quiz on tides/currents
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
coriolis effect
caused by the rotation of the earth
when on a rotating surface, an onject moving on the surface tends to swerve slightly to the left or right rather than continuing ina. straight line
as wind blows across the ocean in a straight line, the water actually moves in a 45 degree angle from the wind rather than completely with the wind
where does the global conveyer belt start
in the arctic
explain the global conveyer belt
starts in the arctic, cold water freezes, leaving behind salt. this denser, high salinity water begins a process - downwelling
this causes a mixing of the water layers until it reaches the bottom
the water will begin to move south through the atlantic ocean towards Antarctica
the belt divides into two sections
one section goes toward the indian ocean
this cold water moves northwards towards the equator, bringing nutrients to eastern african coasts. water increases in temp and moves to the surface
when it cannot rise any higher, it loops back through the south indian ocean as a warm current
what is downwelling
the downward movement of water due tp density differences
explain the other split of the belt
the colder bottom water moves towards the equator to the northern pacific ocean
water starts to warm and rise, becoming a surface current along west coast of north america
warm current wraps around Australia and reconnects with the Indian Ocean portion
last step of the belt
after the two meet again in the Indian ocean the warm currents move back through the Atlantic ocean back towards the North pole
this process starts all over again
define spring tide
greatest tidal amplitude
sun, moon, earth in a straight line
highest high tide and lowest low tide
predicted to happen twice a month
occurs during a full moon and new moon
neap tide
smallest tidal amplitude
sun and moon are at a right angle
crescent moons
highest low tide and lowest high tide
sun and moon pull in opposite directions causing a smaller tidal bilge
diurnal tide
1 high and 1 low tide a day
semidiurnal tide
2 high and 2 low tides a day
water around the equator
warm, less dense, less salinity
water around the poles
cold, more dense, more salinity
surface ocean currents
clockwise spiral in North hemisphere and counterclockwise in southern hemisphere due to coriolis effect
driven by wind
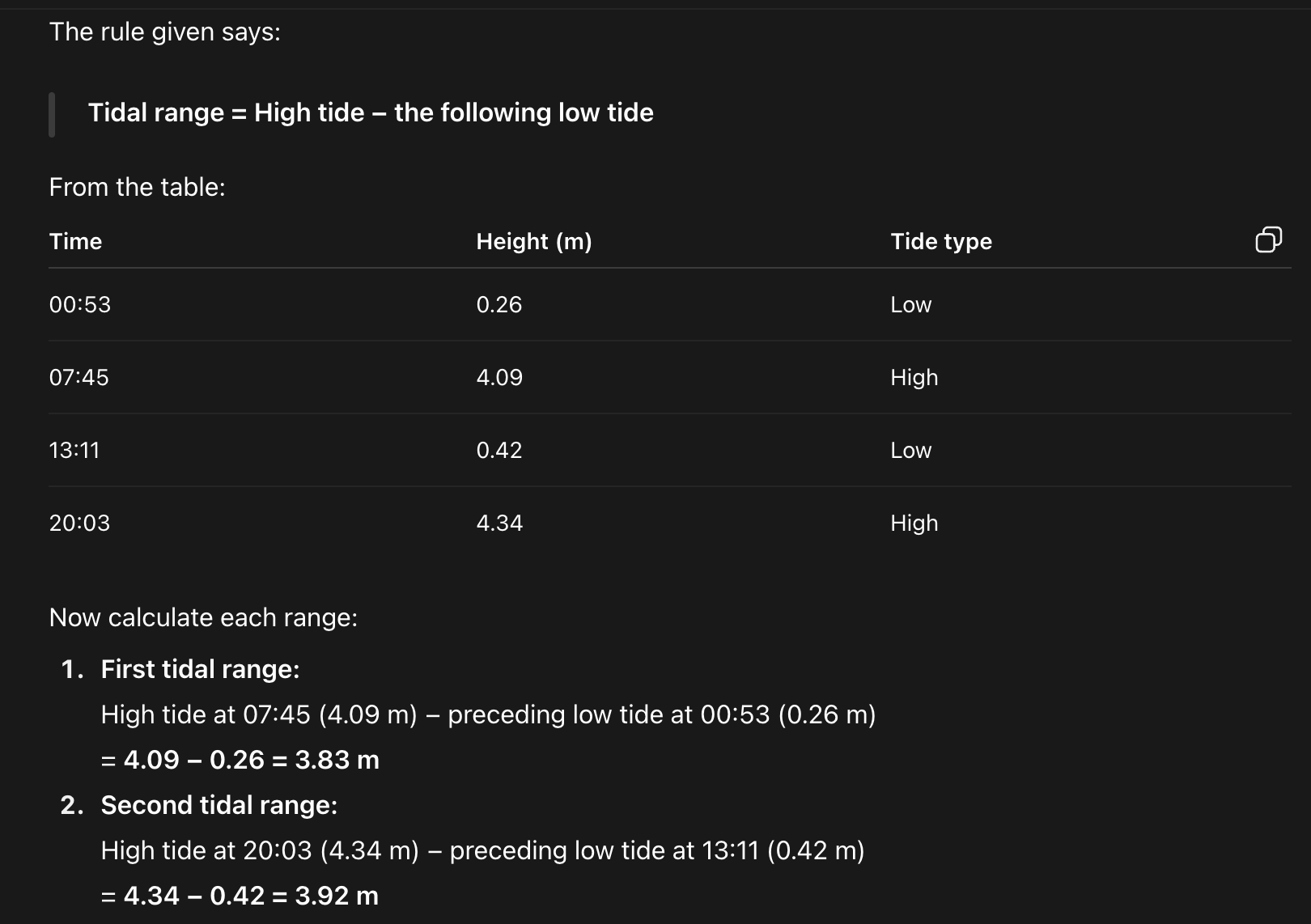
how to find tidal range
high tide minus the following low tide = tidal range
tidal range