Natural Disasters TEST 2
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
4 Main Gases in order from most abundant to least
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, Carbon Dioxide
4 main gases percentages
Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), Argon (1%), Carbon Dioxide (<1%)
Layers of Atmosphere in Order
Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Layers of Atmosphere distances
Troposphere (0-11 km/ 7miles), Stratosphere (11-50 km/ 30miles), Mesosphere (50-80 km/ 50miles), and Thermosphere (80 km and above).
Main Fact of Troposphere
The lowest layer of the atmosphere, where weather occurs and temperature decreases with altitude.
Main fact of Stratosphere
The second layer of the atmosphere, characterized by a temperature increase with altitude and the presence of the ozone layer.
Main fact od Mesosphere
The third layer of the atmosphere, where temperature decreases with altitude
Main fact of Thermosphere
The fourth and outermost layer of the atmosphere, temperature increases with altitude, the ionosphere is in the lower layer, air molecules are ionized by solar energy, and the Northern Lights occur here, including the D, E, and F layers.
Ozone layer
Layer of molecular ozone that absorbs ultraviolet light from UV. The UV breaks the O2 bond, creating free radicals that bonds to another O2 molecule. creating ozone.
Phase Changes of Water
The transitions between solid, liquid, and gas phases of water, including melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation, sublimation, and deposition.
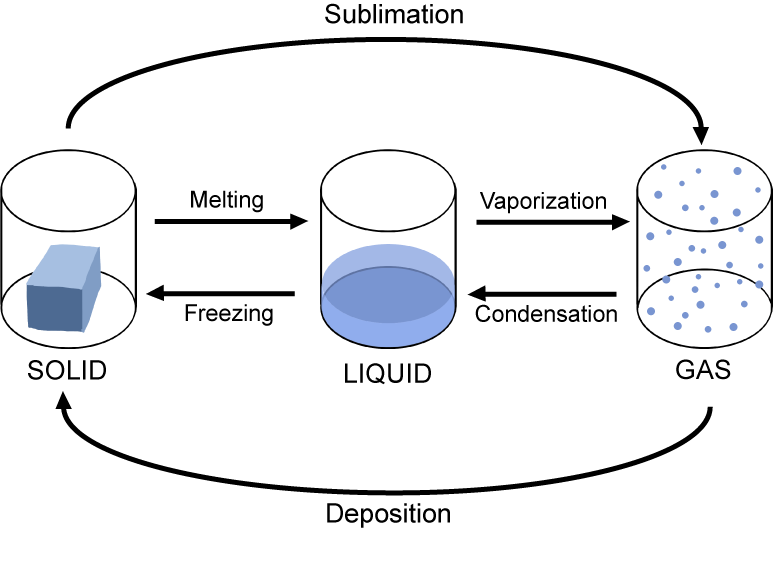
Energy Expenditure of Phase changes of water
Liquid to/from Gas: ±600 cal/gram
Liquid to/from Solid: ±80 cal/gram
Sublimation/Deposition: ±680 cal/gram
Latent Heat
Heat absorbed or released during phase change of water.
What drives weather
Water Vapor rises due to heat from sun until it reaches the L.O.C. where water vapor turns into liquid droplets(cloud). Latent heat from condensation drives vertical development creating storms and weather.
What does cloud height equal
Air temp = dew point
dew point definition
Temperature at which air cannot hold anymore water
6 types of precipitation
Rain, Snow, Hail, Sleet, Glaze/freezing rain, Rime
Rain
Must have radius between 0.05mm and 5 mm.
Snow
It is 6 sided in shape and grows through accumulation. Texture and Form are dependent on temperature.
Sleet
(FREEZES BEFORE HITTING GROUND)
Forms when warm air is ver cooler air
Glaze
(FREEZES UPON IMPACT OF GROUND
A covering of ice over all objects, forms from thin subfreezing air layer
Hail
Forms from convection currents within Thunderstorms, Size between 1-5cm
Rime
Deposit of ICE CRYSTALS on any object whose surface is lower than freezing. Forms from supercooled fog
what do clashing air masses do?
Create Weather
All air mass types
mE, mT, mP, cP, cT, and cA air masses.
Air Mass Characteristics
They assume the temp and moisture of its Source Region
Global Wind Belts
0-30° Trade Winds, 30-60° Westerlies, 60-90° Polar Easterlies
Frontal Wedging
Occurs when a colder air mass lifts a warmer air mass, leading to cloud formation and precipitation.
Warm Front
Warm Moist Air, WInd Shifts from EAST TO SOUTHWEST
Cold Front
Cold Dry Air, Wind shifts from SOUTH TO WEST
Occluded Front
Cold Front overtakes Warm Front. Warm air is forced a loft
Stationary Front
Air mass does not move Shown as line with blue triangles and red semi circles on opposite sides of the line.Winds move from opposite directions on opposite sides of the front.
Stages of a thunderstorm
1. Cumulus- (forming) Updrafts from latent heat only
Mature- (Its on) Updrafts and downdrafts
Dissipating- (falling apart) downdrafts only.
Ordinary Thunderstorm
20,000- 40,000ft, lasting 45 minutes
Severe Thunderstorm
40,000- 60,000ft - lasting 60 minutes
Supercell Thunderstorm
60,000ft -80,000ft, lasts hours
Thunderstorm Overshoot
Cloud is still vertically developing but anvils prematurally.
Squall Line
Cold front moved so fast it subducts a warm front creating rolling tubes of air.
Tornados 3 characteristics
100- 300mph
upwards air currents
pressure change
EF- scale
A scale used to classify the strength of tornadoes based on the damage they cause, ranging from EF0 (weak) to EF5 (incredible).
2 Types of Tornados
GROUND UP- forms form squall lines
CLOUD DOWN- Crossing winds in a front will create tornado
Tornado Equation
Velocity = MVr
Pressure change from tornado
Creates outward explosion in buildings
Fujita Scale
A scale that rates the intensity of tornadoes based on the damage they cause and estimated wind speeds. Scale from F0-F5
Pressure in Troposphere range
950 - 1050 mb
Lighting types
CLOUD TO GROUND- electrons move from cloud to ground (flash of light moves from ground up)
GROUND TO CLOUD- electrons move from ground to cloud ( flash of light moves from cloud down)
CLOUD TO CLOUD- electrons move from cloud to cloud( flash of light moves opposite to movement of electrons)
Return Stroke
Flash of light from lighting that moves opposite to the movement of electrons
30-30 rule for lighting
30 seconds - seek shelter
30 minutes - stay there
Scientific name for a hurricane
Tropical cyclone
Conditions needed for a hurricane
-80° water, must be a large stretch of ocean, large amounts of moisture continuously, wind speed minimum of 73 mph
Why is the Eye wall of a hurricane significant
The eye wall is significant because it is the area surrounding the eye of the hurricane, where the most intense winds and heaviest rainfall occur, leading to the greatest damage.
Parts of a hurricane
The parts of a hurricane include the eye, eye wall, and rainbands, each contributing to the storm's structure and behavior.
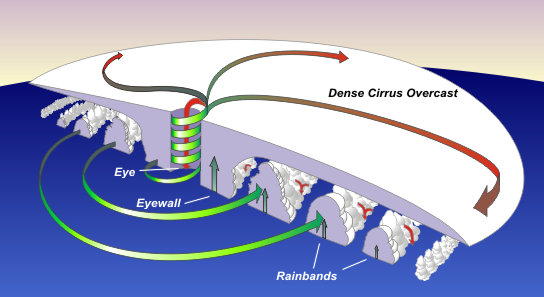
How can we track hurricanes
-Satellites
-aircraft reconnaissance
-Doppler radar
Saffir - Simpson Scale
A classification system for hurricanes that rates their intensity on a scale from 1 to 5 based on sustained wind speeds and potential damage.
Storm Surge
30-50 miles wide, creates most damage, ocean rises 2in per millibar drop. accounts for 90% of hurricane deaths.
2 types of Floods
FLASH FLOOD- Large rainfall over short period of time. Lasts hours to days.
REGIONAL FLOOD- Heavy rainfall for weeks to months. lasts weeks to months.
Stream Equilibrium Elements and definition
Discharge - How much water is flowing in the river. Volume/per unit time
Load - Sediment that the river is carrying
Gradient - The slope of the river
Braided Streams
A type of river channel characterized by multiple interwoven channels. Caused by to much load causing seidiement to build up.
Meandering River
A river channel characterized by looping curves and bends, formed by the erosion of the outer banks and deposition on the inner banks, typically found in areas with gentle slopes.
What is fire
Rapid combustion of oxygen with carbon, hydrogen and other elements that produces flame, heat and light.
Fire Triangle
FUEL, OXYGEN, HEAT
Wildfire Types
Ground Fire- Moves Laterally
Wall Fire- Moves Laterally and Vertically
Crown Fire- moves through the tops of trees laterally
What is a Fire Gap
A fire gap is a controlled area that helps to stop or slow the spread of wildfires. It can include cleared land or natural barriers.
Fire Laddering
The process in which fire moves up objects to get taller and taller such as bushes, trees or buildings.
Guaranteed Impact
Asteroid has to be more than 350 tons to guarantee entry through earth’s atmosphere
Asteroids come from where
The Asteroid belt
Meteoroid definition
(OUT IN SPACE)- Pieces of asteroids and comets orbiting the sun.
Meteor definition
(IN EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE)- Shooting stars blazing through Earth's atmosphere
Meteorite definition
(HIT SURFACE OF EARTH)- Object actually hits the surface of the earth
Types of Asteriods
Metallic (Iron) - Easier to get through atmosphere than stony
Rocky (Stony) - Harder to pass through atmosphere than metallic.
Torino Scale
Assesses comet and asteroid impact hazard on a scale of 0-10.