Social Psych Exam 1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Social psychology
branch of psychological science that is mainly concerned with understanding how the presence of others affects our thoughts feelings, and behaviors
Levels of Analysis
Complementary views for analyzing and understanding a phenomenon.
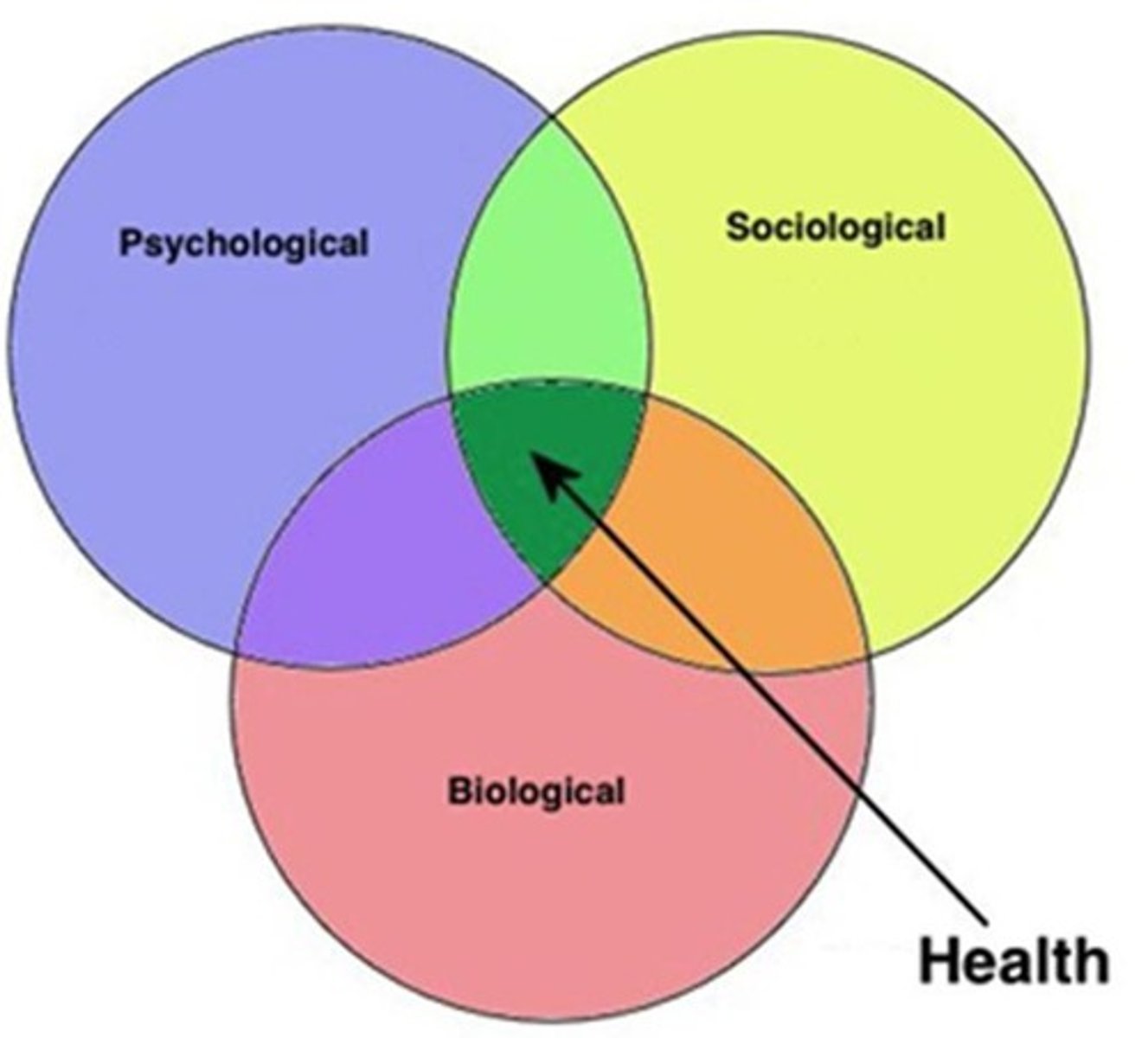
Levels of Analysis for Studying Social Psychology
Culture/environment -> Relationship/Groups -> Behavior -> Thoughts/Feelings/Perceptions -> Physiology -> Chemistry/DNA
Studying Social Psych
observation has an advantage of being entirely naturalistic. We all act as amateur social psychologists arriving at conclusions about our own social worlds through informal observations.
Culture of Honor
The social norm that condones and even encourages responding to insults with aggression
Peace and Conflict
Researchers are interested in why people fight, how they fight, and what the possible costs and benefits of fighting are
What do researchers study regarding negative attitudes?
How people can overcome negative attitudes and feel more empathy towards members of other groups.
What are three examples of social attitudes?
Stereotypes, Prejudice, Discrimination.
Conformity
Changing one's attitude or behavior to match a perceived social norm.
Obedience
Responding to an order or common from a person in a position of authority
Persuasion
delivering a particular message so it influences a person's behavior in a desired way
What is social cognition?
The way we think about the social world and how we perceive others.
What is social attribution?
The way a person explains the motives or behaviors of others.
What is the Fundamental Attribution Error?
The tendency to emphasize another person's personality traits when describing that person's motives and behaviors and overlooking the influence of situational factors.
Artificial environment
allows researchers to control conditions and variables. Can determine causal direction; how one variable might causally influence another. Can be complex with multiple independent and/or dependent variables. Can employ use of a confederate.
Field Experiments
can be elaborate. People in them do not know they are participating in research-so they will act naturally. Uses real-world situations to study behavior. Can employ use of a confederate. Like a laboratory experiment, there is an Independent Variable (IV) and Dependent Variable (DV)
Naturalistic Observation
Unobtrusively watching people as they go about their lives. Researchers study behavior in natural settings. Researchers can immerse themselves in an environment. Researcher can use devices to capture information about participants. No random assignment. Experience sampling methods: recording devices, smart phone apps, EAR diary, etc
need to belong
a motivation to bond with others in relationships that provide ongoing, positive interactions
What is attraction?
The psychological process of being sexually interested in another person.
What are attitudes?
Opinions, feelings, and beliefs about a person, concept, or group.
What types of attitudes are researchers particularly interested in?
Social attitudes people hold about categories of people.
experience sampling techniques
people are asked to report their conscious experiences at particular times
Independent Variable (IV)
The variable that is manipulated or controlled by the experimenter.
Dependent Variable (DV)
The variable that is measured to assess the effect of the IV.
Control Group
A group that does not receive the experimental treatment and is used for comparison
Random Assignment
Participants are randomly assigned to different groups (e.g., control and experimental) to ensure each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group, reducing bias
Operational Definitions
Clear definitions of how variables are measured or manipulated.
Complex Experimental Designs
An experiment with two or more independent variables
Factorial Designs
Studies that involve more than one IV. Each IV can have multiple levels. This design allows researchers to investigate the interaction effects between IVs.
For example, a 2x2 ______________ has two IVs, each with two levels.
Repeated Measures Designs
The same participants are used in all conditions of the experiment. This reduces the variability caused by individual differences.
Participants serve as their own control group.
Mixed Designs
Research designs that combine both experimental and correlational methods. In this design, participants from naturally occurring groups of interest (e.g., people with panic disorder and people with social phobia) are assigned to each experimental treatment, allowing the experimenter to determine whether the effectiveness of the treatments varies by group classification.
Counterbalancing
A method of controlling for order effects in a repeated measure design by either including all orders of treatment or by randomly determining the order for each subject
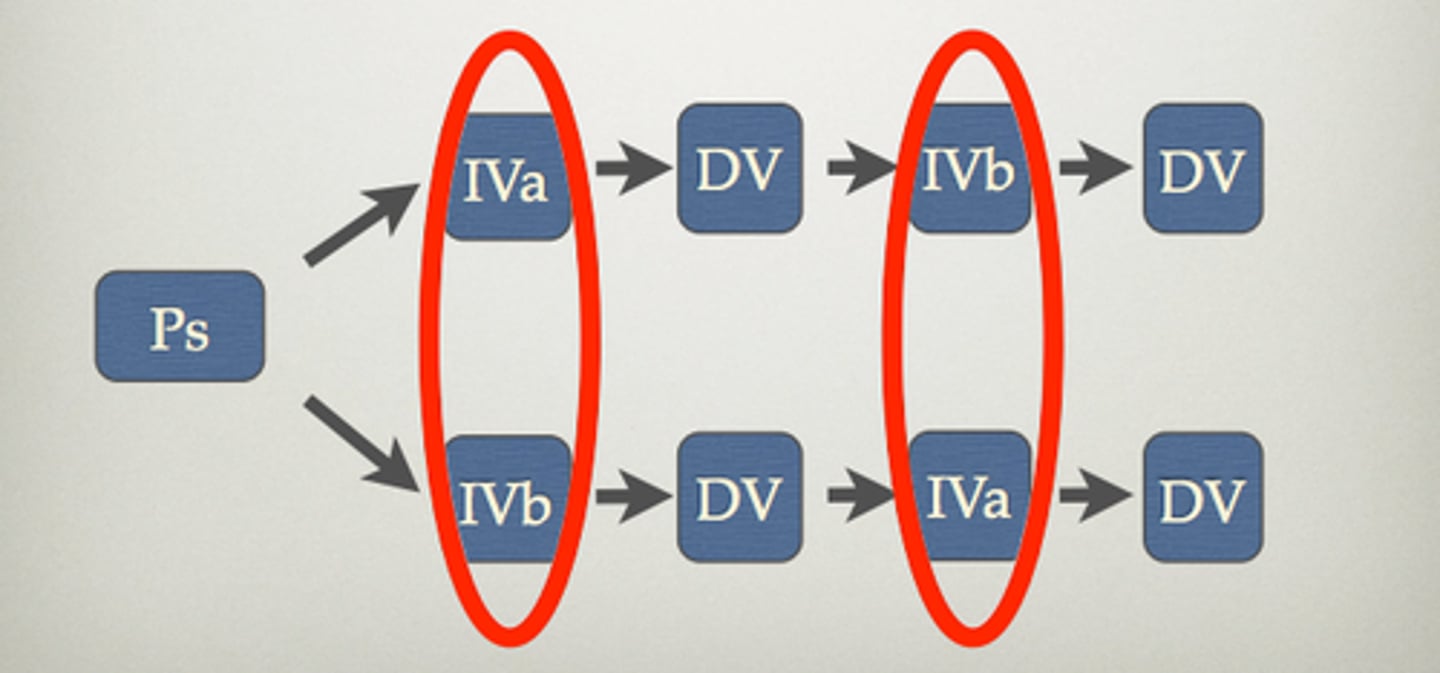
Basic Design Example
A study examining the effect of a new teaching method (IV) on students' test scores (DV) with a control group using traditional methods
Complex Design Example
A factorial design study examining the effects of different types of feedback (positive/negative) and task difficulty (easy/hard) on performance, with each participant experiencing all conditions (repeated measures).
representative sample
a sample that accurately reflects the characteristics of the population as a whole
What are surveys commonly used for in social science research?
Political polling and customer satisfaction.
What are the advantages of using surveys?
They are scalable, relatively inexpensive, and can provide a basis for numerical comparison.
How can electronic platforms enhance surveys?
They can provide more diverse sample sizes.
What is a disadvantage of surveys related to response bias?
The possibility of socially desirable responding.
What is a disadvantage of surveys related to sampling?
They can lead to non-representative sampling.
What limitation do surveys have regarding data collection?
They only capture a single point in time.
Implicit Association Test
A computer-driven assessment of implicit attitudes. The test uses reaction times to measure people's automatic associations between attitude objects and evaluative words. Easier pairings (and faster responses) are taken to indicate stronger unconscious associations.

Priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one's perception, memory, or response
Five Principles of Ethical Research
informed consent, privacy, risks and benefits, deception, debriefing
Social Neuroscience
the study of the relationship between biological systems and social processes and behavior
Social Neuroscience aims to address
how our understanding of social behavior can be expanded when we consider neural an physiological responses
Social Neuroscience Methods
Measuring brain activity:
Electrical activity (EEG)
Blood flow (fMRI)
Measuring hormones
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
a measure of electrical activity (generated by neurons)
It is non-invasive
It is able to precisely measure when brain activity occurs
Use a cap
EEG Research on Social Categorization
Participants view pictures of people of different social categories. Asked to categorize or make judgements. (Race/Gender or Attractiveness/Personality)
Results: Brain activity looks different when viewing members of different social groups.
Race: 100 milliseconds
Gender: 150 milliseconds
fMRI
measures changes in the oxygenation of blood flowing in the brain.
When neurons become more active, blood flow to the area increases to bring more oxygen and glucose to the active cells.
neuroendocrine (hormones) system
Oxytocin, cortisol, serotonin are used in the form of hormones
stress response:
corticotrophin-releasing hormone from the hippocampus-> Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Social Categorization
Mental classifying someone as belonging to a social group.
Stereotypes: Beliefs about social groups.
Social categorization is first step
Research question: how automatic is social categorization
Testing simulation hypothesis
• The same brain regions (e.g. Medial Prefrontal Cortex (mPFC) are active when thinking about the self and when thinking about others.
• mPFC is particularly active when subjects mentalized about people they rated as similar to themselves.
• Evidence for the Simulation Hypothesis
Stress
A threat or challenge to well-being.
Exams
Tripping
Extreme Temperatures
Drama
Threats
Protection against stress
-Social support
-Optimism
-Relaxation
Self
is found when you look at yourself and inside your mind
The Social Actor
The sense of the self as an embodied actor whose social performances may be construed in terms of more or less consistent self-ascribed traits and social roles.
Sense of self emerges as a social actor by
age 2.
By age 4,
someone can describe themself in simple behavioral traits.
By age 10,
we see ourselves in more complex ways
The Motivated Agent
prioritizes the motivational qualities of behavior-inner needs, wants, desires, goals, values, plans, programs, fears, and aversions
Theory of Mind
Understanding that other's behavior is often motivated by inner desires and goals
Age 5-to-7 shift-
Children become more intentional and systematic in their goal pursuit
Narrative Identity
Internalized and evolving story of the self
Temporal Continuity
how I have come to be the person I am becoming. (Past, Present, Future). Reconstructs the past. Anticipates the future. Provides unity, meaning, and purpose.
Autobiographical Reasoning
a narrator is able to derive substantive conclusions about the self from analyzing their own personal experiences
Redemptive Narratives
Track the move from suffering to an enhanced status or state
Heuristics
Mental shortcuts or "rules of thumb" that often lead to a solution (but not always).
Representativeness heuristics
when we judge the likelihood of the object belonging to a category based on the extent to which the object appears similar to one's mental representation of that category
Availability heuristics
evaluate the frequency or likelihood of an event, based on how easily instances of it come to mind
Planning Fallacy
We underestimate the time it will take us to perform a task
affective forecasting
the tendency for people to overestimate how events will make them feel in the future
Cameleon effect
people unconsciously mimic the behaviors, mannerisms, and gestures of those around them, often leading to increased social bonding and rapport. This mimicry happens without deliberate intent and helps to facilitate smoother and more harmonious interactions.
Impact Bias
tendency for a person to overestimate the intensity of their future feelings
Automaticity
the ability to process information with little or no effort
Attitudes
psychological tendency expressed with some degree of favor or disfavor. Can be explicit or implicit
Explicit Attitudes
-Attitudes that we consciously endorse and can easily report.
-Attitudes that are involuntary, uncontrollable, and at times unconscious.
Implicit Attitudes
-Attitudes that are involuntary, uncontrollable, and at times unconscious.
Intrapersonal
Within us
Interpersonal
With others
Cultural Display Rules
help people manage or modify their emotions. They are learned early in life and specify how to exhibit emotions in particular social circumstances.
Amygdala
Emotional processing
What role do emotions play in decision-making?
Emotions help us act quickly with minimal conscious awareness.
How do emotions function as information processing systems?
Emotions are rapid information processing systems.
What would happen to our decision-making without emotions?
Without emotions we could not make rapid decisions (attack, flee, defend, approach, etc.).
What effect do intense emotions have on thinking?
Thinking can be difficult during intense emotions.
What does the James Lange theory of emotion propose?
Physiological arousal causes emotion.
What does the Cannon Bard theory of emotion state?
Physiological arousal and emotion happen at the same time.
What is the Schachter Singer theory of emotion?
We use the situation to cognitively interpret physiological arousal to determine emotion.
social facilitation
stronger responses on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others
visual cliff
a laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals. Mothers stand on the other side. Infants are more likely to crawl over if the parent doesn't seem distressed.
Partners who express contempt and frustration for each other
are more likely to get divorced later