Musculoskeletal System (copy HCF)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
musculoskeletal
pertaining to muscles and the skeleton
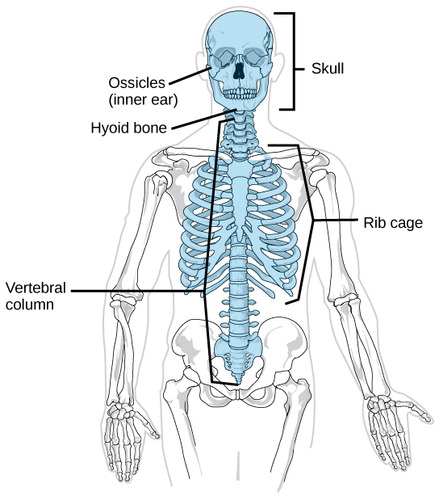
axial skeleton
portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
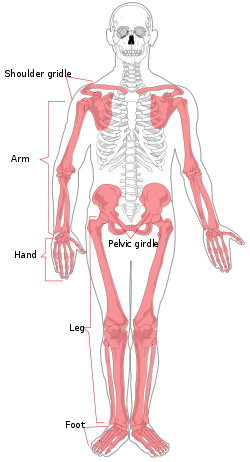
appendicular skeleton
Bones of the limbs and limb girdles that are attached to the axial skeleton
osteo- (prefix)
referring to bones (Example: osteoporosis- decreased bone mass)
musculo- (prefix)
referring to muscles
tendo- (prefix)
referring to tendons
tendon function
attach muscle to bone
ligament function
connects bone to bone and stabilizes joints during movement
fracture
broken bone
arthro- (prefix)
referring to the joint
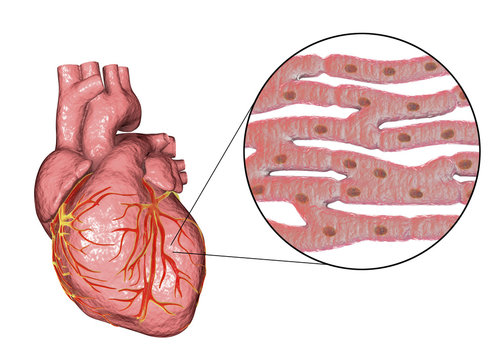
cardiac muscle
involuntary muscle tissue type found only in the heart
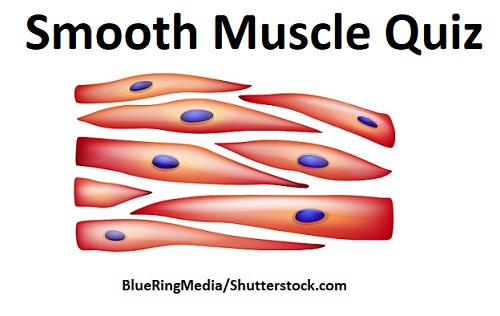
smooth muscle
involuntary muscle tissue type found inside many internal organs of the body
skeletal muscle
a muscle tissue type that forms into groups to form muscles for voluntary movement
tachycardia
fast heart rate (over 100 bpm)
bradycardia
slow heart rate (less than 60 bpm)
blood pressure
the pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels
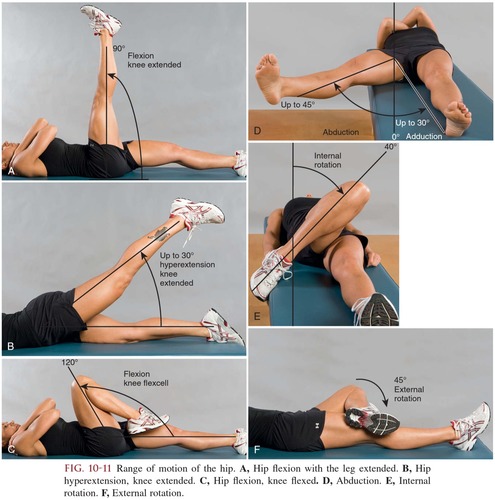
range of motion
abbreviated ROM; complete extent of movement of which a joint is normally capable
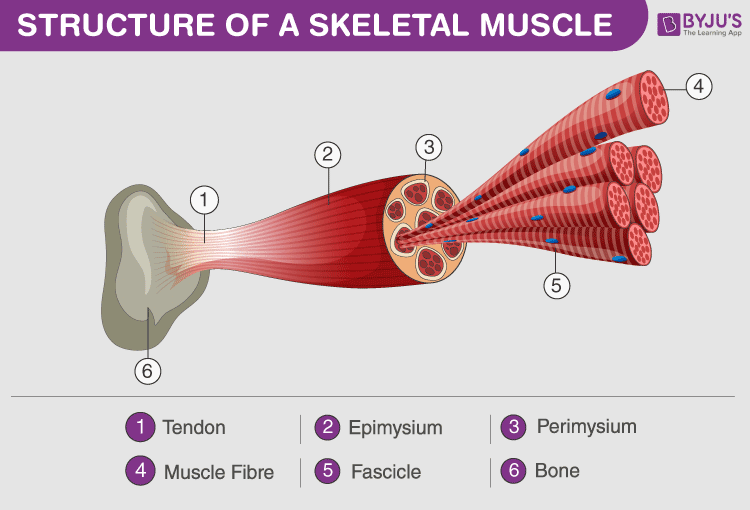
muscle (voluntary movement)
tissue composed of fibers that can contract, causing movement a part of the body; attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
muscle (involuntary movement)
tissue composed of fibers that can contract that responds automatically to brain signals but cannot be consciously controlled; causing movement within hollow organs (GI, bladder)
short bones examples
carpals and tarsals
flat bones examples
bones of the ribs, shoulder blades, pelvis, and skull
muscular dystrophy
group of inherited diseases characterized by progressive weakness and degeneration of muscle fibers without involvement of the nervous system
fibromyalgia
chronic condition with widespread aching and pain in the muscles and fibrous soft tissue
sprain
stretching or tearing of ligaments
strain
A condition resulting from damaging a muscle or tendon
osteoporosis
a condition in which the bones become fragile and break easily
amputation
a surgical removal of all or part of a limb
flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
extension
increases the angle of a joint
long bone
longer than they are wide; femur, humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, metatarsals
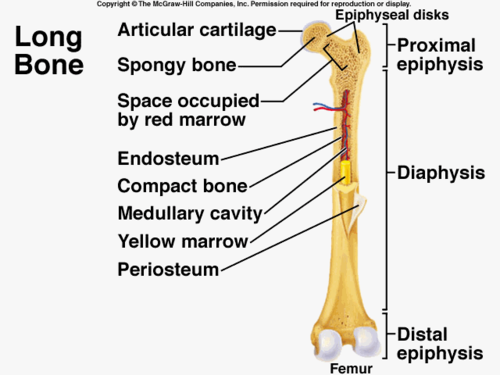
flat bone function
thin and curved bone; serves as a point of attachment for muscles and protects internal organs; ribs, skull, scapula
irregular bone function
bone of complex shape; protects internal organs from compressive forces; vertebrae, pelvis, inner ear bones
short bone
approximately the same length and width, typically cube shaped
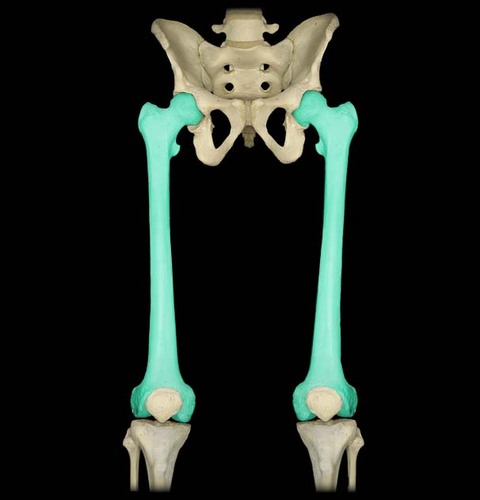
femur
upper leg bone
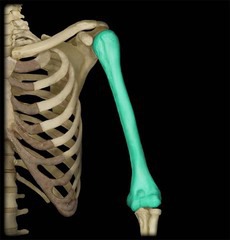
humerus
upper arm bone
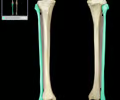
tibia
the medial and larger bone of the lower leg
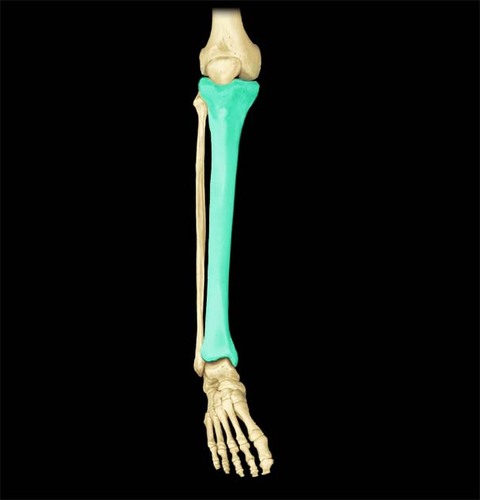
fibula
The lateral and smaller bone of the lower leg
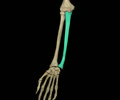
radius
lateral bone of the forearm
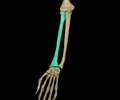
ulna
medial bone of the forearm
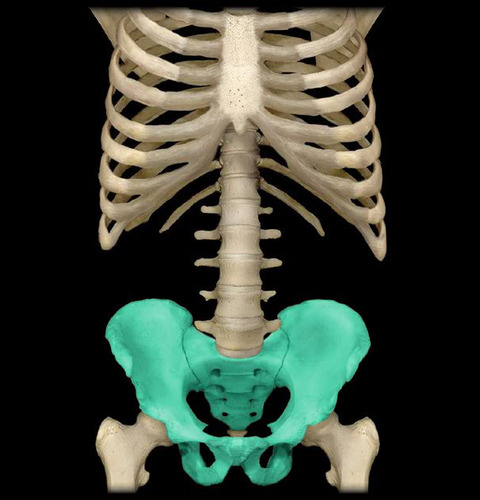
pelvis
hip bone as well as the sacrum and coccyx of the spinal column
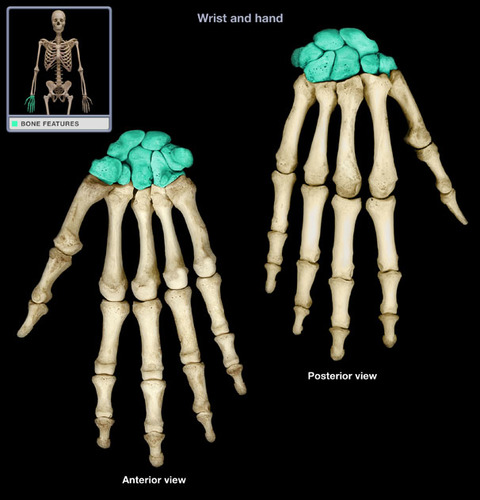
carpal bones
wrist bones
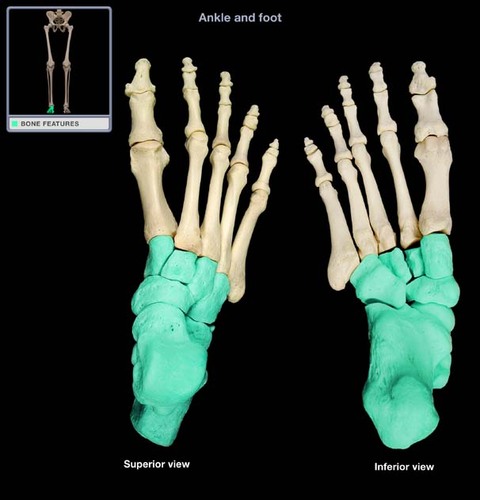
tarsal bones
ankle bones
phalanges (hands)
finger bones
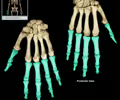
phalanges (feet)
toe bones
post concussive domains
cognitive, vestibular, exercise intolerance, mood, headache, cervical, visual, sleep
muscular system function
movement; posture; heat production; protect organs; helps move blood, food, waste; opens/closes body openings
skeletal system function
protection; movement; calcium (mineral) storage; production of blood
joint
A place in the body where two bones come together
circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
abduction
movement away from the midline
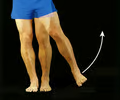
adduction
movement toward the midline

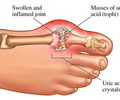
arthritis
joint inflammation and stiffness
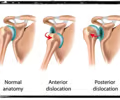
dislocation
displacement of a bone from its joint
What are the four common traits all muscles share?
Excitability/Irritability, contractility, extensibility, elasticity
Excitability/Irritability
ability of muscles to respond to a stimulus
Contractility
ability of muscle cells to forcefully shorten
Extensibility
ability of muscles to stretch
Elasticity
ability of muscles to return to original shape after stretching
Fascia
sheet of tough fibrous tissue that wraps around an individual muscle
Insertion
end connected to the bone that moves when muscle contracts
Ligaments
bands of tough elastic tissue (around joints) that connects bone to bone
Tendons
bands of fibrous tissue that attach muscle to bone