Unit 4 - Work, Energy, Power and Calculus
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the definition of Work done by a constant force?
What is Work’s quantity, symbol, and UNITS???
Def: When a force F causes an object to be displaced by an amount d, the work done by F is equal to the dot product of F and d.
—> W = F⋅d = Fdcosθ
Work is a SCALAR (work can be NEGATIVE!!!)
Units = JOULES
Symbol is just W
What are the 3 different relationships for Work?
W = Fdcosθ (no cosθ if its not angled, cos 0 or 180 = 1 and cos 90 = 0 hence why upward force produces 0 work)
W = ΔKE
W = -ΔU
What are the 3 different directions of work, and what would work be in each?
Angle for Work is determined with the angle between the applied force and direction of motion 🤯
Work to the right with an angle 0 <= θ <= 90
W > 0
Work directly upwards (cos90 = 0)
W = 0
Work to the left with an angle 0 <= θ <= 180
W < 0 (WORK CAN BE NEGATIVE!!!)
What kind of work with friction ALWAYS produce?
Friction will ALWAYS produces a NON CONSERVATIVE FORCE = negative work
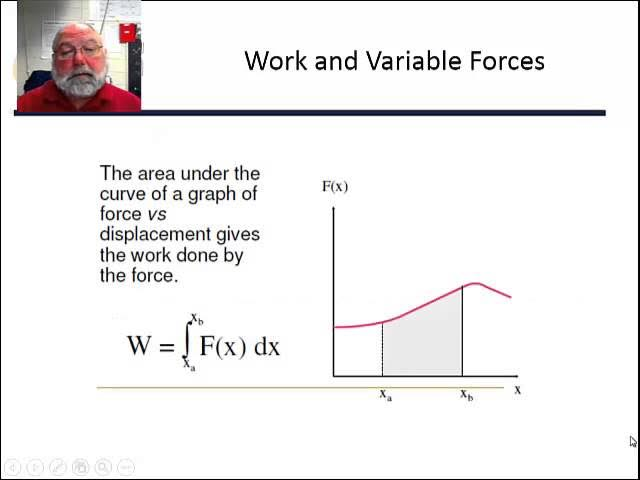
What is the formula for Variable Work?
Look at picture
xa = xi
xb = xf
What MUST you remember about the derivatives and integrals of e, and ln?
The derivative of y = ex does NOTHING
the derivative of eg(x) just means power rule —> = g’(x)eg(x)
The integral of ex does nothing but remember +c
|
The derivative of y = lnx is just y’ = 1/x (inverses anything)
The derivative of ln(g(x)) is CHAIN RULE beacause ln is a function!!!!
The integral of 1/x is ln |x| + c (ABS VALUE!!!)

What is Hooke’s Law?
Hooke’s Law: The force exerted by a spring (Fs) is directly proportional to the extension or compression of the spring. (Spring gives Opposite reaction force to force applied on it)
Fs = -kx
(k = spring constant, x = disp, units are Nm)
In Hooke’s Law, when will Fs be pos and neg? Why?
Fs = force of spring = -kx
Fs is positive when you compress the spring cus x is negative
Fs is negative when you pull the spring cus in Fs = -kx, x is positive
How do you model the Hooke’s Law equation with calculus?
Why does the negative go away?
the reason why the negative disappears is because the the work of the spring is OPPOSITE to the work it takes to affect the Hooke’s Law Eq.
THINK:
The applied Work we give affects the equation F = -kx
—> the Work of the spring is the opposite of resulting Spring Force created by the Force we put in
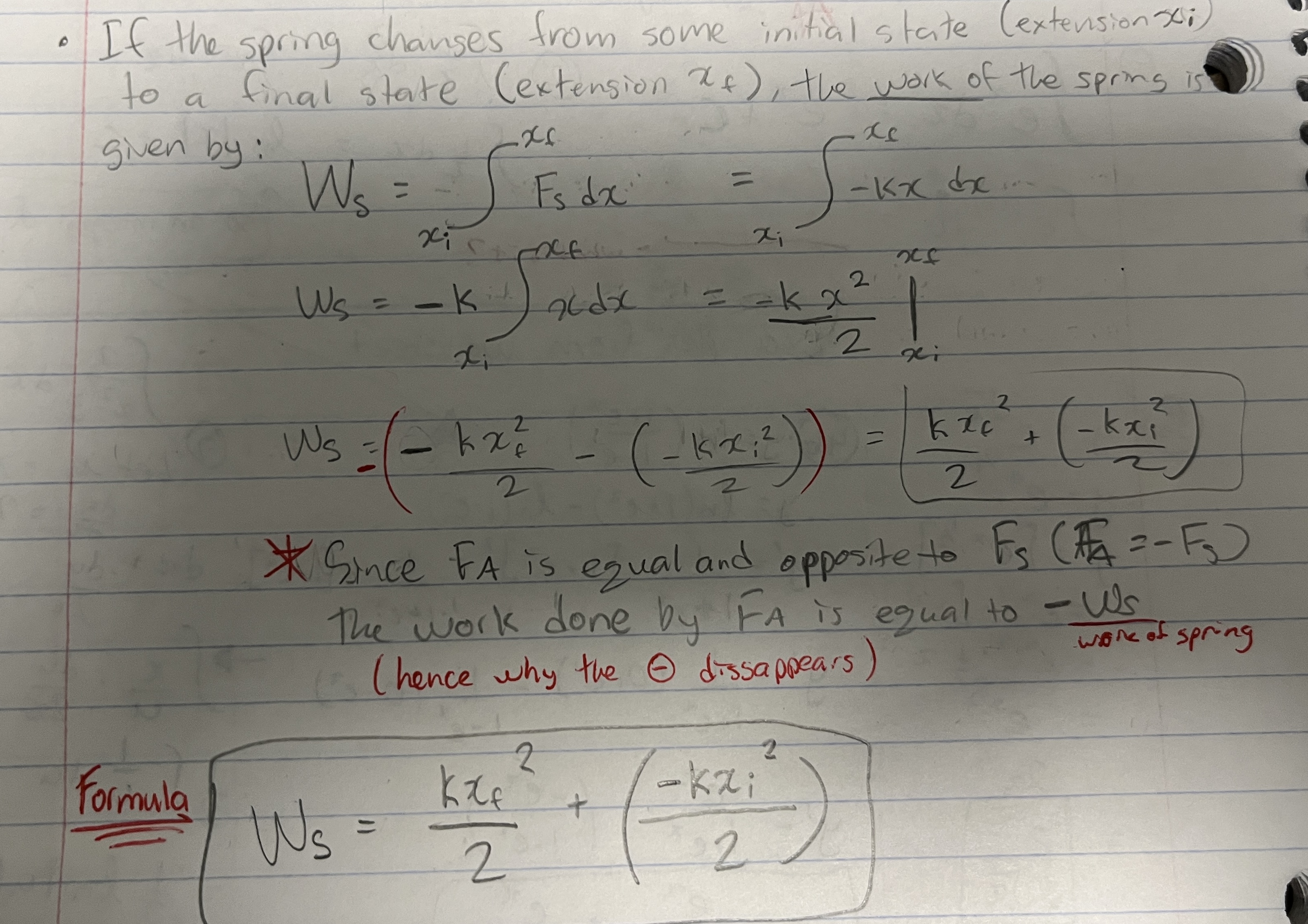
What is Linear Mass Density?
We know that P = density = m/v
For Linear Mass Density, we have the symbol as lambda, and if the mass is distributed along length L, then λ = M/L (units are kg/m)
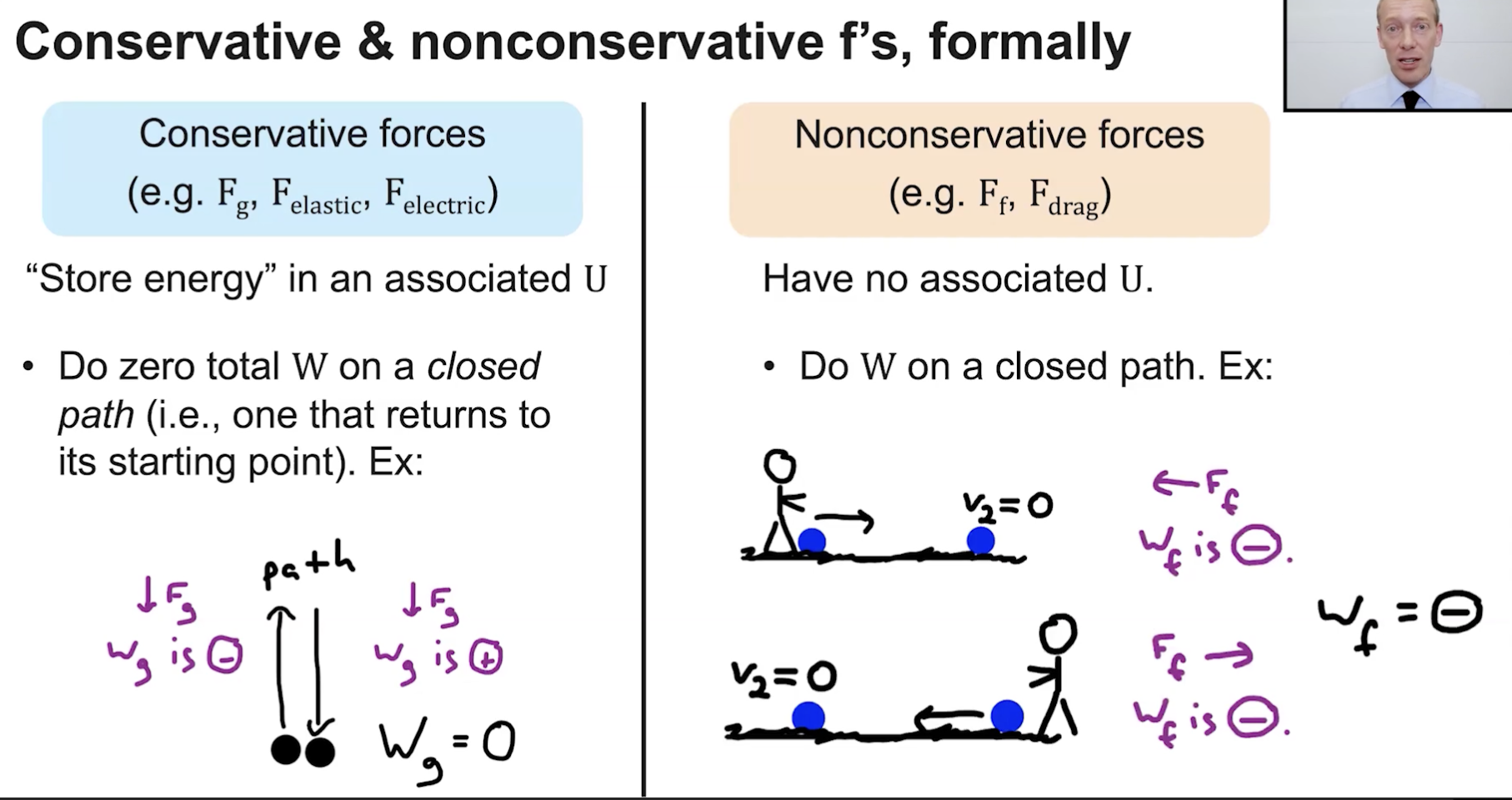
What is a Conservative Force?
What is a Non-Conservative Force?
What is Fnet in terms of Conservative and Non-Conservative Forces?
Conservative Force = A force where the work done by it is independent of path (no matter what path, same Work produced)
—>
Non-Conservative Force = A force where the work done depends on the path (basically any force that causes a loss in KE like friction, heat, sound, drag)
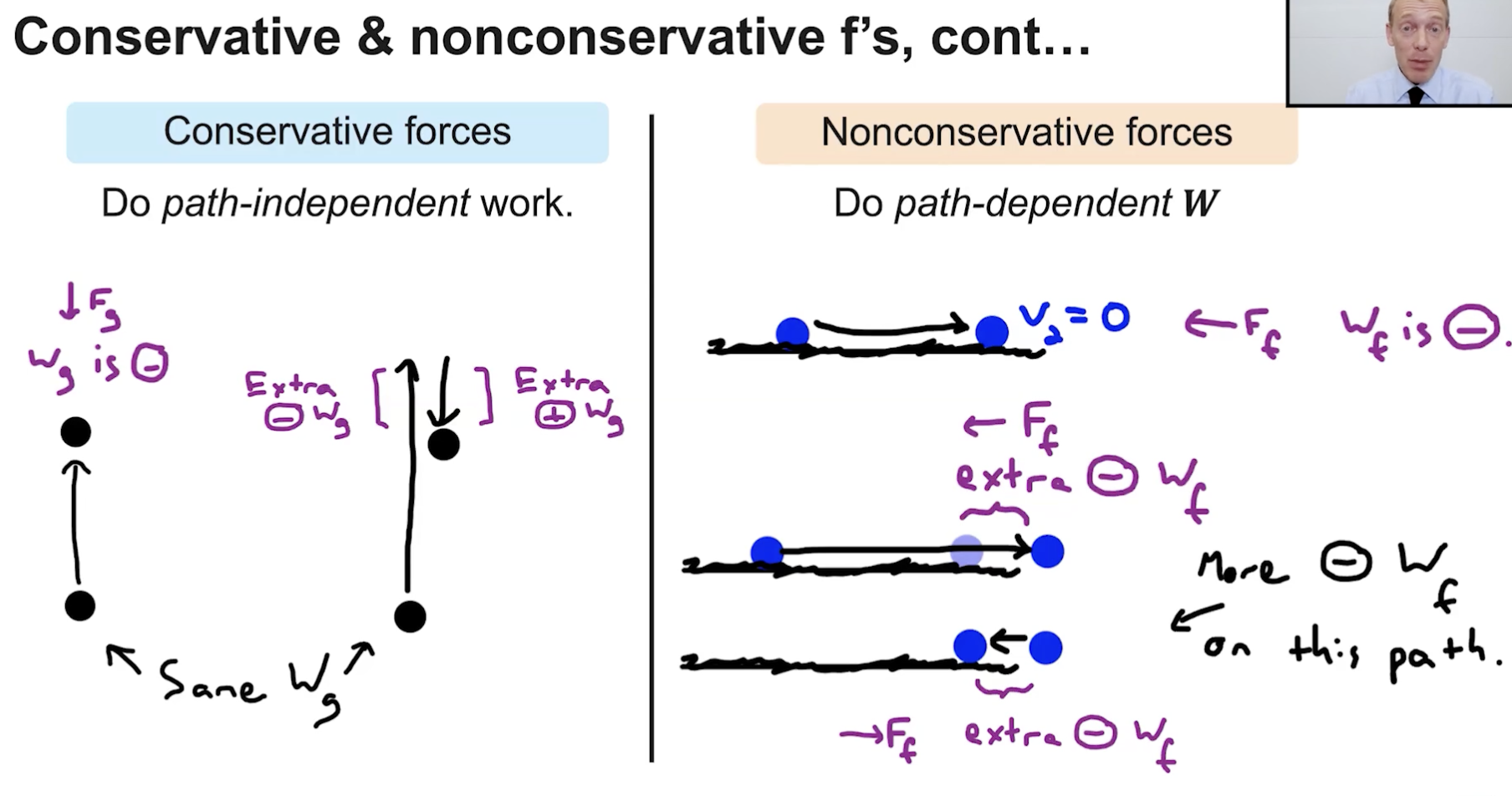
What is something important to know about Conservative and NC forces on a closed path (0 initial speed, speeds up and then ends at 0)
Conservative Forces will do 0 total work in a closed path
NC Forces will ALWAYS do some sort of work even on a closed path
What is Gravitational Potential Energy? (def, magnitude, symbols, formula)
What is Elastic Potential Energy? (def, magnitude, symbols, formula)
Gravitational Potential Energy = Energy associated with the position of a mass in a gravitational field G
Scalar
Symbols are PE or U
ΔUg = -Wg = - (-mgh) = mgh
Elastic Potential Energy = Energy associated with potential energy of a spring
also Scalar
Symbol is Us
Us = 1/2kx²
What is the Conservation of Energy?
In a closed isolated system, there is no change in energy (ΔE = 0)
What is the mechanical energy of a system (E)?
What are the 4 formulas attached to it?
Mechanical energy of a system (E) = the sum of the kinetic and potential energies in a system
|
E = KE + Ug + Us
Ef = Ei (cons of energy) (if we lose energy due to NC force, we say Ef = Ei - NC)
WNC = ΔE = Ef - Ei
KEi + Ugi = KEf + Ugf
What are the 2 ways to find KEf using Force and Distance?
Use Wnet = ΔKE
This will then turn into Fnet d = KEf - KEi
This will then turn into Fnetd = KEf
Now plug in your values for F and d
Use ΔE = Wnc
This will give (KEf +Uf) - (KEi - Ui) = Fnetd
this will become KEf + Uf + 0 = Fnet d
What are PE curves?
What are the 2 formulas?
What is the Calculus Formula?
PE Curve is used to analyze the motion of a particle in 1D. We only consider Conservative Forces!
The 2 formulas are:
1. ΔU = -F(X) x ΔX
2. F(x) = -ΔU/ ΔX
The CALCULUS Formula in differental form is”
F(x) = -du/dx
—>Given a function u(x), the force acting at some positoin x is equal to the negative of the slope of the U vs X graph. (negative of the derivative)
What are the 3 types of equilibirum points on a PE graph?
Stable Equilibrium = typically in a U or bottom of parabola shape part of a function
Unstable Equilibrium = at the crest of a function
Neutral Equilibrium = at a place where -du/dx or slope = 0
What are bounds and what does it mean to be bounded in a PE Curve graph?
The bounds are the 2 points where the PE graph intersects with the total energy of the system (horizontal line)
|
—> to be bounded means the graph needs to stay within those two intersection points.

How do you find KE using a PE graph?
USE THE RELATIONSHIP: E = KE + U
—> knowing this, we can say KE = E- U
—> For this, use the Y-cord for the E line, and the Y-coord for the PE at a certain x-position
How can you tell if a particle can reach a certain position?
A particle should be able to reach a certain position if it falls within the Y-boundary set by the total system E line.
—> Anything below the particle will be able to reach it and IF OVER, NEVER POSSIBLE since U CANNOT be more the the Total Energy

What is Power?
What is its mag, symbol, Units?
What is its Formula if F is const vs F is variable (calc)?
Power is the rate at which work is done OR Power is the rate at which energy is transformed
Power is a Scalar
Symbol is P
SI Units is Watts (W) = J/s
|Formulas"|
if F const: Pav = W/Δt or Pav = ΔE/Δt
if F is variable: Pinst = dW/dt or W = ∫Pinst dt
What is the relationship between Power. Force and Velocity?
Pav = W/Δt = FD/Δt
—> This means Pav = FVav
What is Momentum?
What is its symbol?
What are its Units?
What is its mag?
Momentum (p) is p = mv where p and v are ALWAYS in the same direction
SI units are: kg m/s
Vector
What is Impulse?
What are its units?
What is its mag?
What is its symbol?
Impulse is the product of Fnet and Δt OR the change in Momentum
because impulse can be the product of Force over time its units are always (N/s)
Vector (has direction)
Symbol is J even though its basically Δp
What is conservation of momentum?
What is its formula?
In a close, isolated system, there is no change in momentum (it is conserved)
—> gives us a formula: m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f
What are Oblique Collisions? (Momentum in 2D)
Oblique Collisions are angled collisions.
you will add up the components to make a resultant vector, and that magnitude and direction is the final movement
What MUST ALWAYS be remembered with ANY Collision?
What are the 4 types of Collisions?
In ANY collision, momentum will always be conserved!
(This means either the total momentum is equal before/after or lost in thermal or sound)
Inelastic
KEf < KEi (energy lost to thermal energy and sound)
Elastic
KEf = KEi
Explosion
KEf > KEi
Oblique
Pi = Pf however vector components so add them up
What should you remember about the Center of Mass (CM) of particles?
You must remember that the CM of a particle MUST be broken down into X and Y maybe even Z components.
The component summation is similar to the Translational Equilibrium
CM is also based on the pivot points set by the Q
When do we have to use Calculus for CM?
We will need to use Calculus for SOLID objects or NON- UNIFORM object
|
—> If we have a non uniform rod with a varying density of λ = kx, where k will stay constant
then
λ = dm/dx
xcm = 2/3L
What is a differential equation?
A differential equation (DE) is an equation with a derivative.
The solution to a differential equation is a function y= f(x), that when subbed back into DE, it makes a true statement
EX:
dy/dx = 3x² —> integrate this
y = x³ + C
How do you get Terminal Velocity for a DE?
You dont even need to fully create the differential equation.
—> Just set acceleration (dv/dt) = 0 since at terminal velocity it CANNOT accel more
Then just solve for V