MICP LAB EXAM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:49 PM on 5/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
\
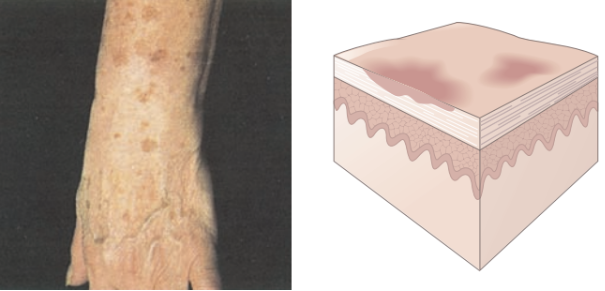
Macule
2
New cards
\
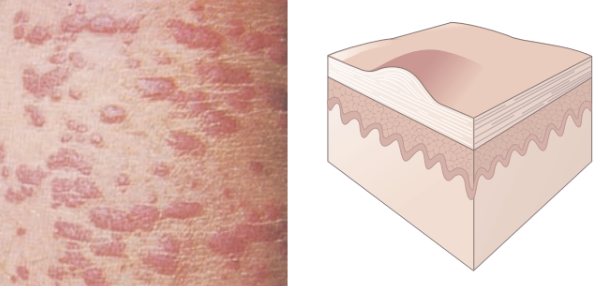
Papule
3
New cards
\
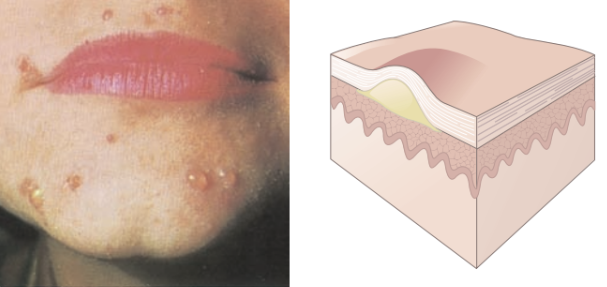
Vesicle
4
New cards
\
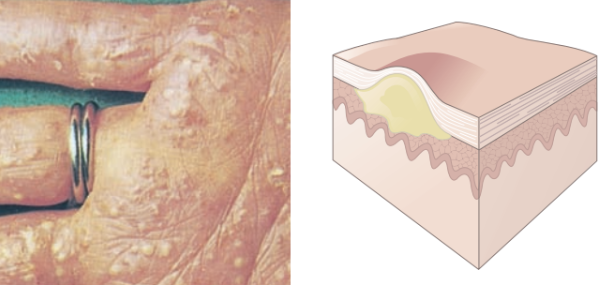
Pustule
5
New cards
\
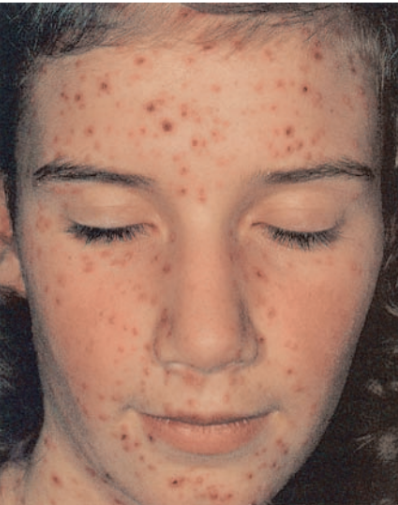
Chickenpox
Varicella-zoster virus
Airborne Precautions
Infected humans
Person-to-person transmission
Varicella-zoster virus
Airborne Precautions
Infected humans
Person-to-person transmission
6
New cards
\
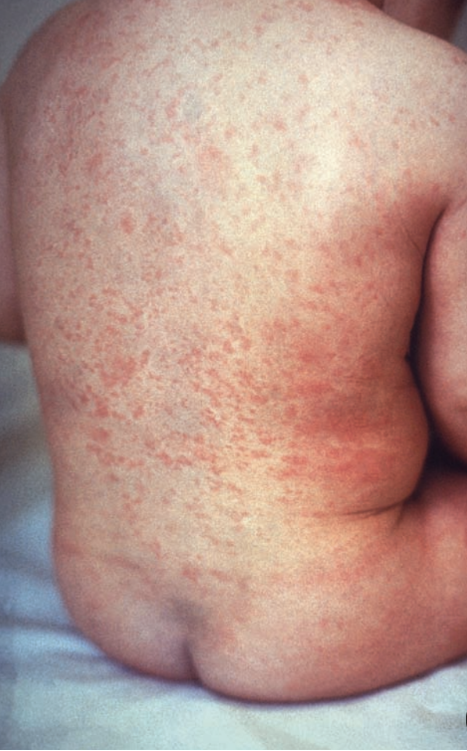
Rubella
Rubella virus
Droplet Precautions
Infected humans
Droplet spread transmission
Rubella virus
Droplet Precautions
Infected humans
Droplet spread transmission
7
New cards
\
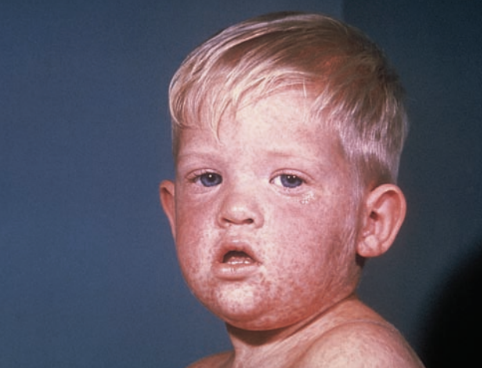
Measles
Rubeola virus
Airborne Precautions
Infected humans
Direct contact with nasal or throat secretions of infected persons,
Rubeola virus
Airborne Precautions
Infected humans
Direct contact with nasal or throat secretions of infected persons,
8
New cards
\
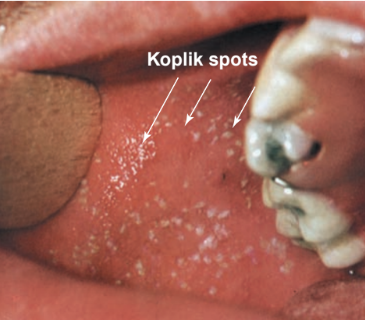
Koplik spots
9
New cards

\
Monkeypox
Monkeypox virus
Airborne Precautions
Infected animals
Animal bite
Monkeypox virus
Airborne Precautions
Infected animals
Animal bite
10
New cards
\
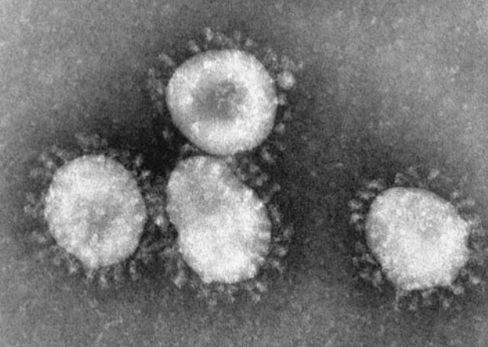
SARS-associated coronavirus
Airborne, Contact, Droplet, and Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Respiratory droplets transmission
Airborne, Contact, Droplet, and Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Respiratory droplets transmission
11
New cards
\
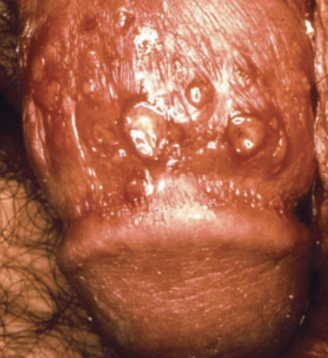
Herpes simplex lesions
Herpes simplex virus 2
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Sexual contact transmission
Herpes simplex virus 2
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Sexual contact transmission
12
New cards
\
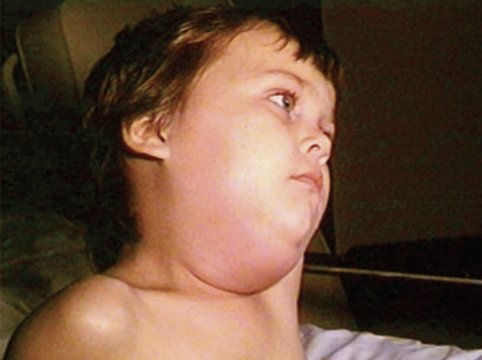
Mumps
Mumps virus
Droplet Precautions
Infected humans
Drop spread transmission
Mumps virus
Droplet Precautions
Infected humans
Drop spread transmission
13
New cards
\
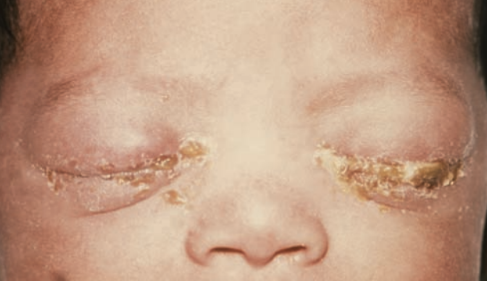
Gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum
Nesseria gonorrhoeae
Standard Precautions
Infected maternal birth canal
Infected birth canal during delivery
Nesseria gonorrhoeae
Standard Precautions
Infected maternal birth canal
Infected birth canal during delivery
14
New cards
\
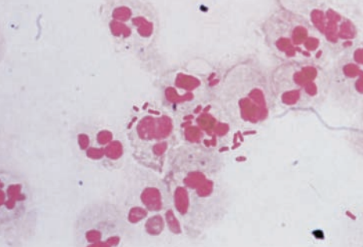
Cystitis
15
New cards
\
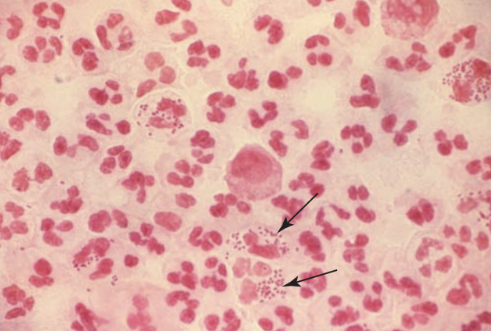
Gonorrhea
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Sexual contact transmission
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Sexual contact transmission
16
New cards
\
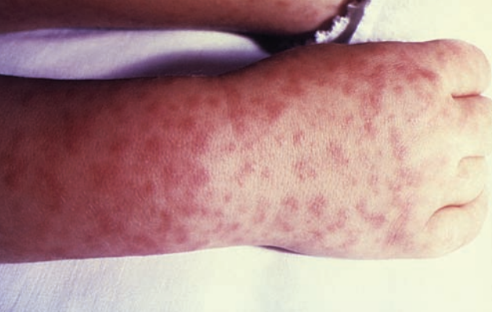
Rocky Mountain spotted fever rash
Rickettsia rickettsii
Standard Precautions
Animals, ticks, rodents
Tick bite
Rickettsia rickettsii
Standard Precautions
Animals, ticks, rodents
Tick bite
17
New cards
\
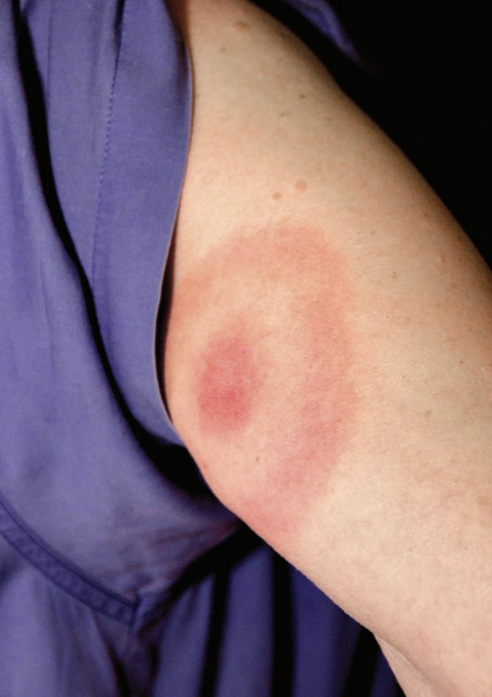
Lyme disease or erythema migrans
Borrelia burgdorferi
Standard Precautions
Mammals, ticks, rodents
Tick bite
Borrelia burgdorferi
Standard Precautions
Mammals, ticks, rodents
Tick bite
18
New cards
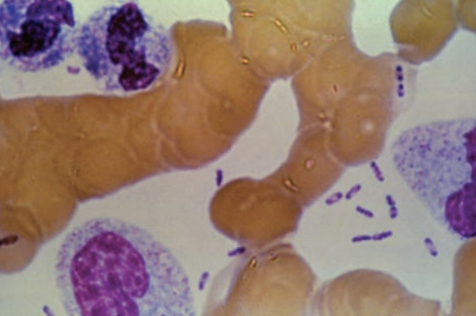
\
Plague
Yersinia pestis
Standard Precautions
Cat
Flea bite
Yersinia pestis
Standard Precautions
Cat
Flea bite
19
New cards
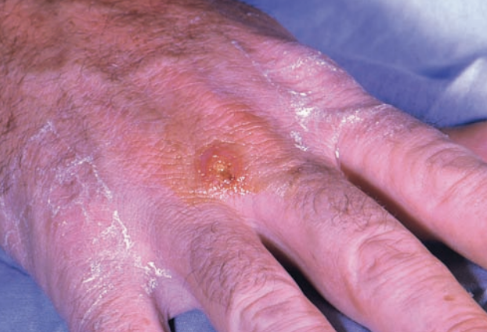
\
Tularemia
Francisella tularensis
Standard Precautions
Tick
Tick bite
Francisella tularensis
Standard Precautions
Tick
Tick bite
20
New cards
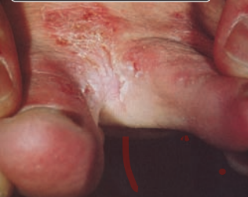
\
Tinea pedis
21
New cards
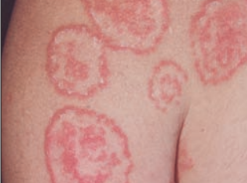
\
Tinea corporis
22
New cards
\
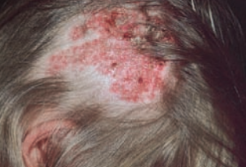
Tinea capitis
23
New cards
\
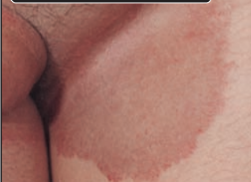
Tinea cruris
24
New cards
\
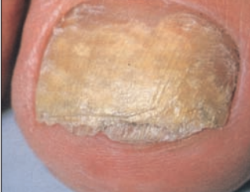
Tinea unguium
25
New cards
\
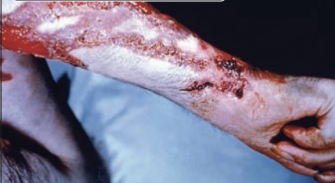
Sporotrichosis
26
New cards
\
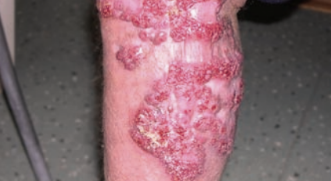
Chromomycosis
27
New cards
\
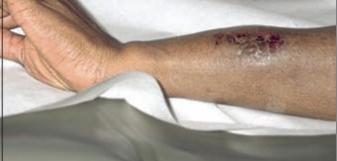
Mycetoma
Nocardia asteroides
Nocardia asteroides
28
New cards
\
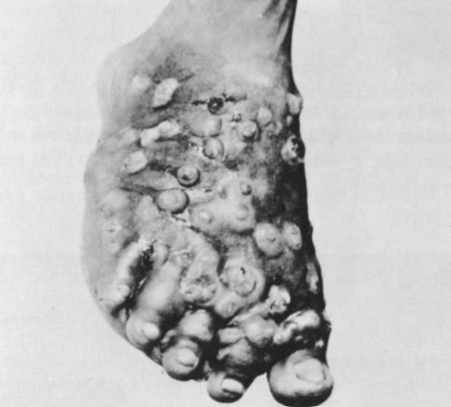
Mycetoma of the foot
29
New cards
\
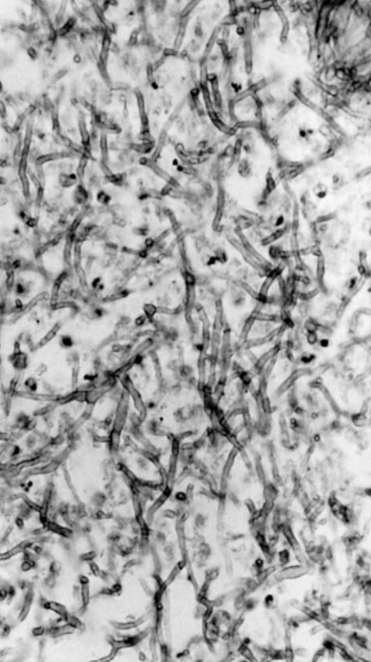
Aspergillosis
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus fumigatus
30
New cards
\
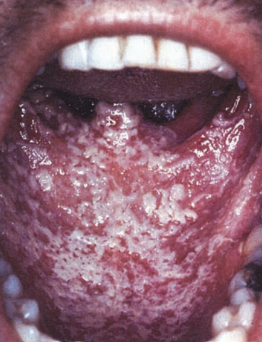
Oral Candidiasis
Candida albicans
Candida albicans
31
New cards
\
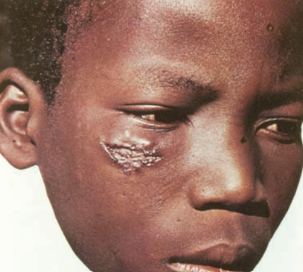
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Flagella protozoa
Sand fly
Flagella protozoa
Sand fly
32
New cards
\
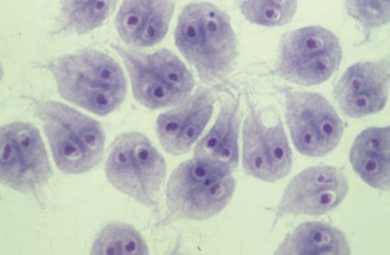
Giardiasis
Giardia lamblia
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Fecal-oral route
Giardia lamblia
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Fecal-oral route
33
New cards
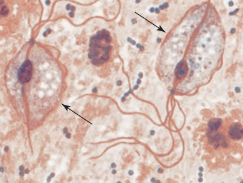
Vaginitis
Trichomonas vaginalis
Trichomonas vaginalis
34
New cards
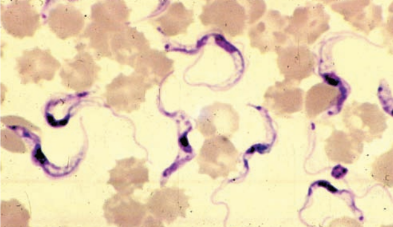
African trypanosomiasis
Trypanosoma brucei
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Tsetse flies
Trypanosoma brucei
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Tsetse flies
35
New cards
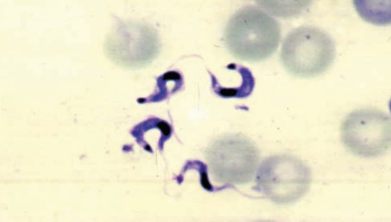
American trypanosomiasis (Chagas’ disease)
Trypanosoma cruzi
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Kissing bugs
Trypanosoma cruzi
Standard Precautions
Infected humans
Kissing bugs
36
New cards
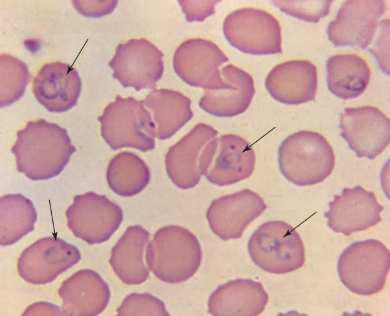
Malaria
Plasmodium falciparum
Standard Precautions
Infected humans and mosquito
Anopheles mosquito
Plasmodium falciparum
Standard Precautions
Infected humans and mosquito
Anopheles mosquito
37
New cards

wood tick
tick vectors of Rocky Mountain spotted fever
tick vectors of Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Dermacentor andersoni
38
New cards
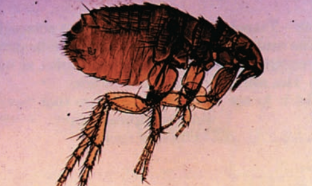
oriental rat flea
vector of plague and endemic typhus
vector of plague and endemic typhus
Xenopsylla cheopis
39
New cards
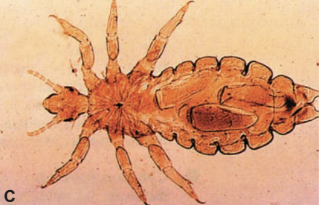
human body louse
vector of endemic typhus
vector of endemic typhus
Pediculus humanus
40
New cards

pubic louse
crab louse
crab louse
Phthirus pubis
41
New cards
LIFE CYCLE OF MALARIAL PARASITE
1. Infected mosquito injects sporozoites.
2. Sporozoites migrate to the liver where they formed merozoites.
3. Merozoites are released and invade the RBC
4. In the red blood cells, merozoites become trophozoites.
5. In the red blood cells, the trophozoite multiple, producing new merozoites. these are released when the RBC ruptures, and can infect other RBC.
6. Some merozoites become gametocytes.
7. The female mosquito picks up gametocytes from an infected human. the sexual cycle occurs in the mosquito, where sporozoites are formed.
42
New cards
1. Unembryonated eggs passed in feces.
2. Eggs embryonate in water.
3. Coracidia hatch from eggs and are ingested by crustaceans.
4. Procercoid larvae in body cavity of crustaceans