5. Fine Motor, Cognitive, Language, Social-Emotional, and Adaptive Development (via joseph_na4)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Aside from the motor system itself, what four sensory and internal regulatory systems contribute to fine motor skill development?
1. Vision 2. Somatosensory 3. Cognition 4. Regulation
What external factors and which primary physiological system are identified as essential contributors to fine motor development?
External: Social and Cultural factors
Physiological: Musculoskeletal system
Developmental progression of vision

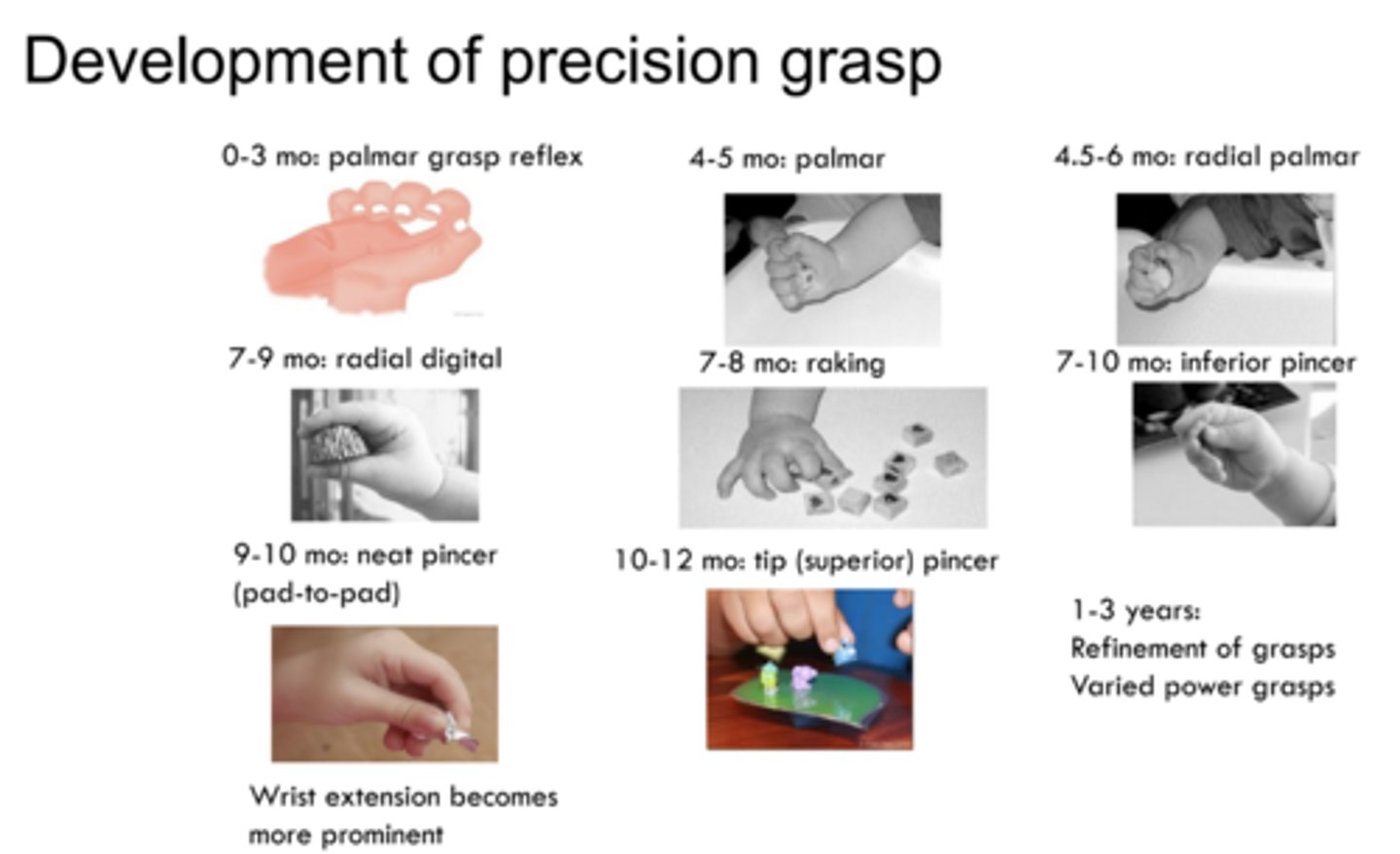
Describe the development of precision grasp
0-3 months:
4-5 months:
4.5-6 months:
7-9 months:
7-8 months:
7-10 months:
9-10 months:
10-12 months:
1-3 years:
0-3 months: palmar grasp reflex
4-5 months: palmar
4.5-6 months: radial palmar
7-9 months: radial digital
7-8 months: raking
7-10 months: inferior pincer
9-10 months: neat pincer (pad to pad)
10-12 months: tip (superior) pincer
1-3 years: refinement of grasps, varied power grasps
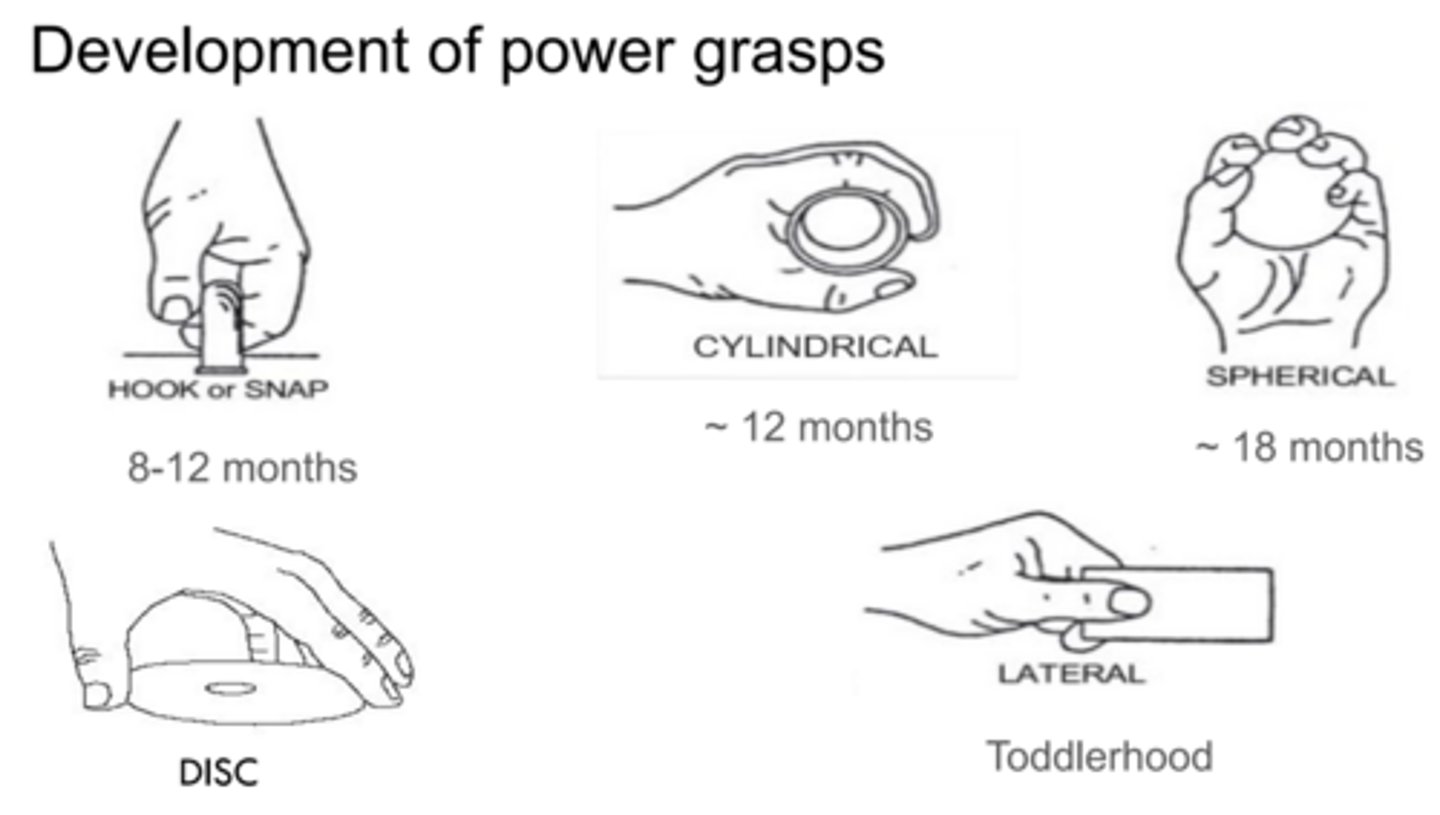
Describe the development of power grasps
8-12 months:
~12 months:
~18 months:
toddlerhood:
8-12 months: hook or snap
~12 months: cylindrical
~18 months: spherical
toddlerhood: disc, lateral
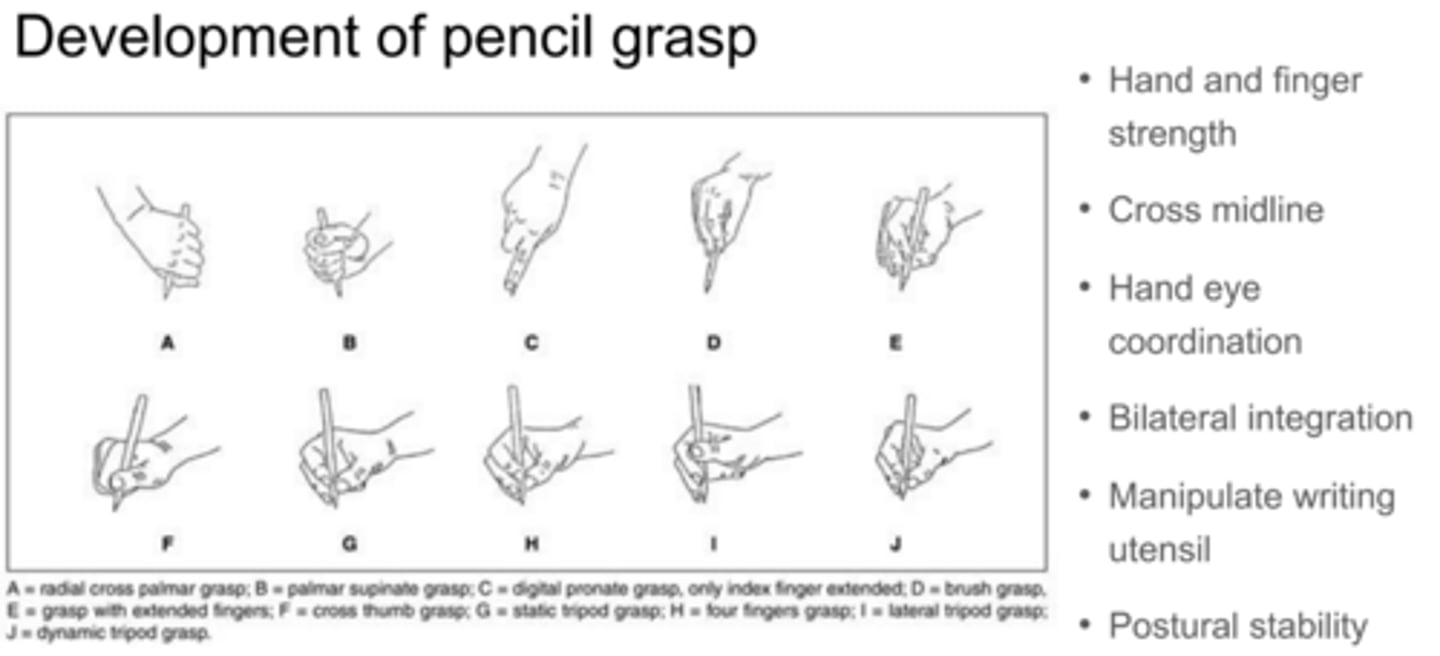
Beyond simple hand strength, what four "coordination" factors are required for a child to develop a mature pencil grasp?
Crossing the midline
Hand-eye coordination
Bilateral integration
Postural stability
What is the primary difference between Language and Speech as defined in clinical development?
Language: Focuses on the meaning and rules of communication (what words mean and how to put them together).
Speech: Focuses on the physical production of communication (how sounds and words are made).
In the context of Language development, what are the three key areas a child must master?
What are the three physical components involved in the production of Speech?
1. What words mean. 2. How to put words together. 3. What should be said and when
1. Articulation 2. Voice 3. Fluency
At 2-3 months, what specific language and gestural milestones should be present?
Communication: Cooing and gooing; alerts to sounds.
Social: Smiles or quiets when talked to.
At 4-6 months, what specific language and gestural milestones should be present?
Vocalizations: Squeals, growls, raspberries, and early babbling (e.g., "babababa", "gagagaga").
Social: Giggles and laughs.
At 7–9 months, what specific language and gestural milestones should be present?
Language: Mature babbling (e.g., "mama", "baba"); looks when their name is called.
Gestures: Functional gestures such as raising arms for "up" or pushing away unwanted items.
What are the key communication milestones expected by the end of the first year (10–12 months)?
Vocal: Babbling with diverse sounds (e.g., "guh-buh-mah") and saying 1–2 words.
Social/Gestural: Pointing, waving, and attempting to copy sounds.
Describe the receptive and expressive language capabilities typical of a toddler between 13–18 months.
Expressive: Uses words for common objects/people and shakes head for yes/no.
Receptive: Follows simple directions and can identify at least one body part.
What significant linguistic "explosion" occurs between 19–24 months?
Vocabulary: Uses and understands at least 50 words.
Syntax: Begins putting 2+ words together (early sentences).
Functional: Uses words to ask for help and follows 2-step directions.
Basic language milestones for 2-3 years (24-30 months usually most significant growth period)
- phrases
- asks why and how
- says name when asked
- uses plurals, -ing verbs, past tense -ed
- uses a variety of sounds including: p, b, m, h, w, d, n
- children should be easier for familiar adults to understand
Define Cognition and identify the three primary sources from which this information is gained.
Definition: The ability to acquire and use information to meet task and environmental demands.
Sources: Information is gained through experience, the senses, and thought.
According to developmental principles, what two environmental/relational factors allow children to learn best?
A nurturing environment.
Secure attachment to a consistent caregiver.
In a clinical PT setting, why is it important to address more than just motor outcomes during an intervention?
Integrating cognitive and motor stimuli together ensures better overall outcomes for the child.
What is the core environment in which children learn according to Vygotsky?
Children learn when trying new things and within the context of social relationships.
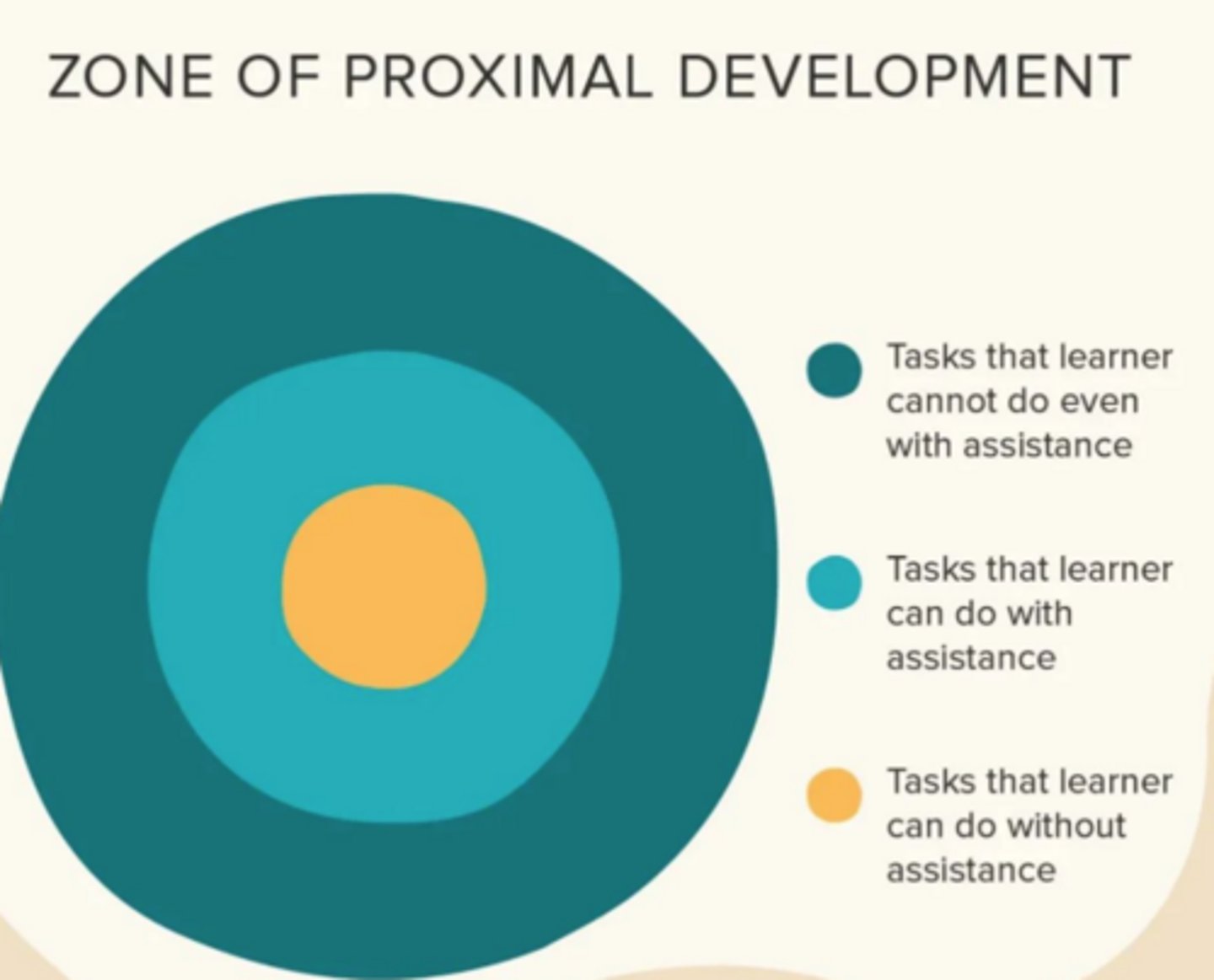
Define the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) and explain its significance in learning.
It is the "sweet spot" of learning consisting of tasks that a learner can do with assistance. It represents the area between what a child can do independently and what they cannot do even with help.
Scaffolding: The process of providing the "just right" challenge—offering enough support to help a child succeed at a task in their ZPD without doing it for them.
Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development
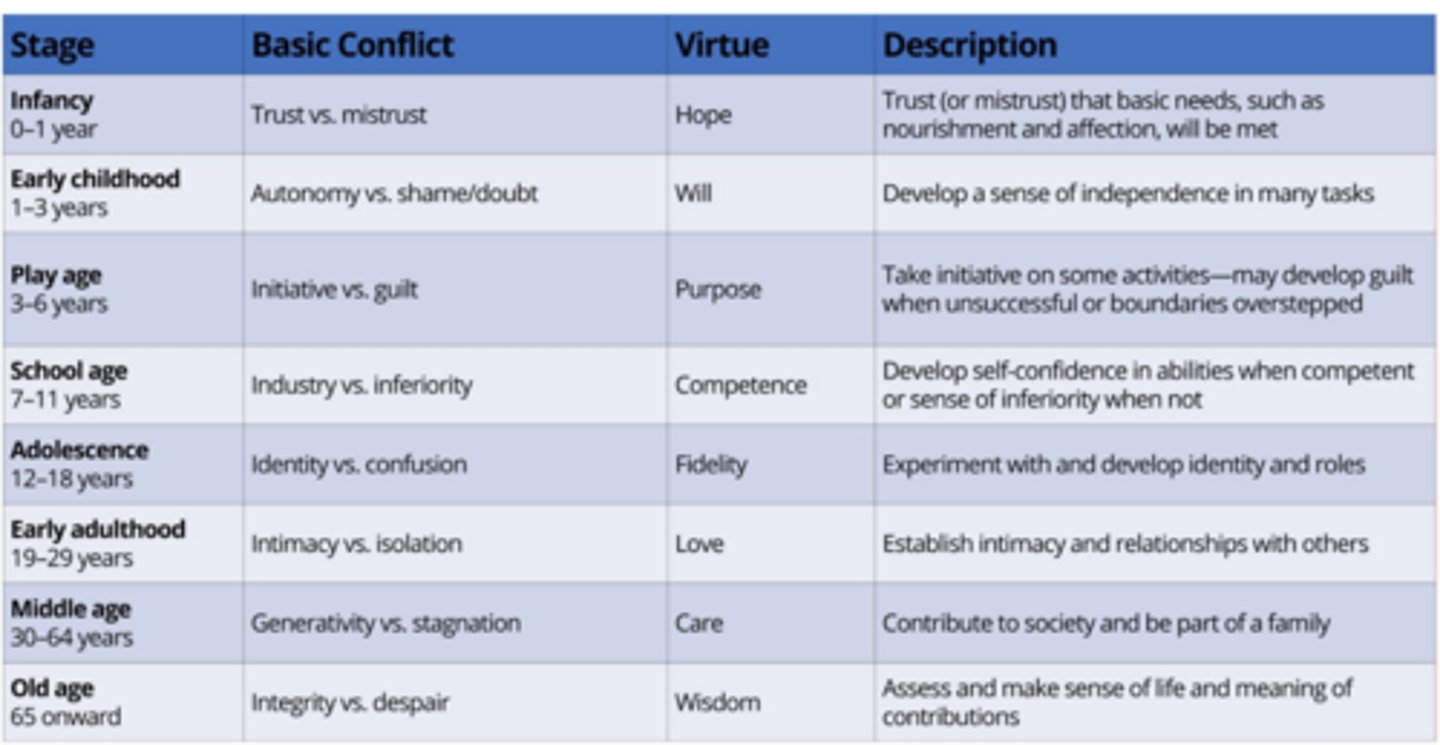
Why is the development of a secure attachment clinically significant for a child's overall growth?
Regulation: Attachment is essential for emotional development and regulation.
Cognition: Children with secure attachments are in a better position to develop cognitive skills.
What are the four types of attachment identified by Bowlby and Ainsworth?
1. Secure 2. Anxious-Ambivalent 3. Anxious-Avoidant 4. Disorganized
Infants automatically seek to attach to their caregivers.
Through what three specific interaction types does early cognitive development begin?
1. Motor experiences 2. Sensory experiences 3. Caregiver interactions
Cognitive milestones:
1-2 months:
~3 months:
~6 months:
~9 months:
~12 months:
~15 months:
~18 months:
~2 years:
1-2 months: follows caregiver's face
~3 months: follows objects in circle, looks at toy, reaches for faces, looks at hands
~6 months: interacts with toys and looks for objects that is dropped
~9 months: search for object under cloth, play peek-a-boo
~12 months: points at objects, first words, find toys in containers
~15 months: turns pages in book, tries to use things the right way, stacks 2 blocks
~18 months: copies things caregiver does
~2 years: plays with two or more objects at same time, pretend play emerges
Social-emotional milestones
1 month:
4 months:
6 months:
12 months:
18 months:
2 years:
3 years:
4 years:
5 years:

Adaptive milestones
6-9 months:
12-15 months:
15-18 months:
2-3 years:
3-5 years:
