CLS Review - Urinalysis
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
237 Terms
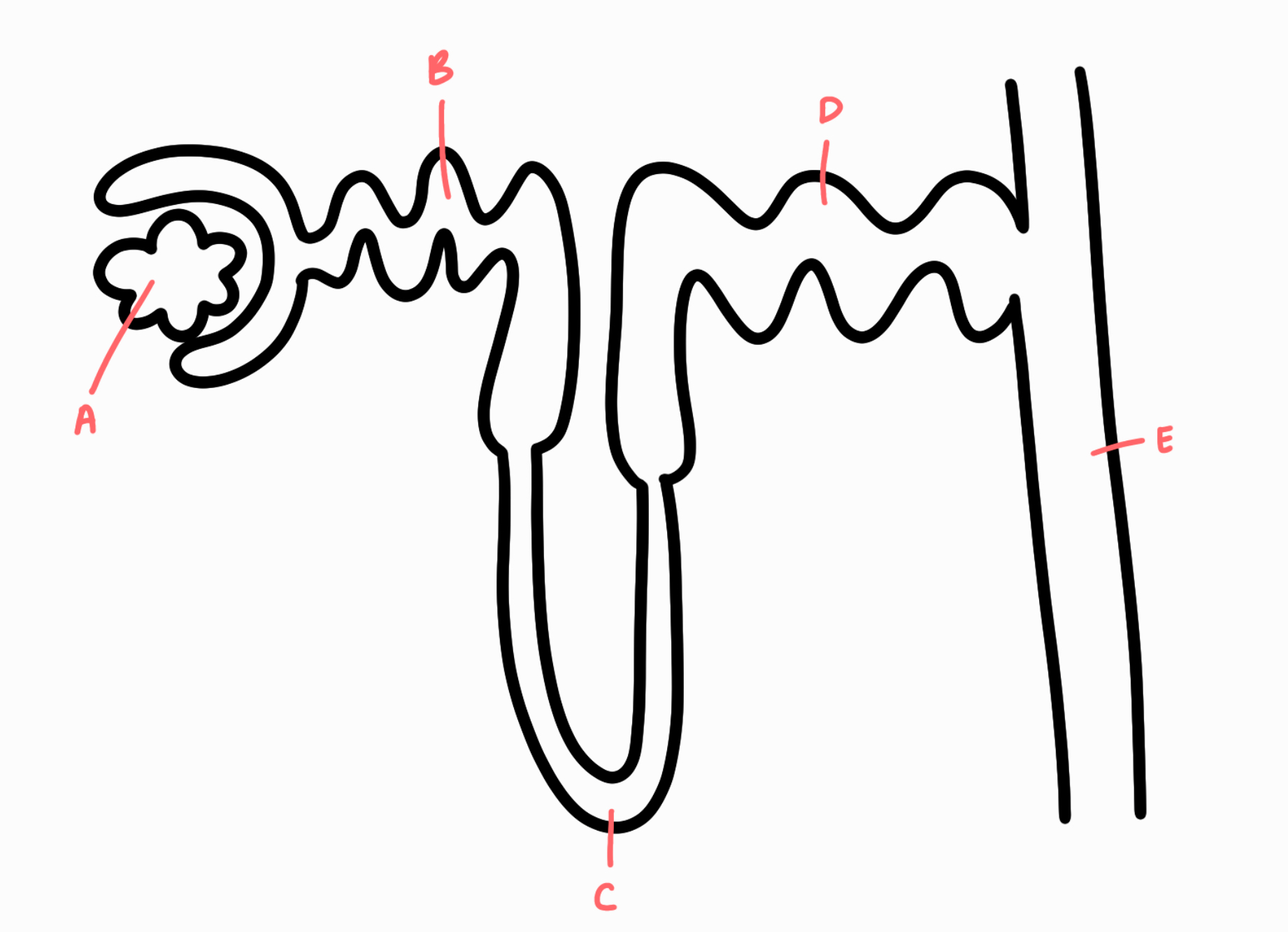
A: Glomerulus
B: Proximal tubule
C: Loop of Henle
D: Distal tubule
E: Collecting Tubule
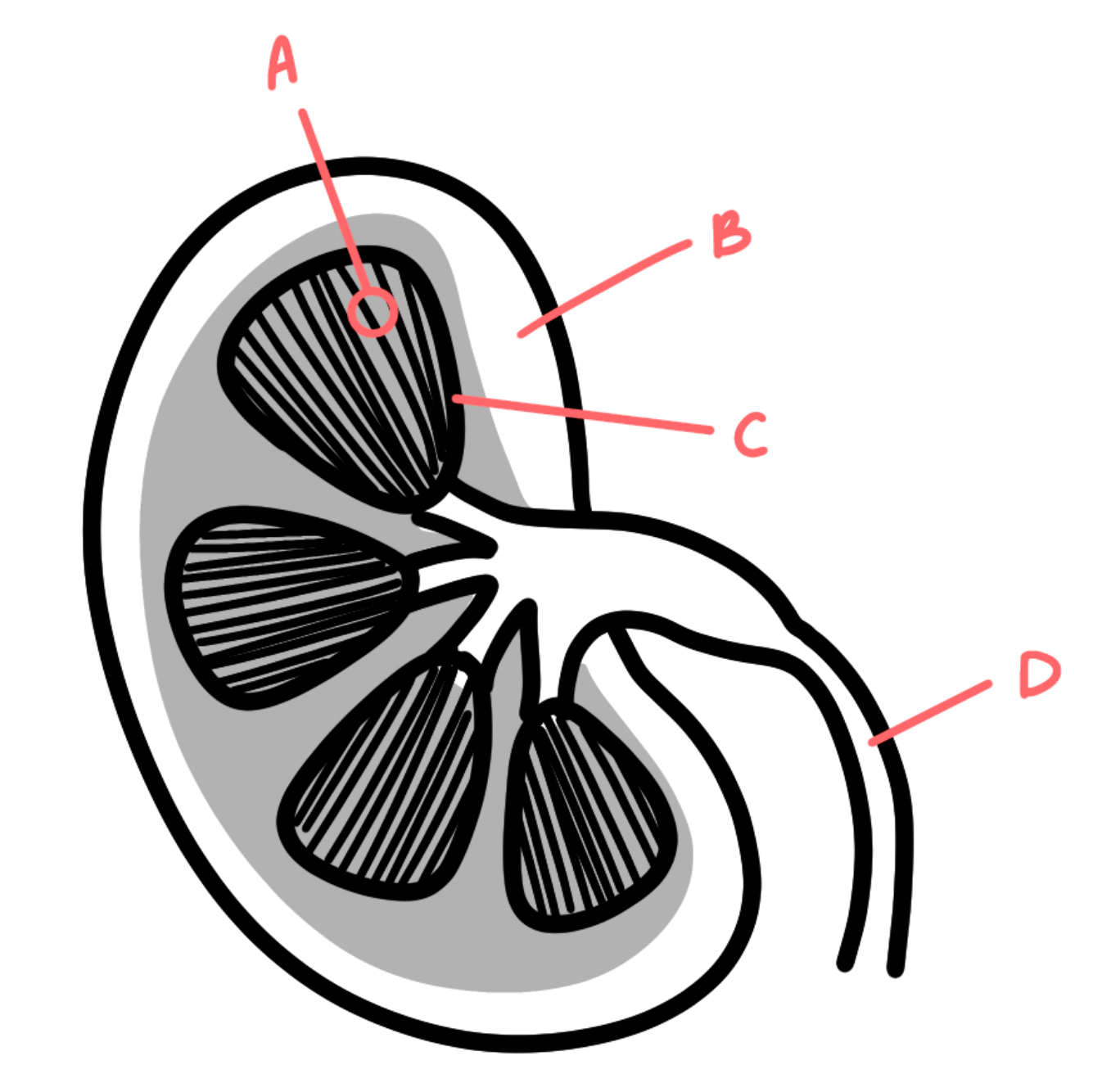
A: Nephron
B: Cortex
C: Medulla
D: Ureter
Major functional unit of kidney
1 million per kidney
Composed of glomerulus and renal tubules
Nephron characteristics (purpose, quantity, components)
Nonselective
<70,000 MW
The glomerulus does (——) filtration of plasma substances tht re less than (——) MW
Water
Glucose
Electrolytes
Amino acids
Urea
Uric acid
Creatinine
Ammonia
Glomerular filtrates (8)
120 mL/min (1/5 renal plasma)
Glomerular filtration rate
Water
Sodium chloride
Bicarbonate
Potassium
Calcium
Amino acid
Phosphates
Protein
Glucose
What does the PCT reabsorb (9)
Glucose
160-180 mg/dL
(——) is the threshold substance of the PCT with reabsorption being (——) or less
Sulfates
Glucuronides
Hydrogen ions
Drugs
What is secreted in the PCT (4)
Reabsorbs water (no solutes)
What is reabsobed in the descending LoH
Reabsorbs solutes (sodium, chloride, calcium, magnesium)
What is reabsorbed in the ascending LoH
Reabsorbs sodium
Secretes potassium, ammonia, and hydrogen
(Potassium exchanged for sodium)
What is reabsorbed (1) and secreted (3) in the distal and collecting tubules
1200-1500 mL/day
Volume for normal urine output
>2500 mL/day
Diabetes insipidus, diabetes mellitus, diuretics, caffeine, alcohol, excessive water intake
Urine output volume for polyuria and associated diseases/causes (6)
<400 mL/day
Dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea, burns, perspiration
Urine output volume for oliguria and its associated diseases/causes (5)
Complete cessation
Kidney damage, decreased blood flow to kidneys
Urine output volume for anuria and its associated deases/causes (2)
Nocturia
Increasd volume of urine output at night
Urea
Other organic solids (Uric acid and creatinine)
Inorganic solids (Chloride*, sodium, potassium)
Water
Composition of urine (4)
Urea
Metabolic waste product produced in liver from breakdown of protein; ½ total urinary dissolved organic solids
Aldosterone
Adrenal gland
What hormone increases the rate of sodium reabsorption, and where is its source
Arginine Vasopressin (AVP/ADH)
Posterior pituitary gland
Which hormone regulates the reabsorption of water from the distal tubules, and where is its source
Diabetes insipidus
What disease has a deficiency in vasopressin (ADH)

Random
(Collection method) most common specimen type; easiest to collect; useful for routine screening tests
First morning
(Collection method) First voided specimen upon waking; ideal screening specimen (most concentrated)
Midstream clean catch
(Collection method) external genital area is cleaned; first an dlast stream of urine voided while midstream is collected; specimen of choice for routine bacterial culture
Catheterization
(Collection method) Insertion of catheter directly into bladder via urethra; avoids external contamination, but may introduce infection
Pediatric
(Collection method) Sterile, plastic collection bag placed over genital area with adhesive; bag checked every 15 minutes; many sources of contamination
Suprapubic aspiration
(Collection method) Insertion of needle through suprapubic abdominal area directly into bladder; avoids external contamination but may introduce infection; optimum specimen for bacterial culture, but invasive
First specimen discarded while all others collected
How is 24 hour urine collected
Creatinine levels (>1.0 mg/dL)
Completeness of 24 hour urine collection is monitored by…
1 hour of voiding (NOT 1 hour after received in lab)
Urine samples should be analyzed within…
Nitrite (bacterial growth)
pH (urea → ammonia)
Turbidity (bact growth, RBC/WBC, amorphous material)
What increases in urine samples that are left in room temperature for too long (3)
Glucose (glycolysis from bact/yeast)
Ketones (volitilization)
Bilirubin (light)
Urobilinogen (oxidize → urobilin)
Cells and casts (lysis)
What decreases in urine samples that are left in room temperature for too long (5)

Refrigeration
Preservation method of choice up to 24 hours
Amorphous crystals
Return to room temperature (15 min)
Refrigeration may result in the formation of (——) in urine samples; fefore testing, the samples must (——)
Fruity → ketones
Ammonia → old urine
Mousy → phenylketonuria (PKU)
Maple syrup → Maple syrup disease (branched chain aminoaciduria)
What may different odors of urine specimens indicate (4)

Urinary elements (cells, casts, crystals) or bacteria
What may make urine cloudy

Urochromes
What gives urine their normal color
Usually slightly acidic (6.0) but can range 4.5-8.0
What is the pH of urine
Eating
Standing at room temp or warmer
Vegetarian diet
What can make urine more alkaline (3)
Metabolic/respiratory acidosis
High protein diet
Cranberry juice
What can make urine more acidic? (3)
Hemoglobin
RBCs
Myoglobin
Porphoryin
Uroerythrin
What makes urine red (5)
Hemoglobin
RBCs
Myoglobin
What makes urine red-brown (3)
Bilirubin
Biliverdin
What makes urine yellow-brown/amber-yellow-green (2)
Bilirubin
Urobilin
Pyridium (drug)
What makes urine yellow-orange (3)
Vitamin C
What makes urine bright yellow
Concentrated specimen
Bilirubin
Urobilin
What makes urine dark yellow (3)
Methemoglobin (oxidized RBCs)
Homogentisic acid (Alkaptonuria)
Melanin
What makes urine brown-black (3)
Indican (Tryptophane metabolic disorder)
What makes urine blue
Old urine
Pseudomonas
What makes urine green/green-blue (2)
Porphyrin
What makes urine a wine color
1.002-1.035 (≤1.040 is physically possible)
Normal urine specific gravity
Glucose or radiographic dyes from renal x-ray
High specific gravity of urine is due to… (2)

Defect: low insulin
SG: ↑
Glucose: ↑
Ketones: ↑
Diabetes mellitus characteristics (defect, specific gravity, glucose, ketones)
Defect: low ADH/AVP
SG: ↓
Glucose: N
Ketones: N
Diabetes insipidus characteristics (defect, specific gravity, glucose, ketones)
Polyuria and polydipsia
Symptoms shared between diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus (2)
“Protein error of indicators” (more sensitive to albumin than globulin)
Test pad kept at pH 3.0
Albumin binds to dye
Dye shifts yellow → green
Principle of protein reagent strip
Highly alkaline urine → false positives
Interfering substances of protein reagent strip
Proteinuria
Best single indicator of renal abnormality, specifically glomerular involvement
Multiple myeloma
Orthostatic proteinuria (benign condition: proteinuria after standing)
Strenuous exercise
Besides glomerular abormalities, what is proteinuria associated with (3)
Diabetes
Hypertension
Peripheral vascular disease
Microalbuminuria can be periodically monitored for patients with (——), so that treatment can begin before kidney disease occurs
Glucose oxidase (double sequential enzyme reaction)
Principle for glucose reagent strip
Sugar or other reducing substances other than glucose
Positive copper reduction test and negative glucose strip test is indicative of…
Low amounts of glucose present
Positive glucose strip test but negative copper reduction test is indicative of…
Oxidizing agents (bleach, peroxide) → false positive
Interfering substances for glucose reagent strip
Glucose
Other reducing sugars
Galactose, lactose, fructose, maltose, pentose
What does clinitest detect in urine (6)
Galactosemia
Clinitest is a screening test for (——), a rare congenital carbohydrate metabolic condition in pediatric patients

Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) high dose → false negative
Interfering substance for clinitest
2 drops (5 drops → pass through rxn negative-positive-negative)
How many drops should be administered in Clinitest
Benedict’s copper reduction
CuSO4 + NaOH + reducing substance = Cu2O
blue-green → orange-red
Principle of clinitest, the chemical reaction, and color change
Acetone
Diacetic acid (acetoacetate)
Beta-hydroxy-butyric acid (fat metabolism end product)
Ketones that can be found in urine (3)
Sodium nitroprusside + ketone = purple color
Principle of ketone reagent strip and tablets
Diacetic acid
Ketone reagent strip is specific for…
Diacetic acid
Acetone
Ketone confirmation tablets (Acetet) are specific for… (2)
Highly pigmented urine and levadopa metabolites → false positive
Interfering substances for ketone reagent strip and tablets (2)
Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
High protein diets
GI disturbances
Which conditions give positive results for ketones (3)
Peroxide on strip + blood = O2
O2 + color producer = color change
Describe the 2-step enzymatic procedure for the detection of blood on a reagent strip
Bleach and other oxidizing agents → false positive
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) → false negative
Interfering substances for blood reagent strip
Hemoglobin and myoglobin
What other substances have peroxidase activity that may affect the detection of blood in reagent strip
Systemic bleeding disprders
Renal diseases
Cystitis
Calculi
Strenuous exercise
Positive blood in urine may be due to hematuria associated with… (5)
Hemolytic anemias
Incompatible transfusions
Malaria
Strenuous exercise
Positive blood in urine may be due to hemoglobinuria associated with… (4)
Muscle destruction
Positive blood in urine may be due to myoglobinuria associated with…
Diazo
Diazonium salt + bilirubin = bluish-purple color
Principle of bilirubin strip reagent or tablet and its associated chemical reaction
Ictotest (tablet)
(——) is more sensitive in the detection of bilirubin in urine than the reagent strip test
Ascorbic acid
Exposure to light
What can cause false negatives in bilirubin strip reagent
Bile duct obstruction
Liver damage (cirrhosis and hepatitis)
Bilirubinuria is associated with… (2)
Erlich’s reaction
Para-dimethylaminobenzaldehide in acid buffer + urobilinogen → pink color
Principle or urobilinogen reagent strip and its associated chemical reaction
Formalin (preservative) → false negative
Highly pigmented urine and some medicatins → false positive
Interfering substances for urobilinogen reagent strip
≤ 1 mg/dL (1 EU)
Normal amount of urobilinogen in urine
Liver damage (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
Hemolytic disease
High urobilinogen is associated with… (2)
Bile duct obstruction
Negative urobilinogen is associated with…
None
Normal level of urine bilirubin
Bilirubin: 0
Urobilinogen: ↑
Expected bilirubin and urobilinogen values for hemolytic conditions
Bilirubin: 0 or ↑
Urobilinogen: ↑
Expected bilirubin and urobilinogen values for liver disease

Bilirubin: ↑
Urobilinogen: ↓ (N on strip)
Expected bilirubin and urobilinogen values for obstructive conditions
Priniciple: Diazo reaction
Nitrite + amine reagent at acidic pH → diazonium compound
Diazonium compound + 2-hydroxy-1,2,3,4 tetrahydrobenz (h) - quinolin → pink color
Principle of nitrite reagent strip and its associated chemical reactions
False negatives
Lack of dietary nitrate
Urine not in bladder long enough (4hr) for bacteria to reduce
Non-nitrate reducing bacteria
Ascorbic acid
Interfering substances/conditions for nitrite detection with reagent strip
Any shade of pink
What result is considered a clinically significant amount of bacteria with nitrite reagent strips
Leukocyte esterase + ester → pyrrole compound
pyrrole compound + diazo reagent → purple color
Principle chemical reaction for leukocyte reagent strip
Pyuria
Positive result for leukocyte reagent strip indicates the presence of leukocytes in urine, also known as…