Cell Parts and Cell Parts
4.7(3)Studied by 88 people
Card Sorting
1/19
Last updated 10:05 PM on 11/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
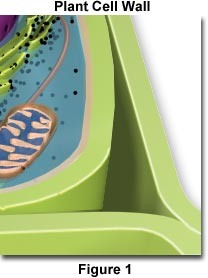
Cell Wall
A rigid layer that protects and supports the cell
2
New cards
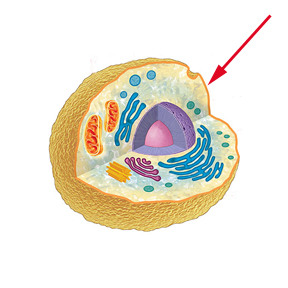
Cell Membrane
Help the organisms move
3
New cards
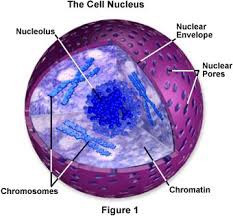
Nucleus
Controls the whole cell, inside is the chromatin which is made of DNA and RNA
4
New cards
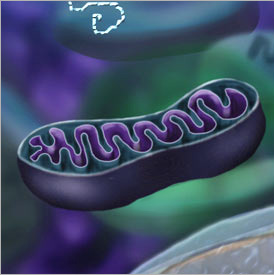
Mitochondria
Makes energy available to the cell
5
New cards
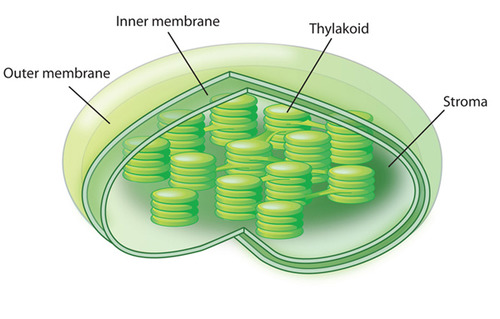
Chloroplast
Capture sunlight energy to make food
6
New cards
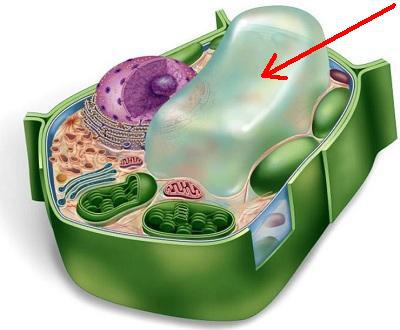
Vacuoles
Stores and transport materials in the cell
7
New cards
Unicellular
Organisms with one cell
8
New cards
Multicellular
Organisms with more than one cell
9
New cards
Cell Theories
-cells are the smallest unit of life, meaning they are the basic units of life
-all living organisms are made of cells, meaning from the smallest organisms to the largest they all have at least one cell
-all cells come from existing cells, meaning cells don't just form randomly, they are divided from other cells
-all living organisms are made of cells, meaning from the smallest organisms to the largest they all have at least one cell
-all cells come from existing cells, meaning cells don't just form randomly, they are divided from other cells
10
New cards
Homeostasis
maintaining a constant internal environment
11
New cards
nuclear membrane
surrounds the nucleus
12
New cards
nucleolus
found inside the nucleus, makes ribosomes
13
New cards
lysosomes
breaks down matter in the cells
14
New cards
prokaryotic
do NOT have a nucleus
15
New cards
Eukaryotic
cells that DO have a nucleus
16
New cards
golgi apparatus
packages and moves things within the cell, delivers to correct place
17
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
produces lipids, moves things through the cell
18
New cards
rough endoplasmic reticulum
contains ribosomes
19
New cards
animal cell
does not have a cell wall or chloroplast and a small vacuole
20
New cards
plant cell
contains a cell wall, chloroplast and large vacuole