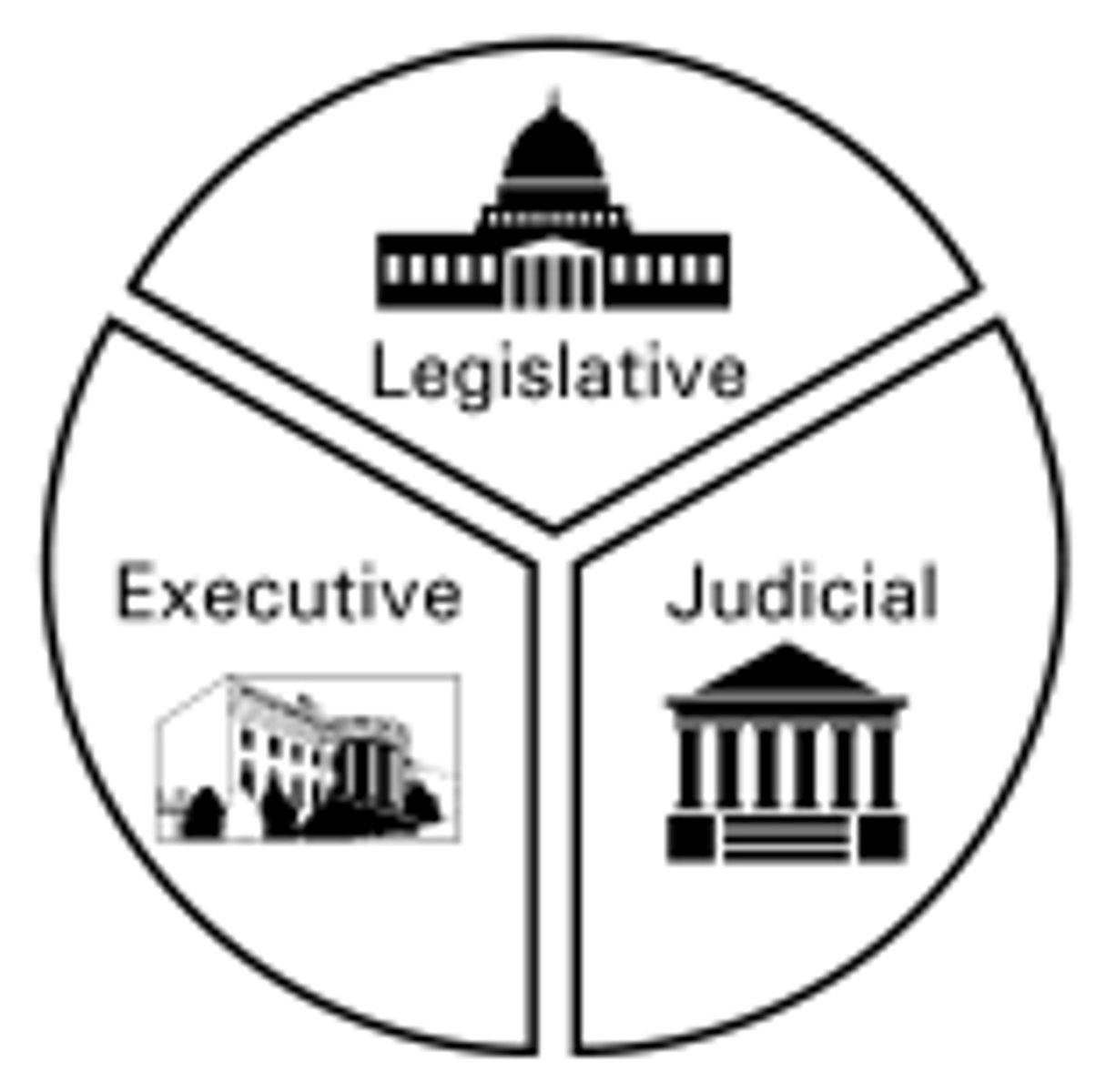
Executive Branch
The branch of government that carries out and enforces the laws.

Higher Law
The idea that lawmakers should not make laws that violate the state or nation's constitution.

Judicial Branch
The branch of government that decides what laws mean and settles conflicts.

Legislative Branch
The branch of government that makes the laws.

Separation of Powers
The idea that power in government should be divided among three branches that all do different jobs.
