polysaccharides
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
How are polysaccharides formed?
the condensation of many glucose molecules
3 types of polysaccharides?
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
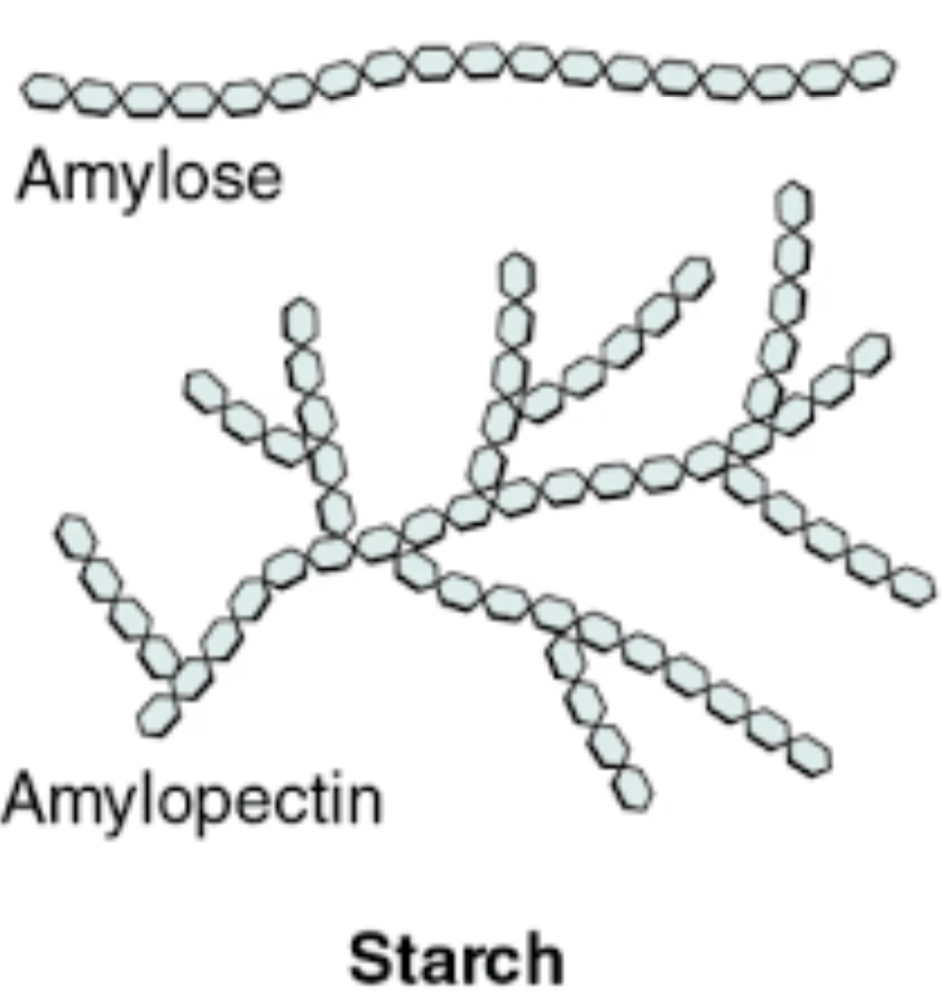
What is starch made up off?
Amylose and Amylopectin
What is starch found in and stored in?
Potatoes, rice
Plants store excess glucose as starch
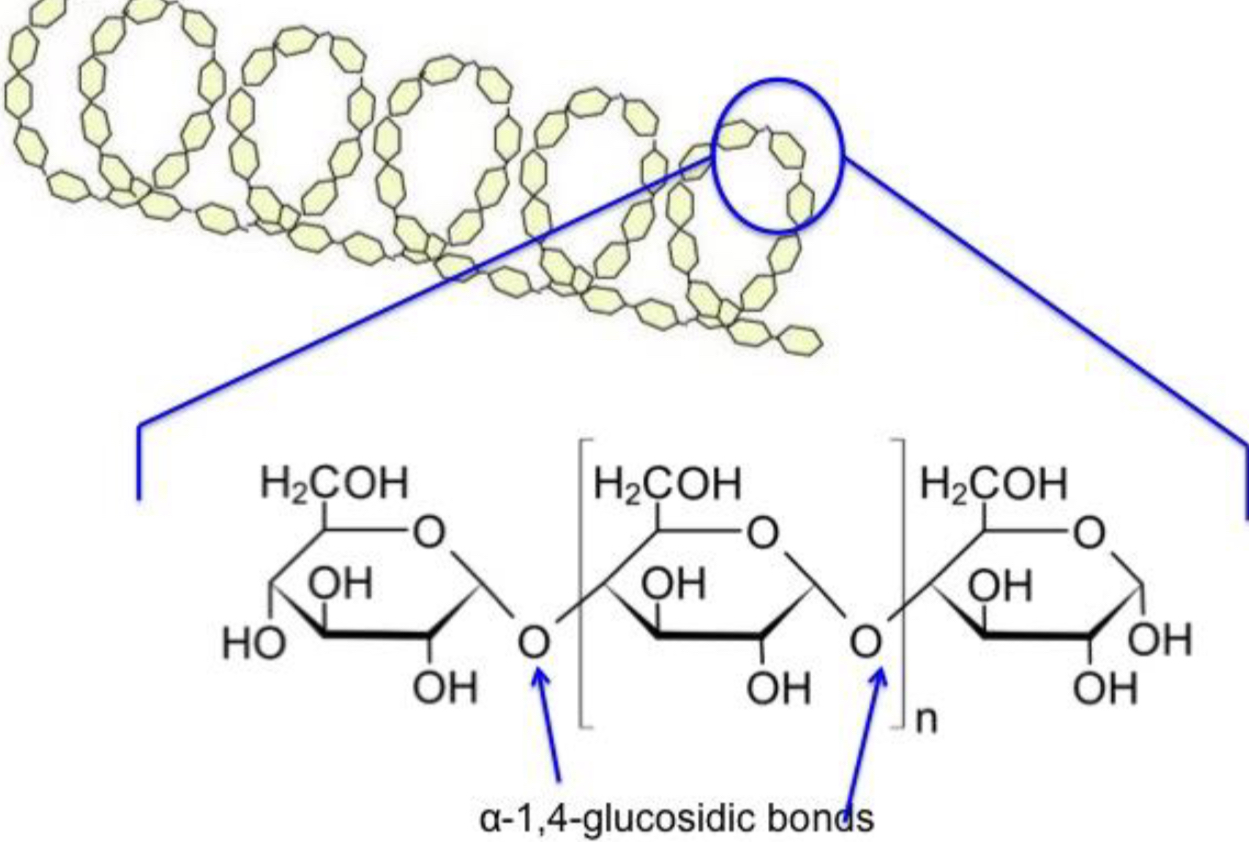
Structure of amylose in starch?
ą 1-4 glycosidic linkage (joins at carbon 1&4)
Straight chain that’s coiled (because of the angle the linkage forms at)
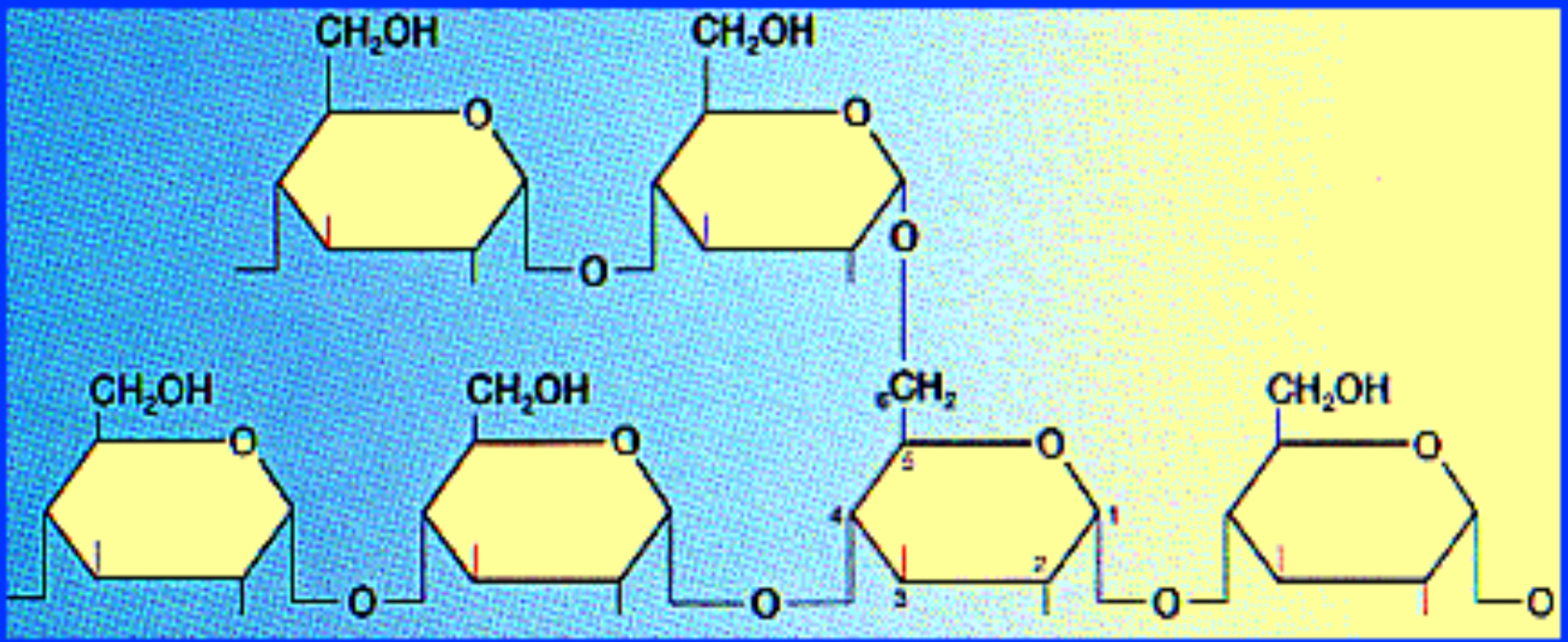
Structure of amylopectin in starch? And why?
ą 1-4 glycosidic linkage (the main chain)
a 1-6 glycosidic linkage (every 25 glucose)
Easier to break off glucose for energy in plants
Function of starch and glycogen?
Energy storage
Starch stored in e.g chloroplasts
Glycogen - muscle and liver cells - hydrolysed into glucose
Structure of glycogen?
ą 1-4 glycosidic linkage
ą 1-6 glycosidic linkage
Highly branched
(Same structure as amylopectin but more branched)
Features of glycogen and why is this useful ?
Highly branched - easily broken down into glucose (fast supply of energy)
Insoluble in water - doesn’t change water potential (water in and out of cell)
Structure of cellulose? Features?
B 1-4 glycosidic linkage
Straight chain - every other B glucose is inverted (flip everytime)
Allows hydroxyl groups - form hydrogen bonds - produces microfibriles (tight bundles) - supportive structure
Insoluble in water
Function of cellulose?
Structural support
Microfibriles form meshwork to support the cell wall
How is glycogen and starch formed?
The condensation of ą glucose
How is cellulose formed?
Condensation of B glucose