dynamics
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Y'all... eish || texbook references: Mike Crundell, Geoff Goodwin - Cambridge International AS & A Level Physics student's book 3rd edition |||
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
What is Newton’s First Law
A body continues in its state of rest, or with uniform velocity, unless acted on by a resultant force
what does it mean when the resultant force is zero
at rest or constant velocity in a straight line
what happens when a resultant force is acting on an object
object accelerating or decelerating
what forces act on an object when it is at rest
Normal contact force and gravity
what forces act on an object when in constant velocity in a straight line
thrust and resistive
what direction do forces act when an object accelerates
same direction
what direction do forces act when an object decelerating
opposite directions
what is Newton’s Second Law
for a body of constant mass, its acceleration is directly proportional to the resultant force applied to it.
define force
rate of change in momentum
what equation do you use for Newton’s Second Law
F = ma
what is a free body diagram
graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces in a given condition
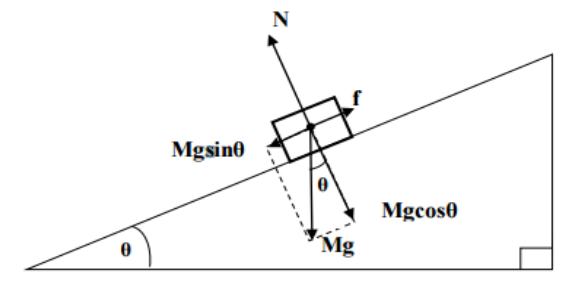
what is mgsine()
horizontal weight component
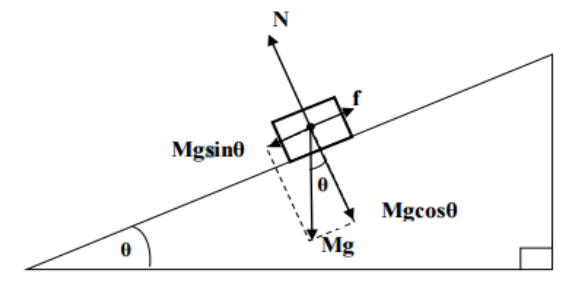
what is N
Normal contact force
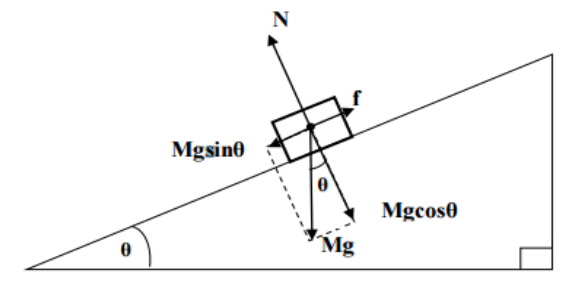
what is f
friction
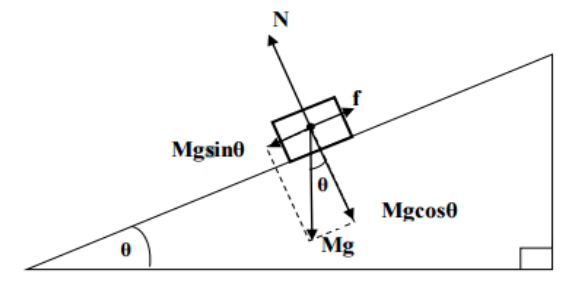
what is Mg
weight
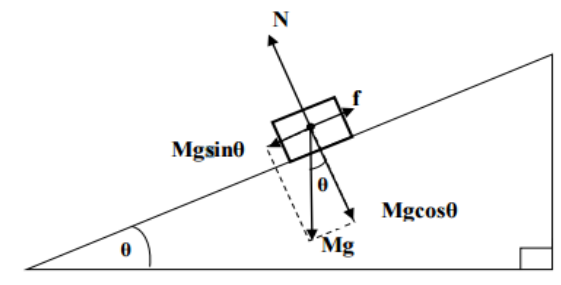
what is mgcos()
vertical weight component
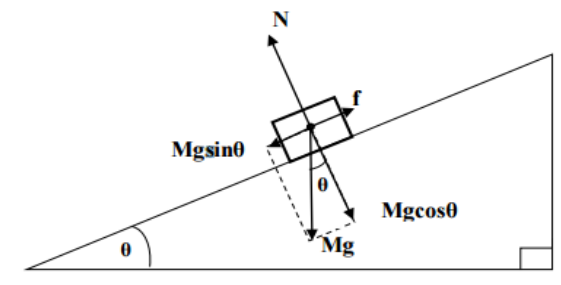
what is the name of this diagram
free body diagram
what is Newton’s Third Law
when two bodies interact, one body exerts a force on the second body and the second one exerts an equal and opposite force on the first one
in Newton’s Third Law, where are the action-reaction forces
on opposite bodies
what is an example of Newton’s first law
a bowl set down on a table
what is an example of Newton’s second law
a parachute being open
what is an example of Newton’s third law
moon orbiting planet
what is the acceleration of connected objects when a force is exerted on them
the same
what is combined effect of several forces
resultant force
what is the SI unit of force
Newton
what can forces do to objects
change shape or dimensions of objects
what kind of quantity is force
vector
why are spring balances called Newton balances
because that is the SI unit of force
what different changes can a force apply to an object
tension, squeezing, pulling, stretching, squishing
what fact should you keep in mind when measuring forces
the fact forces can change the dimensions of objects in a reproducible way
what does changing object dimensions in a reproducible way mean
under the same conditions so that the changes can be measured and replicated reliably
what did Aristotle discover
natural state of object was at rest and is necessary to make it move
who believed in the greater the force, greater the speed
Aristotle
what did Galileo question statement to Aristotle be
motion at constant speed can be as natural as a state of rest
what can make the friction on motion significantly less
pushing an object on a smooth, lubricated surface can make it vanishingly small
what does the force of friction do
oppose pushing force
how many laws does Isaac Newton have
three
what is the formula for force
force equals mass time acceleration
what is 1 Newton defined as
force which will give you a 1kg mass and acceleration of 1ms^-2
what is inertia
what is the property of an object to stay with no resultant force
what quantity is momentum
vector
define momentum
the product of its mass and its velocity
how do you calculate momentum
mass x velocity
what is the unit of momentum
N s
what is the base quantity of momentum
Kg m s^-1
what is momentum when an object is at rest or velocity is uniform
momentum is zero
what is resultant force in terms of momentum
rate of change of its momentum
what is momentum when provided the external resultant force is zero
momentum is constant
what is Newton’s second law of motion in terms of momentum
the resultant force acting on an object is proportional to the rate of change of its momentum
what is Newton’s second law in terms of the constant of proportionality
the resultant force acting on an object is equal of the rate of change of momentum
what is momentum expressed in symbols
F = Δp/Δt
what is momentum expressed in symbols for constant mass
F = Δ(mv)/Δt = m(Δv/Δt) = ma
what is weight
force of gravity which acts on an object
what is the unit for weight
N
why do you never specify the direction of force of gravity even though it goes in the same direction?
always going towards center of Earth
what do newton balances find
weight
why is a balance in a lab called a balance
to represent balance of forces
what is weight equal to on a balance found in a lab
to previous calibration to balance
why do objects at rest have weight
gravity is always acting
what makes an object at rest have zero resultant
normal contact force
what does “normal” in normal contact force mean
acts perpendicularly to plane of contact
what does “contact“ mean in normal contact force
happens because of contact between object and surface plane
what kind of balance is used to compare weight
lever balance

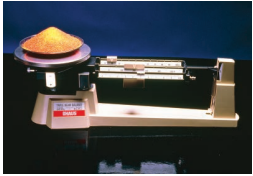
what type of balance is this
top pan balance
what type of balance is this
level balance
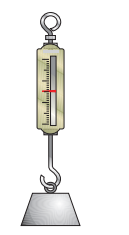
what kind of balance is this
sprig balance
what other body exerts a force on an object at rest other than normal contact force (think of a book and a table)
upward force exerted by the table on the book
what is the principle of conservation of momentum
the total linear momentum of a system of a system of colliding bodies with no external forces acting, remaining constant
what is the meaning of a closed system
matter cannot enter or leave, but energy can flow across the boundaries
what is an isolated system
where both matter AND energy are prevented from entering or leaving the system
what does this represent
isolated energy system
what does this represent
closed energy system
what is the protionality of mass and velocity in momentum
directily proportional
what direction does momentum and velocity work in
same direction
define impulse
product of force acting on an object and the time during which the force acts
symbol for impulse
J
formula for impulse
J = F t
what is the unit for impulse
N s
what quantity is impulse
vector
what happens to the momentum of two colliding bodies hittign each other at the same time
one loses and one gains
what is the firmula for total initial momentum = total final momentum
Mux + Mux = Mvy + Mvy
if no kinetic energy is lost during collisiton, what is said about it
it is perfectly elastic
formula for perfectly elastic collision when velocity directions are defined
u x- uy = vx - vy
what happens when two object collide and no energy is lost
converted to other forms
what happens when pulling force is greater than friction force
object accelerates
what happenes when pulling force is equal to friction force
object is at constant velocity
what happens when pulling force is less thant fricition force
object is decelerating
where does viscouse force happen
in fluids
is water high or low viscosity
low
is glue high or low viscosity
high
what is terminal velocity
maximum constant speed an object reaches when falling through a fluid
what is resultant force downward in viscous fluid
weight - viscous force
what is non-unifrom motion
when acceleration is initially gravity but decreases to zero with time
what is upthrust or bouyancy dependent on
fluid density
what is resultant force downward when talking about buoyancy
weight - (upthrust + visvous force)
how is resultant force during terminal velocity with upthrust / buoyancy
weight = upthrust + viscous force
what is resultant force
combined effects of forces acting on an object
what can forces do to an object
change its shape
SI unit for force
Newton
what is inertia
property of an object to stay in a state of rest or uniform velocity