Structure of DNA and RNA
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the pentose sugars in DNA and RNA?
DNA- Deoxyribose
RNA- Ribose
What do nucleotides consist of?
Nitrogenous base
Pentose sugar
Phosphate group
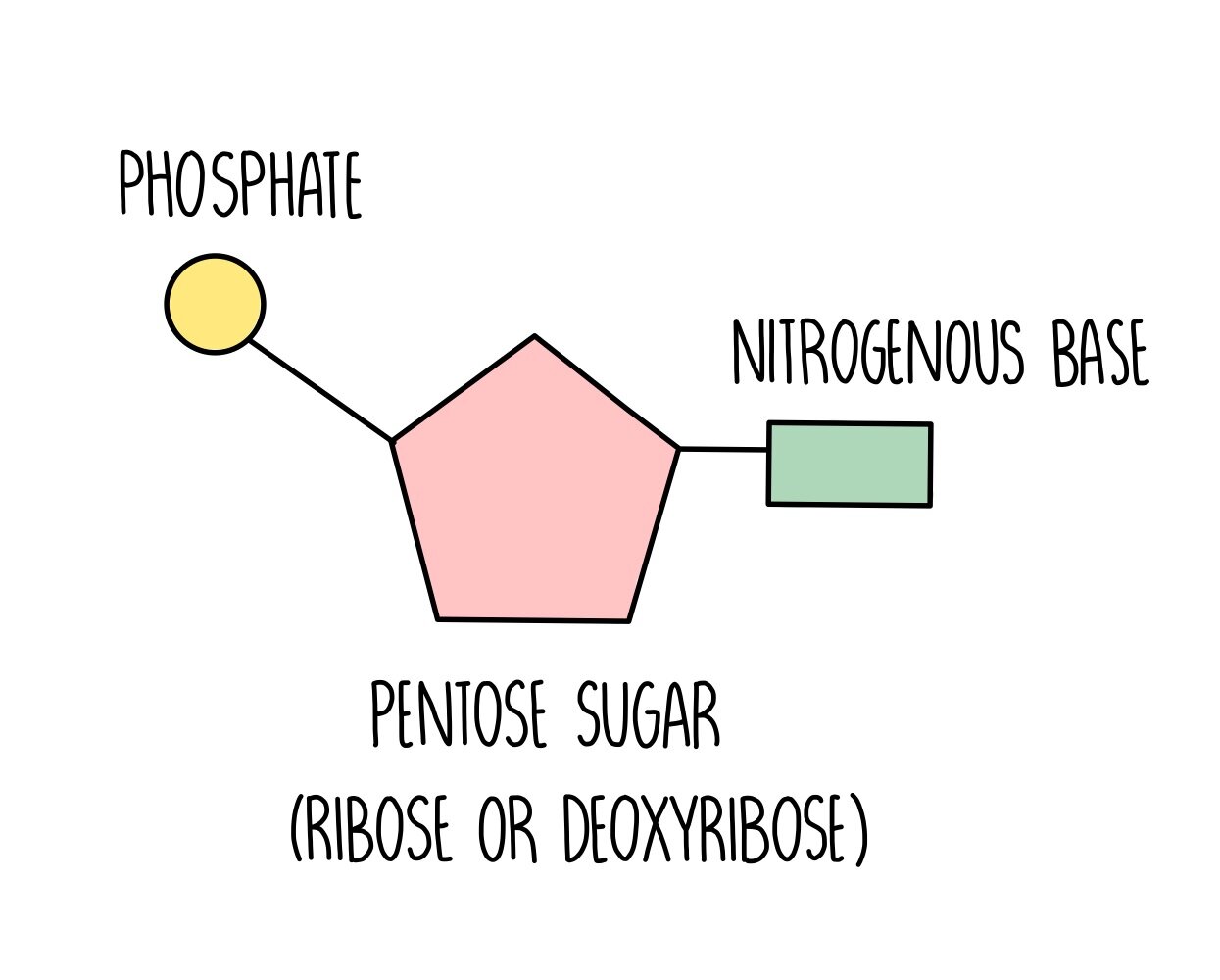
What are the 2 groups of organic bases and what bases do they consist of?
Pyrimidines:
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil
Purines
Adenine
Guanine
Which bases are complementary?
T-A
C-G
U-A (only in RNA, Uracil replaces Thymine)
How are sugar phosphate backbones formed?
Condensation reactions of one nucleotide's phosphate group bonding to another's pentose sugar (continuous bonding forms a polynucleotide chain).
What type of bond is formed between a pentose sugar and phosphate group?
Phosphodiester bond
What bond is formed between organic bases?
Hydrogen bonds
Describe the structure of DNA.
1) Double helix- 2 anti-parallel polynucleotide strands
2) Extremely long
3) Pentose sugar always deoxyribose
4) Organic bases always either- Adenine, Guamine, Thymine or Cytosine
Describe the structure of RNA.
1) Single stranded
2) Pentose sugar always ribose
3) Organic bases always either- Adenine, Guanine, Uracil or Cytosine
How is DNA adapted to its function?
1) Very stable structure, allowing it to pass from generation to generation without changing- only rarely does it mutate.
2) The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds which are weak individually which allow the strands to be separated during DNA replication and protein synthesis for the genes to be read.
3) Extremely large molecule- can carry huge amount of genetic information.
4) Function of gene/protein made from that gene depends on the base sequence.
5) Complementary base pairs means the DNA is replicated accurately.
Why is DNA so stable?
- The sugar phosphate backbone held together by phosphodiester bonds, protect the bases inside the helix.
- Many hydrogen bonds are strong together between the bases.