Atomic Wave Functions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
How do you get the energy of an electron in three dimensions?
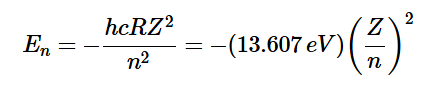
What does a hydrogenic atom mean?
An atom or ion that has only one electron.
What is the radial contribution?
It defines how the wavefunction depends on the distance of the electron from the nucleus.
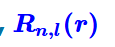
Where does the radial contribution of s-orbitals reach a maximum?
At r = 0 (the nucleus).
What happens to the radial contribution of p and d orbitals as r approaches 0?
It approaches zero.
What is the radial distribution function?
it describes the probability of finding the electron at a distance r from the nucleus.
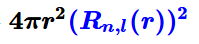
What indicates the most probable distance for finding an electron?
The maximum value of the radial distribution function on its graph.
What is the Bohr radius, and why is it used?
a0 = 52.9pm = 0.529A˚
Used to scale distances for hydrogen atomic orbitals, making plots relative to r/a0 more convenient.
What are radial nodes, and how are they identified?
Points where the radial wavefunction equals zero
Found by plotting Rn,l(r)= 0 or where the radial distribution function is zero.
How do you calculate the number of radial nodes?
n − l − 1
(n = principal quantum number, l = angular momentum quantum number)
What is the angular contribution?
It describes the wavefunction’s shape and angular orientation with respect to a coordinate system.
What are the spherical coordinates used for the angular contribution?
r = distance from the nucleus
φ = angle from positive x-axis in the xy-plane (0 to 2π)
θ = angle from the positive z-axis towards the xy-plane (0 to π)
What does Yl,ml(θ, φ)² describe?
shape of the orbital, determining the angular distribution of the electron
What are angular nodes?
Where Yl,ml(θ, φ)² = 0
Are planar (or conical) depending on l
Number of angular nodes = l