Microbio Ch. 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Antibiotics
Compounds that can inhibit growth of microorganisms. They are made by microbes themselves in a competitive edge over other species.
Streptomyces
Which species has 70% of discovered antibiotics derived from
Sources of antibiotics
Gram-positive rods, actinomycetes, and fungi are -
Narrow spectrum antibiotics
Drugs that affect in a narrow range of microbial types/categories
will reduce risk of multiple bacteria species becoming antibiotic resistant
Broad spectrum antibiotics
Drugs that affect a broad range of gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria
Can risk multiple bacteria species to become antibiotic resistant
Bacteriostatic
A method that will result in competitive inhibition with folic acid synthesis is -
Bacteriostatic
A method that will result in inhibition of protein synthesis is -
Bactericidal
A method that will lead to injury to plasma membrane is -
Bactericidal
A method that will lead to inhibition of cell wall synthesis is -
Bactericidal
A method that will lead to competitive inhibition with DNA gyrase is -
Bactericidal
What will cause irreversible damage?, like holes and membranes, cell walls, super coils in DNA
Translation
Antibiotics that target inhibition of protein synthesis will affect -
Cell wall synthesis
The most common action site of antibiotic drugs is the inhibition of -
Essential metabolite
What action site is this?
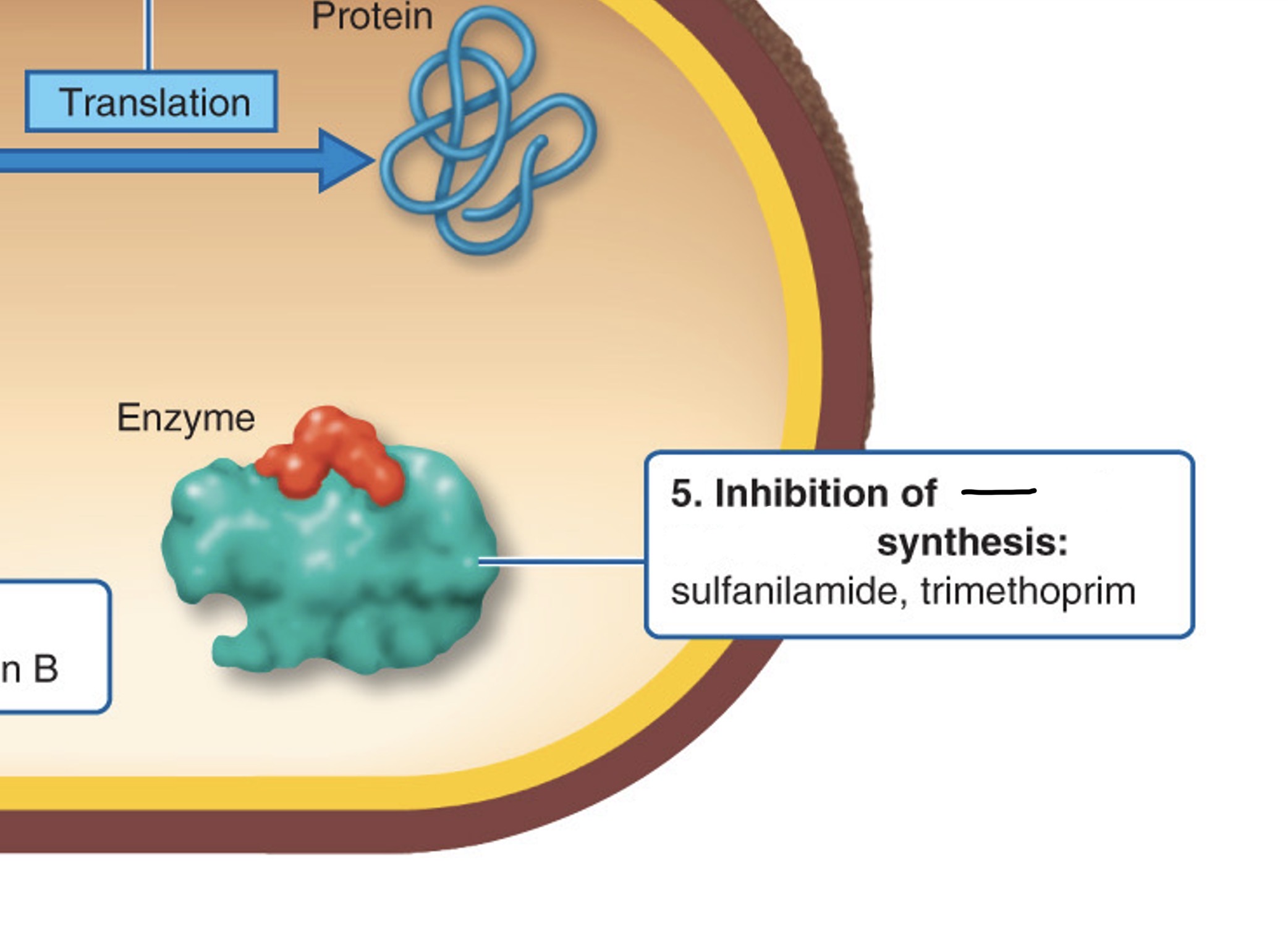
Plasma membrane
Which action site is this referred to?
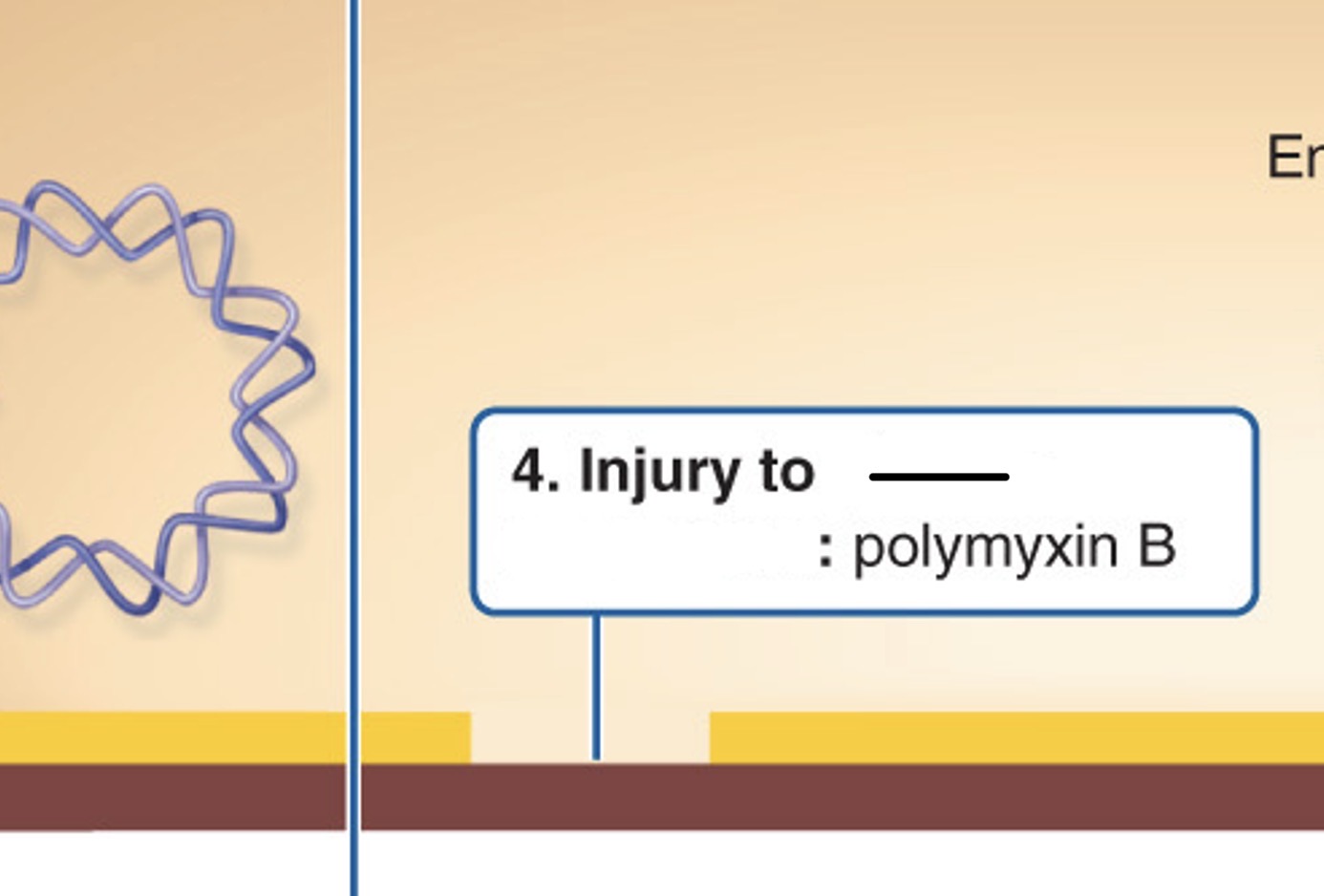
Nucleic acid replication and transcription
Which action site is this referring to?
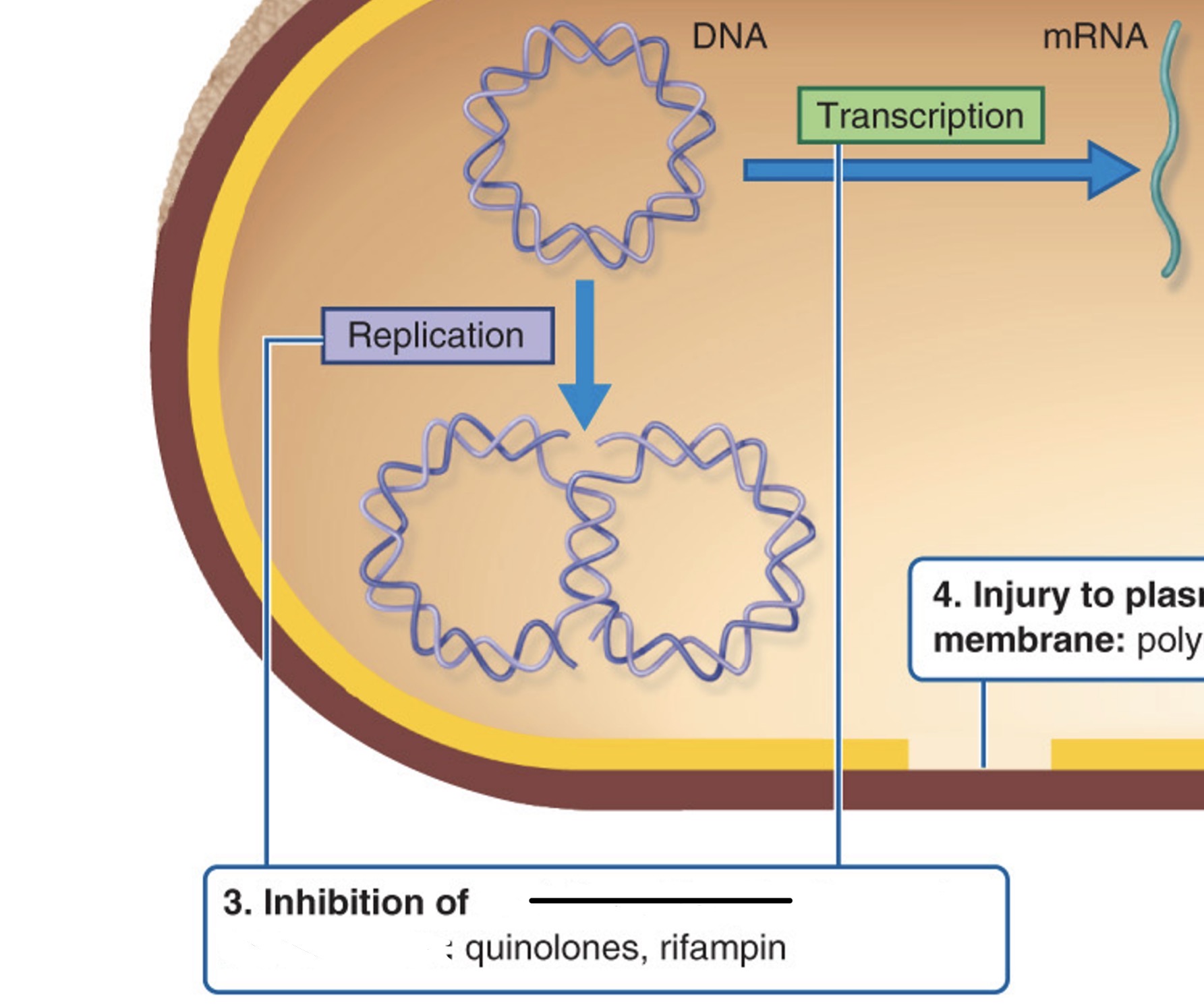
70S ribosomes
What is the target by inhibiting protein synthesis?
Bacteria synthesizes it, humans dont
Both humans and bacteria need para-aminobenzoic acid to make folic acid so why do sulfa drugs adversely impact only bacterial cells?
Antifungal
Which type of drug inhibits microtubule synthesis
Antifungal
Which type of drug inhibits the glucan biosynthesis pathway
Antifungal
Which type of drug inhibits nucleic acid synthesis inside a nuclear membrane
antifungal
Which type of drug inhibits the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway
Antifungal
Which type of drug will bind to ergosterol and disrupt membrane integrity
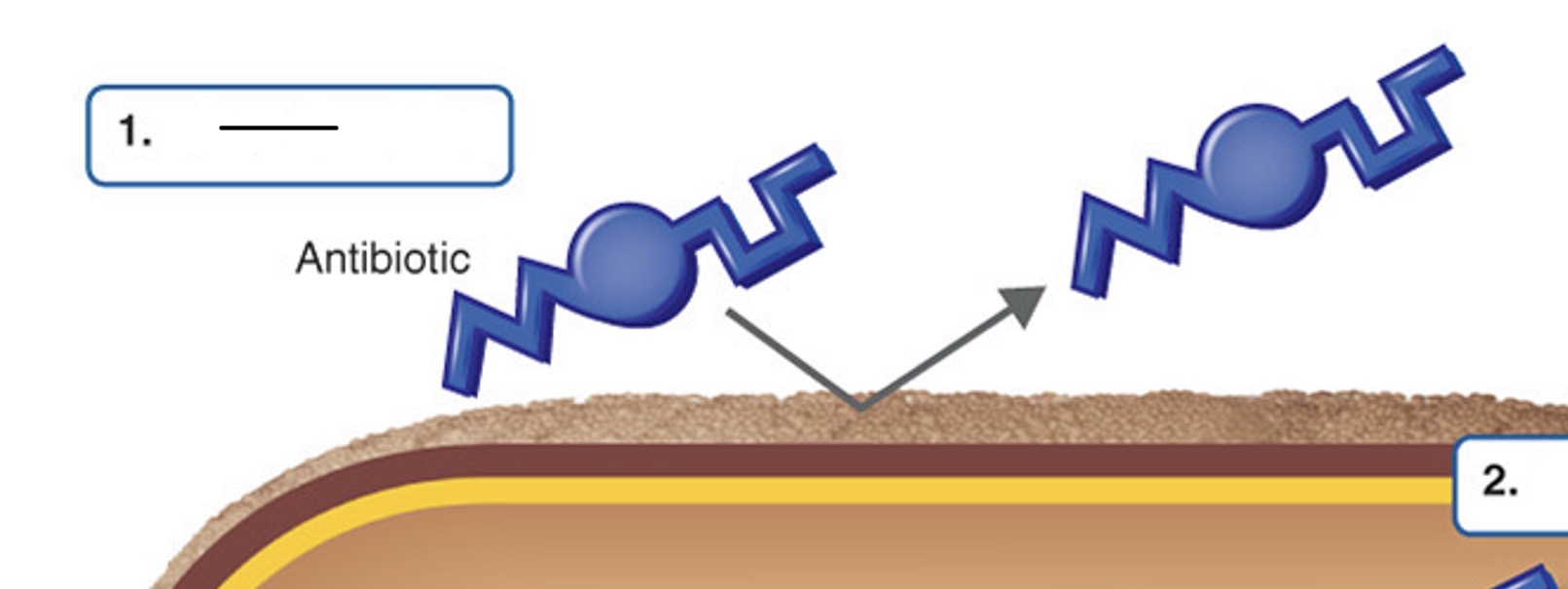
Block drug entry
What type of mechanism of antibiotic resistant is this?
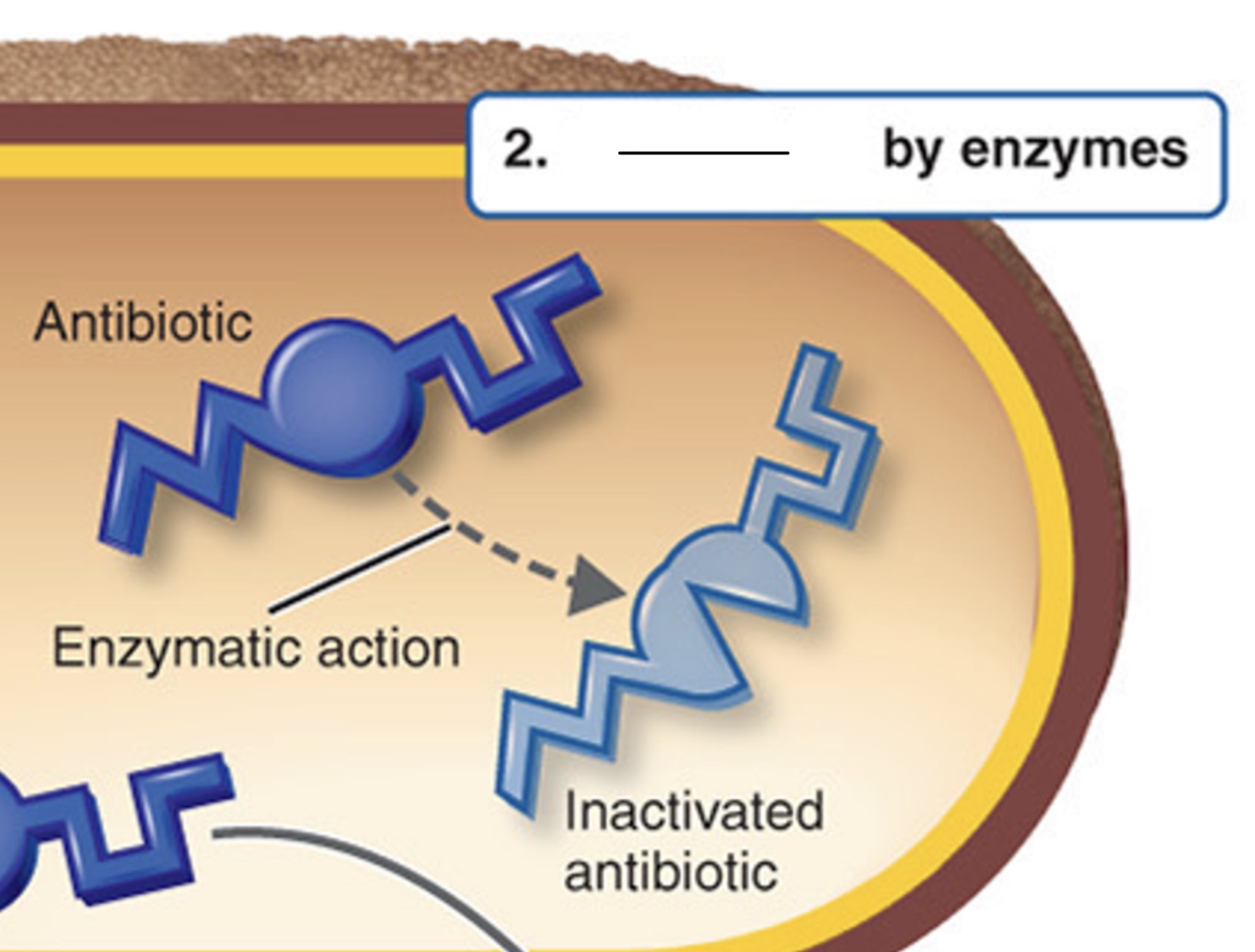
Inactivate drugs
What mechanism of antibiotic resistance is this?
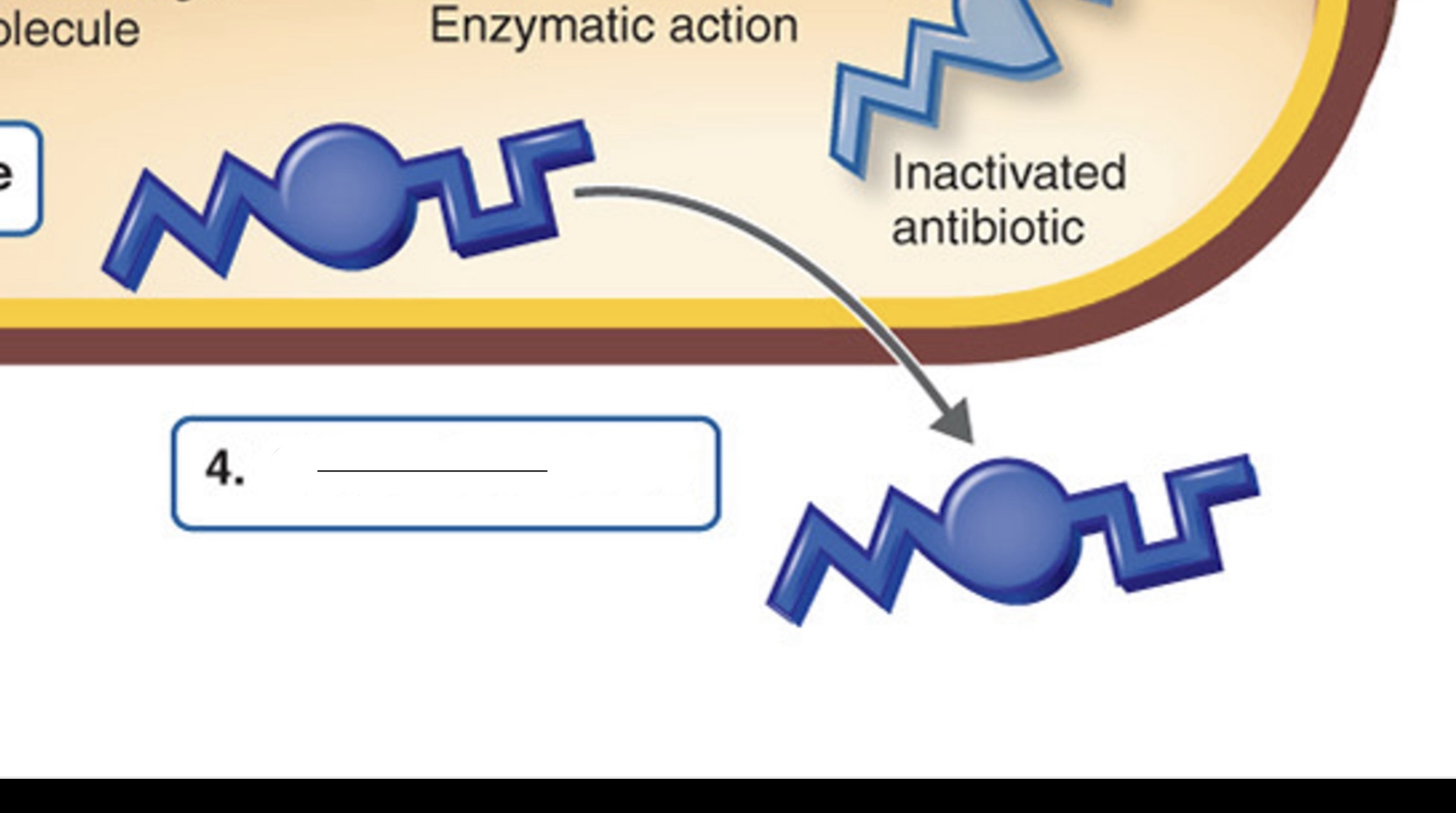
Efflux
Which mechanism of antibiotic resistance is this?
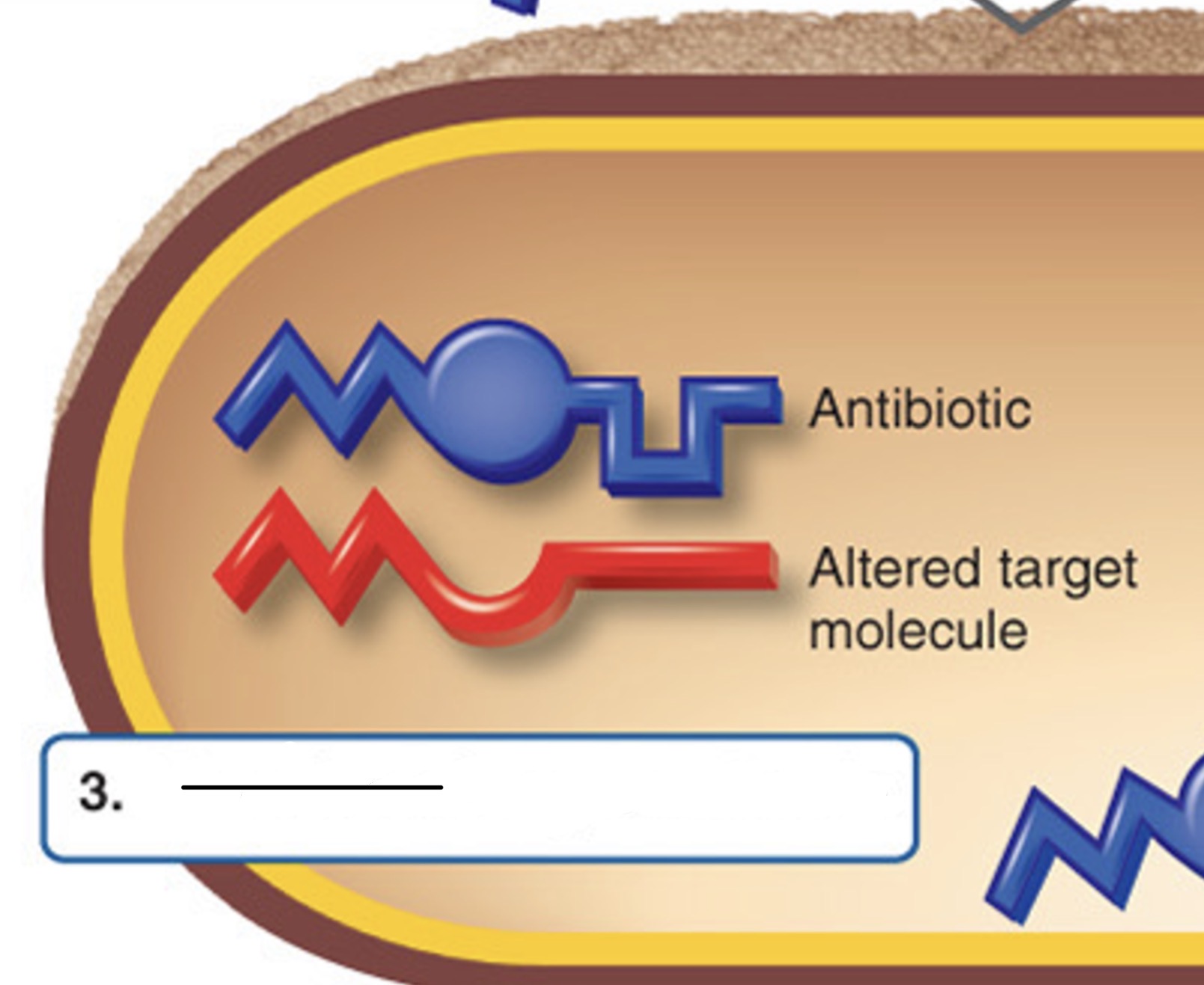
Alteration of target
Which mechanism of antibiotic resistance is this?
Replication or transcription
If a drug binds between alternate G-C base pairs, what process will it inhibit?