ES - Astronomy
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
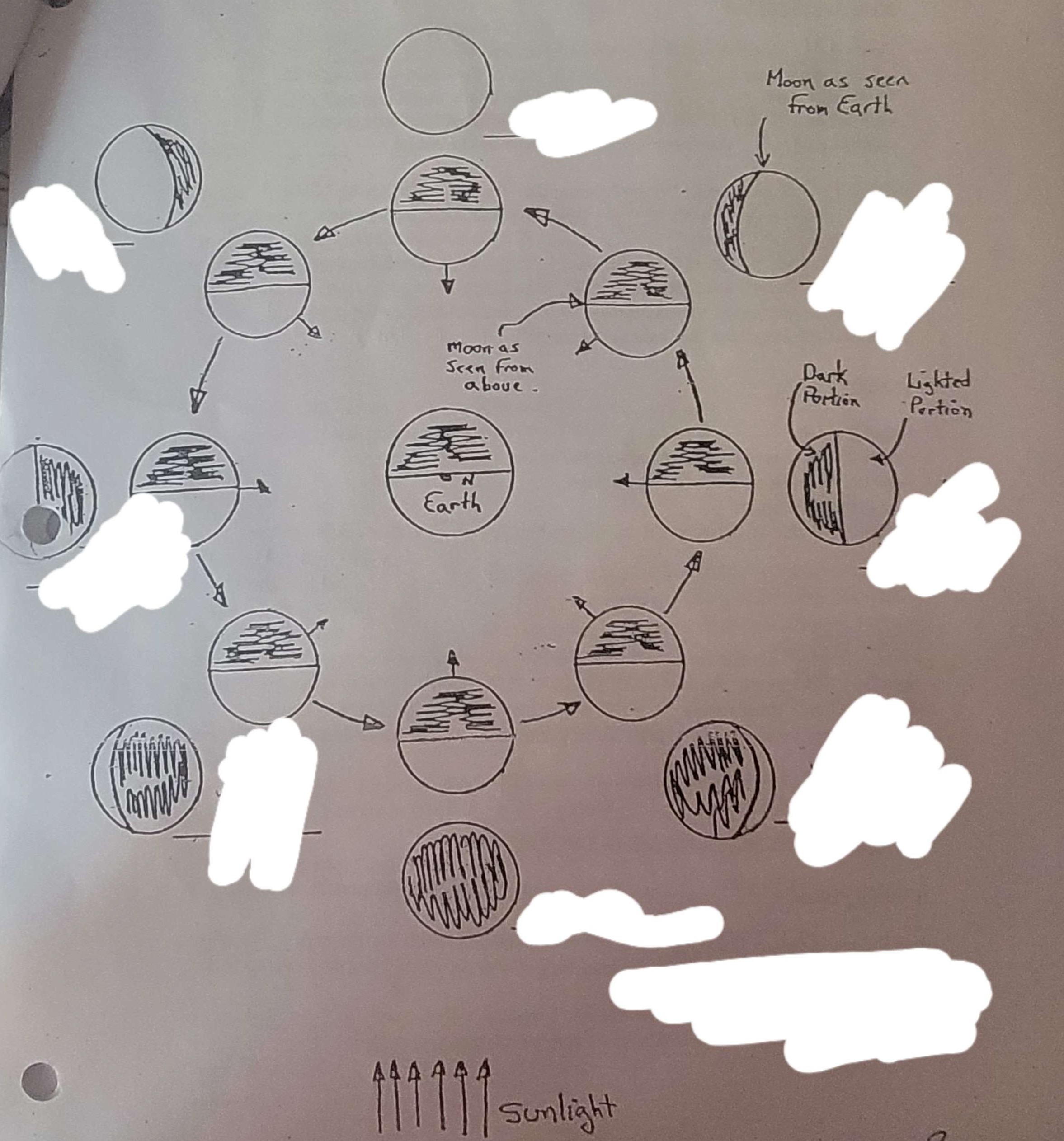
What are all the phases of the moon? (Start from bottom, go right aka how arrows point)
New moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, third/last quarter, waning crescent
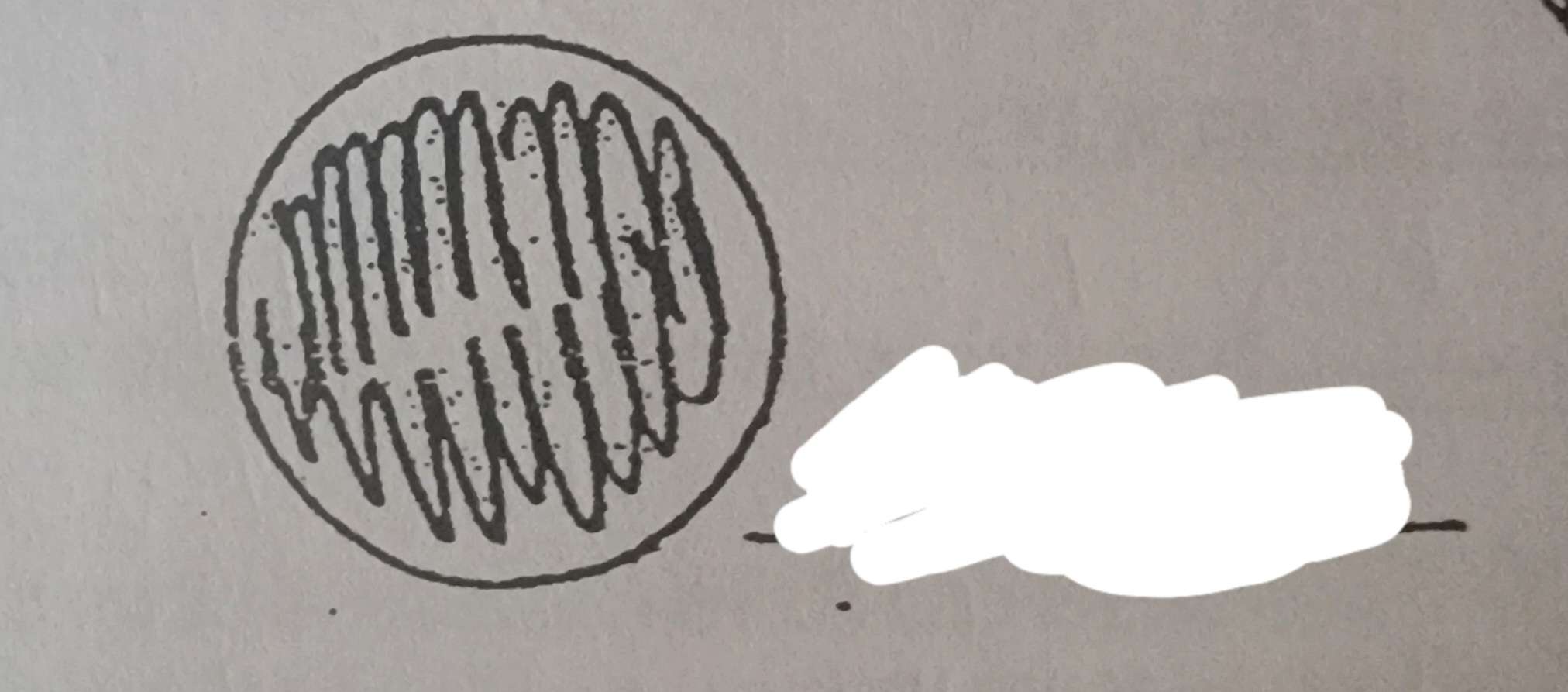

What phase of the moon is this?
New moon
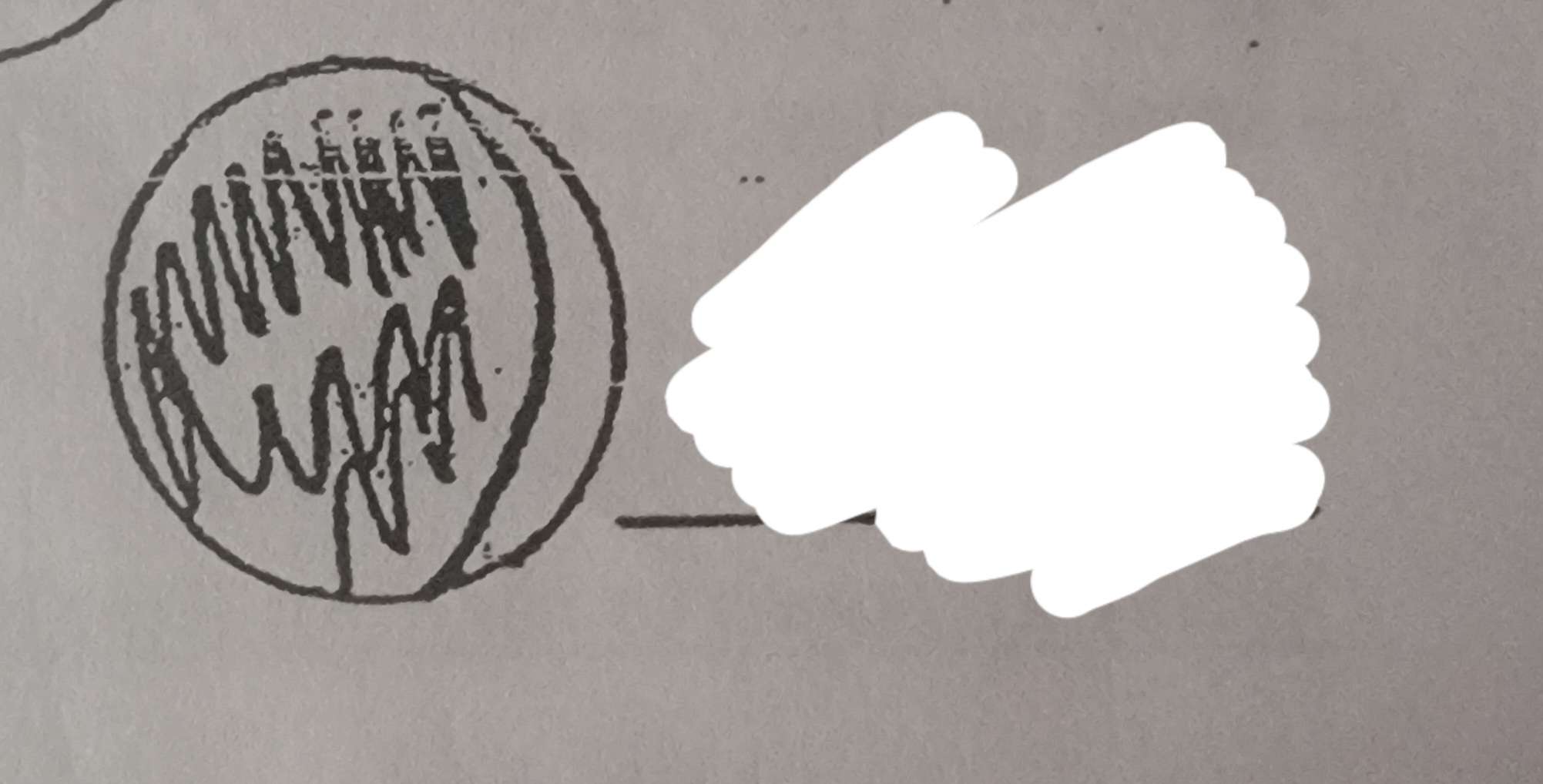

What phase of the moon is this?
Waxing crecent
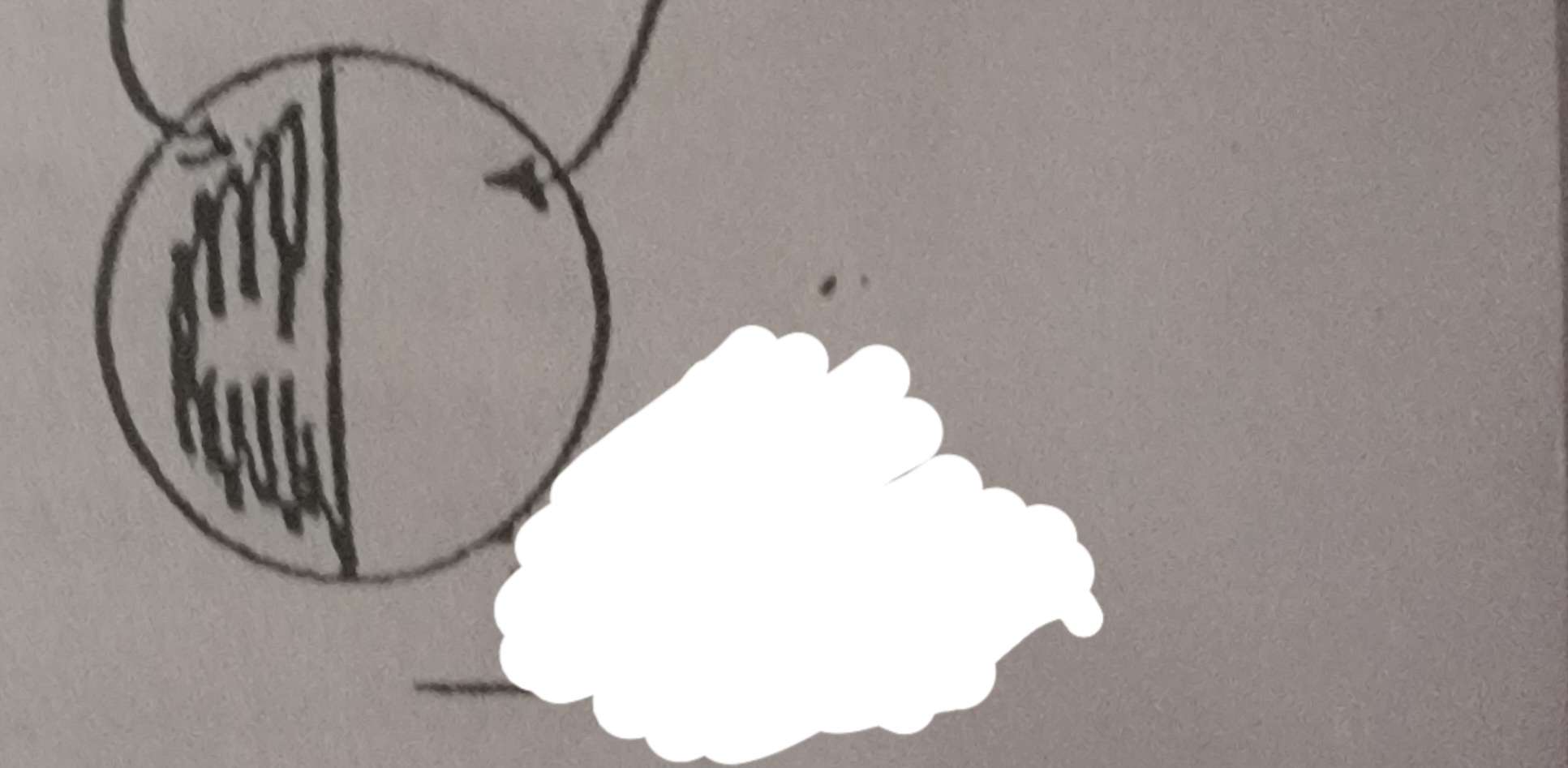

What phase of the moon is this?
First quarter
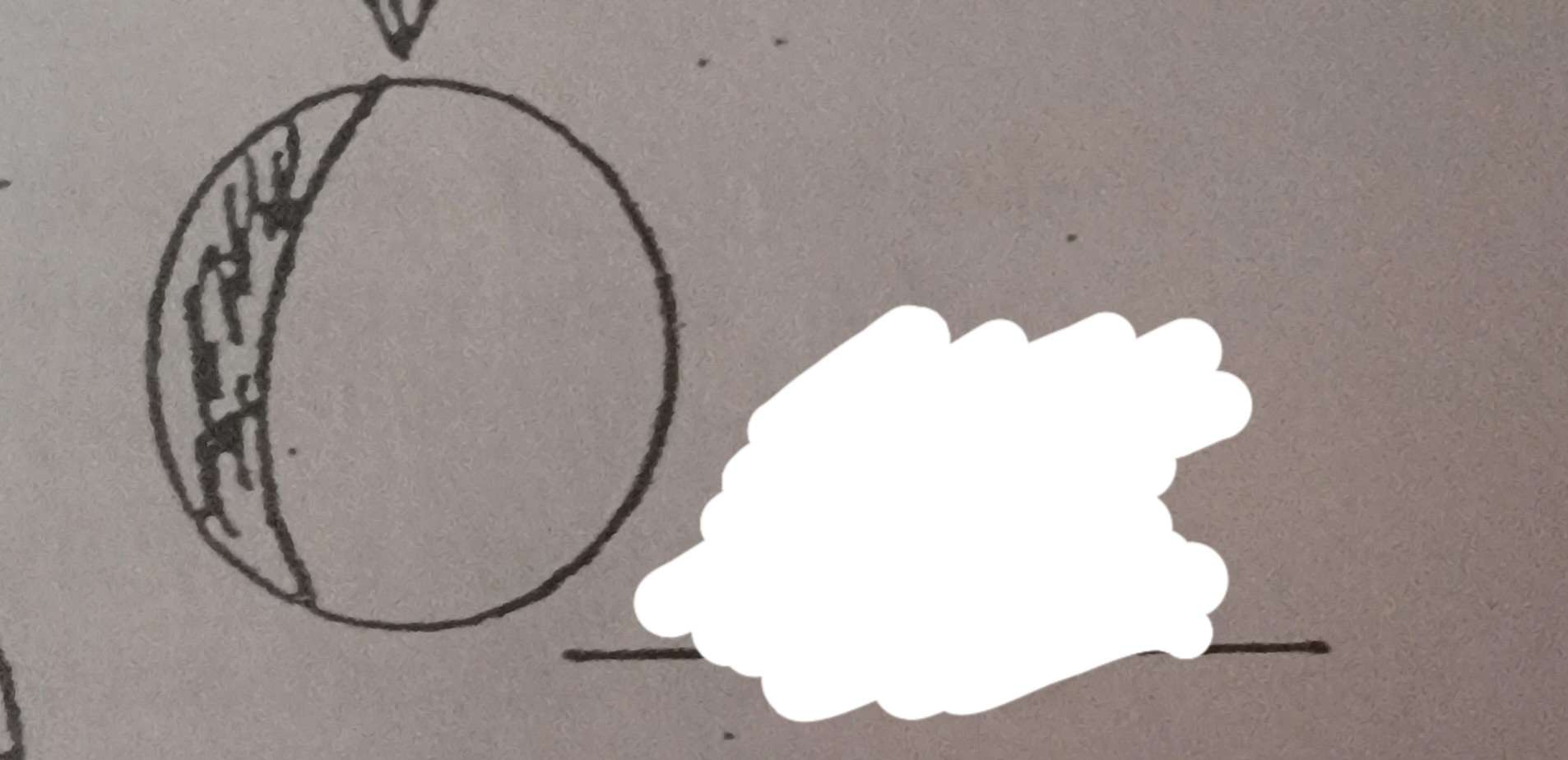

What phase of the moon is this?
Waxing gibbous
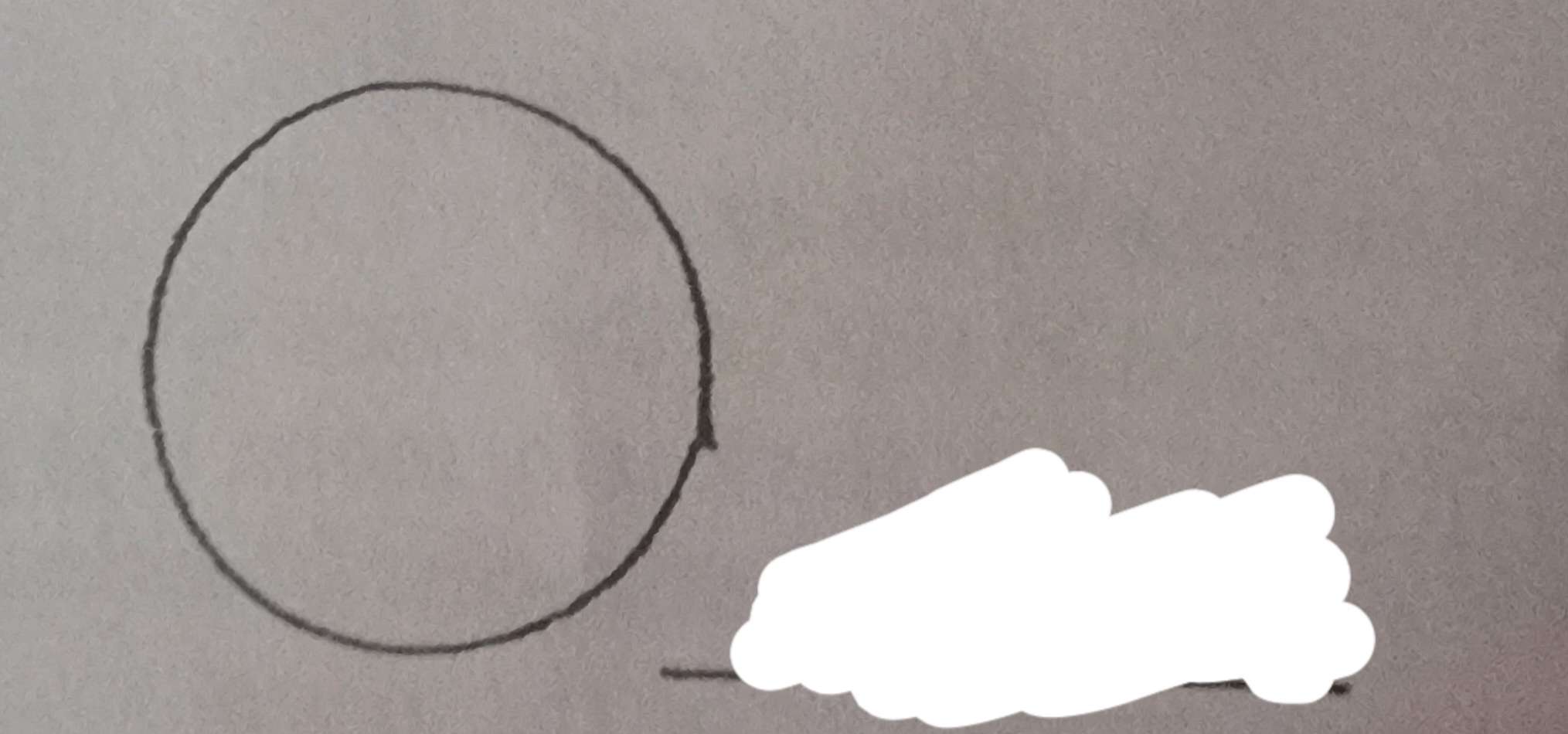
What phase of the moon is this?
Full moon
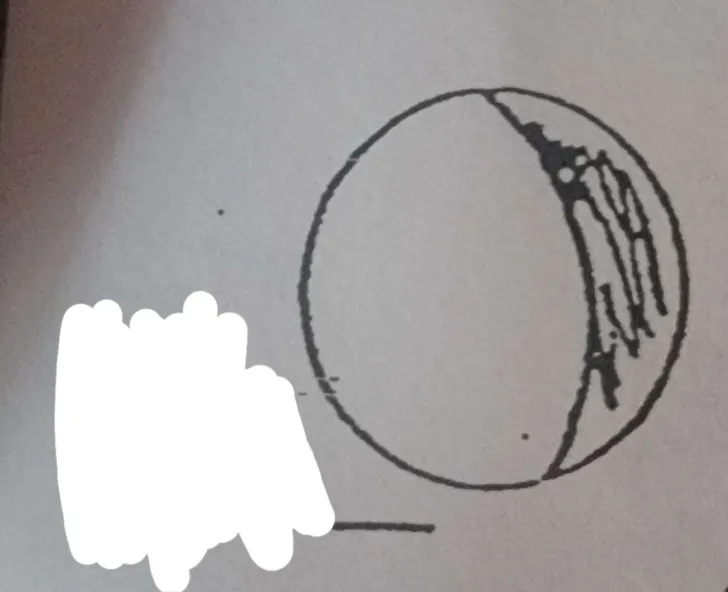

What phase of the moon is this?
Waning gibbous
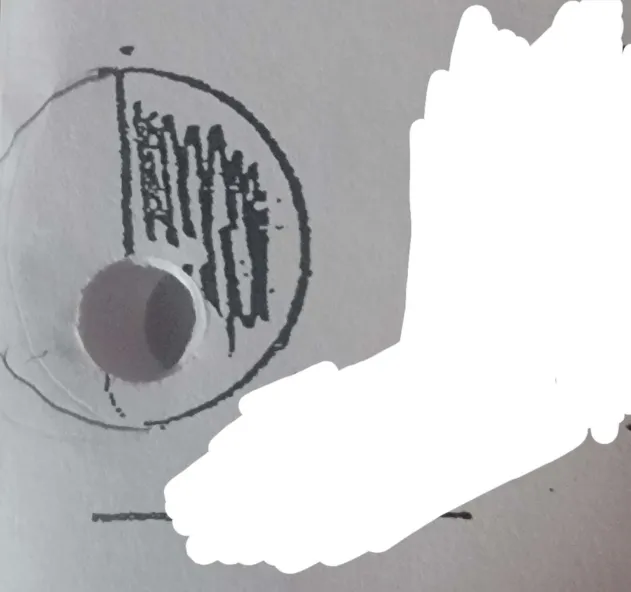

What phase of the moon is this?
Third/last quarter
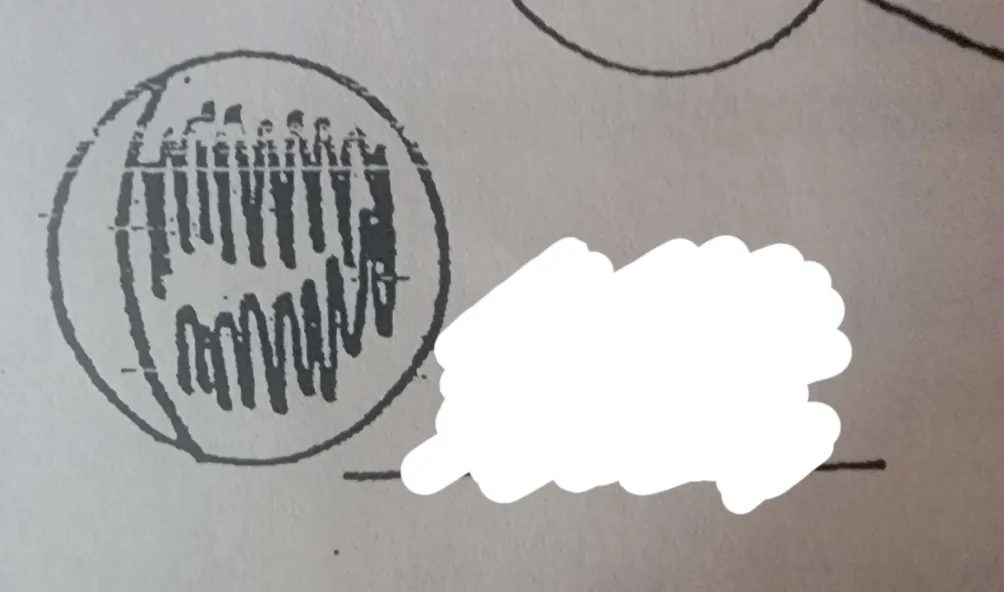

What phase of the moon is this?
Waning crescent
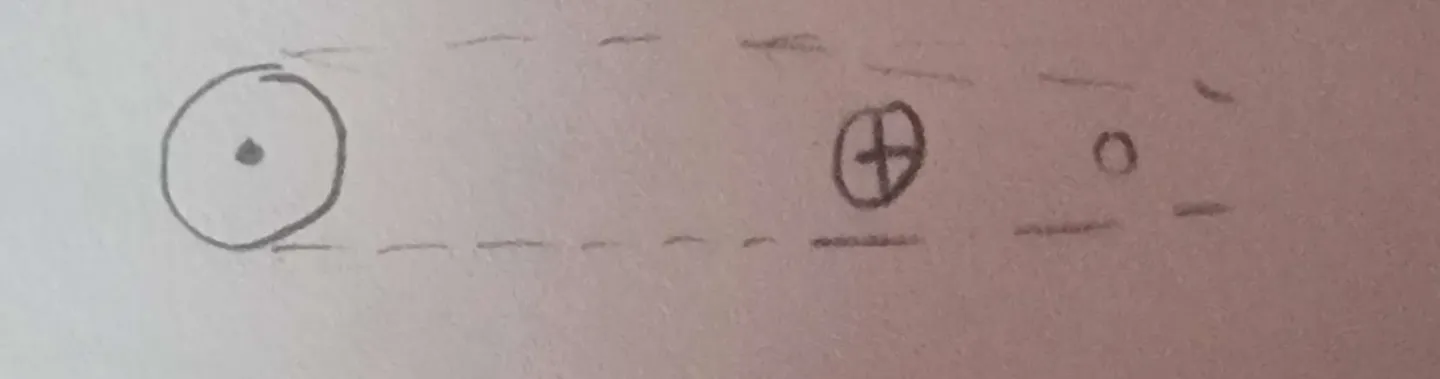
What does this represent?
Lunar Eclipse
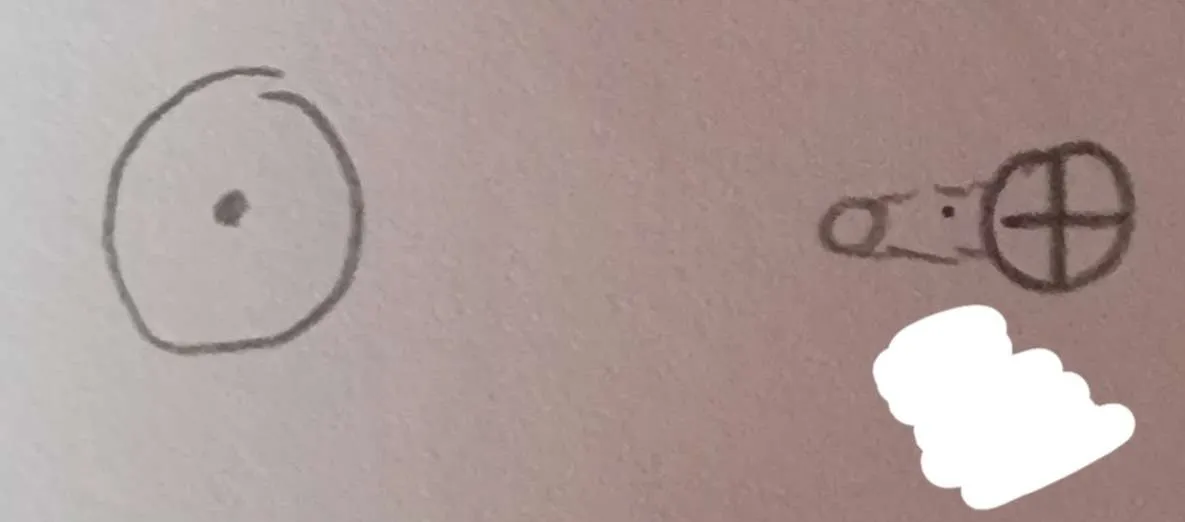
What does this represent?
Solar Eclipse
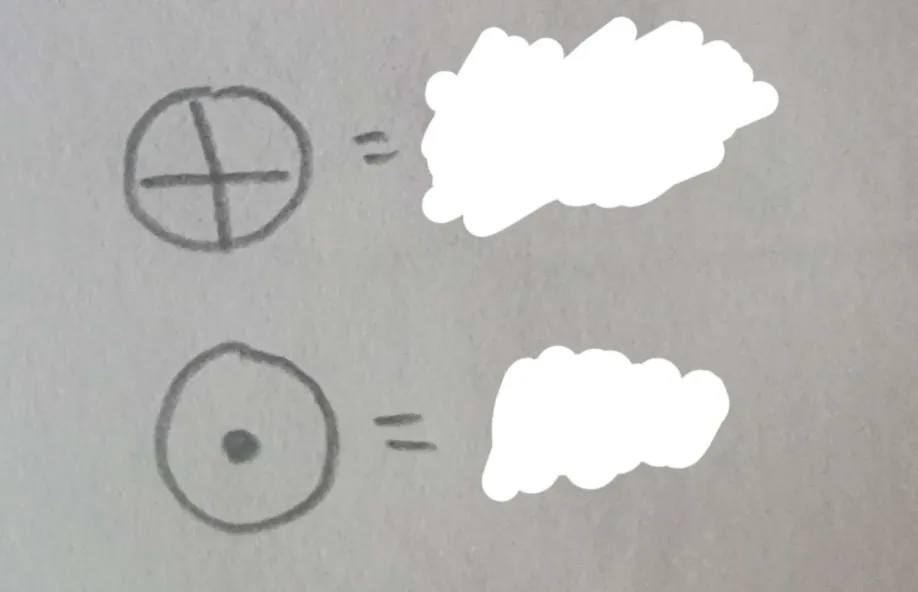
What do these two symbols mean? (top to bottom)
Earth, Sun
Only ___ the moon is lit at one time by the sun
half
Phases depend on ________ of that lit side of the moon we can actually _____
how much, see
depends on the _____ of the Earth, moon, and sun
angles/positions
What are the three components needed for the phases of the moon to occur?
Earth, moon, sun
Moon takes ______ days to ____ the Earth
29.5, orbit
Earth spins on its axis once every _____ hours
24
Phases are ____ the Earth casting its shadow on the moon
NOT
Phases are NOT _____________
The Earth casting its shadow on the moon
A new moon is only “visible” during the ____ (we are “seeing” the ____ side only)
day, dark
a ____ moon is only visible at ____ (rises as the sun sets, set as the sun rises), we are seeing the entire ____ side of the moon
full, night, lit
the moons orbital plane is inclined ____ degrees to our orbital plane around the sun. This is why __________
5, we don’t see eclipses normally - just phases
The moons rotation takes as long as revolution so the ______ always faces Earth
Same side
What is the fact that we only see one side of the moon ever called?
Tidally locked
Lunar Eclipses are when…. (4)
the shadow of Earth covers the moon
can only happen near the full moon phase
happens twice a year
entire night side of the Earth sees it, so we see them more often than solar eclipses
Solar Eclipses are when… (4)
the moon blocks the sun from our view
can only happen near the new moon phase
happens 2-5 times a year
small shadow, only one spot on Earth will see a full solar eclipse once every 300 years
Only one spot on Earth will see a full solar eclipse once every _______
300 years

Is there an atmosphere on Mercury?
No, it has an exosphere
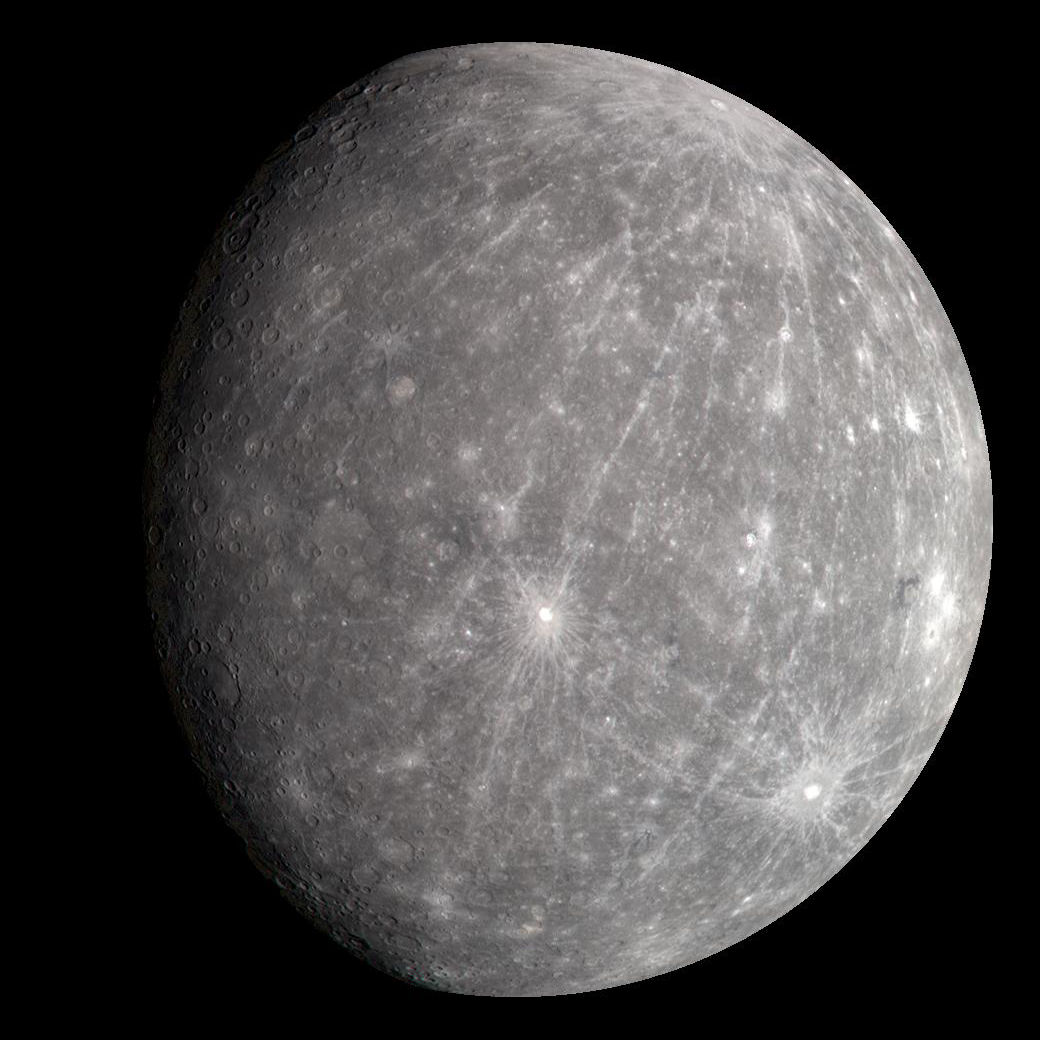

What causes all the craters on Mercury?
collisions with meteoroids and comets
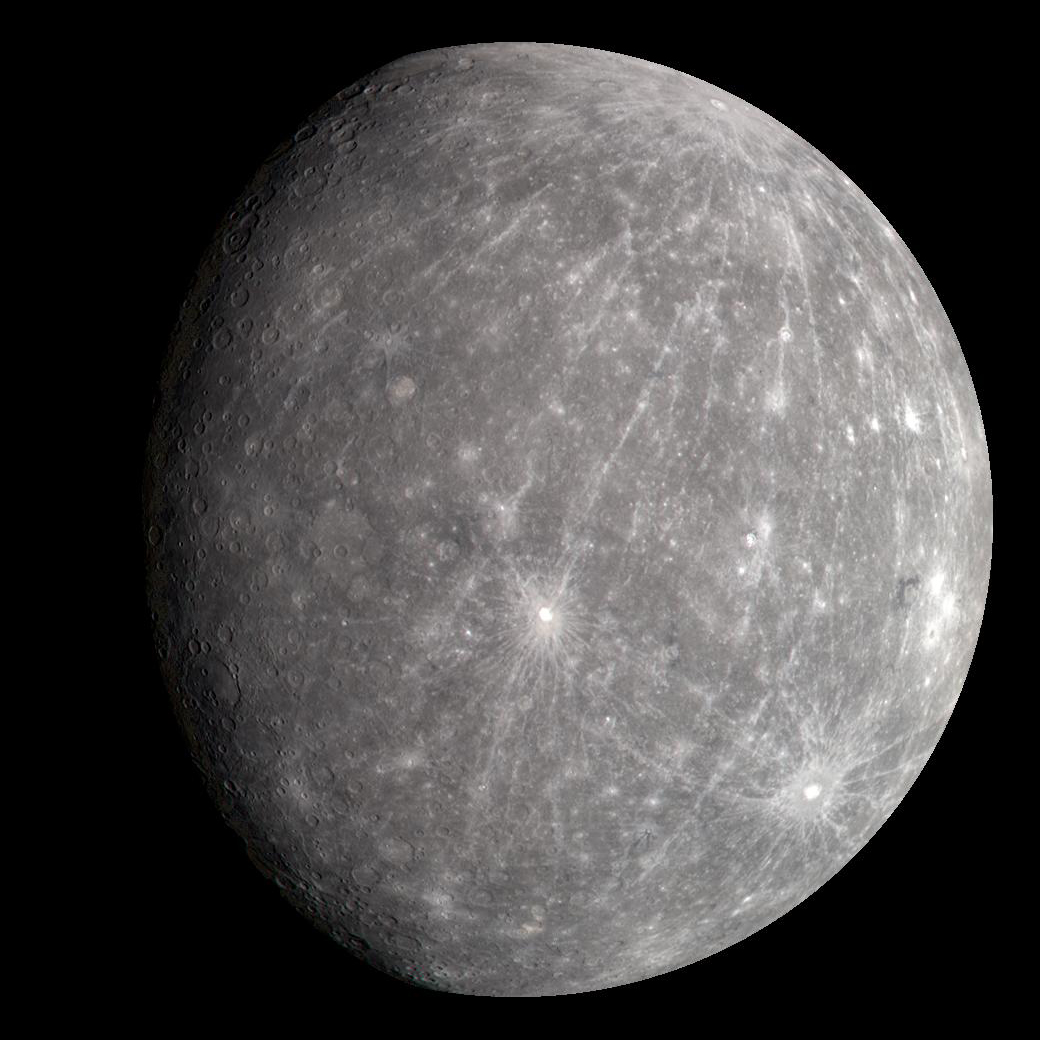

Why does lots of craters mean a surface is old?
Exposed to impacting bodies for longer
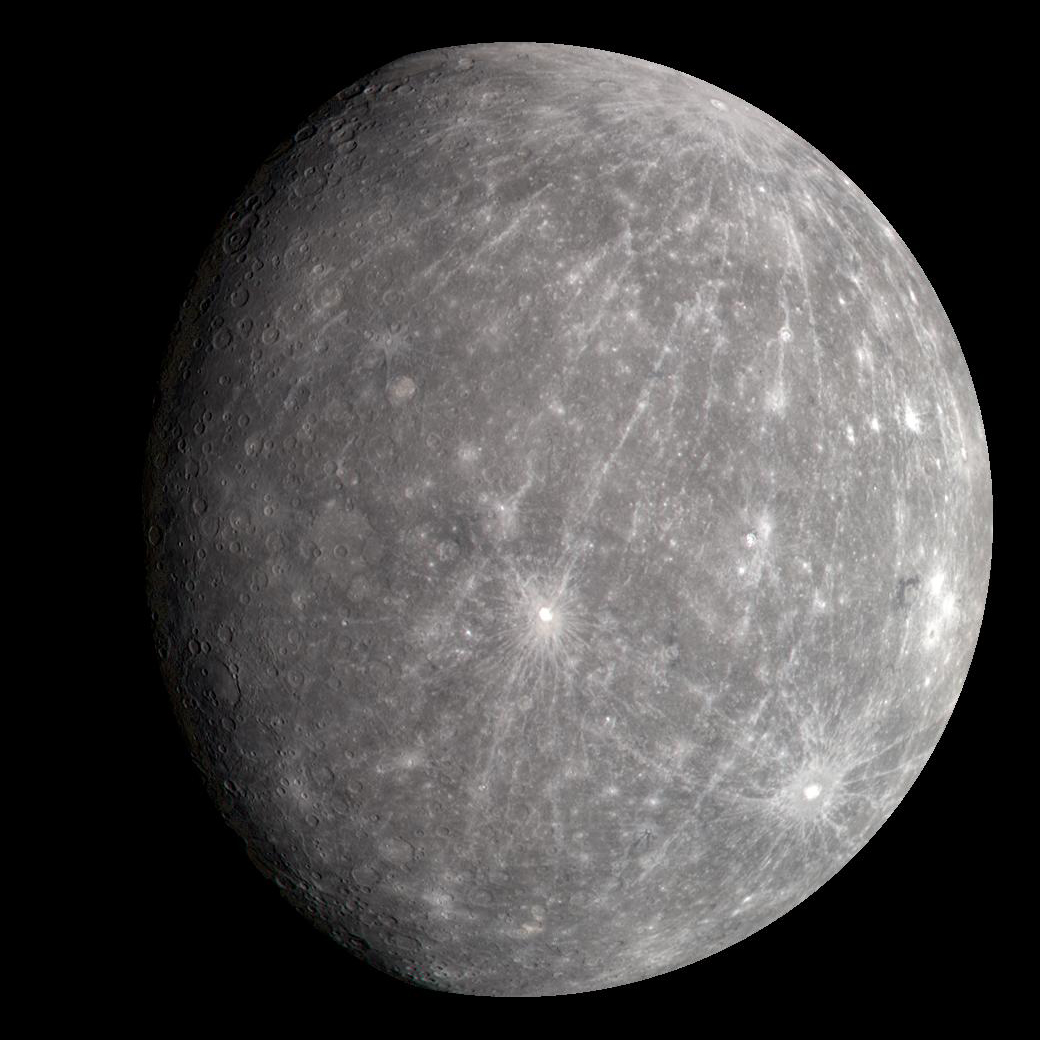

Why does Mercury have lots of craters? (3)
Old
No atmosphere to protect it from impacts
No weather to erode away the craters
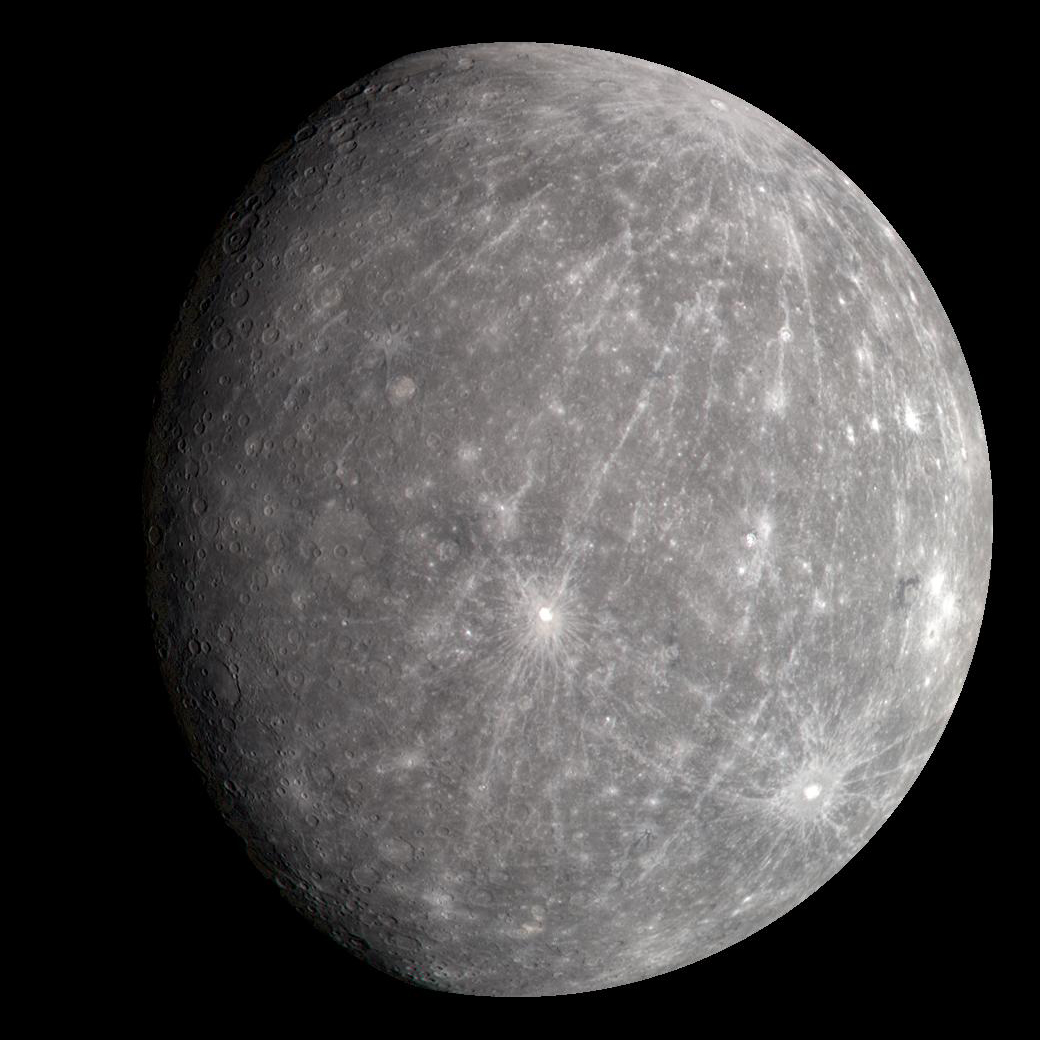

What are the two extreme temperatures on Mercury and what causes them?
Hot - close to the sun
Cold - no atmosphere to trap heat

What direction does Venus rotate (on its axis?)
Clockwise

What is the composition of Venus’s atmosphere?
96% CO2, 3.5% Nitrogen

What is the surface temperature of Venus and why?
867F, atmosphere is very thick so heat can’t escape

Why does Venus not have many craters?
Dense atmosphere
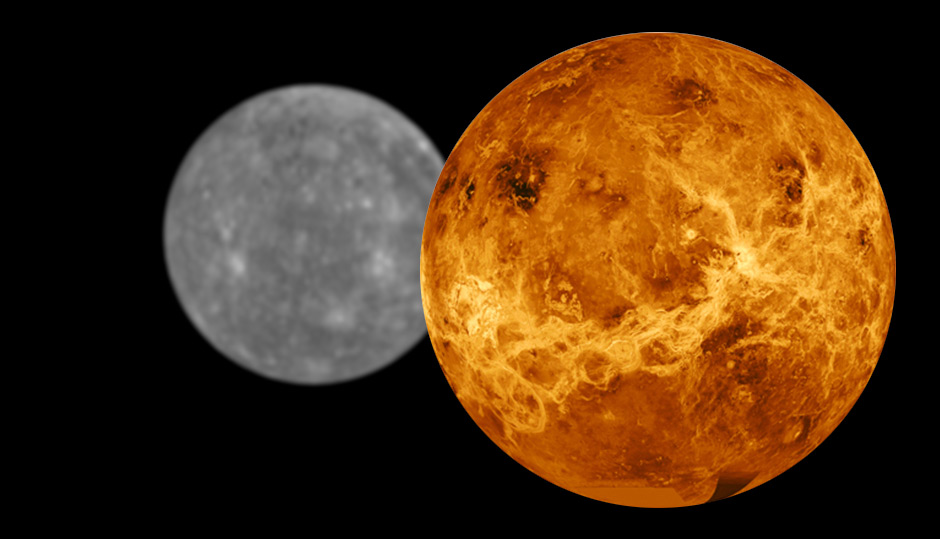

Why do Mercury and Venus have no moons?
Too close to the Sun

Give a brief description of the surface features of Earth
Mountain ranges, subduction trenches, tectonic plates, mid-ocean ridges

Which planet does Earth’s moon most resemble?
Mercury

Why are there huge dust storms are Mars even though there is a thin atmosphere?
Radiative heat of sunlight hitting the surface

Why does Mars appear red?
Rust particles in the soil

What are the ice caps made of?
Dry ice (CO2)

How large is Olympus Mons? What is it?
624km in diameter, shield volcano

How many moons orbit Mars? Where do we think they come from?
2, captured asteroids or debris from the early formation of the Solar System
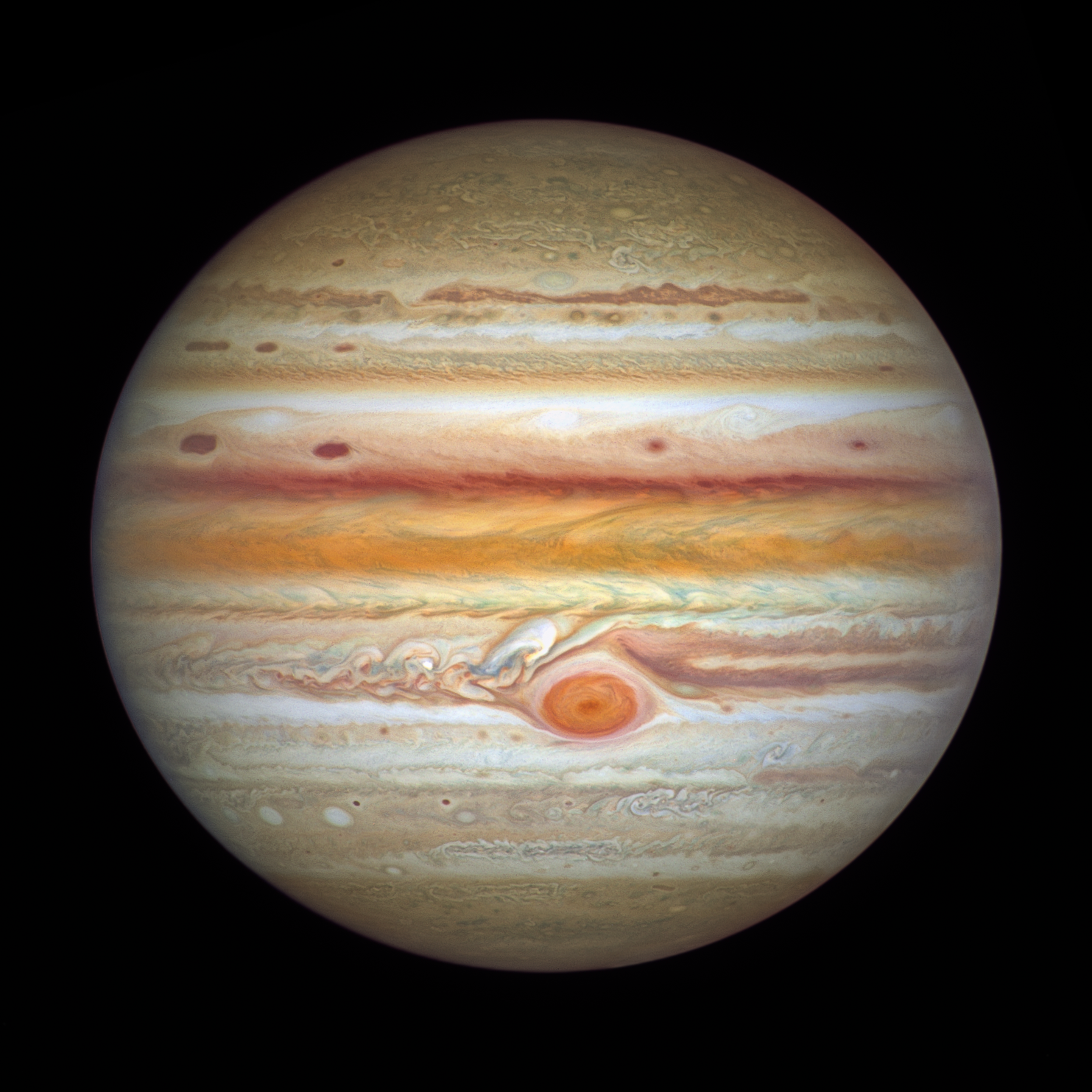

What is Jupiter’s red spot?
A giant storm
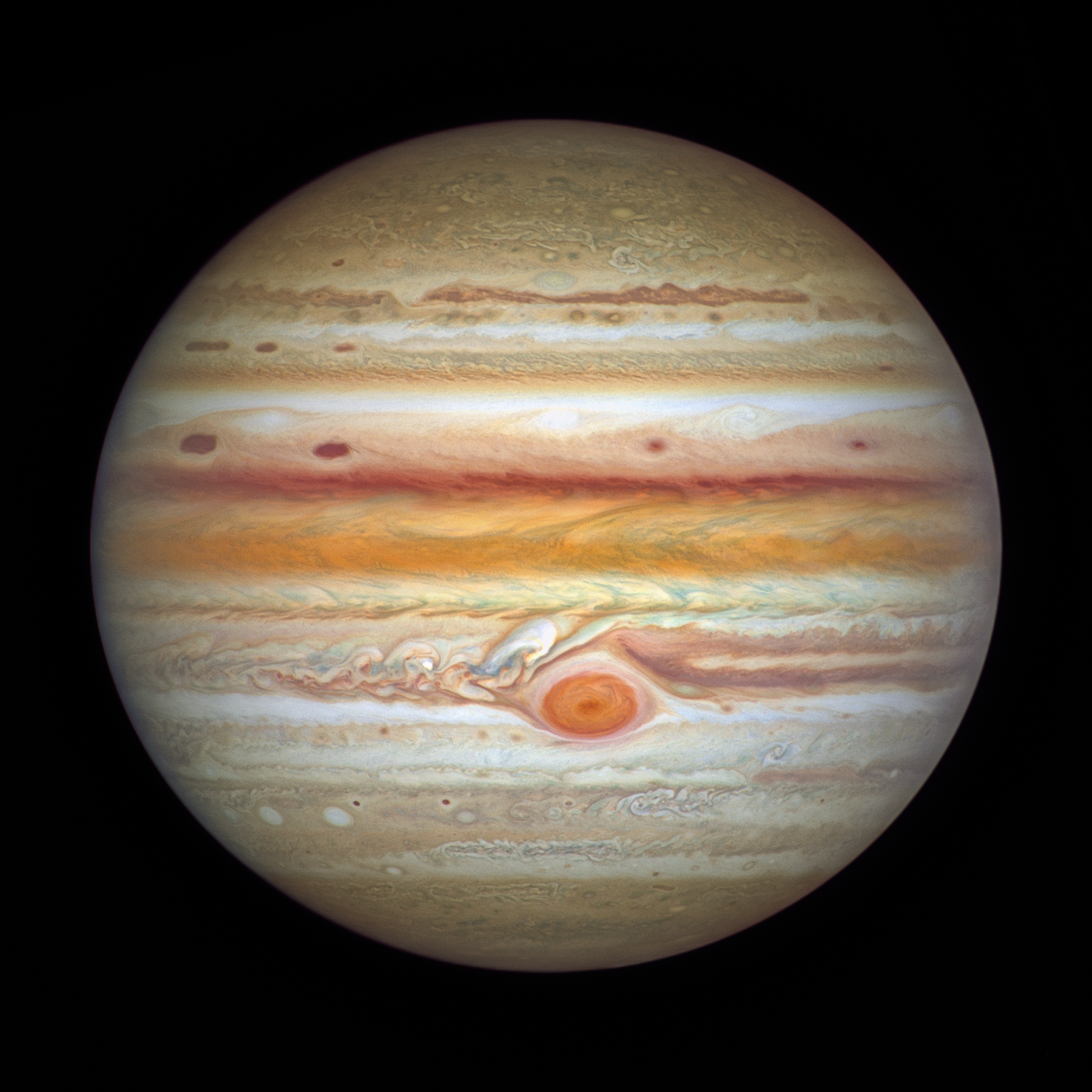

Which of Jupiter’s moons is larger than Mercury?
Ganymede, R = 2631km
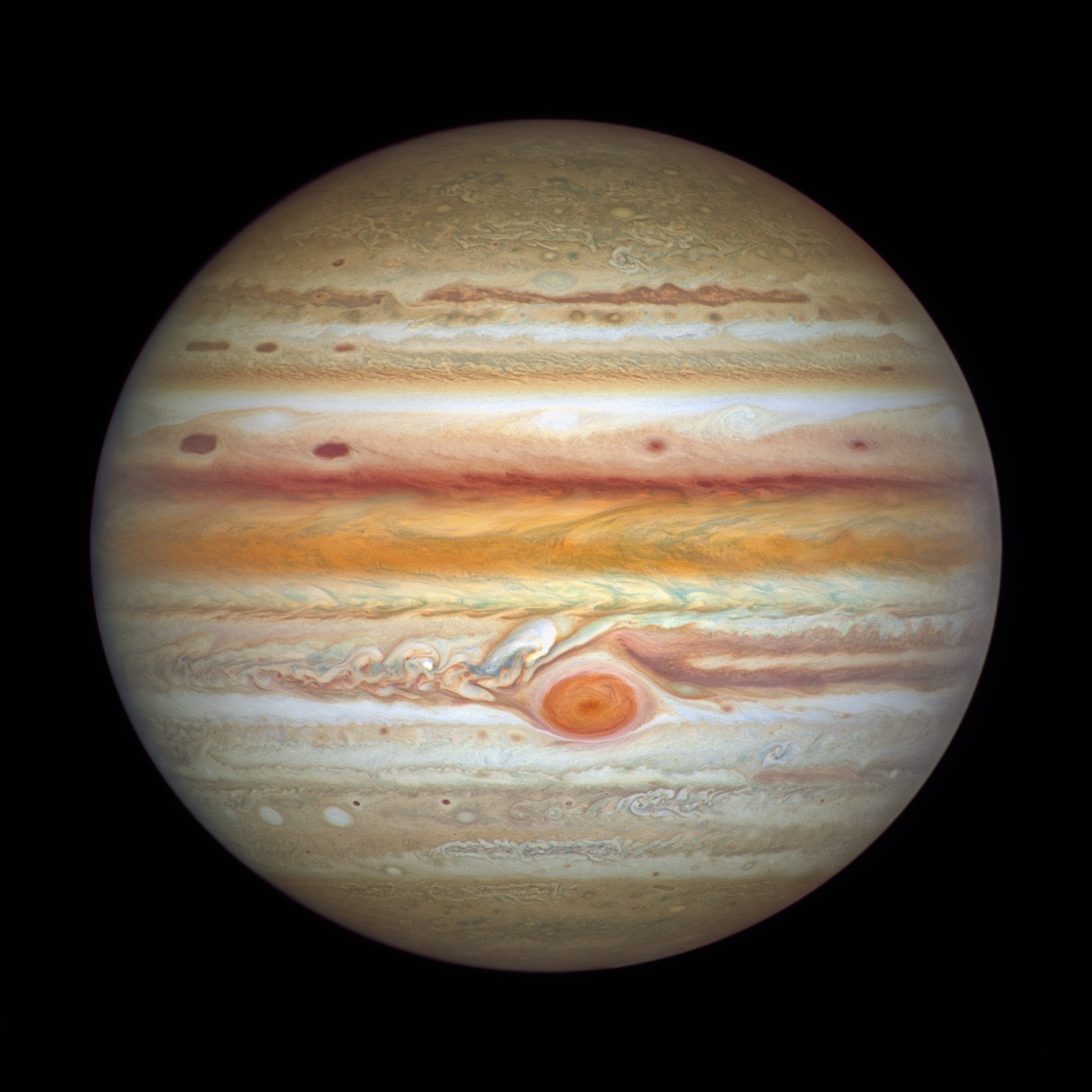

How many moons does Jupiter have currently?
95
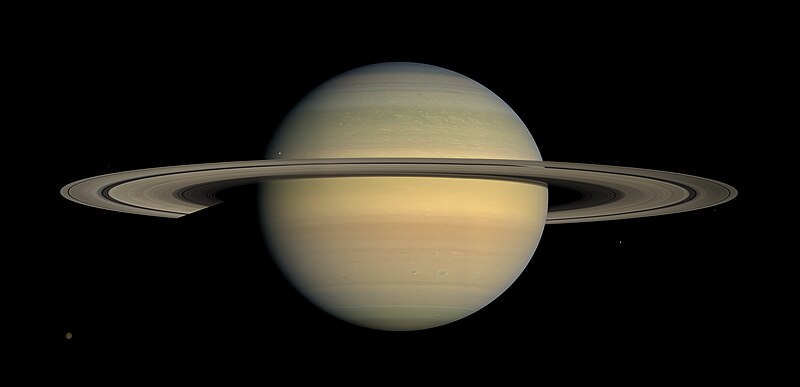
How do Saturn’s rings made of rock and ice form?
Debris broken up by Saturn’s powerful gravity
What other planets besides Saturn have rings?
Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune
How many moons does Saturn have?
146

What angle is Uranus tilted at which makes it spin backwards?
98 degrees

How many moons does Uranus have?
27
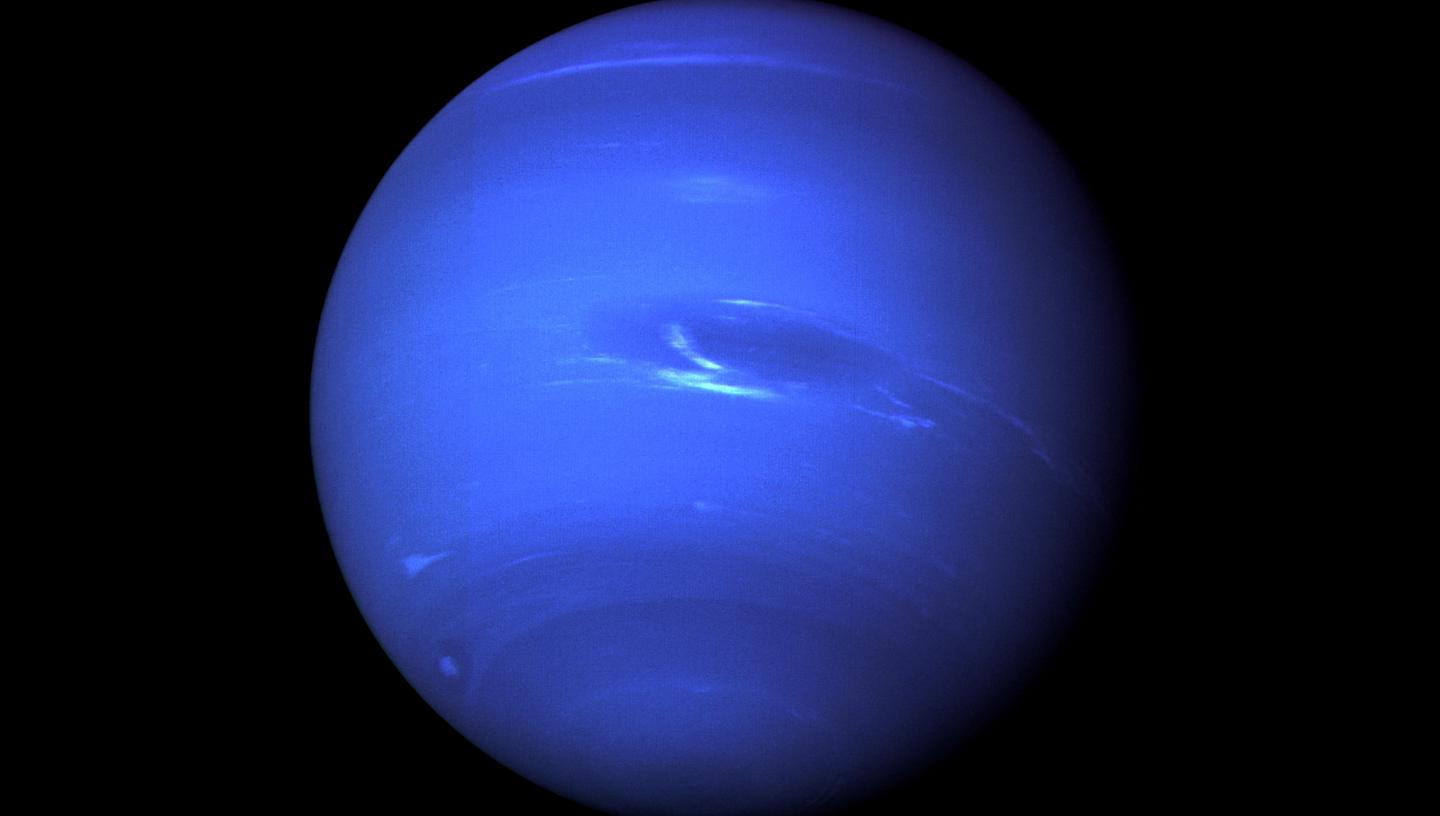

What is the Dark Spot on Neptune thought to be?
A giant storm the size of Earth

How many moons does Neptune have?
14
How do asteroids look?
Irregular, often pitted or cratered. Potatos
How many asteroids are in the singular asteroid belt in our Solar System?
1.1-1.9 million
Where is the asteroid belt located?
Between Mars and Jupiter
How big is the biggest object in the asteroid belt?
4 vesta - 525km in diameter
Where is the Kuiper Belt located?
Far beyond the orbit of Neptune
How many Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs) are there?
About 10% the mass of the Earth, about 70 000 - 100 000
How big is the biggest KBO? What is it called?
2377km in diameter - King of the Kuiper Belt (aka Pluto)
What are the Dwarf planets in our Solar System? (5)
Pluto, Eris, Ceres, Makemake, Haumea
Why is Neptune sometimes further from the Sun than Pluto?
Pluto’s orbit is oval shaped, making it sometimes closer to the Sun
What are the 3 requirements for something to be considered a planet?
It has to be round, orbit the Sun, and has gravitationally “cleared” its orbit of other objects
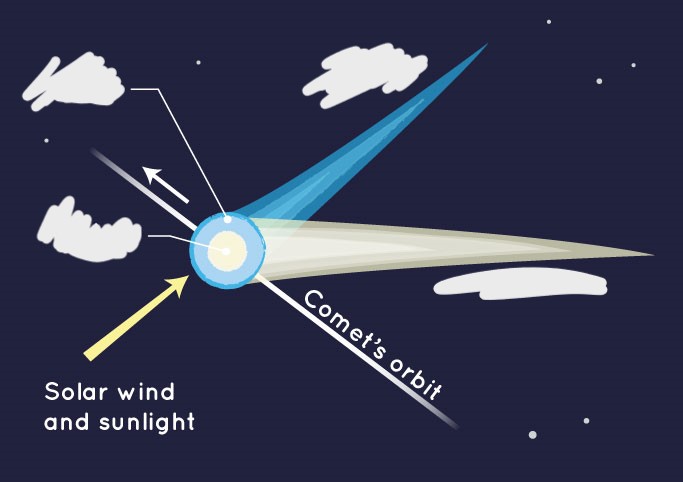
What are the parts of a comet? (4)
Nucleus, coma, ion tail, dust tail
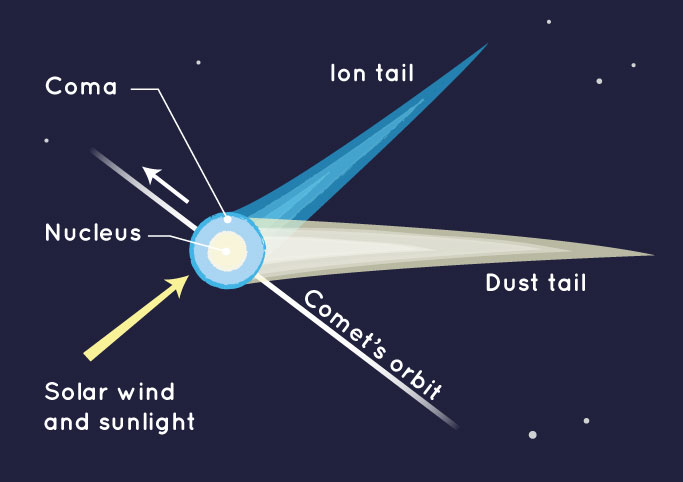
What is a nucleus? (comet)
Center of comet made of an icy dirtball
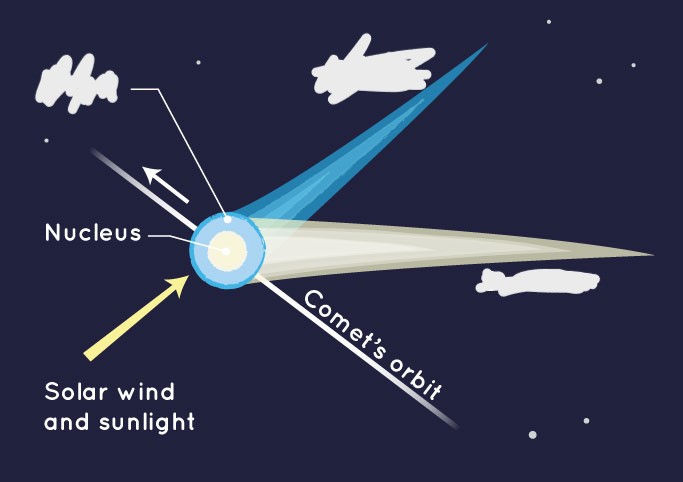
What is a coma? (comet)
Nebulous envelope around the nucleus
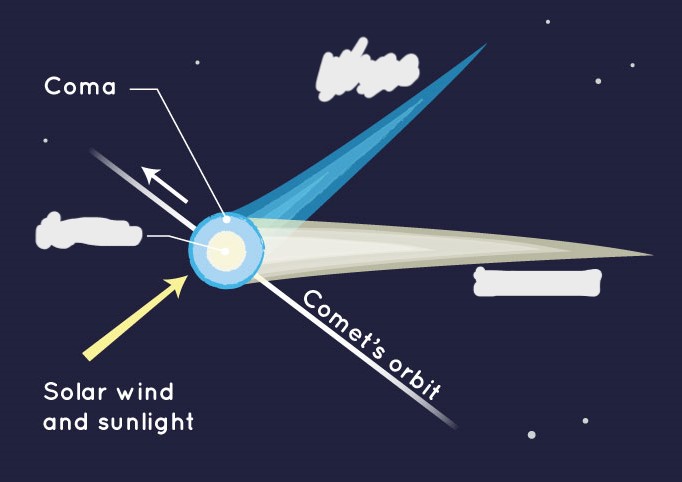
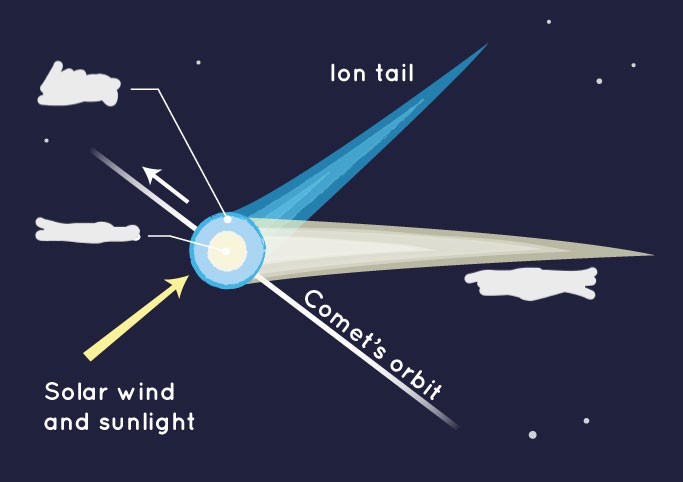
What is a ion tail? (comet)
Gases from coma ionized
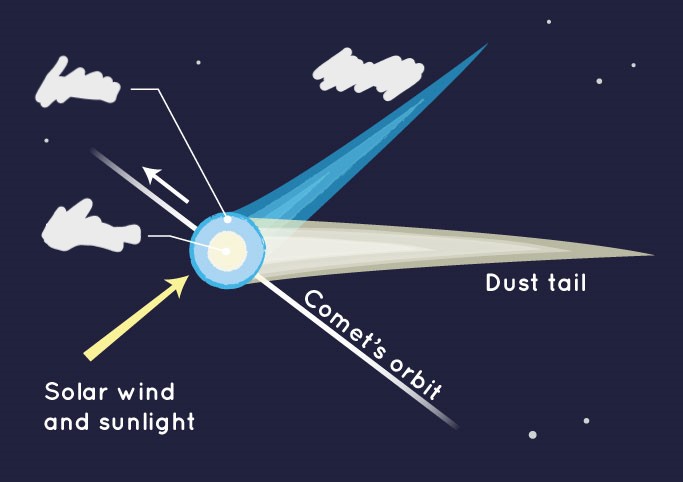
What is a dust tail? (comet)
Micrometer-scale particles
Why does the tail of a comet always point away from the Sun?
Radiation pressure of sunlight
What is a possible solution to losing the Moon?
Capture a new moon (asteroid)
Send an artificial moon to mimic the effects (satellite)
Have something on Earth that stabilizes the climate
Colonize another planet that is habitable and has a moon
Other things as well :)
Which planet is the furthest from the Sun?
Neptune
Which planet is the coldest?
Uranus
Closest planet to the earth
Venus
Which is the slowest rotating planet?
Venus
What planet is called the Morning/Evening star?
Venus
Earth’s “twin”
Venus
Stages of a low mass star
Cloud of dust and gas (nebula) contacts due to gravity
Friction causes temp to rise, then fusion
When fuel inside star is used up, an envelope of H expands outward —> red giant
H envelope dispenses, leaving a core called a white dwarf
Eventually white dwarf burns out, leaving a hunk of dirt (black dwarf) where the star used to be in space
Stages of a medium mass star
Cloud of dust and gas (nebula) contacts due to gravity
Friction causes temp to rise, then fusion
When fuel inside star is used up, an envelope of H expands outward —> red giant
When fuel used up, the star explodes —> supernova
Half mass flies away to become nebula
Remaining mass becomes a very dense neutron star
Stages in a high mass star
Cloud of dust and gas (nebula) contacts due to gravity
Friction causes temp to rise, then fusion
When fuel inside star is used up, an envelope of H expands outward —> red giant
When fuel used up, the star explodes —> supernova
Half mass flies away to become nebula
Remaining mass becomes a very VERY dense black hole
Is a black hole a hole?
NO, it is a dense point/object
Why can’t light escape a black hole?
They have so much gravity that even light can’t escape
What is the mass of a low mass star?
Less than 4 times the mass of our sun
What is the mass of a medium mass star?
Between 4 and 10 times the mass of our sun
What is the mass of high mass star?
Greater than 10 times the mass of our sun
What happens in a neutron star?
The electron and proton join to become a neutron and the empty space is gone —> very dense
In a normal atom there is mostly what?
Empty space
How are HR diagrams numbered?
Logarithmic scale
What is a logarithmic scale?
Goes up by 1 order of magnitude
Where is the sun on the HR scale?
(5800, 1)
Where are most stars in an HR diagram?
The main sequence
Where are the least stars in an HR diagram?
The white dwarfs
Groups in an HR diagram
Main sequence, super giants, giants, white dwarfs
Where is the main sequence?
A line from top left to bottom right
Where are the supergiants?
Very top right
Where are the giants?
Top right, below supergiant
Where are the white dwarfs?
Bottom middle-ish
What is the significance of the HR diagram to modern astronomy?
Shows relationship between luminosity and temperature in stars
What are the axis in an HR diagram?
y - luminosity (Sun = 1), x - temperature (degrees Kelvin)