Physics - 6 Molecules and Matter - 6.5 Specific Latent heat & 6.6 Gas Pressure and Temperature & 6.7 Gas Pressure and Volume
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Pressure and volume
Latent heat of fusion
energy required to change the state of 1 kg of a substance from solid to liquid
Specific latent heat is measured in...
J/kg
Specific latent heat of fusion =
energy ÷ mass
Lf =
E ÷ m
How do you measure the Lf of ice? [3]
- fill a funnel with ice chips and suspend it over a beaker/measuring cylinder
- use a low-voltage heater attached to a joulemeter to melt the ice
- use the measurement of the mass and of the energy supplied to find the Lf
Latent heat of vaporisation
energy required to change the state of 1 kg of a substance from liquid to gas
Specific latent heat of vaporisation =
energy ÷ mass
Lv =
E ÷ m
What causes gas pressure?
collision of gas molecules with the sides of their container
Why does temperature increase gas pressure?
the particles have more kinetic energy, so they move faster, so they make collisions more often and with more force with the container
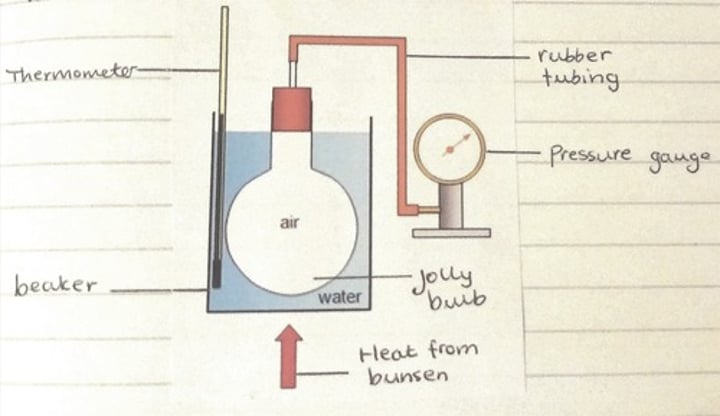
Gas pressure and temperature experiment
use dry air in a water bath attached to a pressure gauge to observe the effect of rising temperature
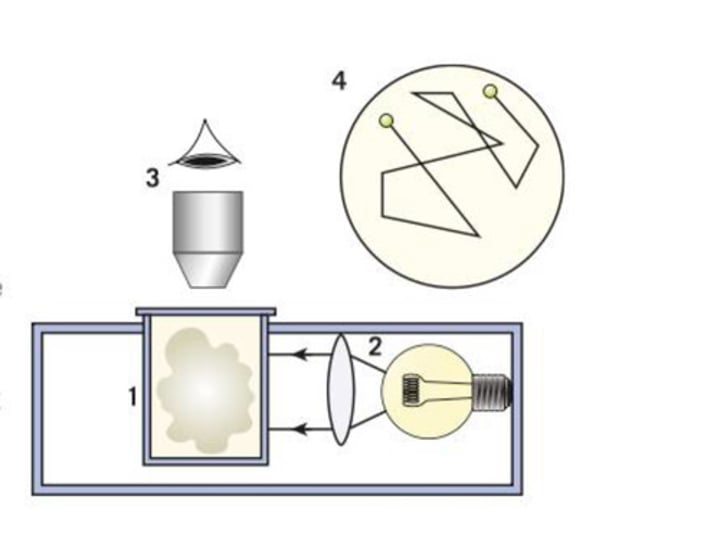
Smoke cell
a small glass cell filled with smoke
Random motion
movement in all directions and at different speeds
Observing random motion [4]
1. a small glass cell is filled with smoke
2. light is shone through it
3. smoke is viewed through a microscope
4. see the smoke particles moving a changing direction
What do we see in the smoke cell?
air particles hitting the smoke and influencing its direction
Pressure produces a net force at right angles to the...
wall of the container of the gas
Why do we compress gas slowly?
otherwise, the work done would increase the internal energy store of the gas and its temperature
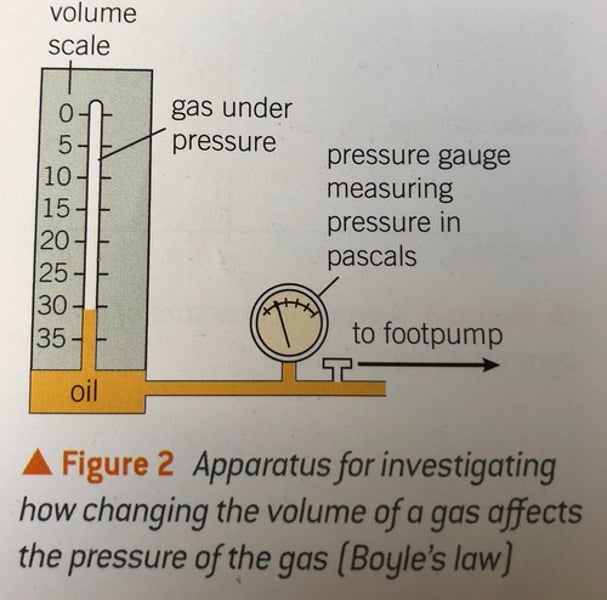
Investigating pressure and volume experiment
slowly increase the pressure and observe the effect it has on the volume
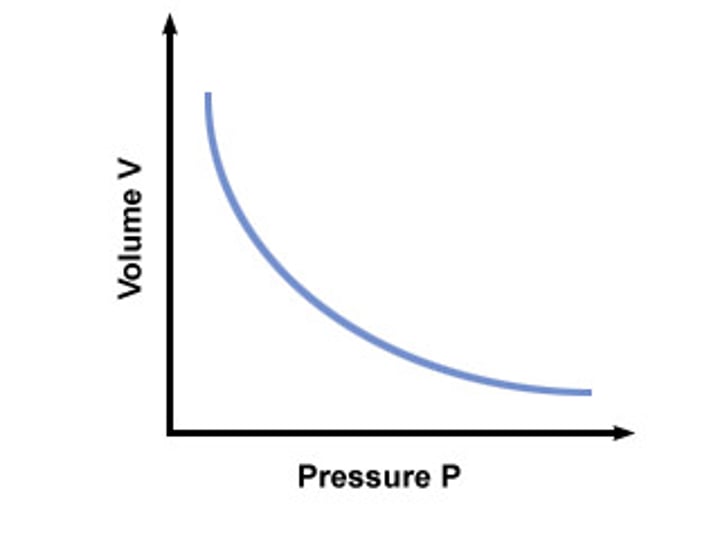
Boyle's law
pressure x volume is constant for a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature
Why does pressure increase as volume decreases? [3]
- the number of gas molecules is constant
- if the space is reduced, the particles don't travel as far between each impact with the container
- the molecules hit the surface more often, so the impacts per unit of space increase
Pressure is measured in...
Pascals (Pa) or N/m²
Pressure is ... to volume of gas
inversely proportional
(BL, w) constant =
pressure x volume
(BL, s) constant =
pV