3.4- Computer Systems
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
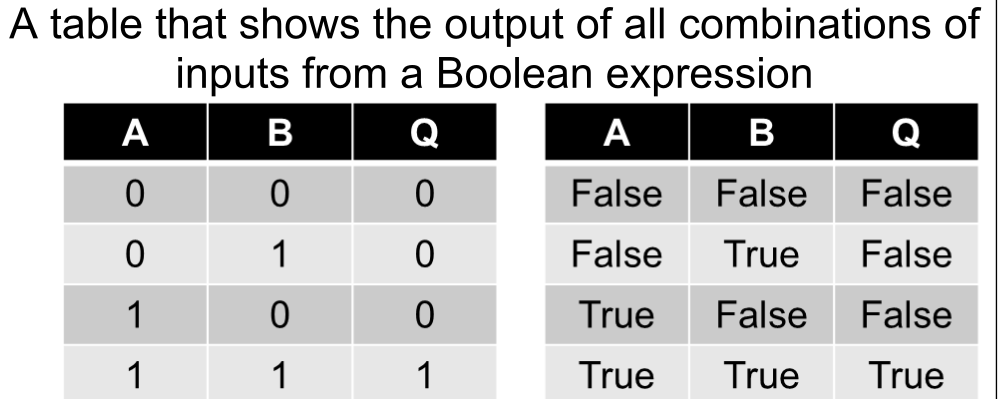
Truth Table
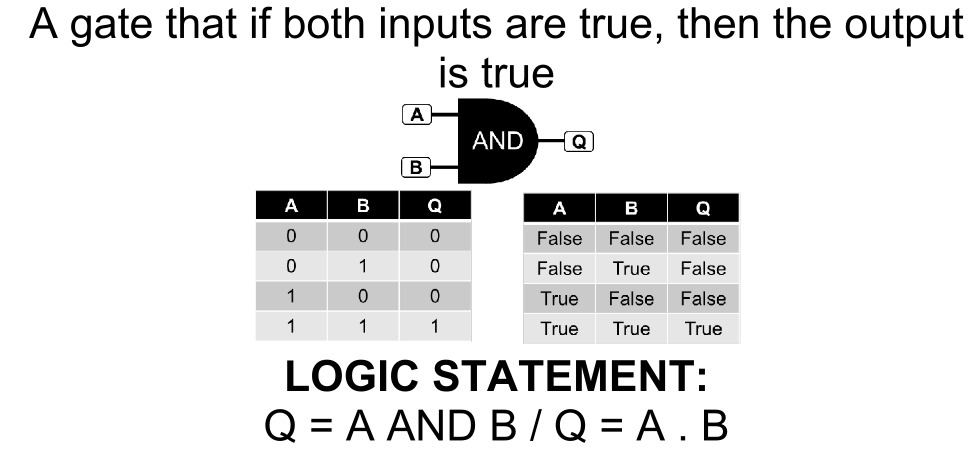
AND Gate
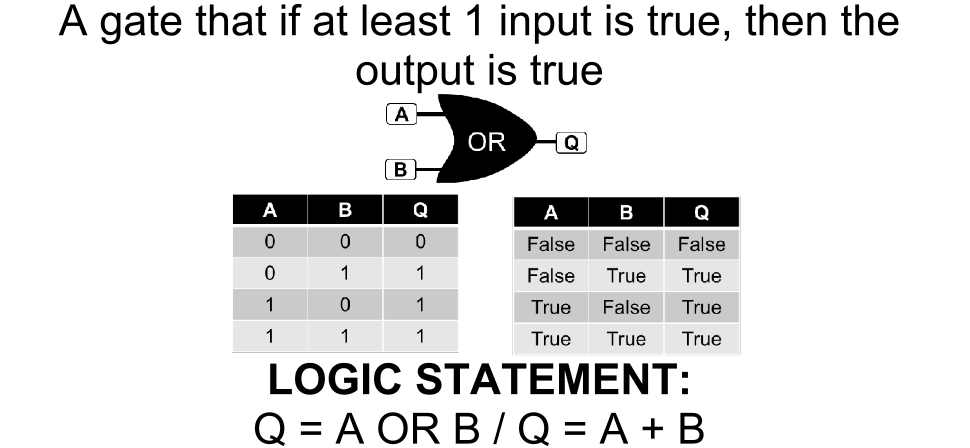
OR Gate
NOT Gate
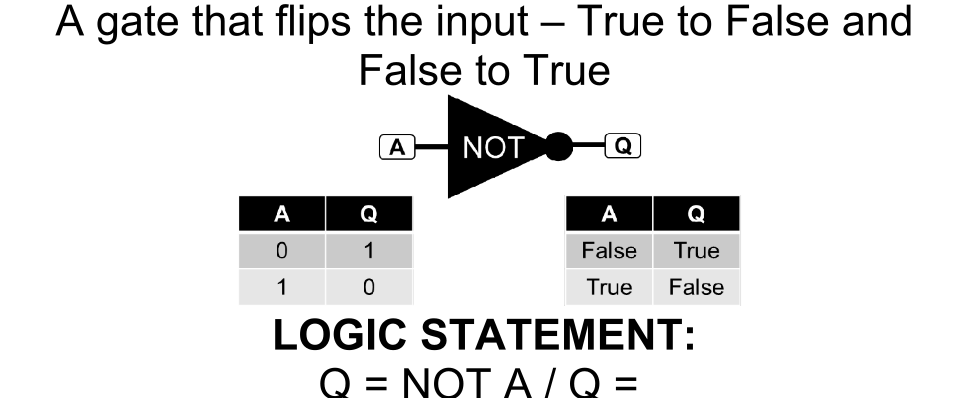
XOR Gate
A gate that if either input is true, then the output is true
Hardware
The physical components that make up a computer system
Software
The non-physical programs that are stored by and run on a computer system
System Software
System software controls / manages / runs the computer
System software enables the computer to function
System software manages the computer hardware application software
System software provides a platform for other software / provides a platform to run application software
Operating System (OS)
A group of programs which are essential for managing the computer’s resources
Functions of the operating system
Processor Management
Memory Management
Input/Output (Peripheral) Management
Application Management
Security Management
Processor Management
OS coordinates the CPU to schedule processes to be executed.
Responsible for deciding which software runs on the processor and the time it gets
The CPU switches between these tasks rapidly so they seem like they are happening at the same time
This is called multi tasking
It also manages interrupts
Memory Management
The OS moves files in and out of memory (from the hard drive or virtual memory) to process tasks as required by different processes
Keeps a record of where each program is and its data are located
Ensures no data or existing software is overwritten
Peripheral Management
Peripheral device drivers are controlled by the CPU
Interrupt message such as ‘out of paper’ must come from the CPU
A buffer is used to compensate for the difference in speed of sending and receiving data between the CPU and the device
Application Management
OS manages the process of installing new applications
Allocates memory space for the application
Controls what data the application has access to
Provides a graphical user interface (GUI)
Manages user access to programs
Installs and updates programs
Security Management
OS controls controls user access to prevent users from accessing files they are not supposed to
Downloads security updates from software manufacturers to help fix bugs and improve security against malware
Files on the hard disk can be encrypted
Utility Software
Small programs that used in conjunction with the main OS to manage extra features or functions.
They are not essential to the running of the computer but make specific tasks easier or add an additional layer of housekeeping
Encryption Software
Used to encrypt or decrypt files or folders on a computer, transmitted across a network or when they are transferred to external devices (eg a USB flash drive)
Uses an algorithm and a key to turn plaintext into cipher text
In order to decrypt the data, one would need both the algorithm and the key
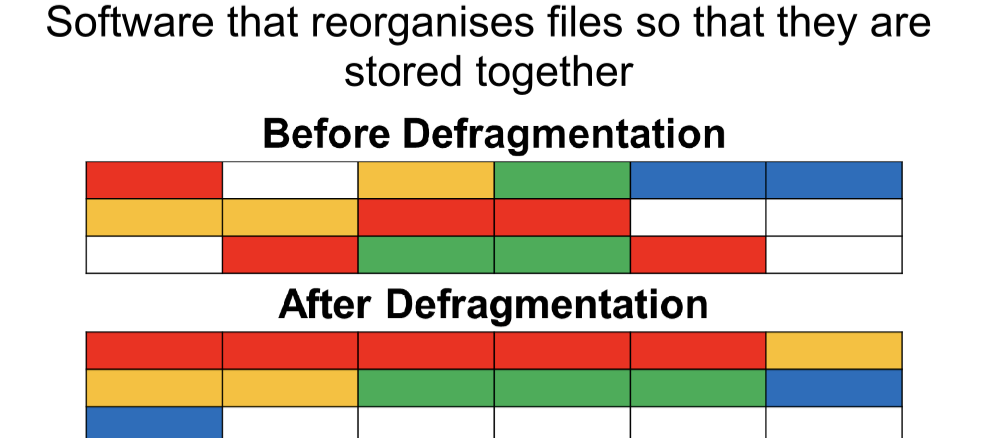
Disk Defragmentation Software
Disk defragmentation is the process of reorganizing fragmented data on a hard drive to improve efficiency and speed. Over time, files are stored in non-continuous sectors due to frequent modifications and deletions, causing the disk to take longer to access them.
Defragmentation works by:
Rearranging file fragments so they are stored contiguously.
Grouping free space together to reduce future fragmentation.
Improving read/write speeds by minimizing the time the disk head moves to access data.
Compression Software
Software that compresses files and folders in order to reduce the amount of storage space required. They can also decompress the files and folders.
Application Software
Application software is for end user tasks;
Multi-Tasking
Where more than one operation is happening at the same time
Interrupts
Signals sent to the CPU from external devices that indicate an event that needs immediate attention. Can be hardware interrupts (printer out of paper) or software interrupts (divide-by-zero error)
Access Rights
The permissions that users have to files and folders. Common permissions are: Read, Write, Execute, Comment
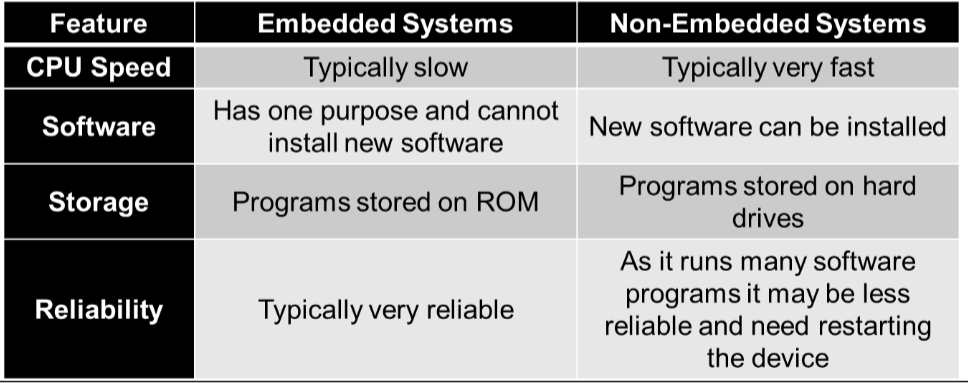
Embedded System
A single microprocessor that includes RAM, ROM and a CPU
Embedded Systems vs Non-Embedded Systems
Low-Level Language
Languages that sit close to the computers instruction set (the instructions that the processor understands)
Machine Code
A programming language that uses binary digits as instructions. Machine code is processor specific EXAMPLE: 1011 1001 0110 1001
Assembly Language
A programming language that uses mnemonics as instructions that directly map to machine code. Assembly language is processor specific. EXAMPLE: LDA 51
Compare assembly language and machine code
Processors execute machine code and that each type of processor has its own specific machine code instruction set
Assembly language is often used to develop software for embedded systems and for controlling specific hardware components
Assembly language has a 1:1 correspondence with machine code.
High-Level Languages
A set of programming languages that use English/Maths like instructions that must be translated in order to be executed. High-Level Languages are not processor specific and have data structures. EXAMPLE: print(“Hello World!”)
Advantages of low-level language
A program written in a low-level language can run very quickly
The code will usually require less RAM
Statements in a low-level language can be used to control and manipulate specific hardware components
Advantages of High-Level Languages
A high-level language is easier to learn
Programs can be written faster in a high-level language
It is easier to understand and debug and find mistakes a high-level language
Built in functions
Fewer lines of code
More support/help
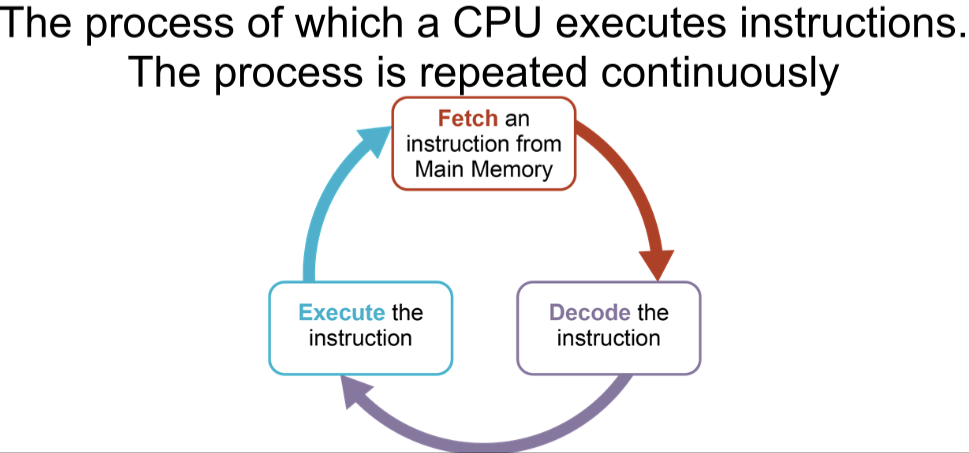
Translators
A program that translates from one programming language to another programming language. There is 3 types of translator: Compiler, Interpreter and Assembler
Interpreter
Code needs to be translated each time the file is executed.
Code is translated a line at a time, and executes immediately
Interpreters do not generate machine code directly (they call appropriate machine code subroutines within their own code to carry out statements).
If an error occurs the interpreter stops
Produces no object code
Translates high-level language
Compiler
Translates high-level language into machine code
Produces an object code that can be saved and ran when required
Translates all code at the same time
Processor specific
Assembler
Translates assembly language into machine code
Runs quickly as low level language is closer to machine code
Each line of assembly language is assembled into a single machine code instruction
Advantages of using assembly language
• Programs written in assembly language run faster // use less processor time;
• Programs written in assembly language can interact directly with hardware (when executing);
• Assembly language programs require less memory (when executing);
• Programs written in assembly language have no unnecessary code added by a compiler;
Compare translaters
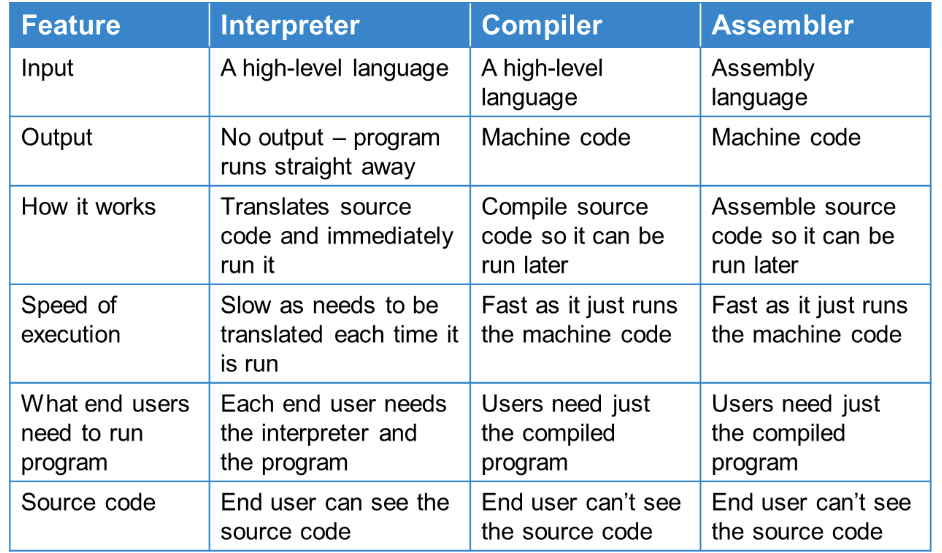
Main Components of a Computer
CPU
A component in the computer that processes instructions. Is often thought to be the ‘Brains’ of the computer. There is many components inside the CPU: The Control Unit, The Arithmetic Logic Unit as well as Registers and Cache
Stored Program Concept
The concept of storing program instructions and data in memory
Von Neuman Architecture
An Architecture where instructions and data are both stored in the same memory
What do registers do
Holds data used when executing an instruction // holds the result of executing an instruction // holds an instruction (CIR) // holds a memory address (MAR);
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Performs Arithmetic (+, -, / ,*) and Logical(>,<, =) Operations
Control Unit
Coordinates the actions of the CPU // decodes instructions // sends control signals; A. controls the flow of data through the CPU
Clock
Regulates the timing and speed of (computer) operations // sends out a regular electronic pulse / timing signal;
Bus
A bus is a collection of wires through which data/signals are transmitted from one component to another.
What are the three types of buses
Data
Address
Control
What is the data bus
Data Bus
Carries actual data between the processor, memory, and other components.
It is bi-directional, meaning data can travel in both directions.
The width of the data bus (e.g., 32-bit or 64-bit) determines how much data can be transferred at once.
What is the address bus
Address Bus
Carries memory addresses from the processor to other components, such as RAM or storage.
It is uni-directional, meaning it only sends addresses from the CPU to memory or I/O devices.
The width of the address bus determines how much memory the CPU can access.
What is the control bus
Control Bus
Carries control signals that manage how data moves around the system.
It sends signals for operations like read, write, and clock synchronization.
It can be bi-directional since control signals may come from various components.
Factors Affecting the CPU Performance
1. Clock Speed
2. Number of Cores
3. Cache Size
What is the clock
Sends out regular electronic pulses
Synchronises the operations of the CPU
How does Clock Speed affect CPU performance
the more pulses a second the more fetch-execute cycles / processes per second;
each instruction starts on a clock pulse;
the more pulses per second the more instructions are likely to be carried out // a higher clock speed means more instructions can start per second;
How does number of cores affect CPU performance
affects the number of instructions that may be executed simultaneously // the greater the number of (processor) cores the greater the number of instructions that may be executed simultaneously;
different (processor) cores dealing with different types of instruction (eg graphics, maths) (improve the execution of software);
each (processor) core can fetch / execute its own instructions (which increases the speed at which instructions can be executed);
Multi-Core Processors
Processors that have more than one core, so can process more than one instruction at a time
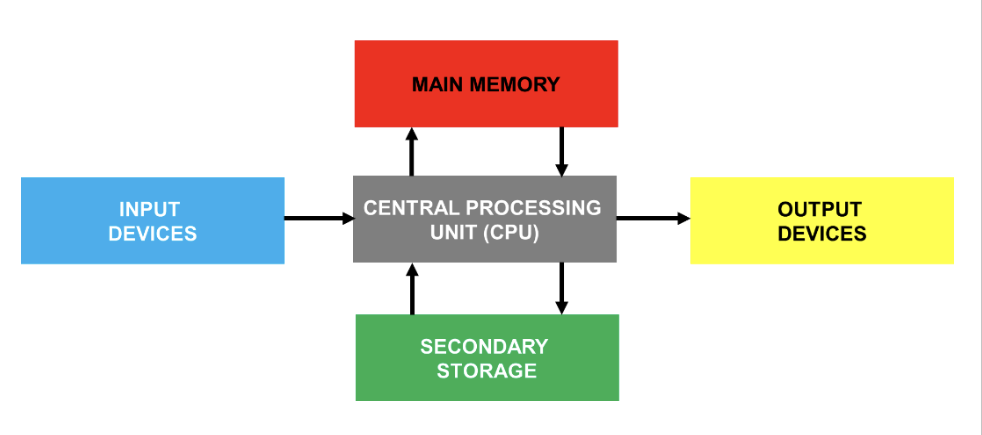
What is cache memory
Very small fast memory that is more expensive than RAM- can transfer data to CPU faster than RAM
How does Cache Memory affect CPU performance
instructions / data take less time to transfer to the processor from cache;
because cache is held closer to the processor;
the more cache the more data / instructions can be held (close to the CPU);
the more cache the faster the CPU can access frequently needed instructions / data;
Levels Of Cache Memory
Level 1 cache is extremely fast but small (between 2-256KB), located on the CPU. Each core will have its own level 1 cache
Level 2 cache is usually also given to each core. It is very fast, but a little slower than level 1 cache. The typical size is256KB-8MB
Level 3 cache is the slowest type of cache, but still faster than RAM. It is usually located on the CPU and stores 4MB-50MB. The cache is shared between all the cores on the processor
Memory Diagram
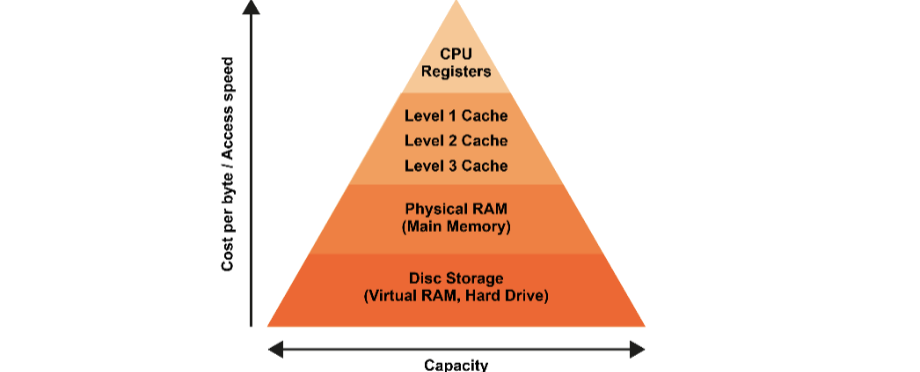
Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle
Fetch Operation
Fetch: the next instruction is fetched to the CPU from main memory
Decode Operation
Involves the instruction being decoded by the Control Unit to work out what it is
Execute Operation
Involves the Control Unit telling the relevant components to execute the instruction (Load data from memory, store d
The instruction is executed (carried out). This may include reading/writing from/to main memory.
Main Memory
Storage used to store programs that are currently run and and need to be accessed by the CPU. There is 2 Types of Primary Storage: Random Access Memory and Read Only Memory
Main memory is any form of storage which can be directly accessed by the CPU, except from registers and cache
RAM
A type of primary storage which can be read from and written to. It normally stores the operating system, the software currently in use and the data which the software is using. RAM is volatile (Loses data if the power is turned off)
ROM
A type of primary storage which can only be read from. It normally stores the bootstrap (The initial program that tells the computer to find the OS on the hard drive) and the BIOS((Basic Input/Output System) The program that controls basic technical configuration of the computer)). ROM is non volatile (Does not lose data if the power is turned off)
Secondary Storage
A type of storage where the data remains when there is no power. It can’t directly be accessed by the CPU.
Why is secondary storage needed
Storing data / files when the computer is turned off // on a long-term basis // using non-volatile storage;
Types of secondary storage
Secondary storage:
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
Solid State Drive (SSD)
Offline secondary storage:
Compact Disc (CD), Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) or BluRay
Flash memory, SD cards
Removable HDD or SSD
Magnetic tape
Storage Method
The method which data is stored on the secondary storage. There is 3 methods of storage: Magnetic, Optical and Solid State
Magnetic Storage- how it operates
On a hard disk binary data represented by tiny magnetised regions;
where the magnetic orientation in one direction represents 0, and the other direction represents 1;
When reading data the read/write head is moved (to be over correct track);
and the platter/disk spins round;
A whole sector/block read in one go (by the read/write head);
Magnetic storage- advantages, disadvantages
Advantages:
- Large storage capacity
- Widely used (highly compatible)
- Cheap per gigabyte
- Fast write speed
Disadvantages:
- Very easy to break if dropped due to lots of moving parts (not durable)
- Effected by electromagnetic fields
- If the HDD is built into the PC then it won’t be portable
Optical Storage- how it works
The laser is shone on to the disk
The CD is spun to ensure all data can be read
The laser is reflected. Depending on the angle it reflects back determines if that is a 1 or a 0
The tracking mechanism moves the laser into the correct position over the CD
Bumps/pits form a spiral from the centre to the outside of the disk
Bumps/pits and lands represent the two possible bit values
The CD spins slower when the laser/read- head is above the outer tracks
Optical Storage- advantages, disadvantages and uses
Advantages:
- Cheap
- Portable
- Small (takes up little physical space)
Disadvantages:
- Easily damaged (not robust) and scratched
- Lower storage capacity
- Slow write speeds
- Required a CD reader
Solid State Storage- how it works
A large electric current is used to force electrons through a barrier and trap them on the other side
They remain on the other side until flashed with another current
These charges remain even when the power is turned off, allowing data to be saved permanently
When data is read, the device checks for the stored charges and converts them back into digital data (1s and 0s).
Writing data involves changing the electrical charges in the memory cells.
Solid State Storage- advantages, disadvantages, and uses
Advantages:
- Durable- not affected by magnetic fields, no moving parts, more robust
- More energy efficient- quiet, doesn’t heat up a huge amount, uses less power
- Smaller- more portable
Disadvantages:
- More expensive
- Lower storage capacity than magnetic
- Limited number of write cycles before memory wears out
Storage Characteristics
Capacity: How much data can be stored – e.g. 700 MB, 50GB or 2 TB
Speed: The rate (usually in MB/s) at which data can be read or written
Portability: how easy it is to carry – is the device small?
Durability: will the device break if dropped? How well does it work with extreme temperatures or magnetic fields?
Reliability: how likely is the data (or some of it) to be lost?
Cost: what is the cost of a device? How much is it to store 1 MB of data
Cloud Storage- how it works
Data is saved to servers at a remote, offsite location by a third party
These servers can use magnetic and/or solid- state storage
The data is accessed via the Internet
Cloud storage may make use of multiple copies of the same data stored at different locations – Redundancy
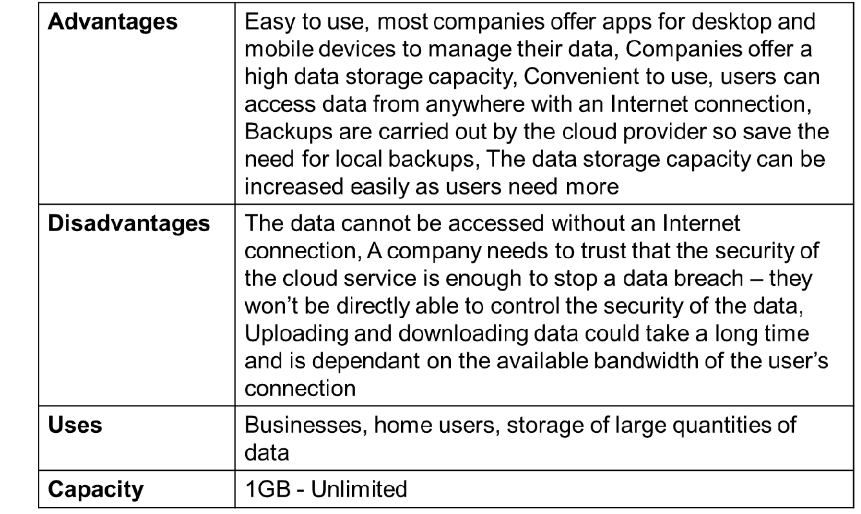
Cloud Storage- advantages, disadvantages, and uses
Adv-
To allow sharing of files;
To backup files from a PC;
To allow remote access of files/access from anywhere;
To allow access from any computer/device (with internet access);
To give access to a larger amount of storage capacity;
To allow concurrent access\collaboration;
Can purchase a cheaper (lower spec) computer;
Cloud storage is automatically backed up by the host;
May be more fault tolerant/resilient than local storage;