Anatomy & Physiology (LAB 5) - Muscles PT.1: Muscles of Head, Neck & Trunk
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
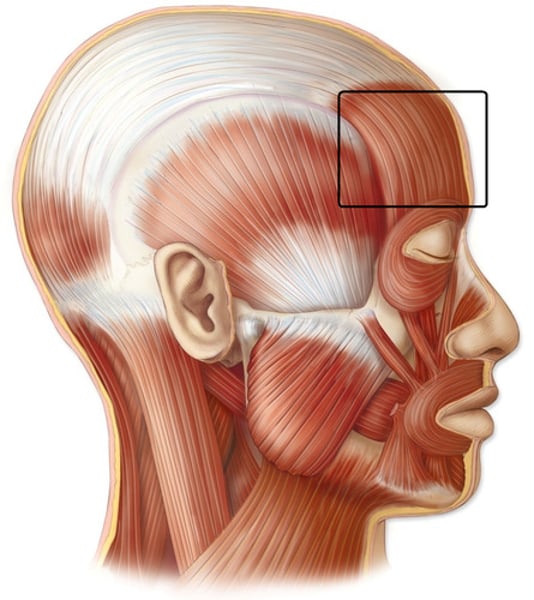
Frontalis (frontal belly)
raises the eyebrows; innervated by facial nerve (cranial nerve VII)
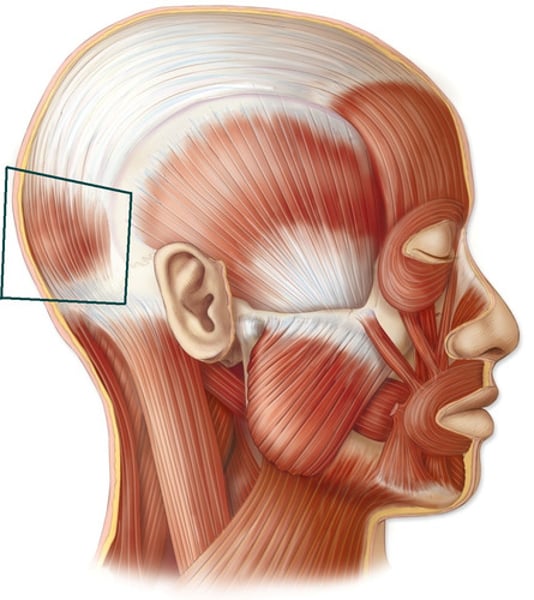
Occipitalis (occipital Belly)
fixes aponeurosis & pulls scalp posteriorly; innervated by facial nerve
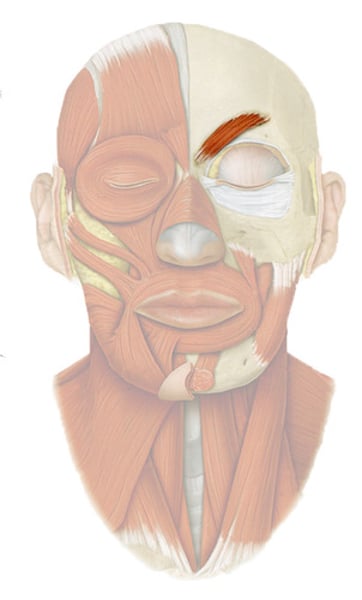
Corrugator supercilii***
pulls eyebrows medially & inferiorly; innervated by facial nerve
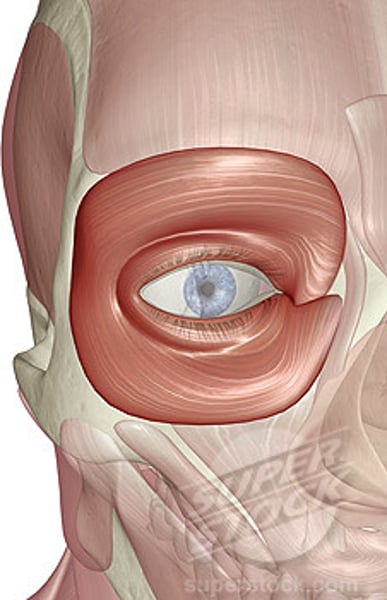
Orbicularis oculi
closes eye for blinking & squinting; innervated by facial nerve
Zygomaticus major & minor
responsible for smiling; innervated by facial nerve
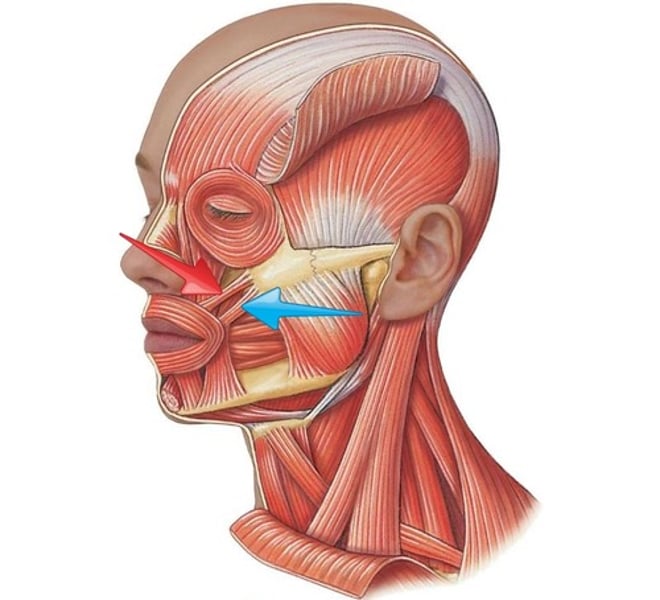
Risorius
pulls corner of lip laterally; innervated by facial nerve

Levator labii superioris
opens lips; innervated by facial nerve
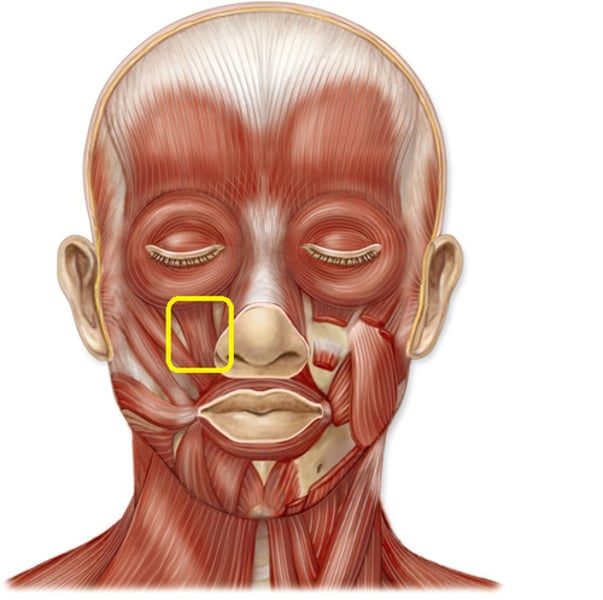
Depressor labii inferioris
pulls lower lip inferiorly; innervated by facial nerve
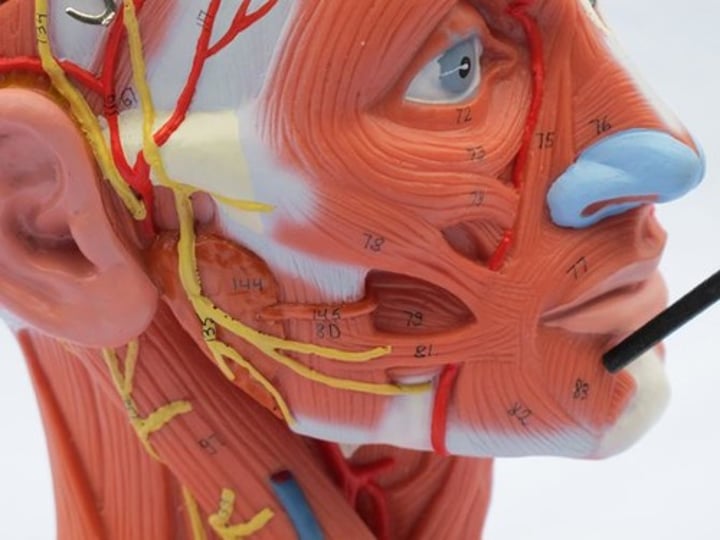
Depressor anguli oris
pulls corner of mouth down & laterally; innervated by facial nerve
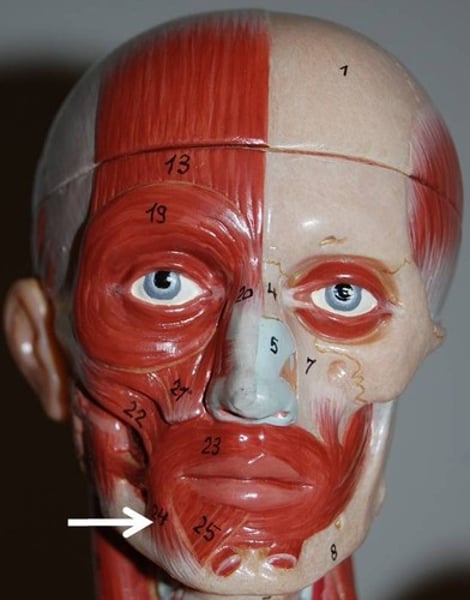
Orbicularis oris
closes lips; innervated by facial nerve
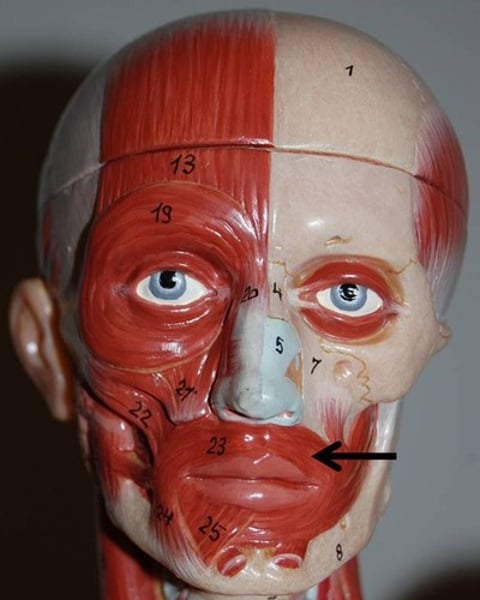
Platysma
tenses skin of neck; innervated by facial nerve
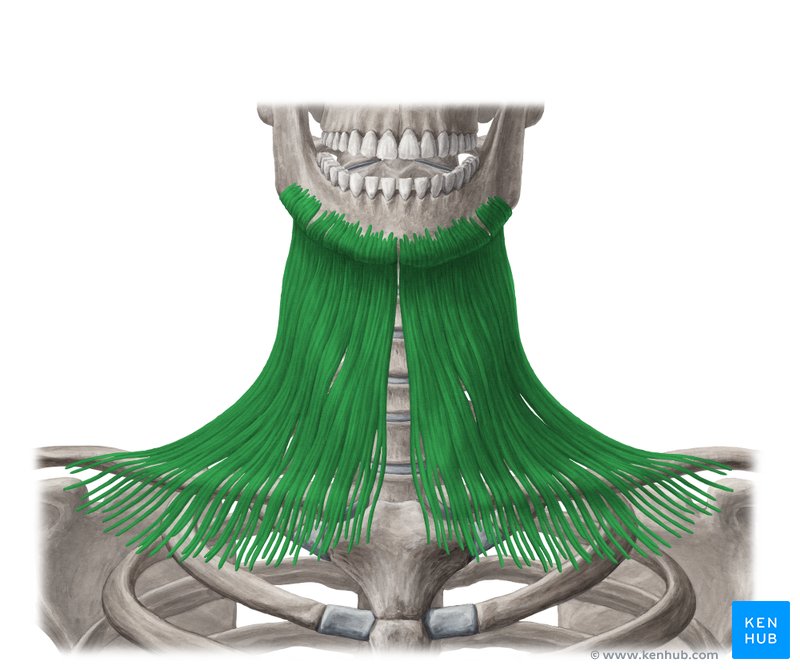
epicranial aponeurosis
connects the frontal and occipital region of our head; innervated by facial nerve
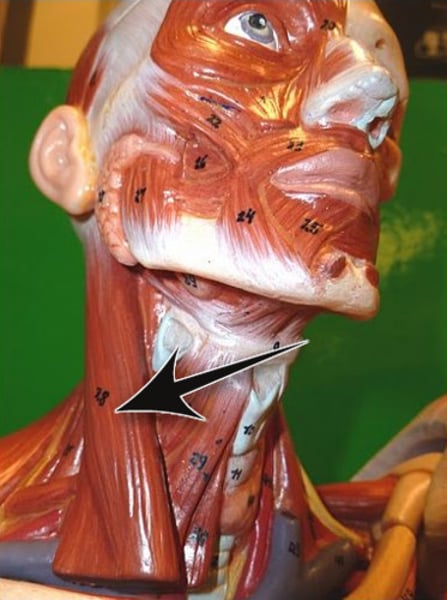
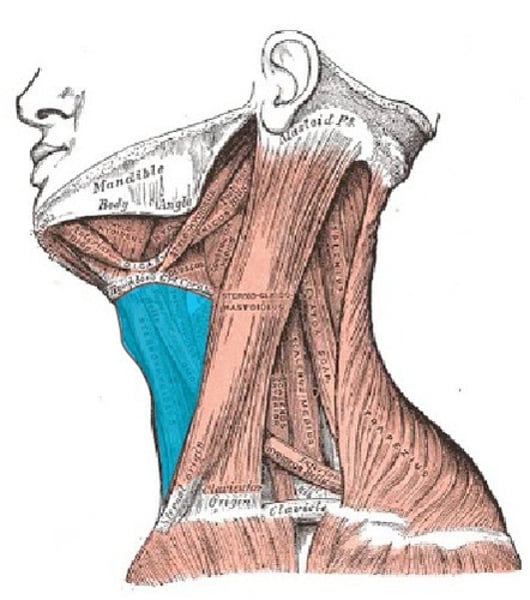
Sternocleidomastoid
flexes and laterally rotates the head; innervated by cranial nerve XII
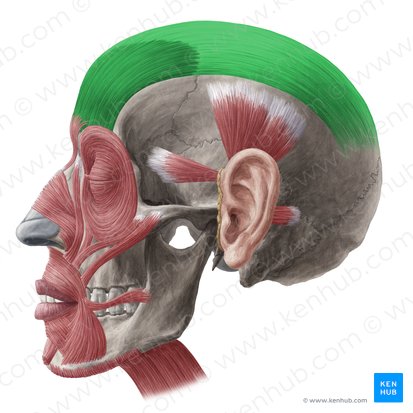
Scalenes***
elevates first two ribs (superior, middle, inferior); innervated by cervical spinal nerves
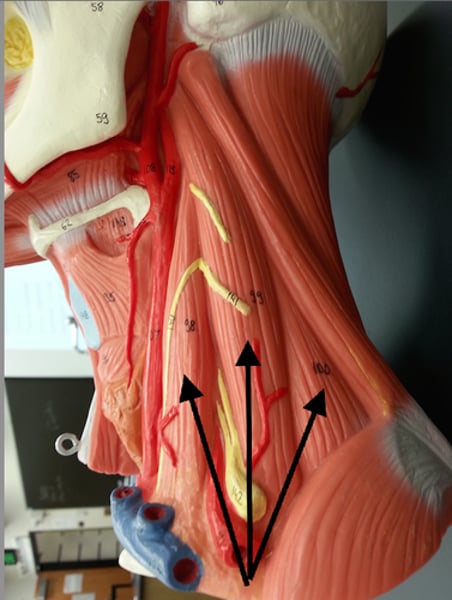
Mentalis
wrinkles chin; innervated by facial nerve
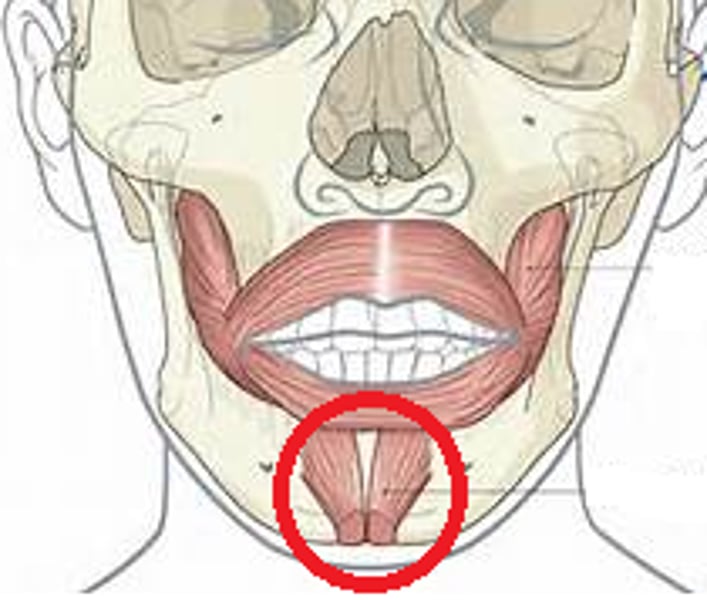
Buccinator***
compresses cheek; innervated by facial nerve
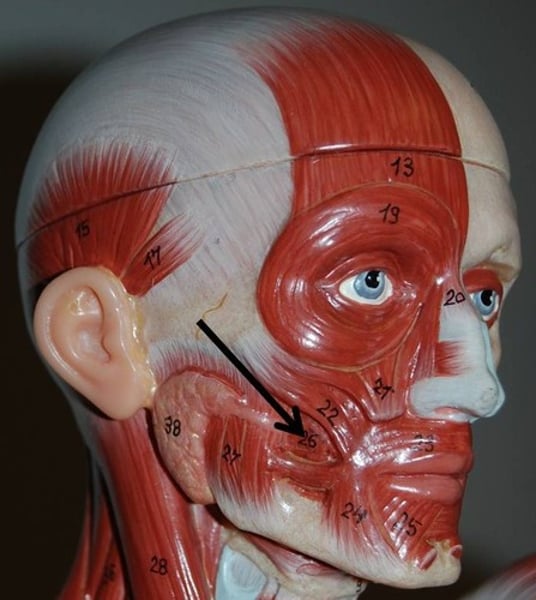
Masseter
primary mover of jaw closure; innervated by trigeminal nerve
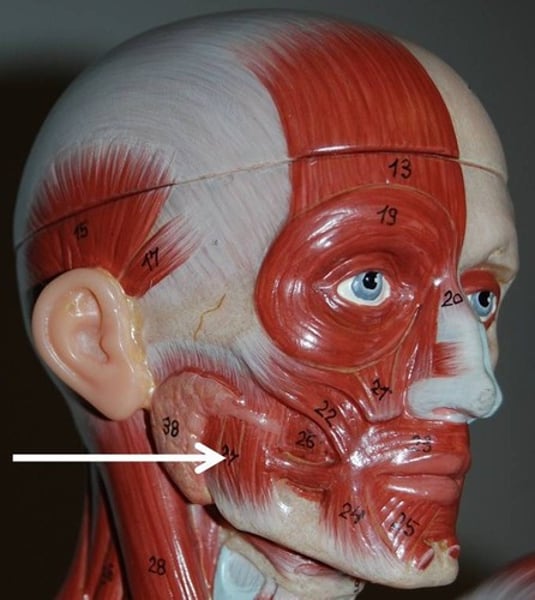
Temporalis
closes jaw; innervated by trigeminal nerve
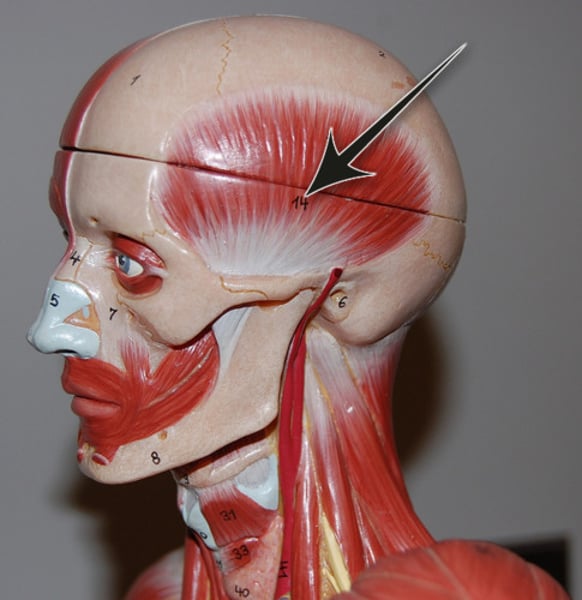
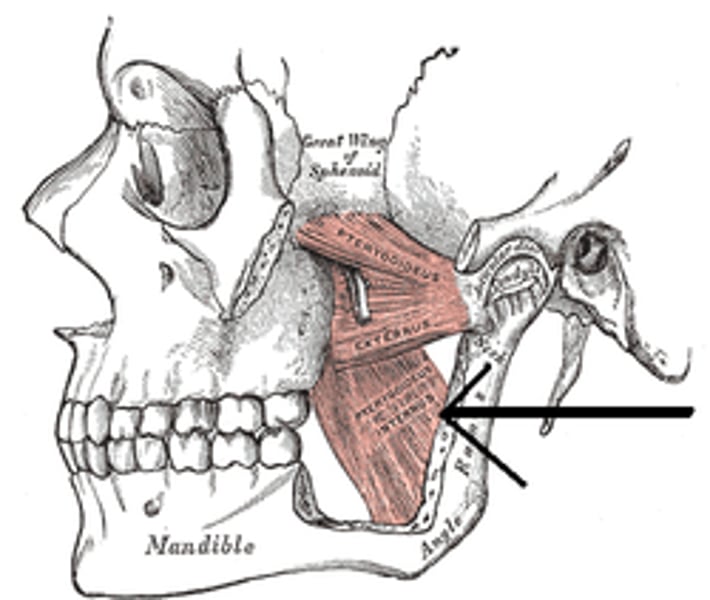
Pterygoid (lateral)
provides side-to-side grinding movements; innervated by trigeminal nerve
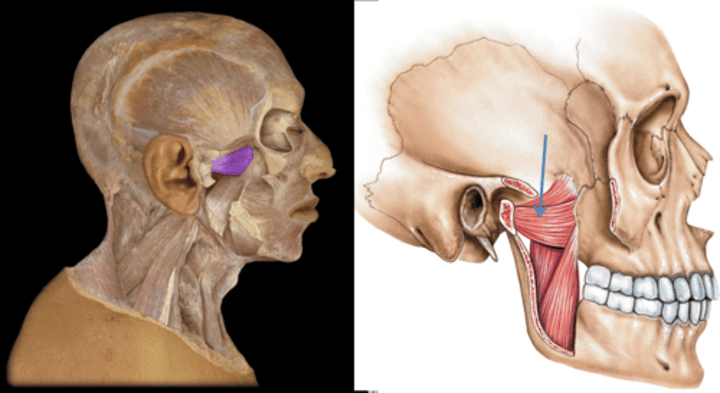
Pterygoid (medial)
acts w/ lateral pterygoid to protract mandible & promote side-to-side grinding movement; innervated by trigeminal nerve
facial nerves
Muscles of Facial Expression Innervated by
Trigeminal Nerves
Muscles of Mastication innervated by
Suprahyoid
above the hyoid bone
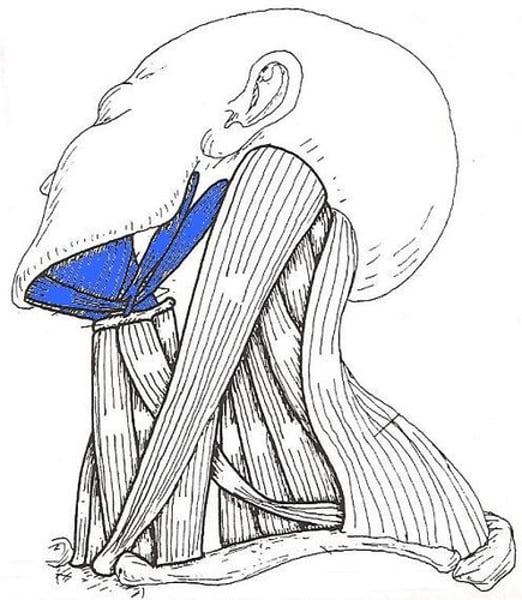
Infrahyoid
below the hyoid bone
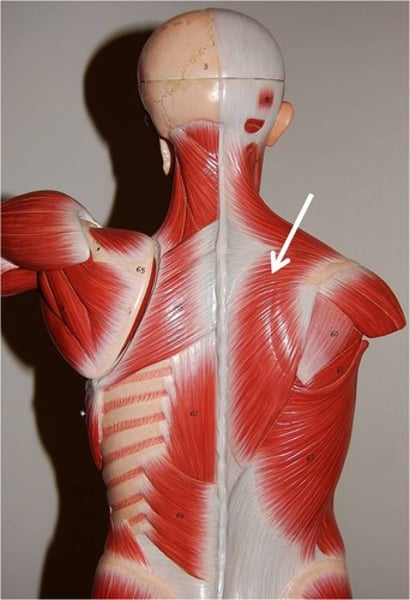
Trapezius
stabilizes, elevates, retracts, & rotates scapula; innervated by cranial nerve XI
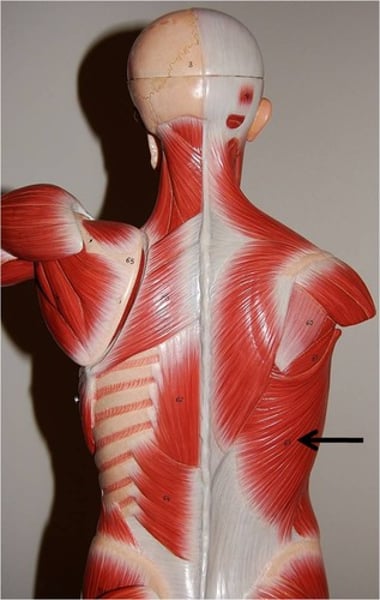
Latissimus dorsi
prime mover of arm extension; innervated by thoracodorsal nerve
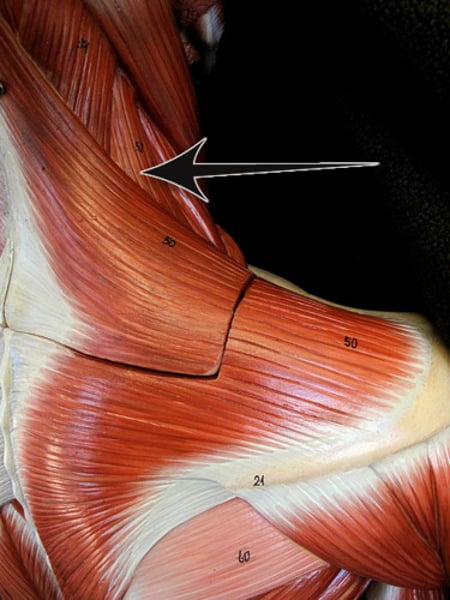
Levator scapulae***
elevates & adducts scapula; innervated by cranial spinal nerves & dorsal scapular nerves
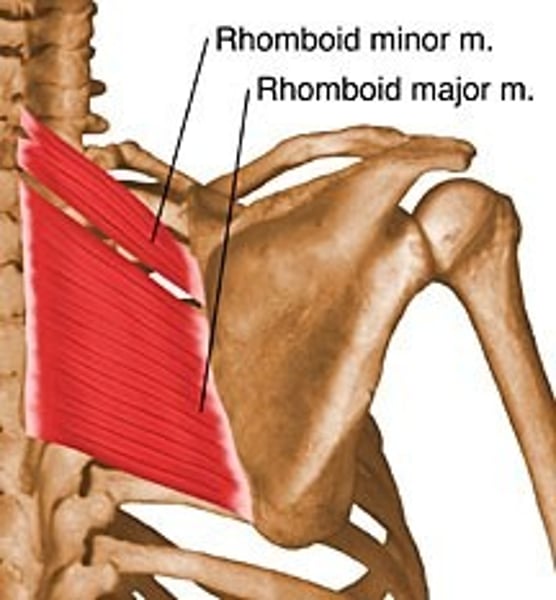
Rhomboid major & minor***
stabilize scapula; innervated by dorsal scapular nerves
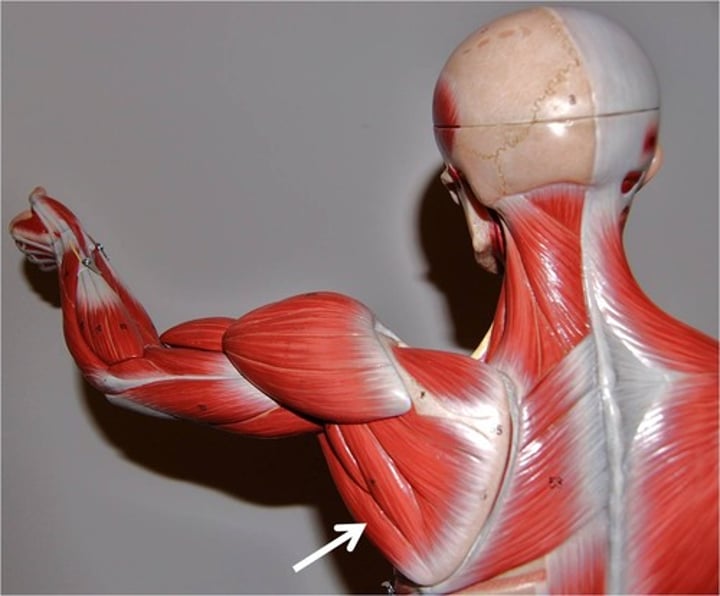
Teres major
extends, medially rotates, & adducts arm; innervated by lower subscapular nerve
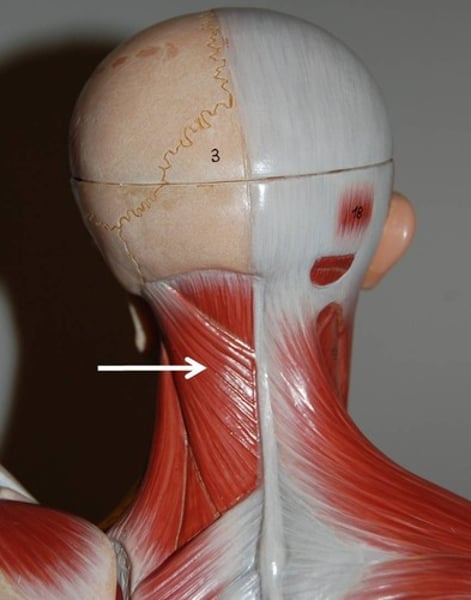
Splenius capitis & cervicis***
extend/hyperextend head; innervated by cervical spinal nerves
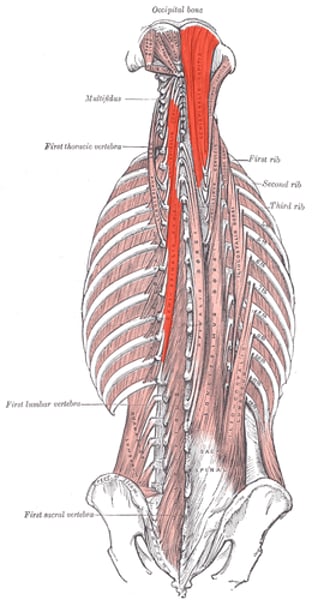
Semispinalis: capitis, cervicis & thoracis***
extends vertebral column; capitis is top, cervicis middle, and thoracis bottom; innervated by spinal nerves
Quadratus Lumborum
laterally flexes vertebral column; innervated by upper lumbar spinal nerves
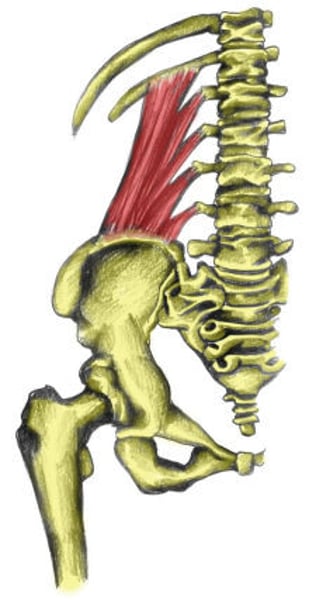
Erector spinae/Paraspinal
group of 3 muscles:
- Iliocostalis
- Longissimus
- Spinalis
Iliocostalis
extends vertebral column & laterally flexes vertebral column; innervated by spinal nerves
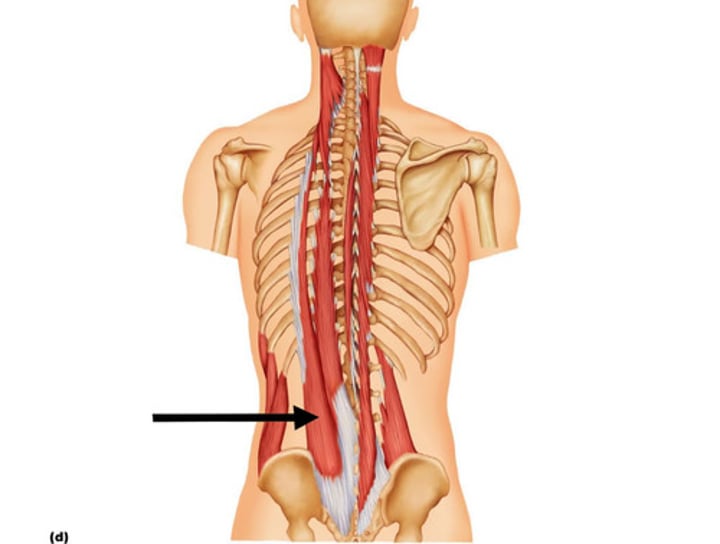
Longissimus
extends vertebral column & extends & rotates head; innervated by spinal nerves
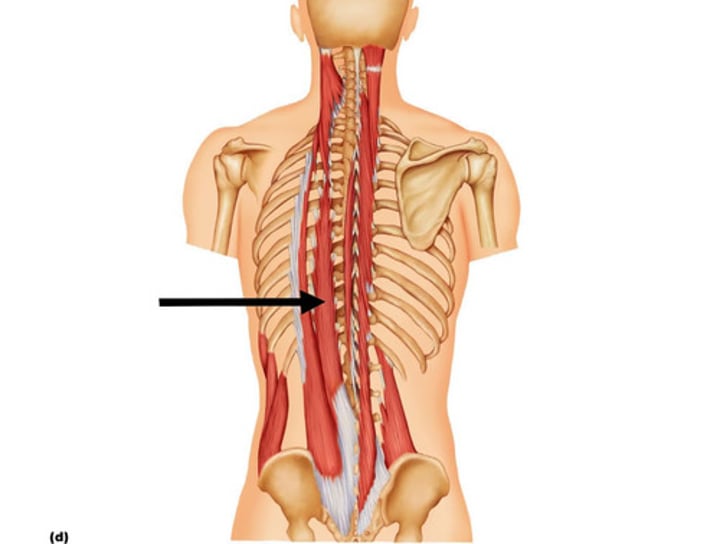
Spinalis
extends vertebral column; innervated by spinal nerves
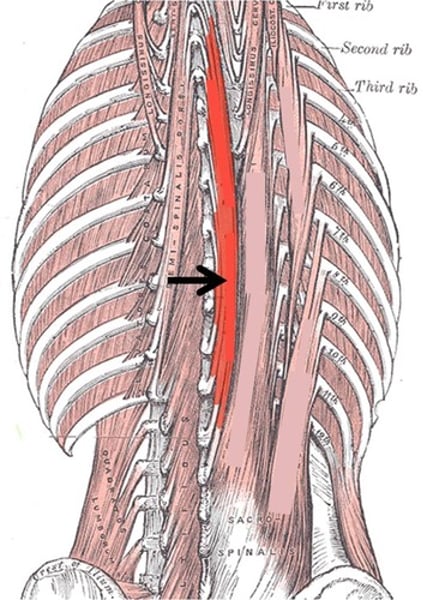
Deltoid
prime mover of arm abduction when all its fibers contract simultaneously; innervated by axillary nerve
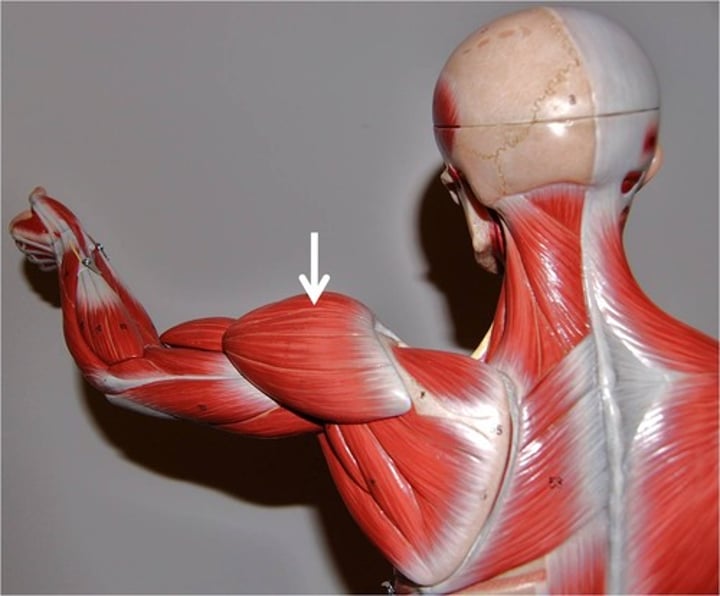
Supraspinatus***
initiates abduction of arm; innervated by suprascapular nerve
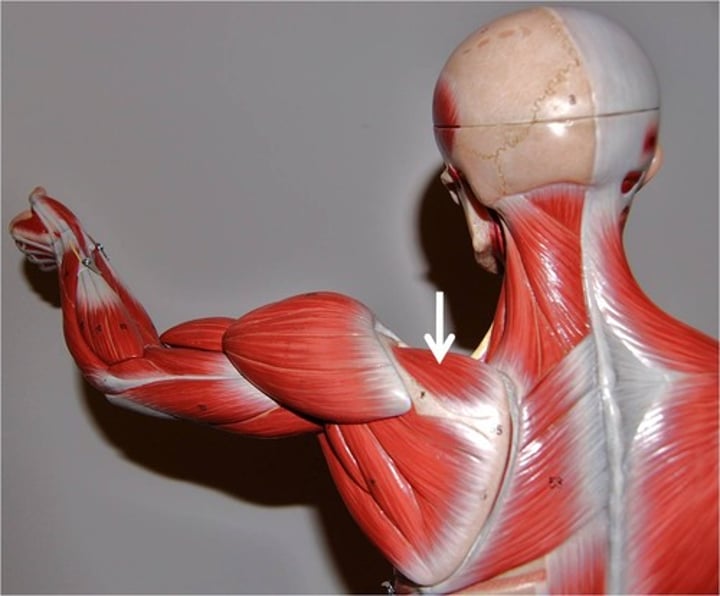
Infraspinatus***
rotates arm laterally; innervated by suprascapular nerve
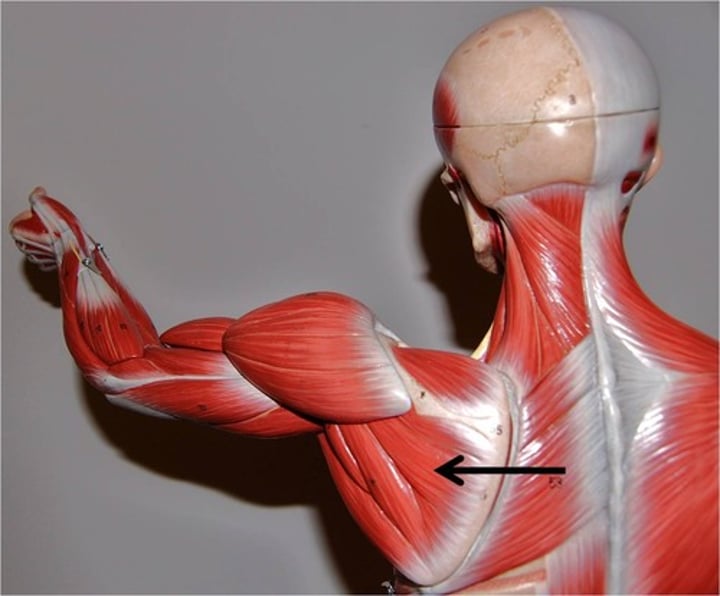
Subscapularis***
rotates arm medially; innervated by subscapular nerves
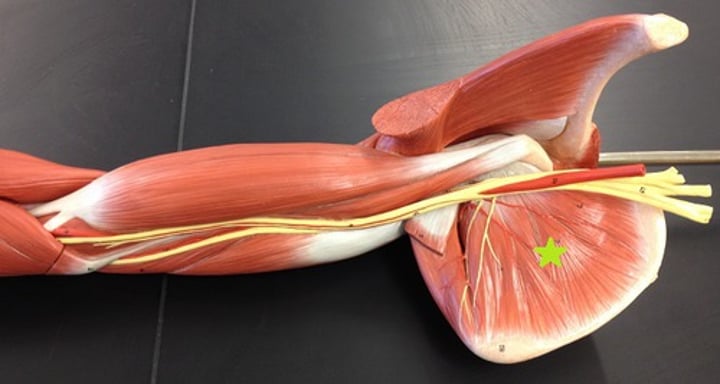
Teres minor***
same actions as infraspinatus muscle; innervated by axillary nerve
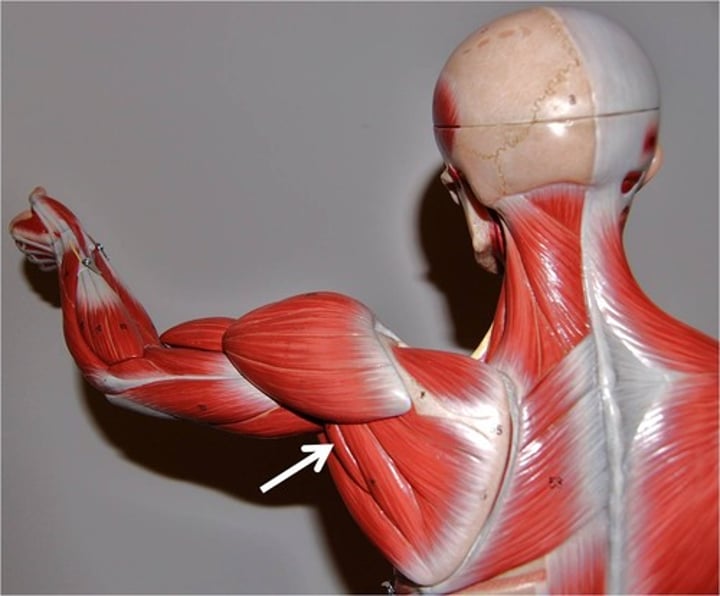
Pectoralis major
adducts & medially rotates arm; innervated by lateral & medial pectoral nerves
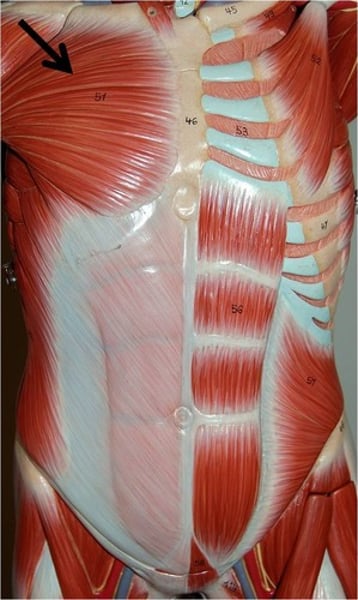
Pectoralis minor***
w/ ribs fixed, pulls scapula forward & downward; innervated by lateral & medial pectoral nerves
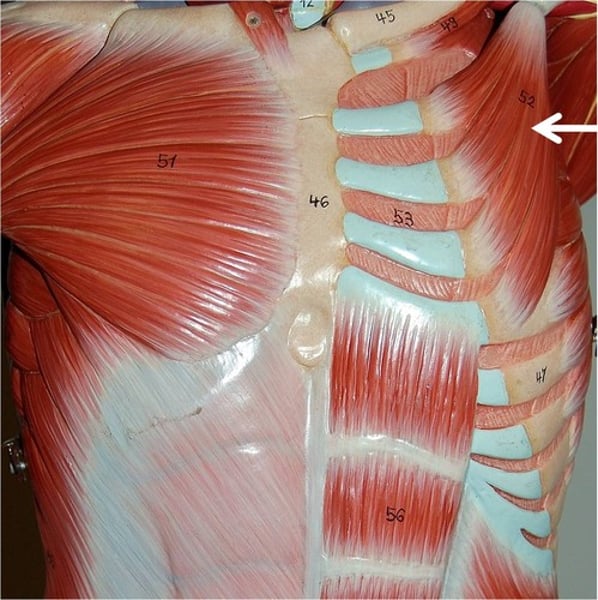
Serratus anterior***
rotates scapula so it moves laterally & upward; innervated by long thoracic nerve
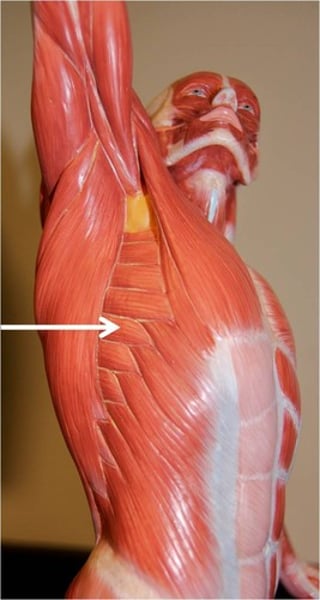
Rectus abdominus
flex & rotate lumbar region of vertebral column; innervated by intercostal nerves
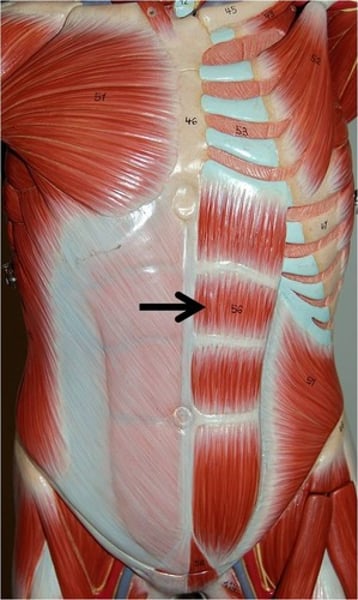
External oblique
flex vertebral column & compress abdominal wall. trunk rotation & lateral flexion; innervated by intercostal nerves
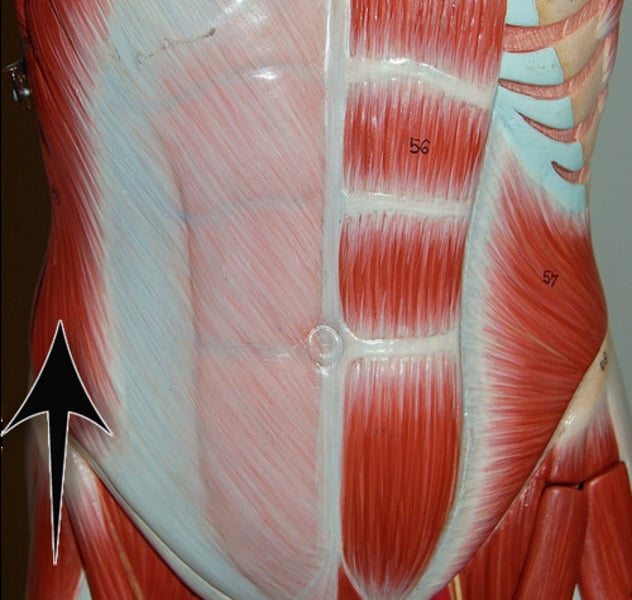
Internal oblique***
same action as its external counterpart; innervated by intercostal nerves
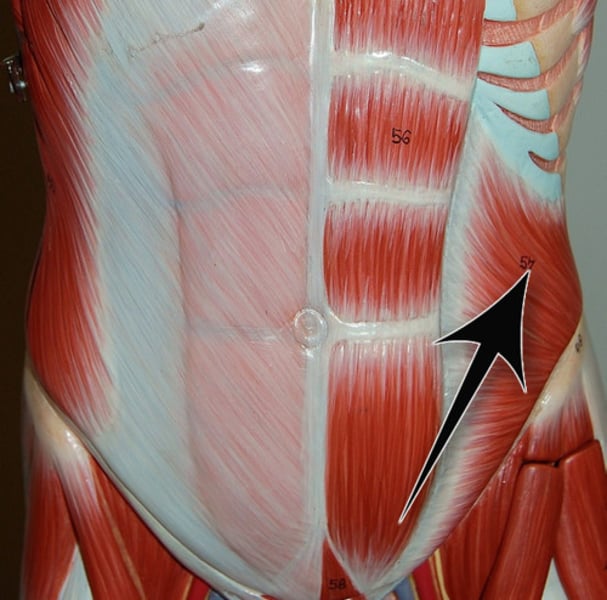
Transversus abdominus***
compresses abdominal contents; innervated by intercostal nerves
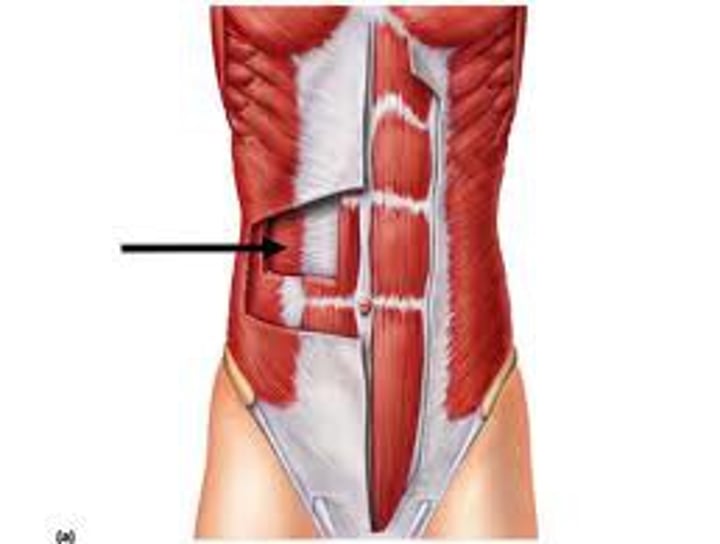
Linea Alba
midline tendinous seam joining the abdominal muscles
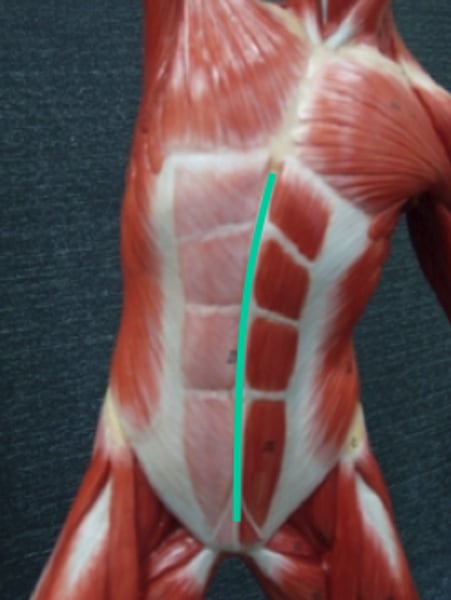
Aponeurosis of external obliques
the white part most inferior part of the abdomen
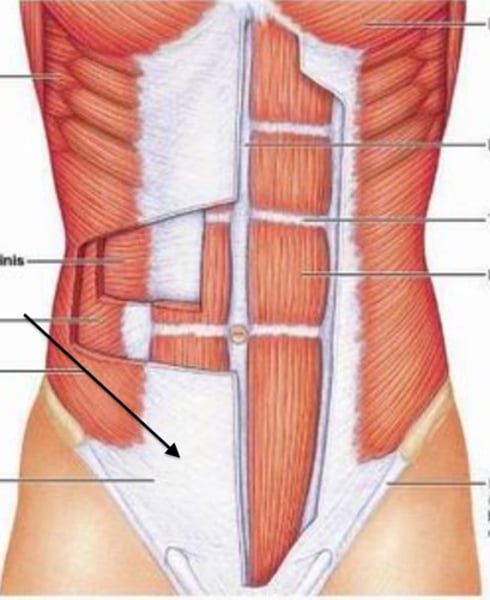
Intercostal Nerves
Abdominal Muscles are innervated by
Diaphragm***
prime mover of inspiration & flattens on contraction; innervated by phrenic nerve
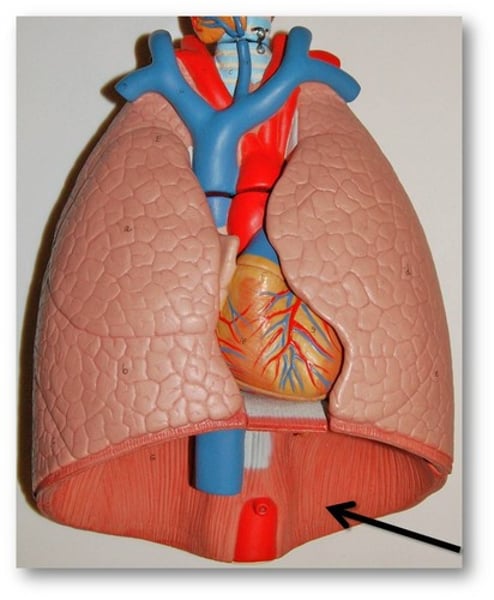
Phrenic Nerve
The diaphragm is innervated by the
External intercostals
pull rubs toward one another to elevate rib cage & responsible for inspiration; innervated by intercostal nerves
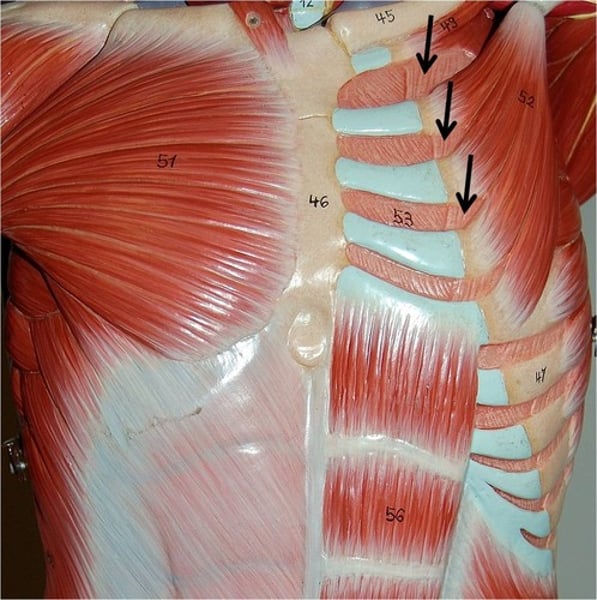
Internal intercostals
pull ribs together and depress rib cage; innervated by intercostal nerves
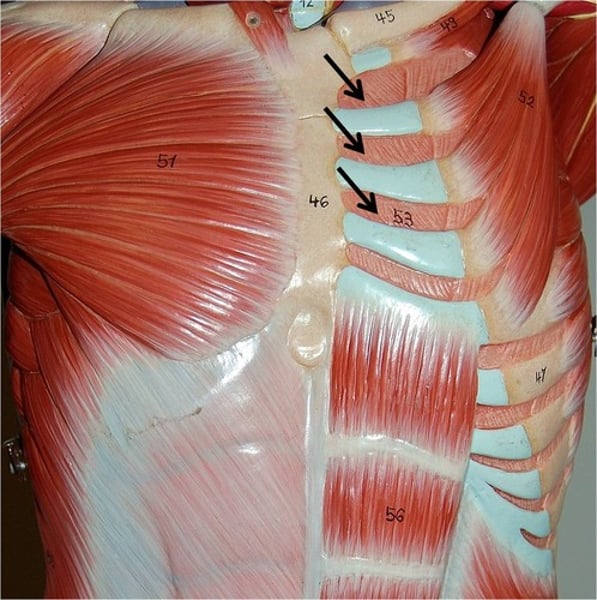
Intercostal nerves
Intercoastals innervated by the
Levator Ani
supports & maintains position of pelvic organs; innervated by inferior rectal nerve
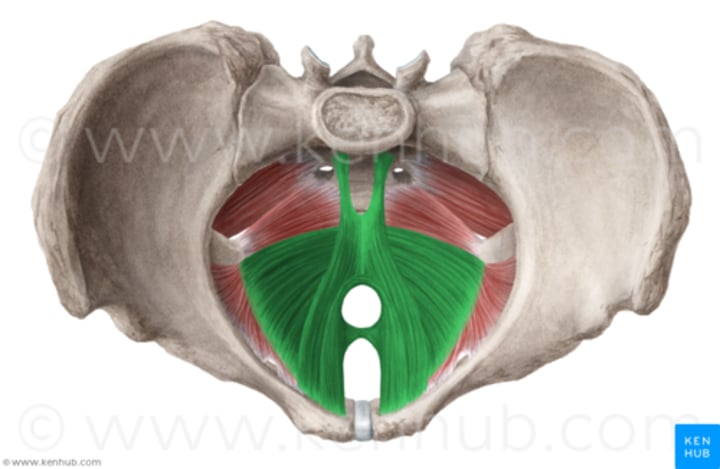
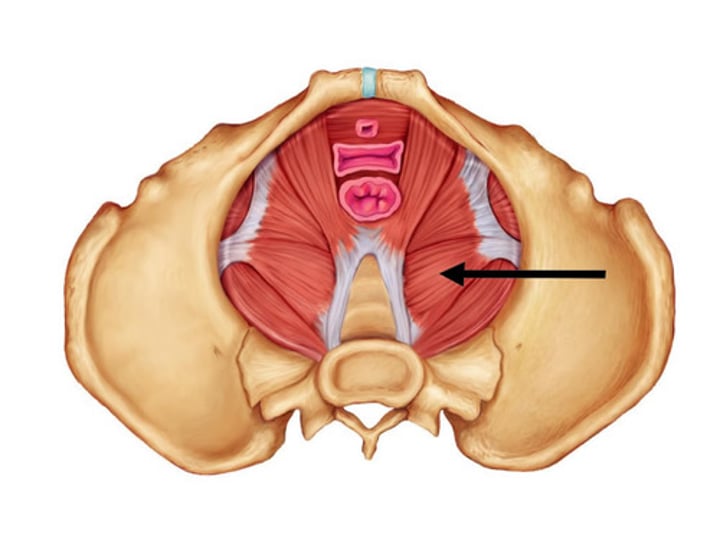
Coccygeus
supports pelvic organs; innervated by S4 & S5
Ischiocavernosus
retards venous drainage & maintains erection of penis/clitoris; innervated by pudendal nerve
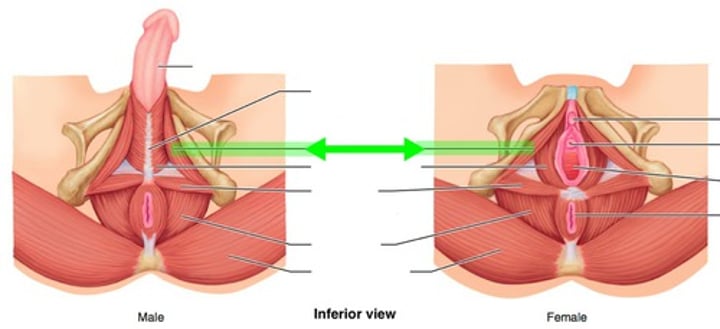
Bulbospongiosus
empties male urethra; innervated by pudendal nerve
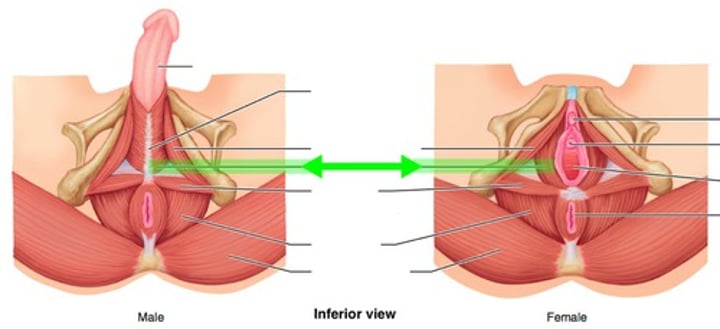
Pudendal nerve
Pelvic Floor & Perinium innervated by
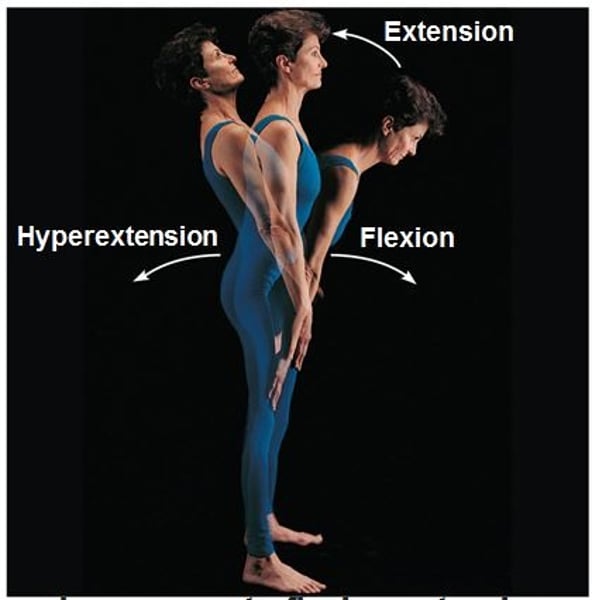
Flexion
bending movement along sagittal plane that decreases angle of joint
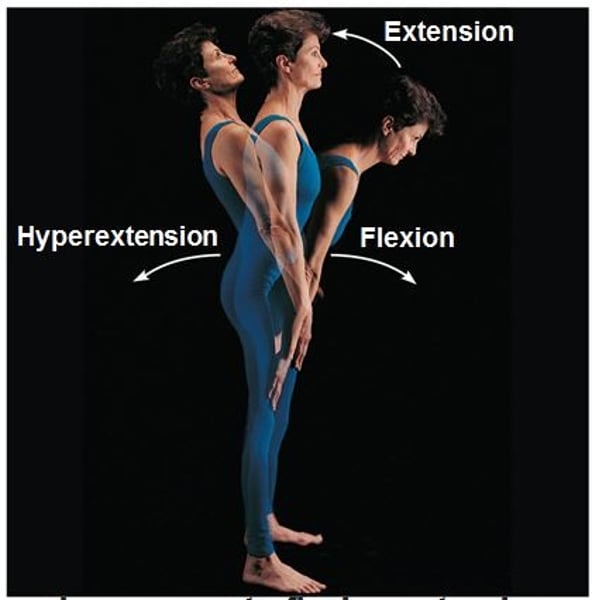
Hyperextension
opposite of flexion; involves increasing the angle btw bones in the sagittal plane
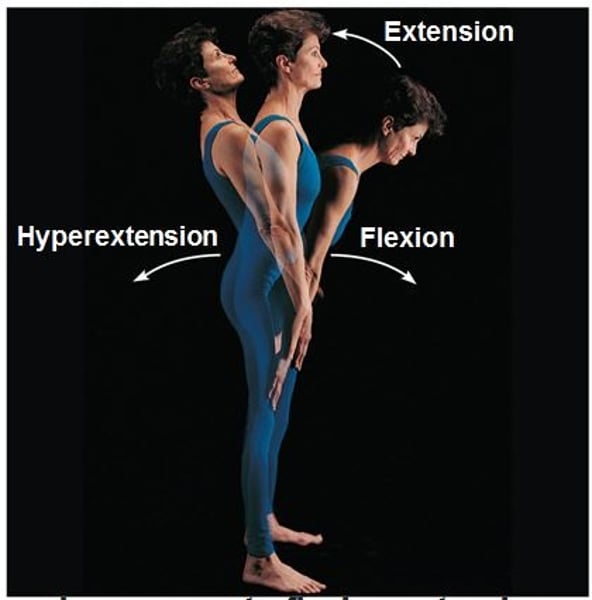
Extension
Straightening of a joint
Dorsiflexion
"toes up"; raising foot upwards
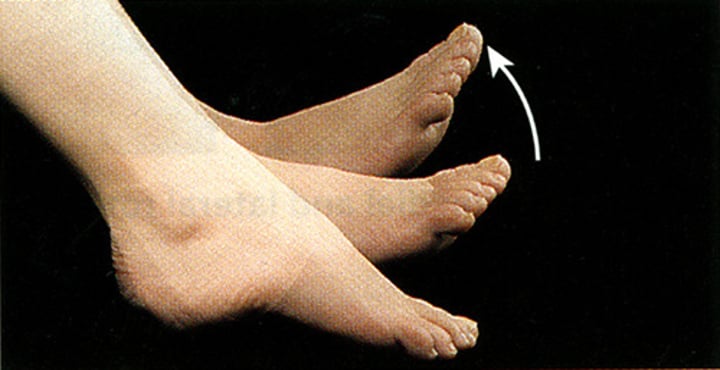
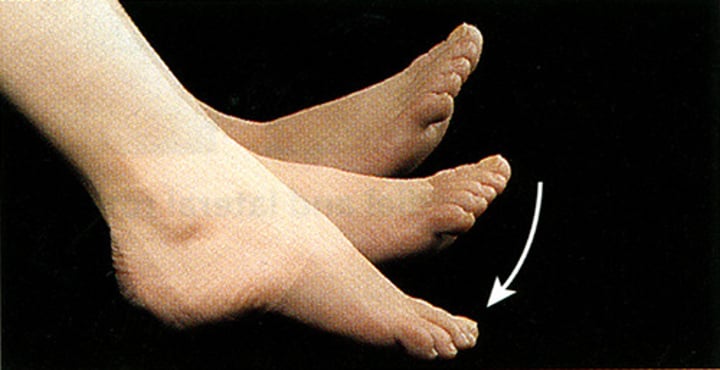
Plantarflexion
"toes down"; pointing foot downwards
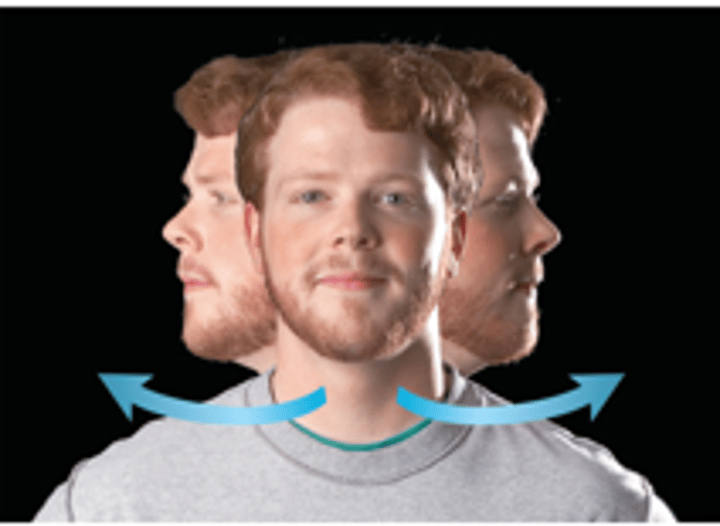
Rotation
Turning a bone around its own long axis

Pronation
rotating the forearms from a "palms forward" to a "palms backward" position
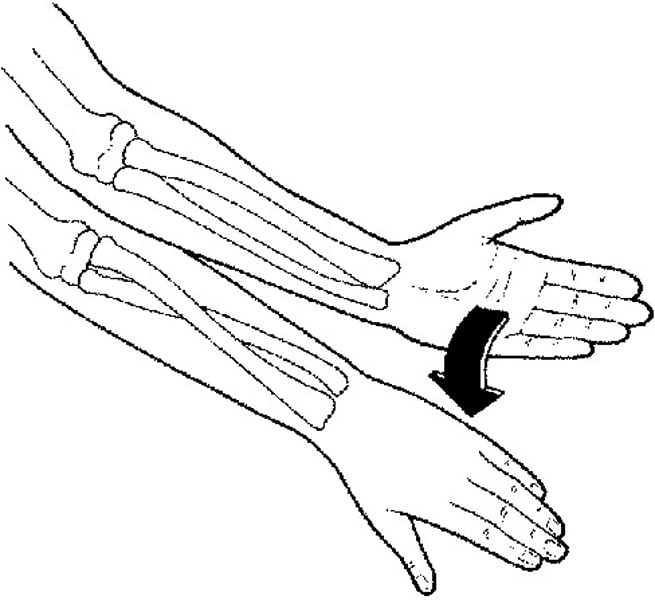
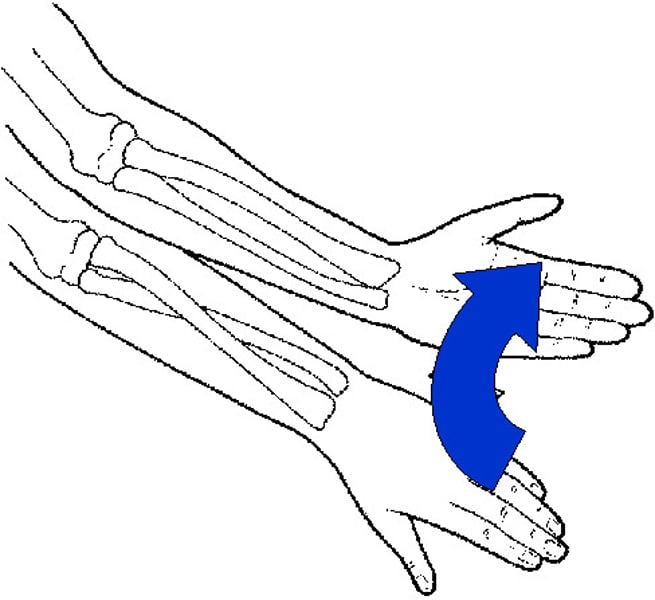
Supination
rotating the forearms from a "palms backward" to a "palms forward" position
Circumduction
moving a limb so that the distal end of that limb draws a circle (think "circumference" of a circle)
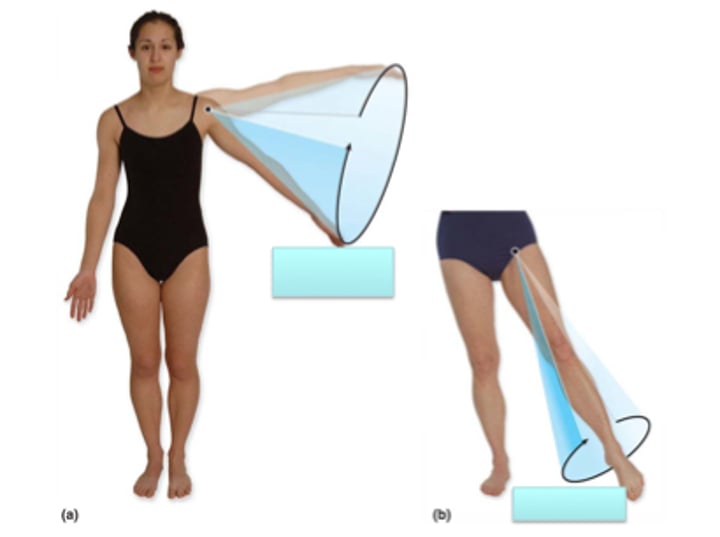
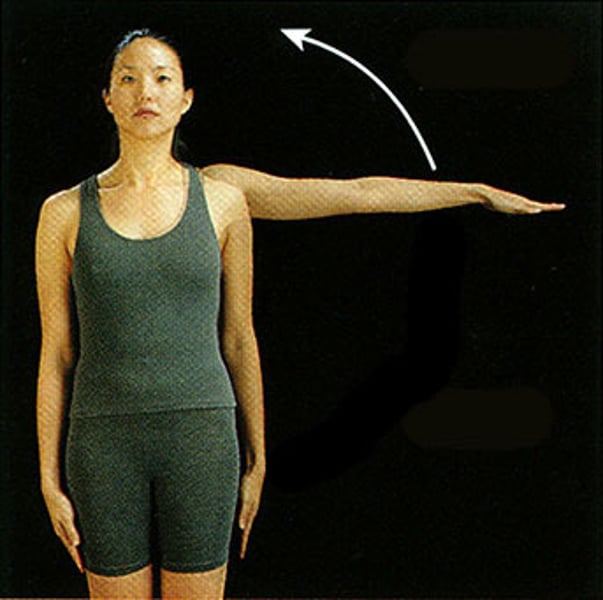
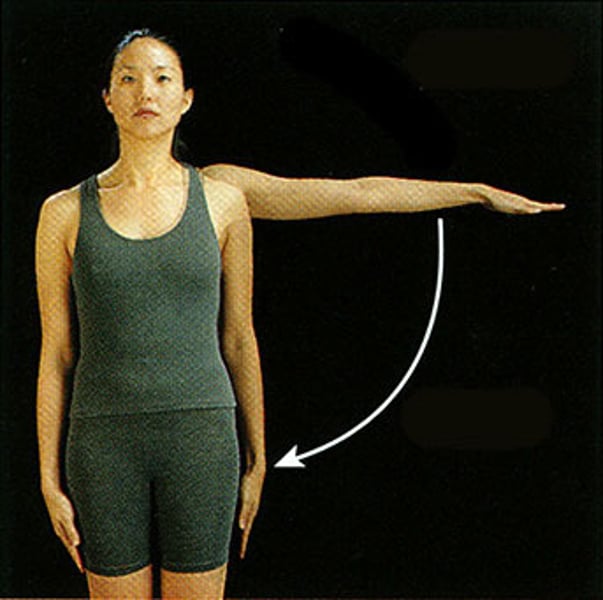
Abduction
movement of a limb away from a midline of the body within coronal plane (think reaching out arms to abduct someone)
Adduction
movement of a limb toward the body (think adding to your body)

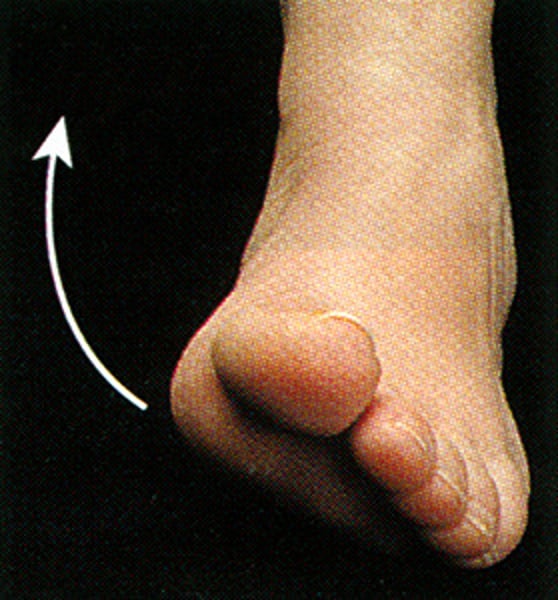
Inversion
Turning side of foot medially (standing on lateral side of foot)
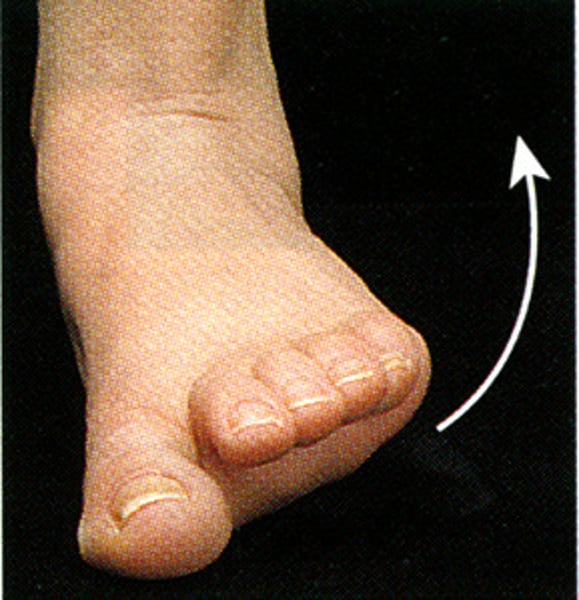
Eversion
Turning sole of foot laterally (standing on medial side of foot)
Protraction
movement of a body part in an anterior direction
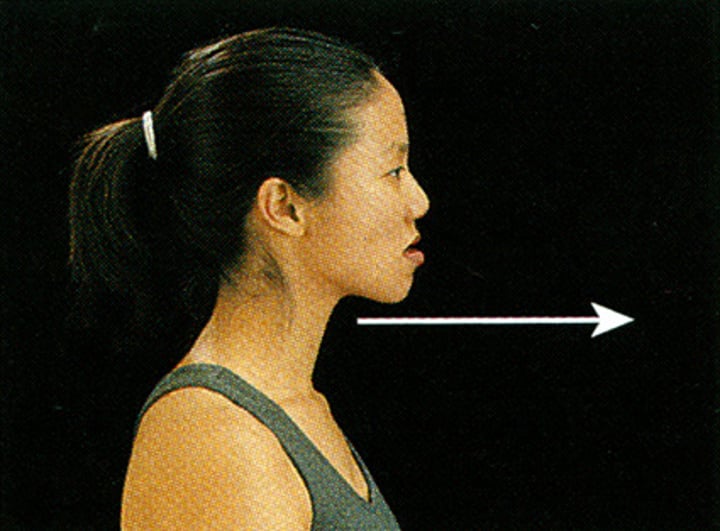
Retraction
movement of a body part in an posterior direction
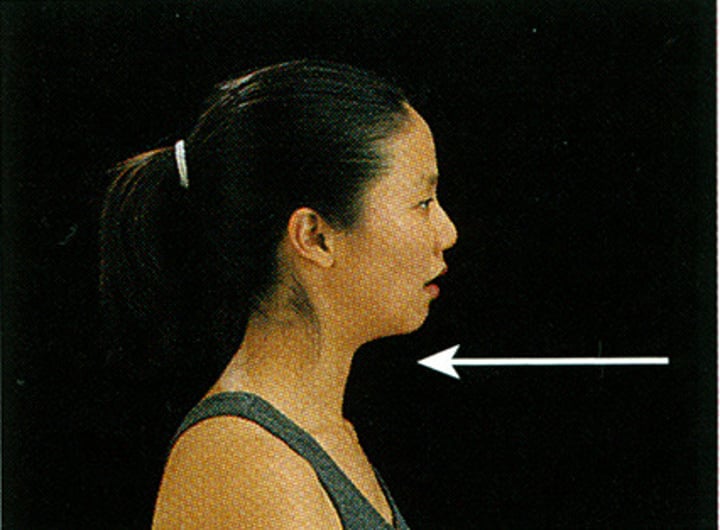
Elevation
movement of a body part superiorly
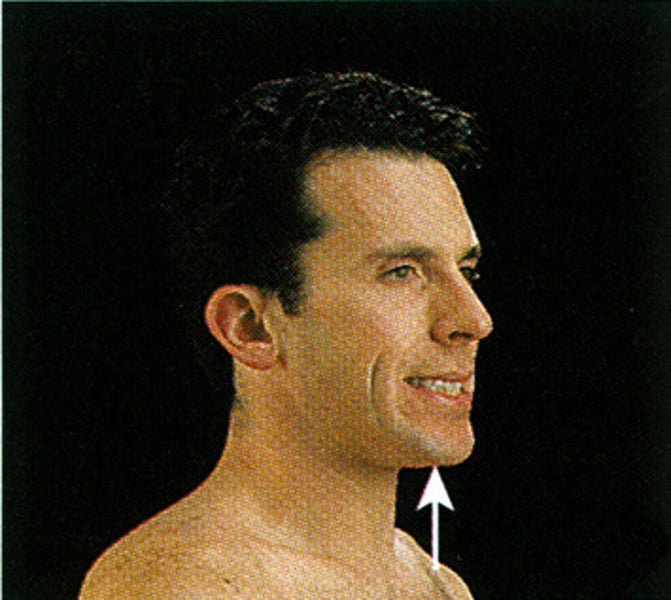
Depression
movement of a body part inferiorly
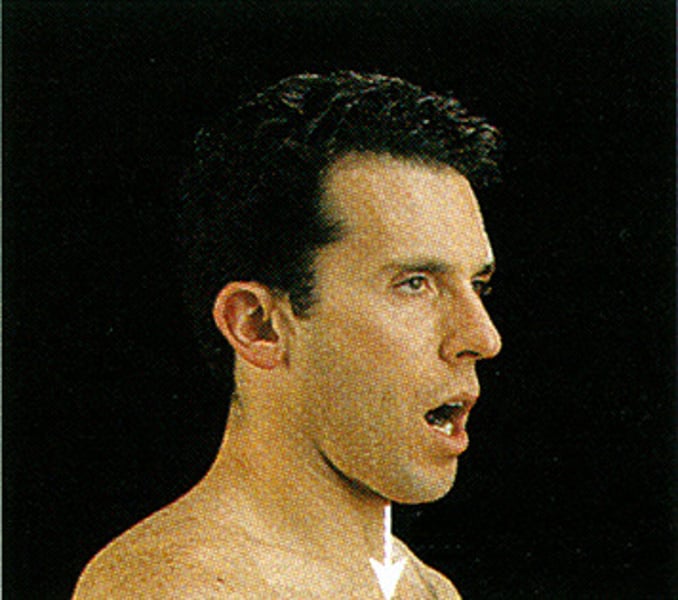
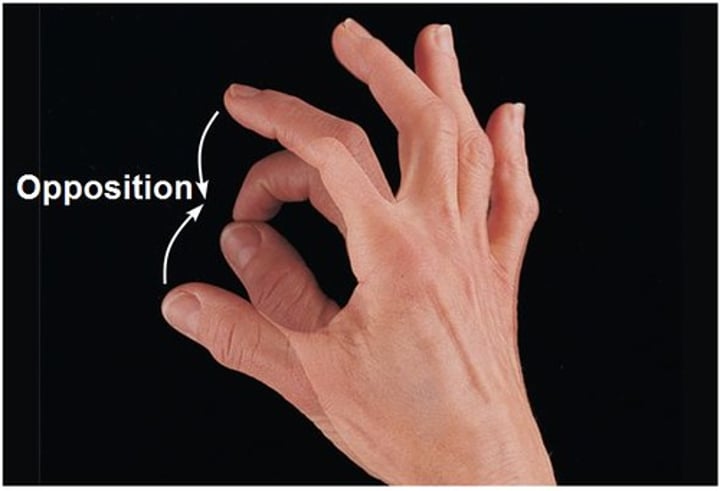
Opposition
touching the thumb to the tips of other fingers on same hand (pinching/grasping)
Agonist
the muscle that provides most of the force for a particular action (aka prime mover)
Antagonist
a muscle that opposes/does the opposite of the agonist
Synergist
muscles that work to accomplish the same action (assists/helps the prime mover)
Fixator
muscle that helps stabilize/immobilize a bone; important for posture
origin
attached to immovable bone
insertion
attached to moveable bone