Anatomy Unit 3 (7, 8 & 9)[54]
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
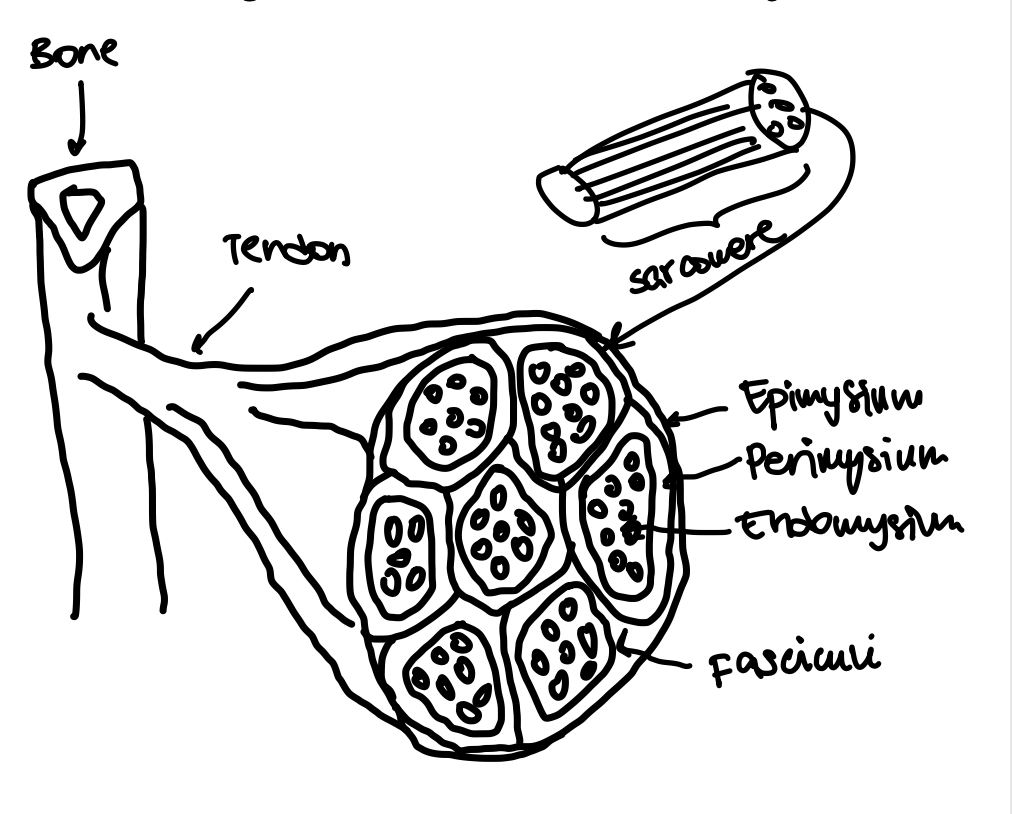
Epimysium
The outermost layer of connective tissue surrounding a muscle.
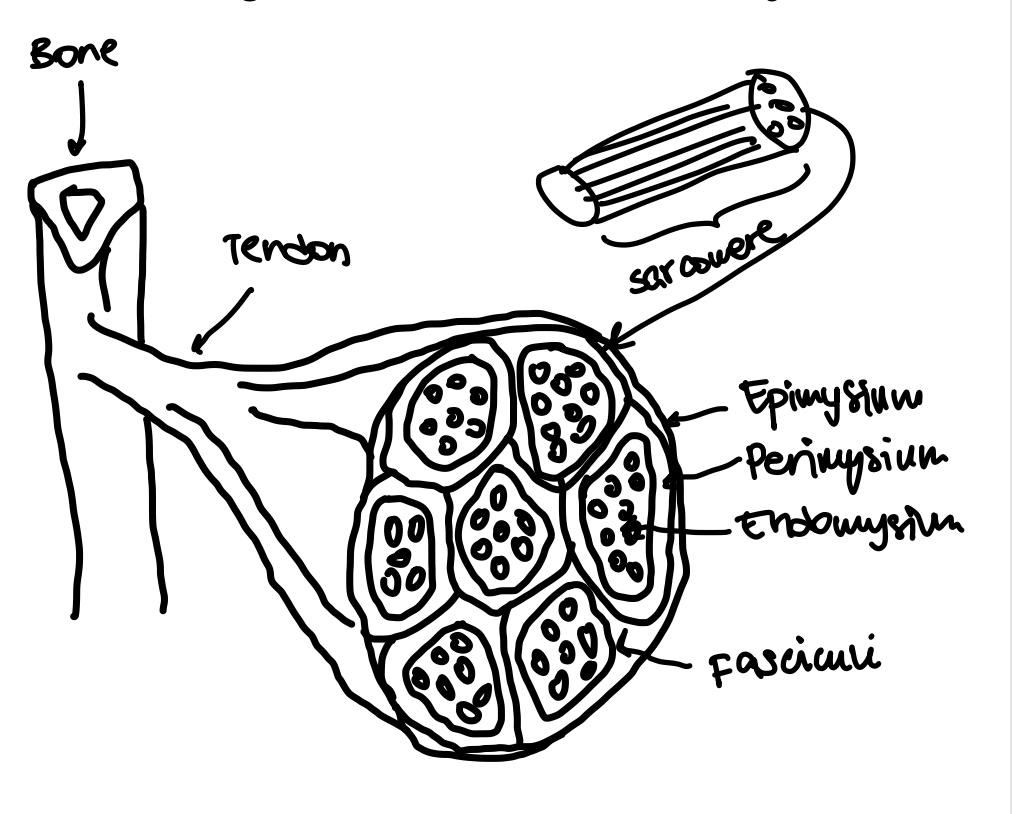
Perimysium
The connective tissue that surrounds bundles of muscle fibers (fasciculus).
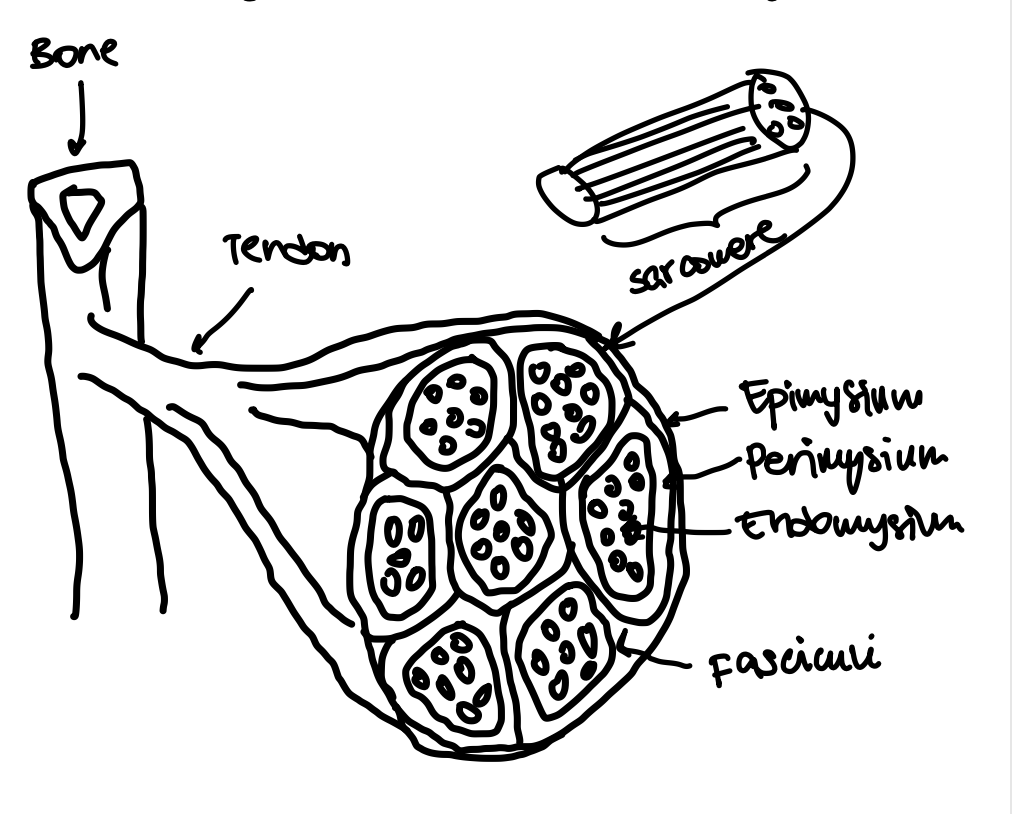
Endomysium
The innermost layer of connective tissue that surrounds individual muscle fibers.
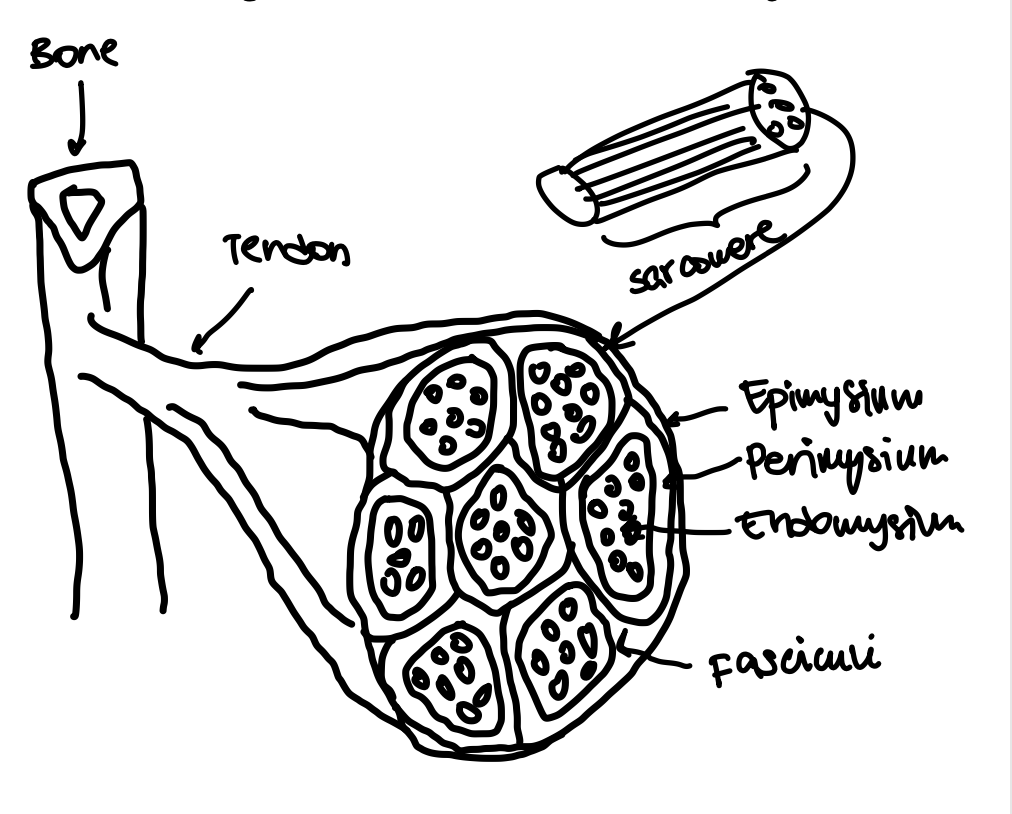
Fasciculi
Bundles of muscle fibers within a muscle.
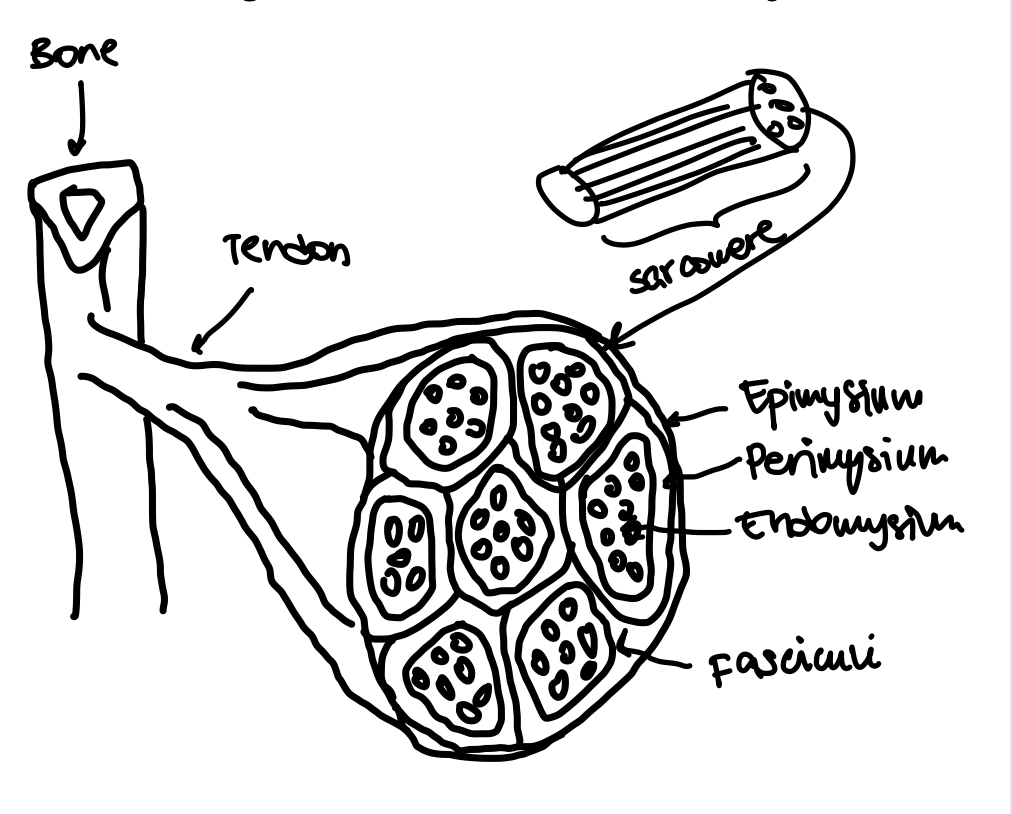
Sarcomere
The basic contractile unit of a muscle fiber.
Parallel Fasciculi Arrangement
Fascicles run parallel to the muscle’s long axis; e.g., sartorius.
Circular Fasciculi Arrangement
Fascicles form concentric rings around openings; e.g., orbicularis oris.
Fusiform Fasciculi Arrangement
Spindle-shaped muscles tapering at both ends; e.g., biceps brachii.
Convergent Fasciculi Arrangement
Fascicles converge from a broad origin to a tendon; e.g., pectoralis major.
Unipennate Fasciculi Arrangement
Fascicles attach to one side of a tendon; e.g., extensor digitorum longus.
Bipennate Fasciculi Arrangement
Fascicles attach to both sides of a tendon; e.g., rectus femoris.
Multipennate Fasciculi Arrangement
Fascicles converge on several tendons; e.g., deltoid.
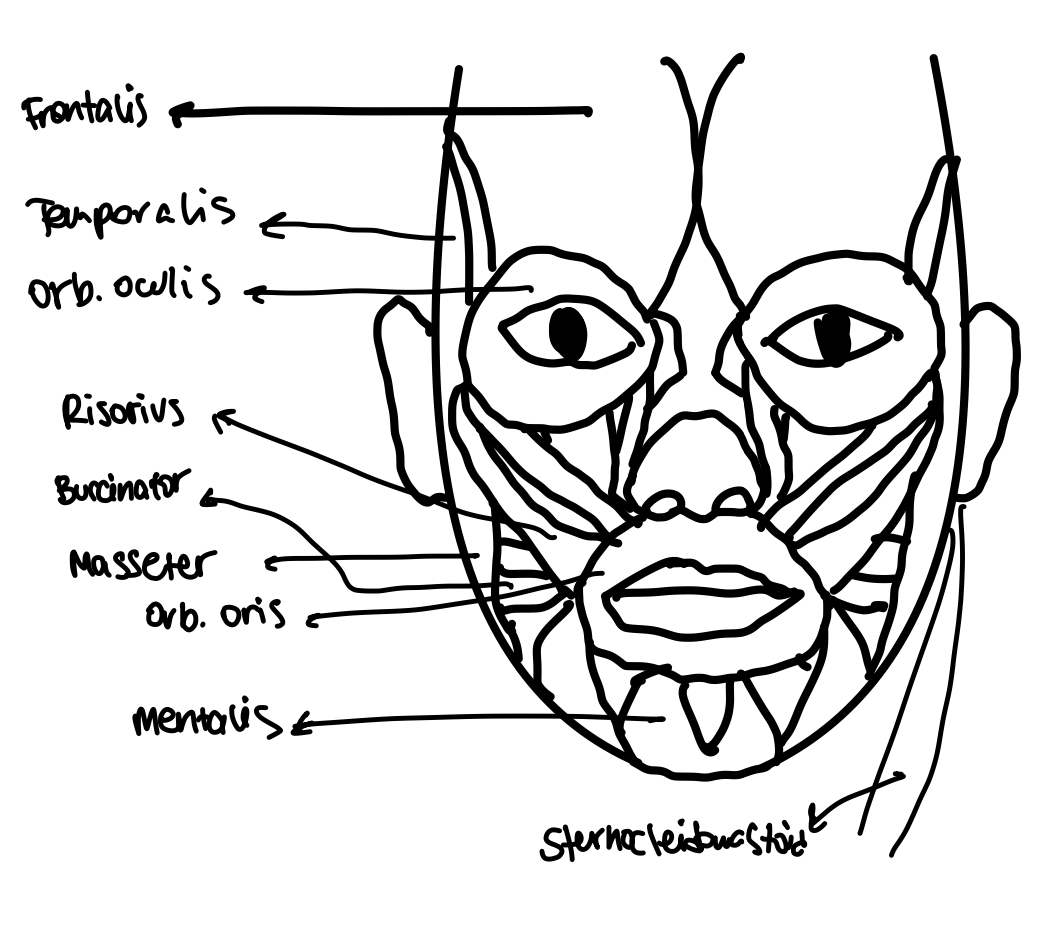
Frontalis Muscle
Muscle that allows blinking and closing eyes.
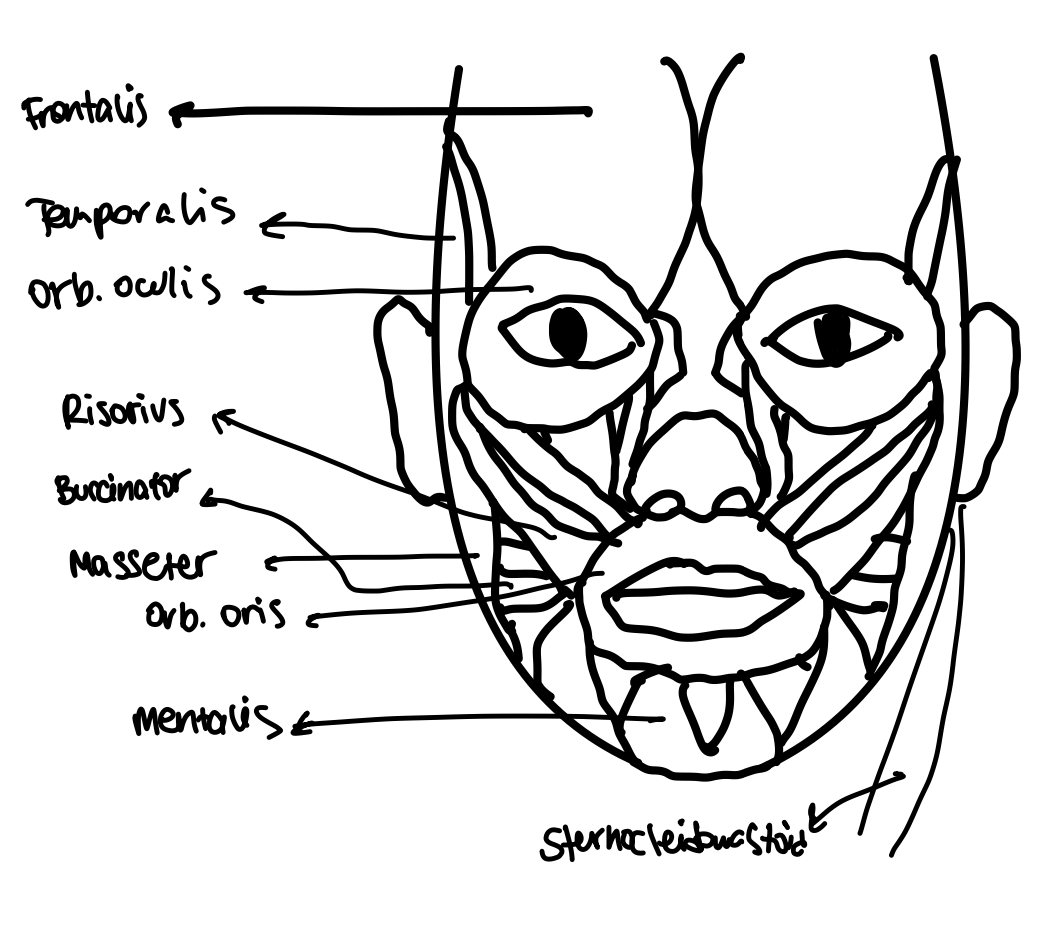
Temporalis Muscle
Muscle involved in mastication (chewing).
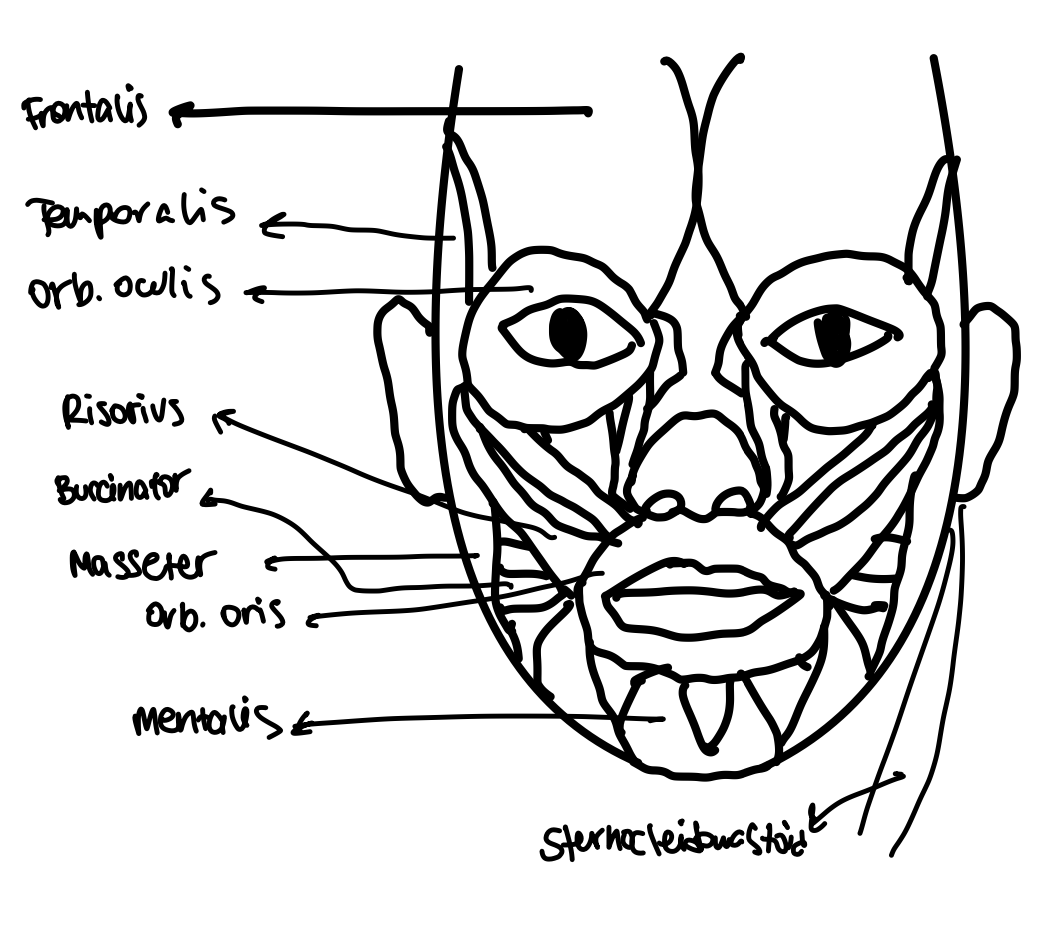
Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
Muscle that rotates and flexes the neck.
Rotator Cuff
Group of muscles that stabilize the shoulder.
Prime Mover
The main muscle responsible for a specific movement.
Synergist
A muscle that assists the prime mover.
Antagonist
A muscle that opposes the action of the prime mover.
Concentric Muscle Contraction
Muscle shortens while generating force.
Eccentric Muscle Contraction
Muscle lengthens while controlling force.
Isometric Muscle Contraction
Muscle generates force without changing length.
Slow Oxidative Fiber Type
Muscle fibers suited for endurance activities.
Fast Glycolytic Fiber Type
Muscle fibers adapted for short bursts of power.
Fast Oxidative Fiber Type
Muscle fibers combining speed and endurance.
Dendrites
Parts of a neuron that receive input signals.
Axon
Part of a neuron that transmits output signals.
Astrocytes
Glial cells that maintain the blood-brain barrier and support neurons.
Oligodendrocytes
Glial cells in the CNS that form the myelin sheath around axons.
Schwann Cells
Glial cells in the PNS that myelinate axons and aid in nerve repair.
Neuromuscular Junction
The site where a motor neuron communicates with a muscle fiber.
Neurotransmitter Receptors
Found on the postsynaptic membrane, they bind neurotransmitters to initiate a response.