02.0C BIO Energy Flow in Ecosystems (BASIC VOCAB - SIMPLE) (PART C)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Autotrophs
Organisms that are able to make their own food "primary producer". Examples include plants on land and autrophic bacteria and algae in water.

Producer
An organism that makes its own food.

Heterotrophs
Another name for consumers. Means "other feeder". Organisms that rely on other organisms for energy and nutrients.

Consumers
Organisms that rely on other organisms for energy and nutrients.

Herbivore
Consumers that obtain energy by only eating producers like plants, algae, and bacteria. Examples include rabbits, deer, and zooplankton. Examples include cows, rabbits, deer, and zooplankton.
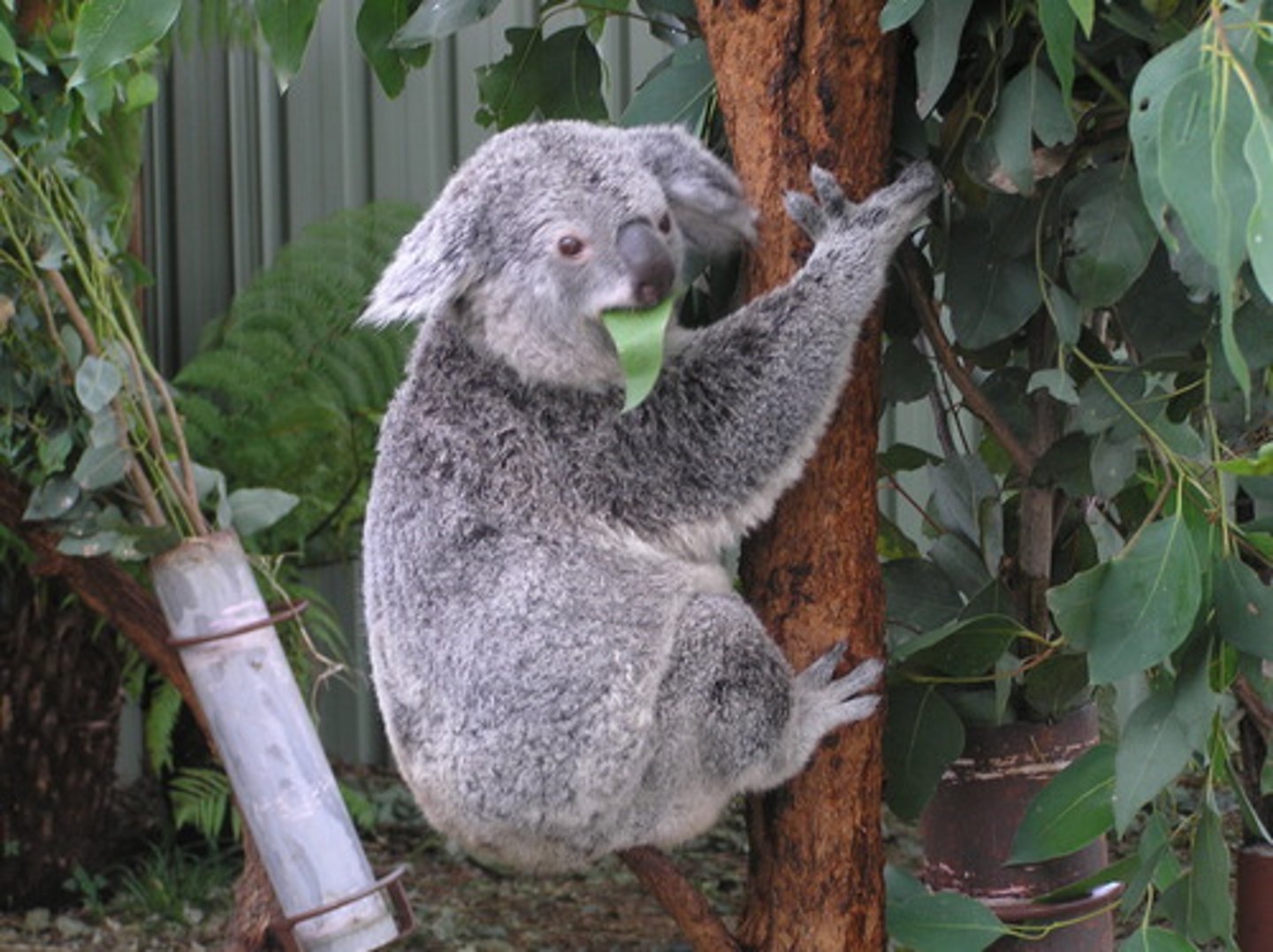

Carnivore
Consumers that obtain energy by eating animals. Examples include dogs, wolves, and cougars.
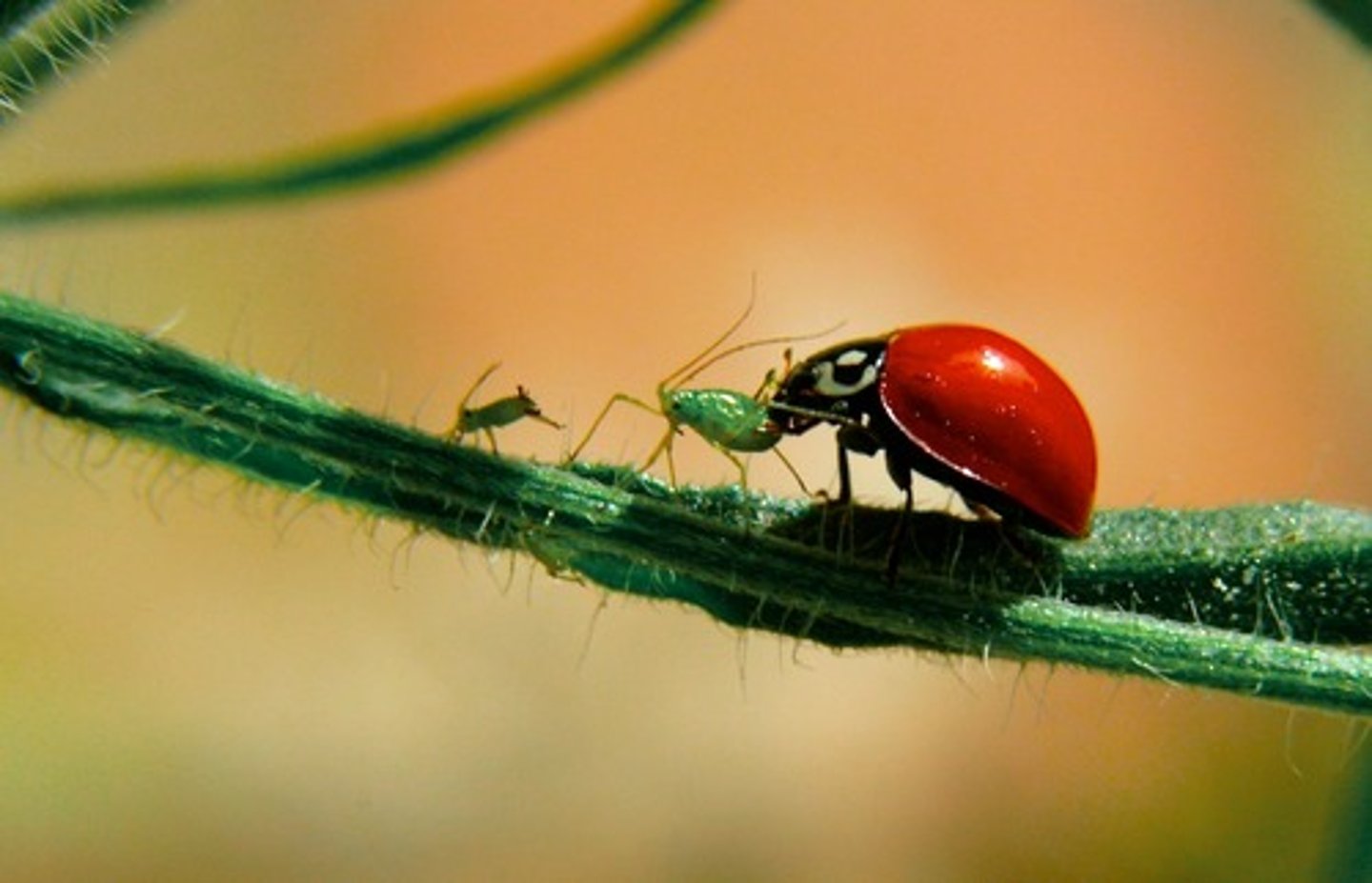

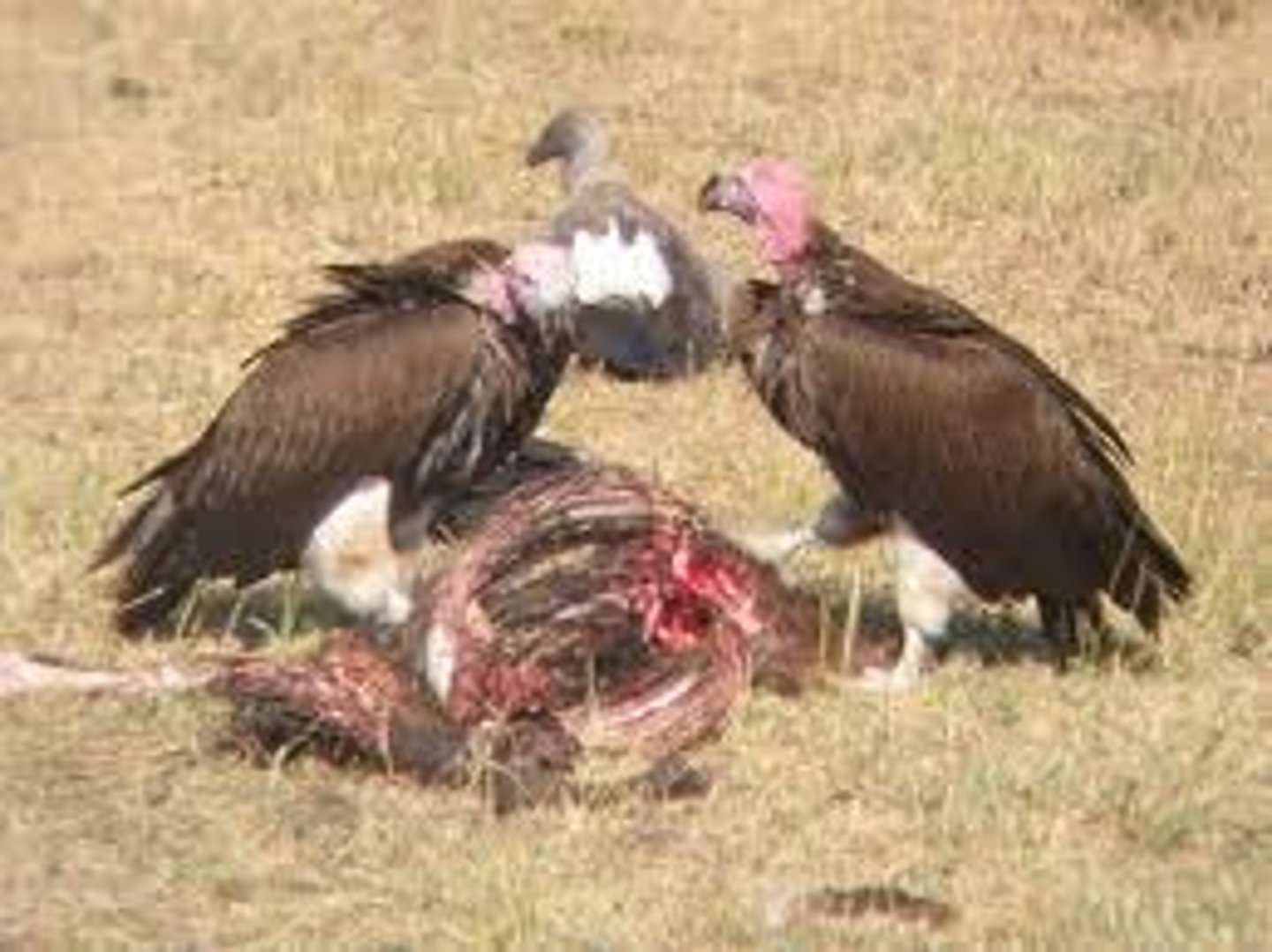
Scavengers
Consumers that obtain energy by consuming the carcasses of other animals that have been killed by predators or have died of other causes. Examples include vultures, hyenas, and raccoons.

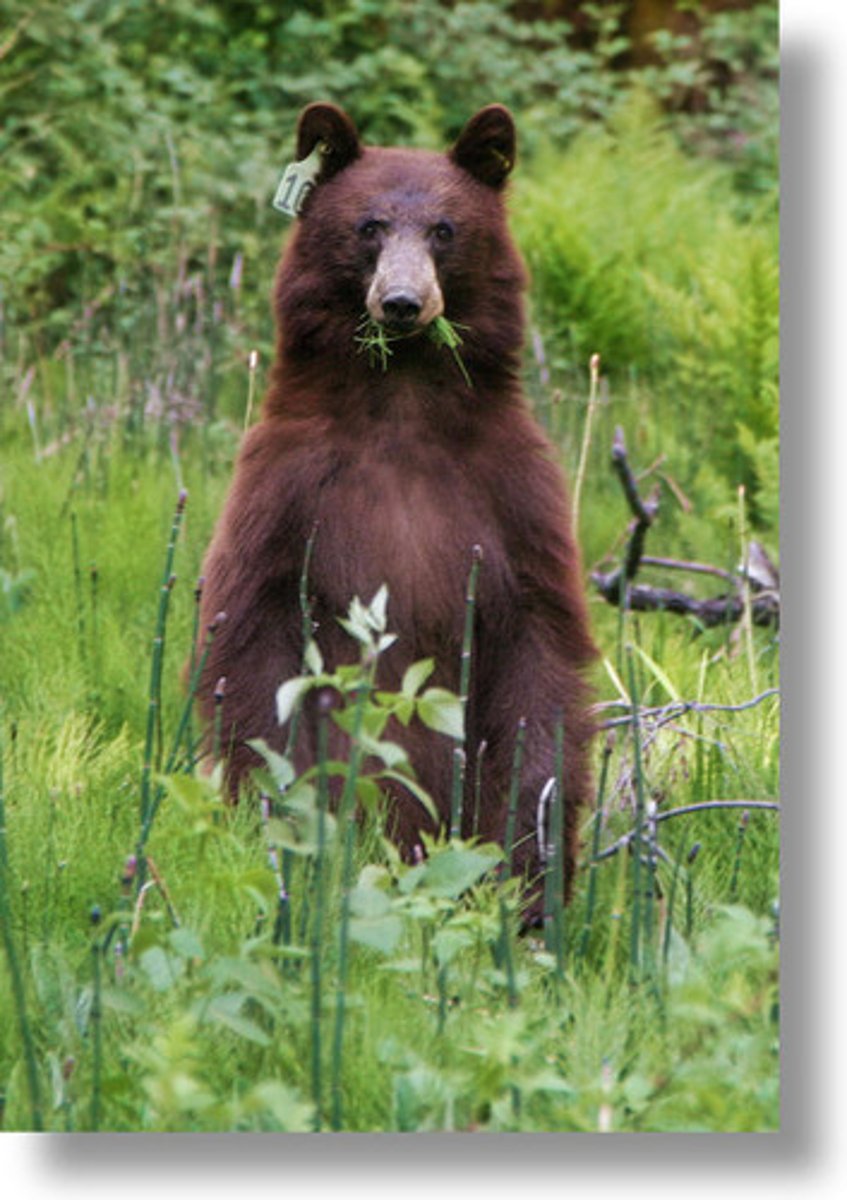
Omnivores
Consumers that obtain energy by eating both plants and animals. Examples include humans, bears, and owls.

Pedator
Organism that preys upon or eats another organism.
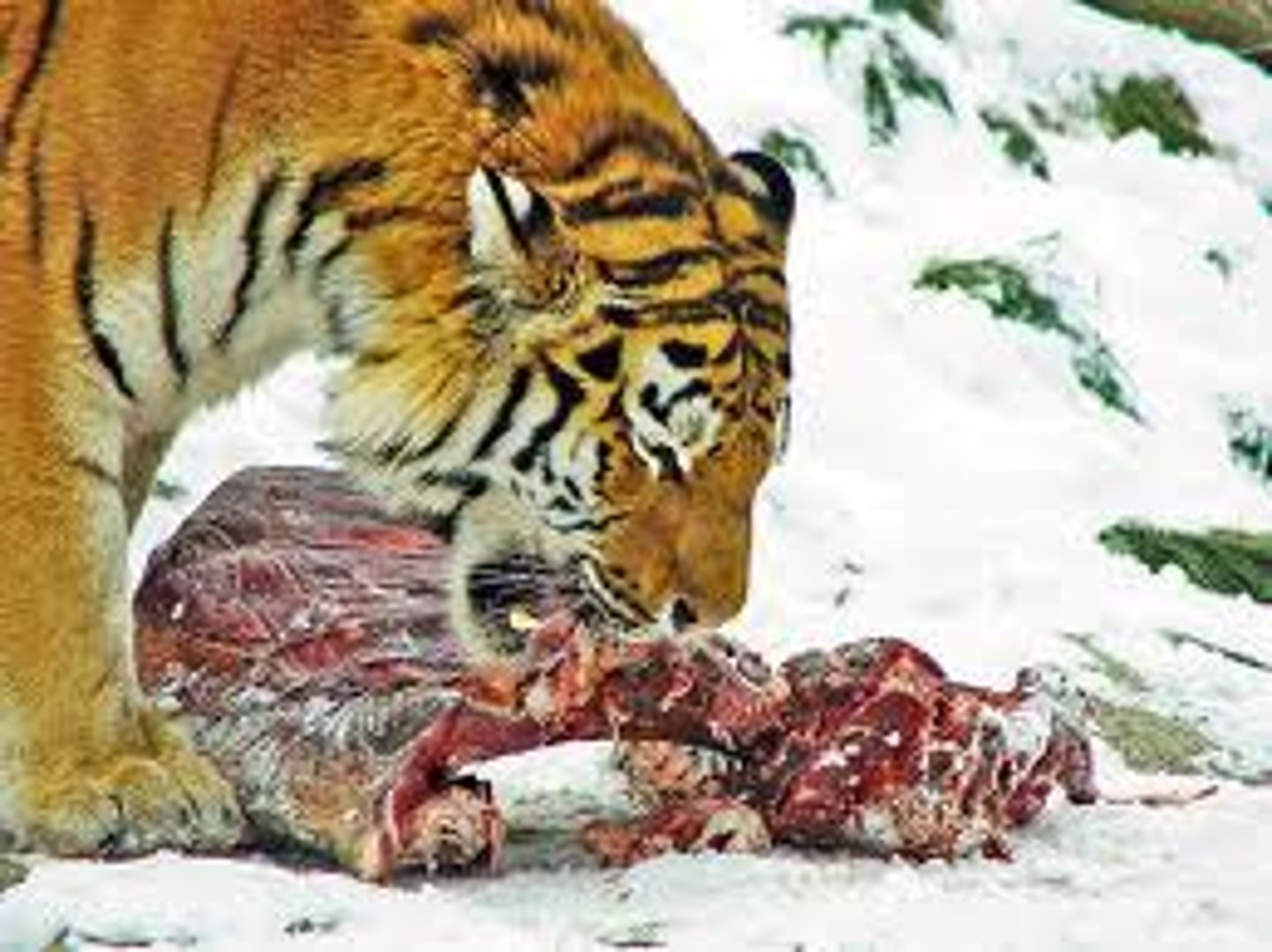

Prey
An organism that is killed and eaten by another organism. For example the the fox (the predator) is feeding on the squirrel (the prey).

Detritivores
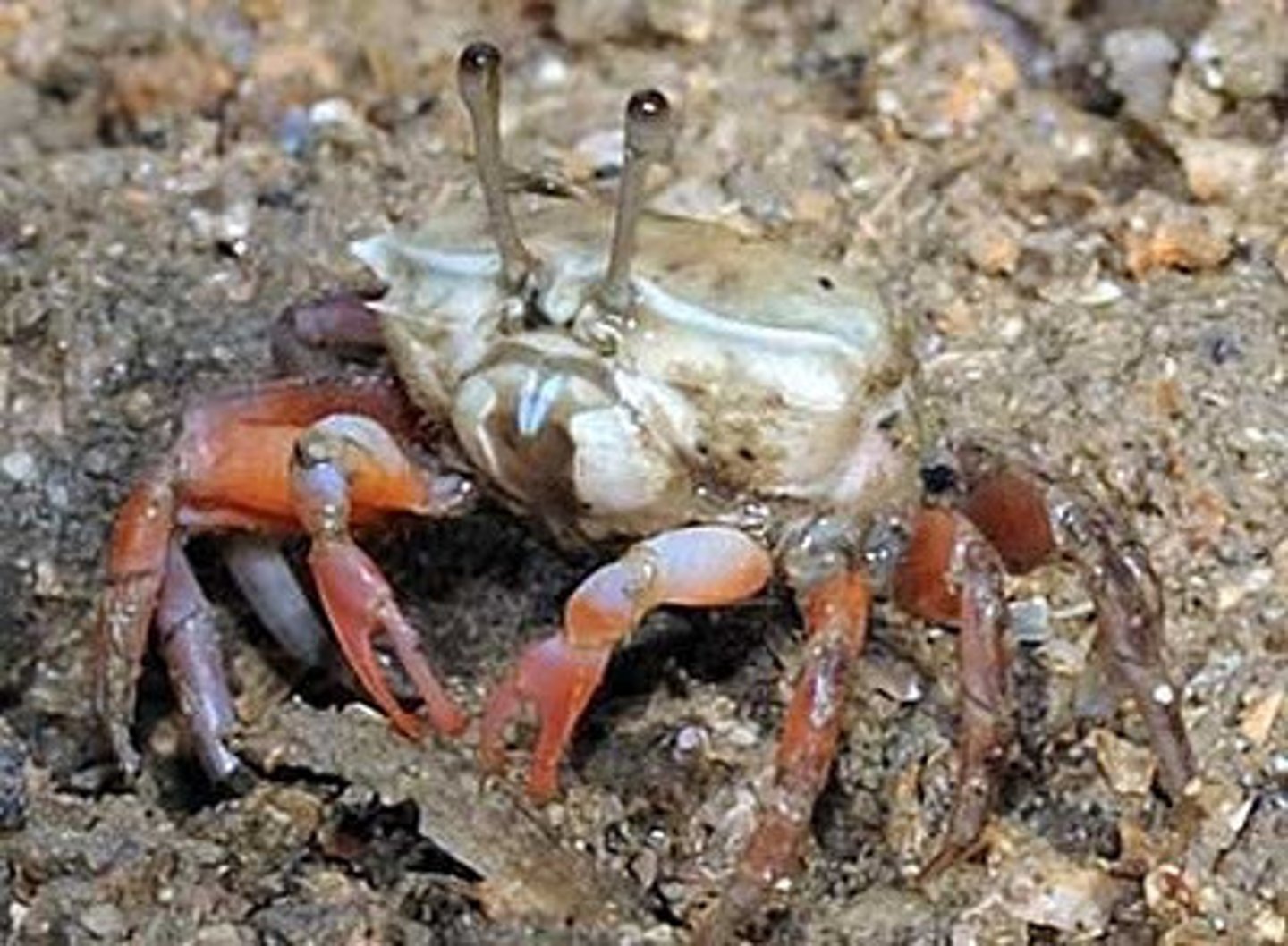
Consumers that feed on bits of plant and animal remains and other dead organic matter called detritus. Examples include mites, earthworms, snails, crabs, and insects.

Abiotic Factors
The nonliving parts of an organism's environment. Examples include the wind, temperature, moisture, sunlight, rocks, soil, salinity (salt), and acidity (pH).
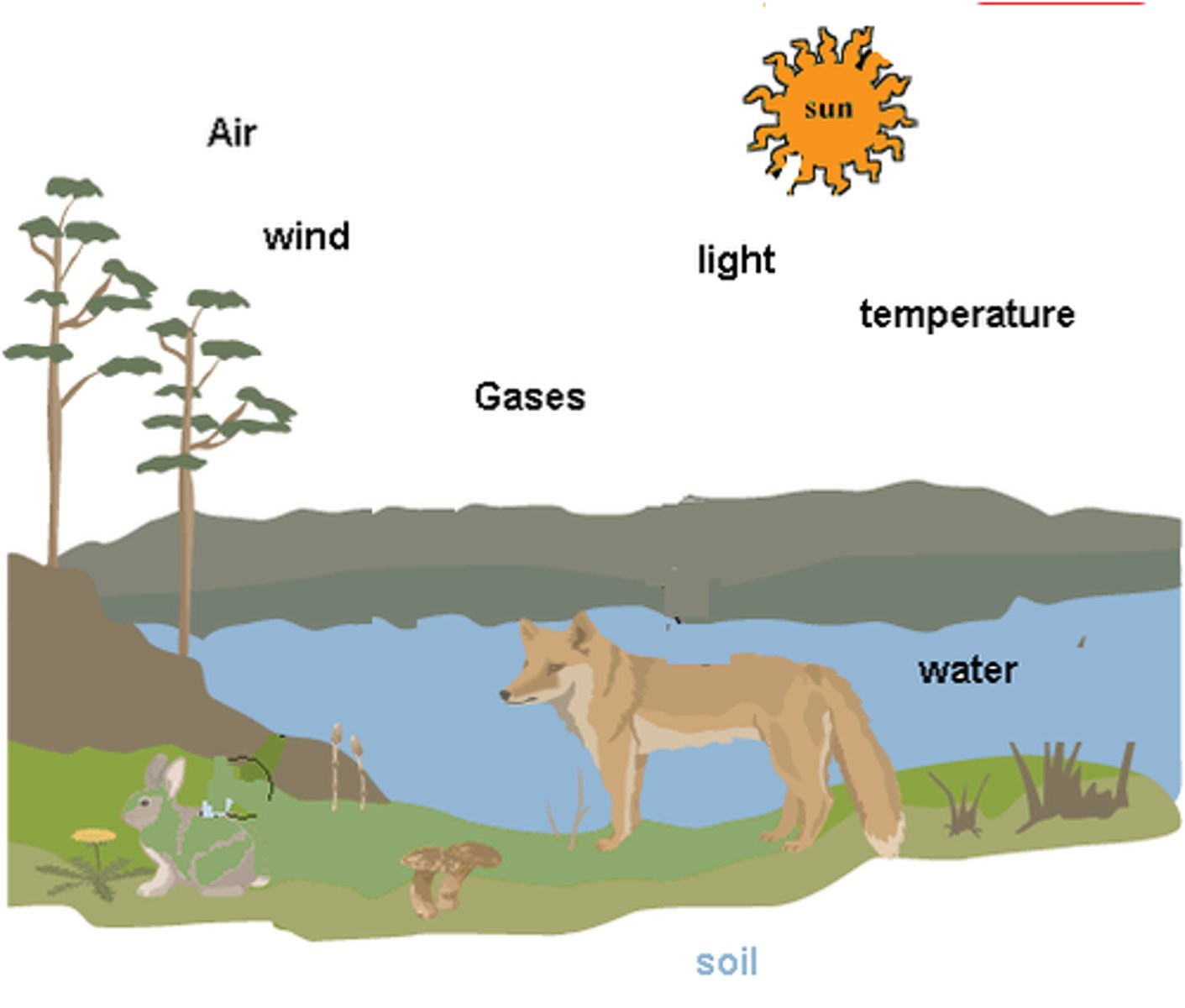
Biotic Factors
All the living organisms that inhabit an environment. Examples include bacteria, plants, animals, and fungi.
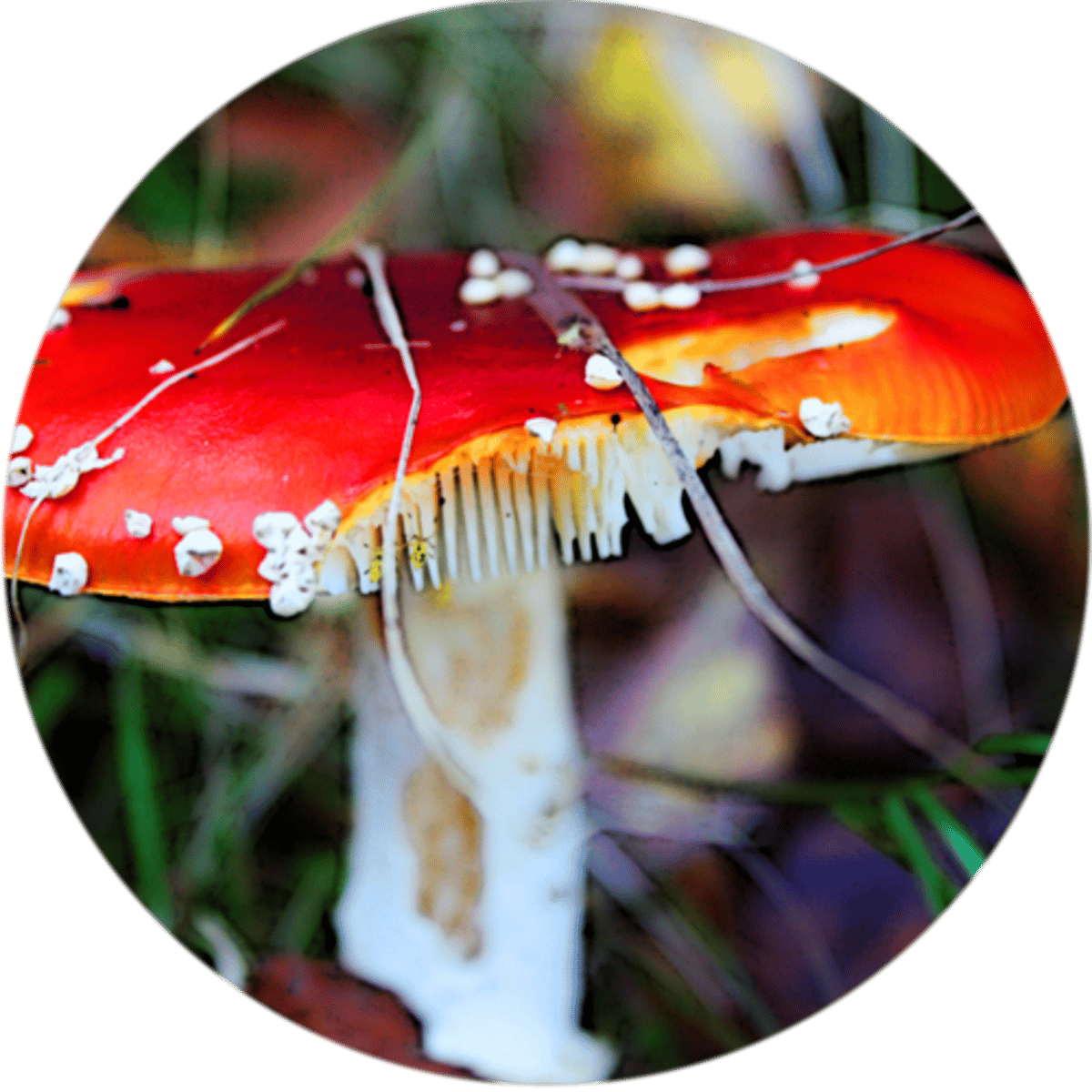
Decomposer
Consumers that chemically break down dead or decaying matter. Examples include fungi, bacteria, and insects. Examples include fungi and bacteria.

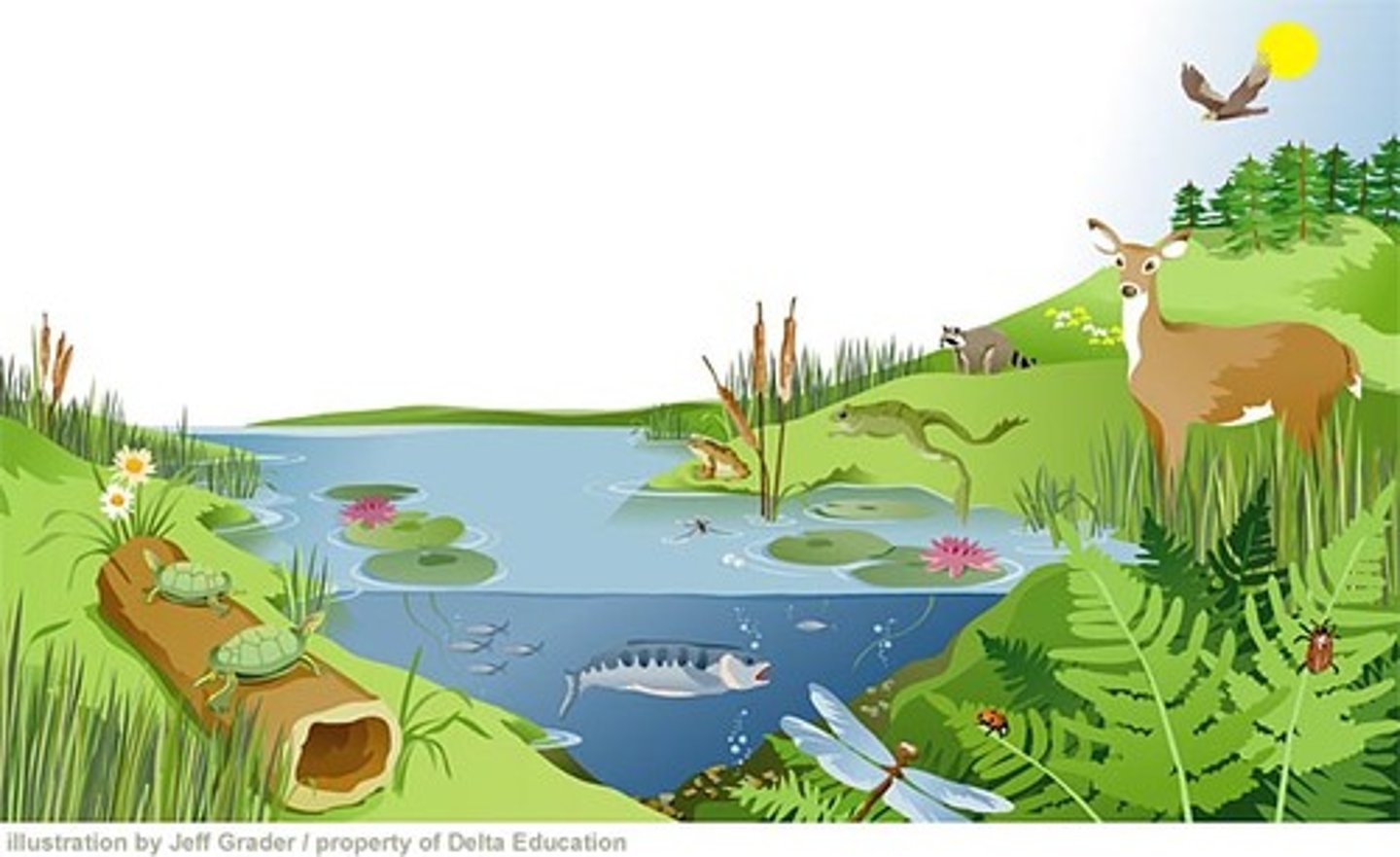
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.

Food Chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten.
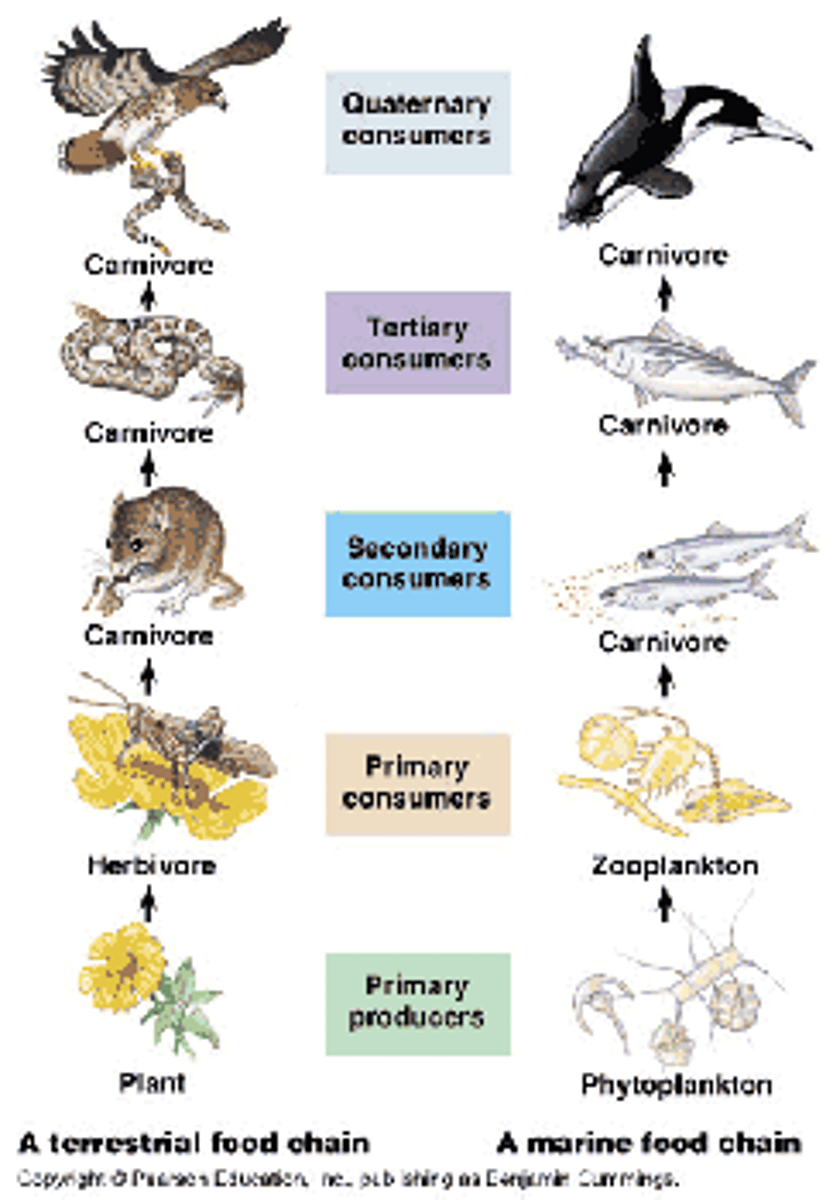
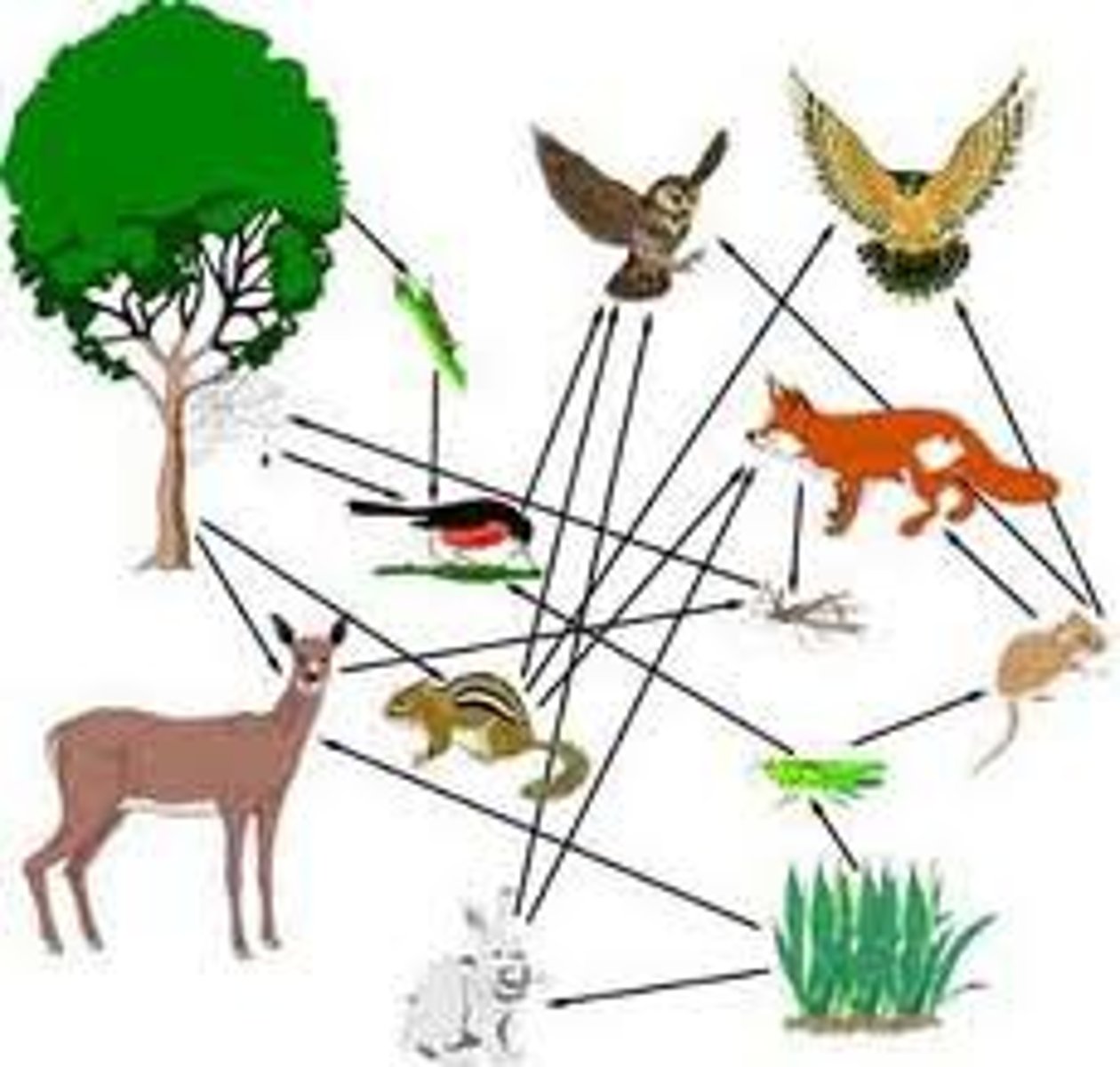
Food Web
shows all possible feeding relationships in a community at each trophic level.
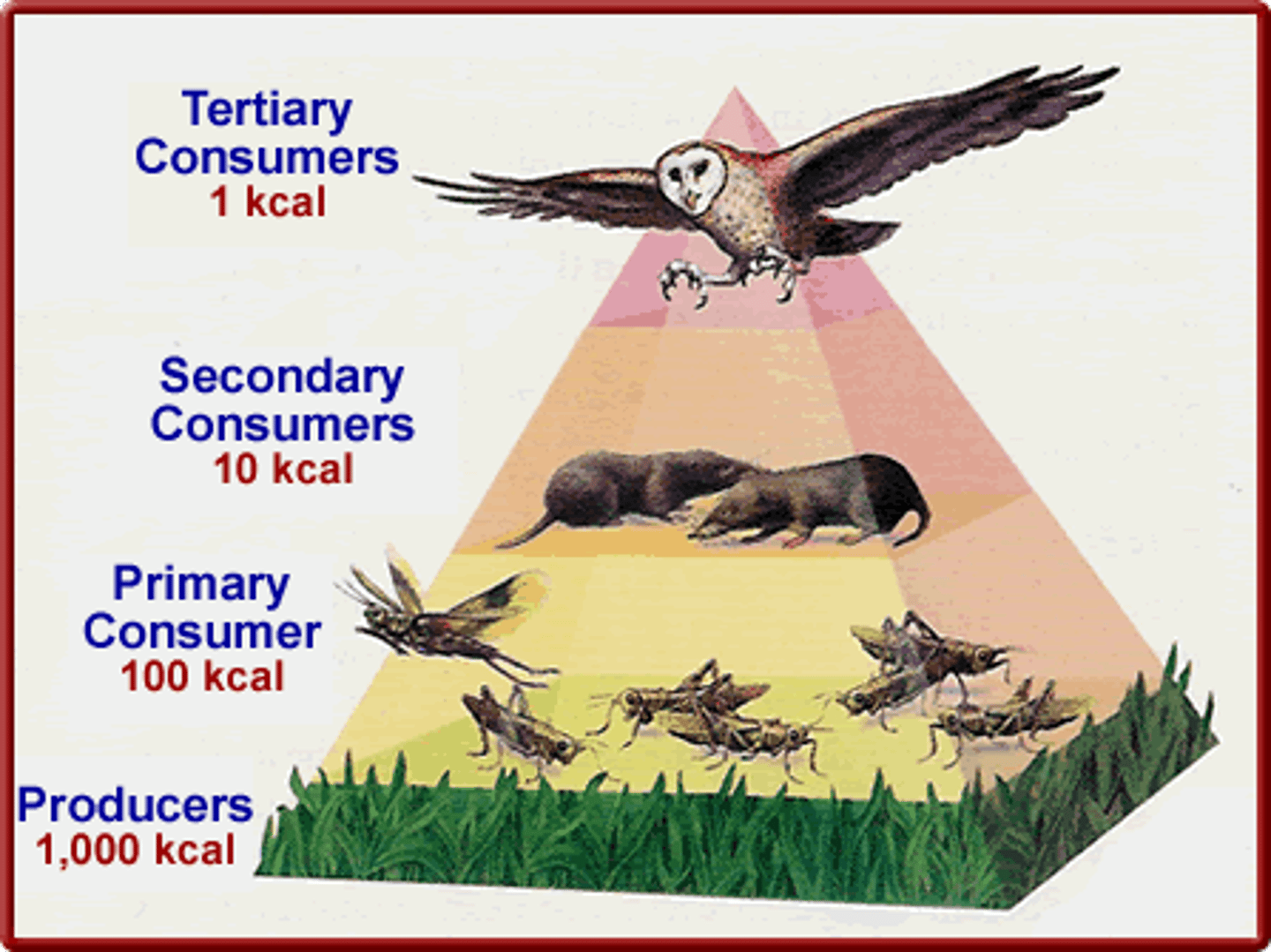
Trophic Level
A feeding level within a food chain or food web which includes producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, etc.