3️⃣ Spinal Deformities & Orthotics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Classification of orthoses according to region?
CO | Cervical orthoses |
HCO | Head-cervical orthoses |
CTO | Cervicothoracic orthoses |
Halo device | |
TLO | Thoracolumbar orthoses |
LSO | Lumbosacral orthoses |
TLSO | Thoracolumboscaral orthoses |
Classification of orthoses according to motion restriction?
FE | Flexion-extension control |
FER | Flexion-extension-rotation control |
FELR | Flexion-extension-lateral bending-rotation control |

Name this cervical orthosis. Uses? Motion limitation?
Flexible soft collar
Uses:
Provides mechanical restraint
Psychological comfort
Head support when acute neck pain occurs
Relief from minor muscle spasms
Relief from cervical strain
Limitation:
Flexion & extension limited by 5-15%
Lateral bending limited by 5-10%
Rotation limited by 10-17%

Name this cervical orthosis. Uses? Advantages and disadvantages?
Headmaster collar (adjustable wire frame cervical collar)
Uses:
Weak neck extensors
Advantages:
Lightweight and open.
Comfortable in warm climates.
Disadvantage:
If weakness is present in rotation or lateral flexion, the collar will not be adequate and more support is required.
What classification do the semi-rigid collars fall under?
Head-cervical orthosis
Name 6 semi-rigid collars.
Thomas collar
Philadelphia collar
Miami J collar
Malibu collar
Aspen collar
Jobst vertebrace
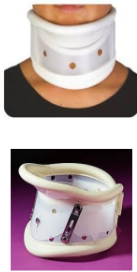
Name this collar. How is it constructed?
Thomas collar
Made of firm plastic with superior and inferior paddings that wrap around the neck and is secured by velcro.
It may be adjustable in height and may contain an adjustable chin piece.
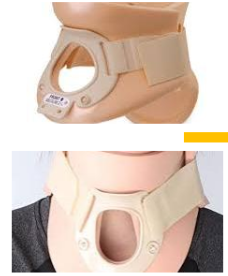
Name this collar. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Philadelphia collar
The upper portion supports the lower jaw and occiput, while the lower portion covers the upper thoracic region.
Velcro straps are used for easy wear and removal.
An anterior hole for a tracheostomy is available.
A thoracic extension can be added to increase motion restriction and treat C6-T2 injuries.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension limited by 65-70%
Rotation limited by 60-65%
Lateral bending limited by 30-35%

Name this collar. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Miami J collar
The anterior piece has a tracheostomy opening similar to the Philadelphia collar.
Velcro straps are used for easy wear and removal.
A thoracic extension can be added to increase support and treat C6-T2 injuries.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension limited by 55-75%
Rotation limited by 70%
Lateral bending limited by 60%

Name this collar. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Malibu collar
2-piece orthosis with an anterior opening for a tracheostomy.
Adjustable. Straps around the chin, occiput, and lower cervical area provide for tightening.
A thoracic extension can be added to increase and treat C6-T2 injuries
Limitation:
Flexion & extension limited by 55-60%
Rotation limited by 60%
Lateral bending limited by 60%
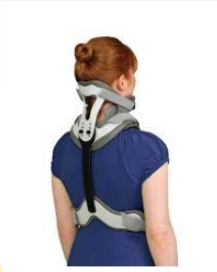
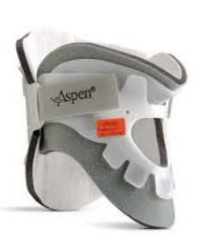
Name this collar. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Aspen collar
2-piece orthosis with an anterior opening for a tracheostomy.
Velcro straps for easy wear and removal.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension limited by 55-60%
Rotation limited by 60%
Lateral bending limited by 60%

Name this collar. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Jobst vertebrace
Designed for use in emergency transport situations.
Provides full contact along its costal ends to the sternum and cradles the mandible for stability.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension limited by 55-60%
Rotation limited by 60%
Lateral bending limited by 60%
Indications for Philadelphia, Miami J, Malibu, Aspen & Jobst vertebrace?
To provide immobilization:
Anterior cervical fusion
Halo removal
Dens type I cervical fractures of C2
Anterior discectomy
Suspected cervical trauma in unconscious patients
Teardrop fracture of the vertebral body
Cervical strain
What is the use of cervicothoracic orthoses?
Provide greater motion restriction in the middle to lower cervical spine (the upper cervical spine has less motion restriction).
Used in minimally unstable fractures.

Name this CTO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
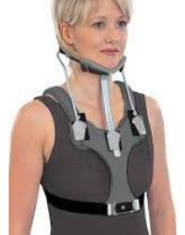
Sternal-occipital-mandibular-immobilizer (SOMI)
Rigid, 3-poster CTO that has an anterior chest plate extending to the xiphoid process (the 2-poster CTOs start from the chest plate and attach to the occipital component).
Metal or plastic bars that curve over the shoulder.
A removable chin piece attaches to the chest plate with an optional headpiece that can be used when the chin piece is removed for eating.
The SOMI is ideal for bedridden patients because it has no posterior rods.
Limitation:
Controls extension less effectively than the other braces, controls flexion in the C1-C3 segments better than the CT braces.
Flexion & extension limited by 70-75%
Rotation limited by 60-65%
Lateral bending limited by 35%
Indications for SOMI?
Atlantoaxial instability caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
Neural arch fractures of C2, because flexion causes instability.

Name this CTO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
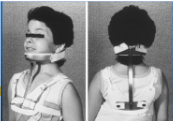
Poster brace
4-poster brace rigid orthosis with anterior and posterior chest pads connected by a leather strap.
Has occipital and mandibular support pieces (mandibular plate can interfere with eating).
This brace uses shoulder straps, but it has no underarm support.
The open design allows heat loss from the neck.
Limitation:
The brace is better than the Philadelphia collar in controlling flexion in the mid-cervical area. The 4-poster design limits lateral bending and rotation better than the 2-poster brace.
Flexion & extension limited by 80%
Rotation limited by 70%
Lateral bending limited by 55-80%
Name this CTO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
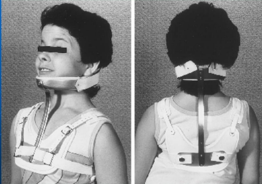
Guildford brace
Rigid CTO with a 2-poster design.
Anterior and posterior chest plates are connected by shoulder straps, along with a chin plate and an occipital piece.
Underarm straps circle the lower chest wall for stability.
Limitation:
The brace has poor control of flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral bending at C1-C2.
Limits flexion and extension from C3-T2.
Indications for Guilford brace?
Minimally unstable fractures from C3-T2
Post-operative use after Internal fixation from C3-T2
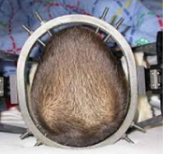
Name this orthosis.
Halo brace
The halo ring is made of graphite or metal, with pin fixation on the frontal and parietal-occipital areas of the skull (the development of lightweight composite material led to the design of radiolucent rings compatible for magnetic resonance imaging).
The halo ring attaches to the vest anteriorly and posteriorly via 4 posters.
An improper fit can allow 31% of normal spine motion.
Limitation:
The halo provides greater motion restriction than do other cervical orthoses.
Flexion & extension limited by 90-96%
Rotation limited by 98-99%
Lateral bending limited by 92-96%
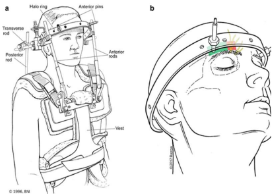
Indications for halo brace?
Most common device for the treatment of unstable cervical and upper thoracic fractures and dislocations as low as T3.
Dens type I, II, or III fractures of C2.
C1 fractures with rupture of the transverse ligament.
Atlantoaxial instability from rheumatoid arthritis, with ligamentous disruption and erosion of the dens.
C2 neural arch fractures and disc disruption between C2 and C3.
Bony, single-column cervical fractures.
Post-operative use after cervical arthrodesis.
Post-operative use after cervical tumour resection in an unstable spine.
Post-operative use after debridement and drainage of infection in an unstable spine.
Spinal cord injury.
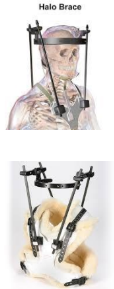
Complications associated with halo brace?

Which orthoses are best for controlling specific regions?
All orthoses tend to control flexion better than extension:
Movement | Orthosis | Note |
Flexion & extension at C1-C3 | Halo | Followed by the 4-poster brace, then CTOs. |
Flexion at C1-C5 | SOMI | SOMI controls extension less effectively than other orthoses. |
Flexion & extension at C3-T1 | CTOs | |
Rotation & lateral bending at C1-C3 | Halo | Followed by the CTO braces for rotation, but the 4-poster brace is slightly better than CTOs for lateral bending. |
What region are thoracolumbar orthoses (TLOs) mainly used for?
Mainly used to treat fractures between T10 and L2, because their mobility is not restricted by the ribs (unlike fractures between T2 and T9).

Name this TLO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
CASH (cruciform anterior spinal hyperextension) brace
Anterior sternal and pubic pads produce force to oppose the posterior pad and strap around the thoracolumbar region.
Provides greater breast and axillary pressure relief than the Jewett hyperextension brace. Two round upper chest pads can be used instead of the sternal pad to decrease discomfort around the breast area.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension at T6-L1.
Ineffective in limiting lateral bending and rotation of the upper lumbar spine.
Indications for CASH brace?
Flexion immobilization to treat thoracic and lumbar vertebral body fractures.
Reduction of kyphosis in patients with osteoporosis.

Name this TLO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Jewett hyperextension brace
Uses a 3-point pressure system with 1 posterior and 2 anterior pads.
The anterior pads place pressure over the sternum and pubic symphysis. The posterior pad keeps the spine in an extended position.
Its lightweight design makes it more comfortable than the CASH brace.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension at T6-L1.
Ineffective in limiting lateral bending and rotation of the upper lumbar spine.

Indications for Jewett brace?
Symptomatic relief of compression fractures.
Immobilization after surgical stabilization of thoracolumbar fractures.

Name this TLO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Knight-Taylor brace
Corset-type front with lateral and posterior uprights and shoulder straps (straps may cause discomfort in some patients).
The posterior portion of the brace has added cross supports below the inferior angle of the scapula and features a pelvic band fitted at the sacrococcygeal junction.
Limitation:
Lateral bending
Flexion
Extension
Indication for Knight-Taylor brace
Flexion immobilization to treat lower thoracic and lumbar vertebral body fractures.

Name this orthosis. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Thoracolumbosacral orthosis (TLSO) or custom-moulded plastic body jacket or referred to as the clamshell
Lightweight design and is easy to wear and remove.
The material is easy to clean and comfortable to wear.
Velcro straps are used to tighten the brace.
Provides efficient force transmission, with pressure distributed over a wide surface area (ideal for use in patients with neurologic injuries).
Offers the best control in all planes of motion.
Frequent checks to ensure proper fit will aid in preventing pressure ulcers.
Limitation:
Lateral bending
Flexion & extension
Rotation (to some extent)
Indications for the TLSO?
Immobilization for compression fractures from osteoporosis.
Immobilization after surgical stabilization for spinal fractures.
Bracing for idiopathic scoliosis.
Immobilization for unstable spinal disorders at T3-L3.

Name this LSO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Chairback brace
Uses a 3-point pressure system.
Short and rigid LSO with thoracic and pelvic bands.
The abdominal apron has straps in front for adjustment.
The pelvic band is placed as low as possible without interfering with sitting comfort. Posterior uprights (metal or plastic) are positioned over the paraspinal muscles.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension at L1-L4
Rotation (minimal)
Lateral bending by 45% (in the thoracolumbar spine)

Indications of chairback brace?
Unloading of the intervertebral disks and the transmission of pressure to soft-tissue areas.
Relief of low back pain.
Immobilization after lumbar laminectomy.
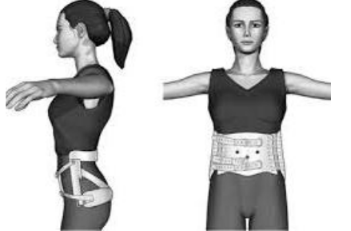
Name this LSO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Williams brace
Short LSO with an anterior elastic apron to allow for forward flexion.
The abdominal apron is laced to the lateral uprights.
Limitation:
The brace limits extension and lateral trunk movement but allows forward flexion.
Extension
Lateral bending at the terminal ends only
Indications and contraindications of the Williams brace?
Indications:
Spondylolysis
Spondylolisthesis
Contraindication:
Spinal compression fractures
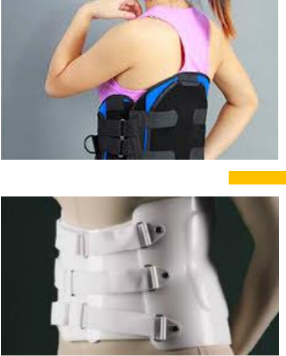
Name this LSO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Standard lumbosacral orthotic corset
Has metal bars within the cloth material posteriorly that can be removed and adjusted to fit the patient.
The anterior abdominal apron has pull-up laces in the back that are used to tighten the orthosis. The abdominal apron can come with a Velcro closure for easy wear and removal.
Anteriorly, the brace covers the area between the xiphoid process and the pubic symphysis. Posteriorly, it covers the area between the lower scapula and the gluteal fold.
Limitations:
Flexion
Extension
Indications for the standard lumbosacral orthotic corset?
Low back pain
Immobilization after lumbar laminectomy
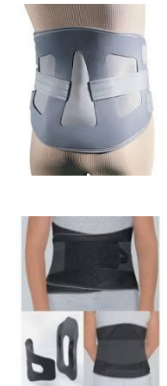
Name this LSO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Rigid LSO
Custom-made orthosis that is moulded over the iliac crest for an improved fit. Plastic anterior and posterior shells overlap for a tight fit.
Velcro closure in the front is designed for easy wear and removal.
Multiple holes can be made for aeration to help decrease moisture and limit skin maceration.
Can be trimmed easily to make adjustments for patient comfort and it may be used in the shower if necessary.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension
Rotation and lateral bending (some)
Indications for the rigid LSO?
Postsurgical lumbar immobilization.
Treatment of lumbar compression fractures.

Name this LSO. How is it constructed? Motion limitation?
Rigid LSO with hip spica
Uses a thigh piece on the symptomatic side and extends to 5 cm above the patella. The hip piece allows flexion to allow sitting and walking.
After the orthosis is applied, some patients require a cane for ambulation.
Limitation:
Flexion & extension
Rotation and lateral bending (some)
Indications for a rigid LSO with hip spica?
Lumbar instability at L3-S1.
Post-operative use after lumbosacral fusion with anchoring to the sacrum.
What type of braces can be used for scoliosis?
Milwaukee
Boston
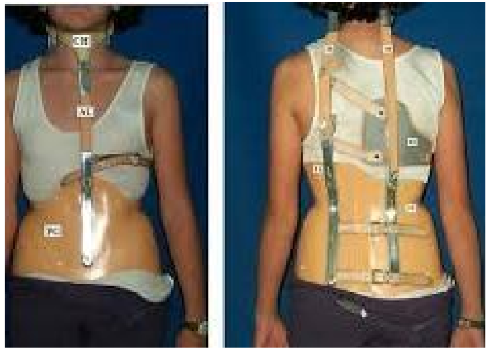
Name this brace. How is it constructed?
Milwaukee brace
A CTLSO originally designed to help maintain post-operative correction in patients with scoliosis secondary to polio.
The pelvic portion helps reduce lordosis, de-rotates the spine, and corrects the frontal deformity.
As a child grows, the brace length can be adjusted. Pads can be changed to compensate for spinal growth BUT, the brace needs to be changed if pelvic size increases.
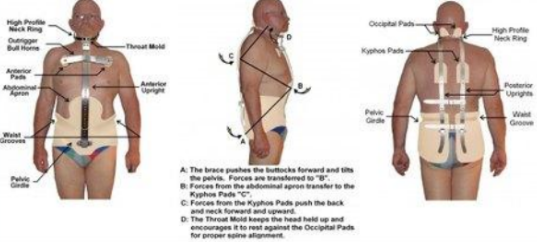
Indications for Milwaukee brace?
Patients with a curve that is greater than 20-30° and that progresses by 5° over 1 year.
Curves of 30-40° (NOT curves of less than 20°).
Problems associated with the use of the Milwaukee brace?
Jaw deformity
Pain
Skin breakdown
Unsightly appearance
Difficulty with mobility
Difficulty with transfers
Increased energy expenditure with ambulation

Name this brace. How is it constructed?
Boston brace
Unlike the Milwaukee brace, the Boston brace cannot be adjusted if the patient grows in height.
Braces need to be changed if pelvic size increases).
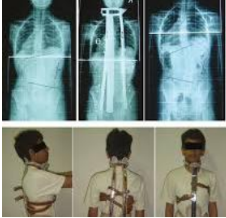
Indications for Boston brace?
Curve of 20-25° with 10° progression over 1 year.
Curve of 25-30° with 5° progression over 1 year.
Skeletally immature patients with a curve of 30° or greater.
Problems associated with the use of the Boston brace?
Local discomfort
Hip flexion contracture
Trunk weakness
Increased abdominal pressure
Skin breakdown