26.2 homogenous and heterogenous catalysts
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Define homogeneous catalyst
Define heterogenous catalyst
What do most examples of homogenous catalysts involve
Redox reactions
Define adsorption
The first stage in heterogeneous catalysis when reactant molecules form bonds with atoms on the catalyst surface.
Explain the stages in adsorption of hydrogen onto nickel
hydrogen gas diffuses to the surface of the nickel
Hydrogen is physically adsorbed onto surface: weak forces link H2 molecules to the nickel
H2 becomes chemically adsorbed onto surface: this causes stronger bonds to form betwee hydrogen and nickel.
This causes weakening on H-H covalent bond
Explain the haber process in terms of heterogenous catalysis DARDD
Diffusion: N2 gas and H2 gas diffuses to the to the surface of the iron
Adsorption: reactant molecules are chemically adsorbed onto the surface of the iron. The bonds formed between the reactant molecules and the iron are strong enough to weaken covalent bonds with N-H so the atoms can react with each other and weak enough to break and allow the products to leave the surface.
Reaction: adsorbed N and H atoms react on surface of iron to form ammonia
Desorption: bonds between the ammonia and the surface of the iron weaken and are eventually broken
Diffusion: ammonia ammonia diffuses away from surface
Explain the structure of platinum in the catalytic removal of nitrogen oxides from the exhaust gases of car engines
2NO + CO → N2 + CO2
And
2NO2 + 4CO → N2 + 4CO2
The ‘honeycomb’ structure in the catalytic converter contained small beads coated with platinum which act as heterogenous catalysts
Explain the catalytic process of to reduce the amount of harmful nitrogen oxides.
adsorption of nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide onto the catalyst surface
weakening of the covalent bonds within the nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide
formation of new bonds between:
adjacent nitrogen atoms (to form nitrogen molecules)
carbon monoxide and oxygen atoms to form carbon dioxide
desorption of nitrogen molecules and carbon dioxide molecules from the surface of the catalyst.
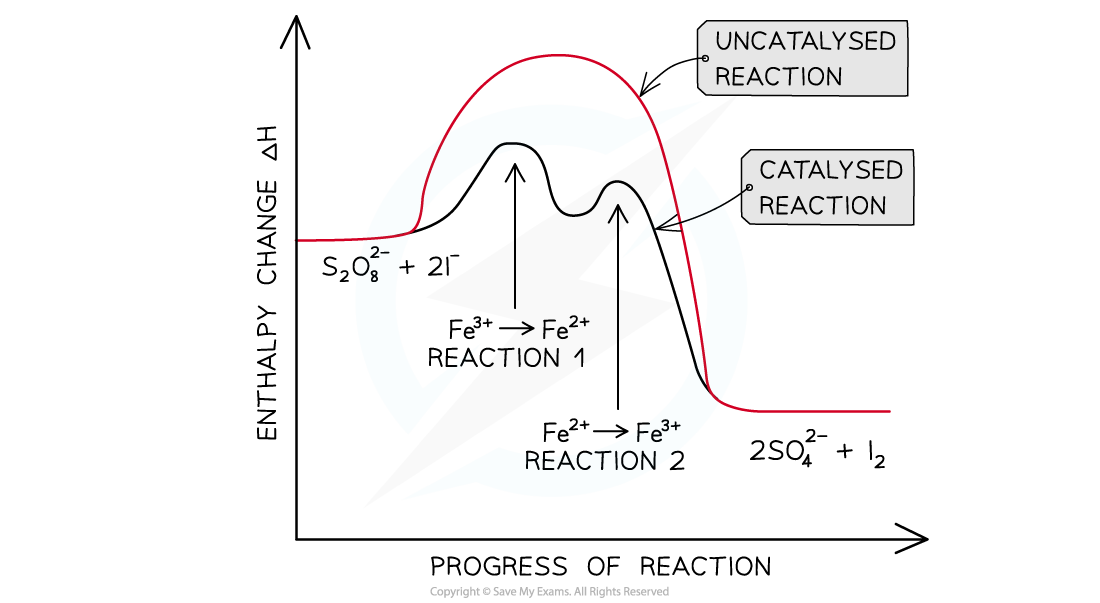
Explain the homogenous catalysis in the iodine-peroxodisulfate reaction
very slow reaction in which the peroxydisulfate (S2,O82- ) ions oxidise the iodide to iodine
S2O82- (aq) + 2I- (aq) → 2SO42- (aq) + I2 (aq)
Since both the S2O82- and I- ions have a negative charge, it will require a lot of energy for the ions to overcome the repulsive forces and collide with each other
Therefore, Fe3+ (aq) ions are used as a homogeneous catalyst
The catalysis involves two redox reactions:
First, Fe3+ ions are reduced to Fe2+ by I-
2Fe3+ (aq) + 2I- (aq) → 2Fe2+ (aq) + I2 (aq)
Then, Fe2+ is oxidised back to Fe3+ by S2O82-
2Fe2+ (aq) + S2O82- (aq) → 2Fe3+ (aq) + 2SO42- (aq)
Draw the reaction pathway for a two-stage catalysed reaction
Nitrogen oxides and acid rain: explain how NOx can act as a catalyst
As fossil fuels contain sulfur, burning the fuels will release sulfur dioxide which oxidises in air to sulfur trioxide
dilute H2SO4 is formed by reaction with water, causing acid rain
Nitrogen oxides can act as catalysts in the formation of acid rain by catalysing the oxidation of SO2 to SO3
NO2 (g) + SO2 (g) → SO3 (g) + NO (g)
The formed NO gets oxidised to regenerate NO2
NO (g) + ½ O2 (g) → NO2 (g)
The regenerated NO2 molecule can again oxidise another SO2 molecule to SO3 which will react with rainwater to form H2SO4 and so on