Dunn M&C - Electrophoresis & Blotting
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
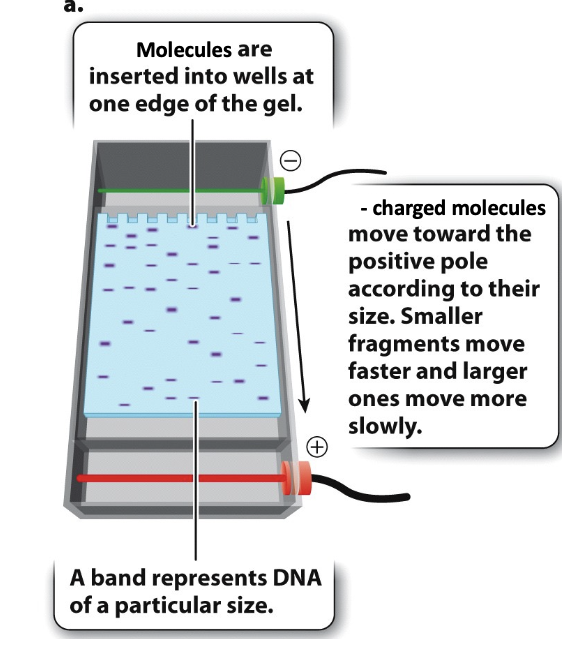
gel electrophoresis
a laboratory technique that separates molecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins by size and charge.
the molecules are negatively charged and inserted into walls at one side of the gel (- side)
smaller molecules move faster/further, larger ones move slowly
RNA/DNA gel electrophoresis
both migrate toward the positive electrode because of the negative charge in the phosphodiester backbone
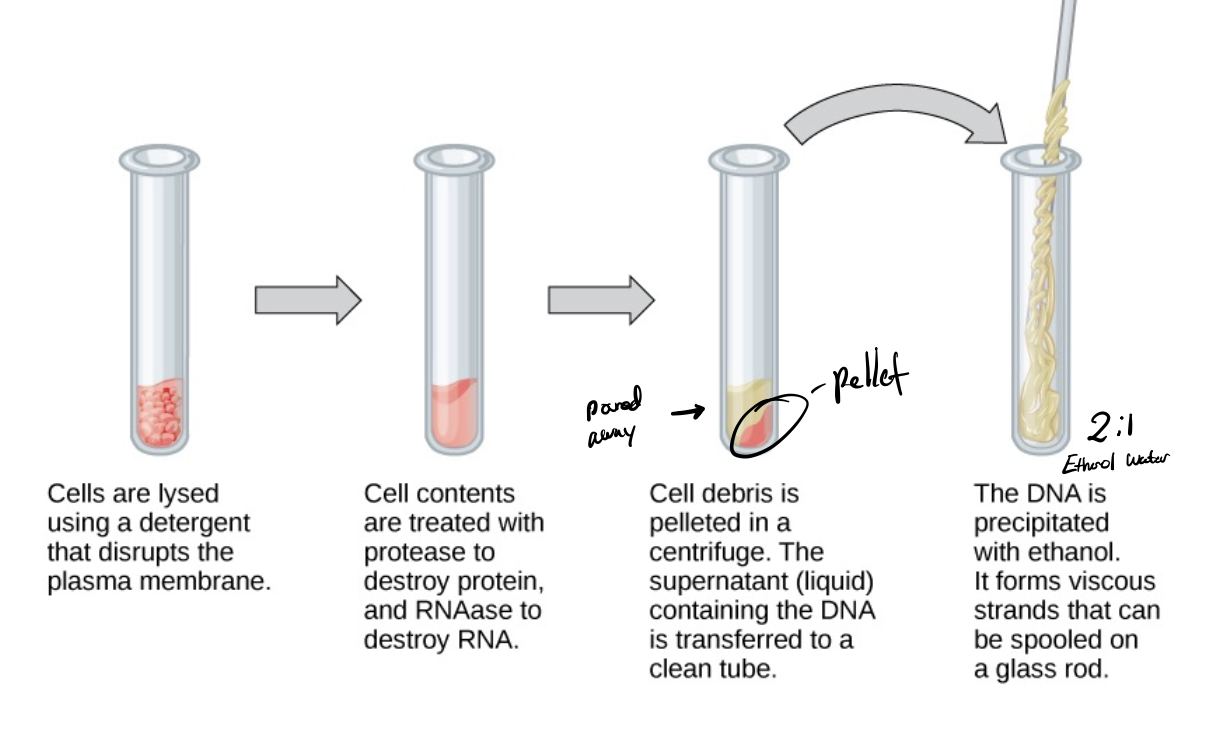
DNA purification
cells are lysed using a detergent that disrupts the plasma membrane
protease and RNAase used to destroy protein and RNA
centrifuged, and a pellet is formed at the bottom. supernatant moved to a clean tube
DNA is precipitated w/ ethanol and forms viscous strands that can be spooled on a glass rod.
500-amino acid polypeptide length
172nm in length
gel electrophoresis process
biological molecules need to be uniformly negatively charged and be shaped like a noodle.
load cavities (“wells”) in gel with samples
hook up power supply and run gel. molecules separate over time as some migrate faster than others
remove gel after samples have run its length
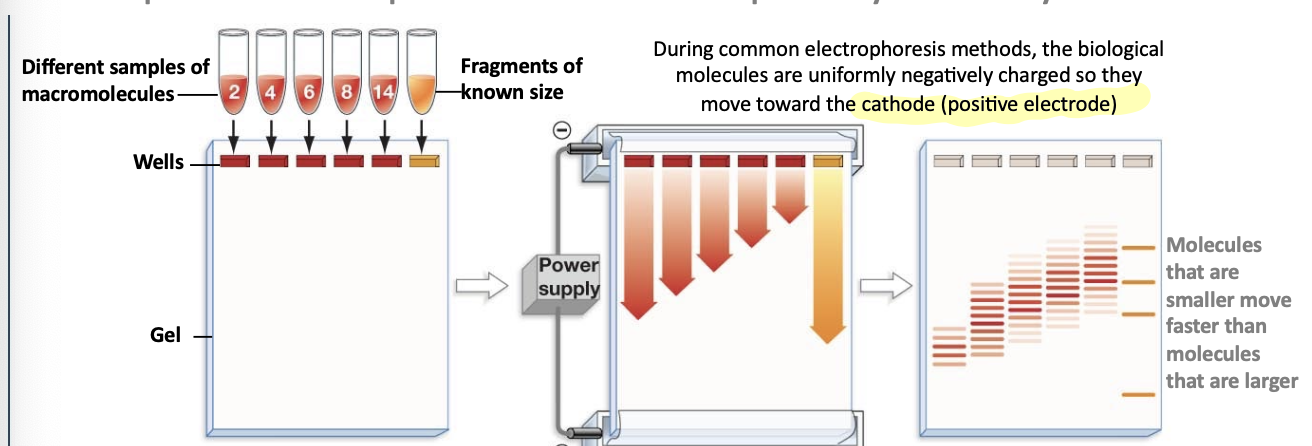
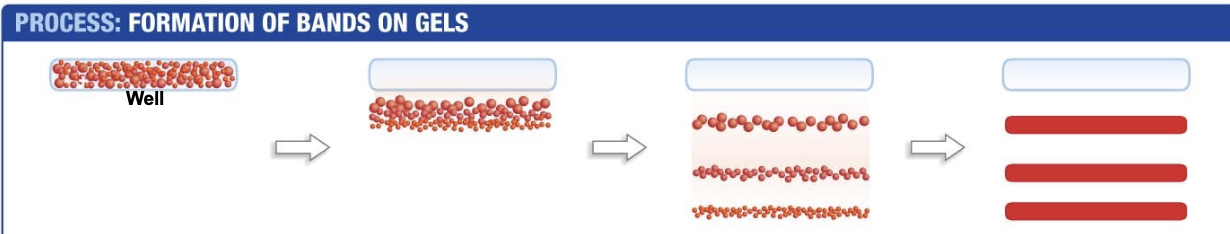
process: formation of bands on gels
start with a mixture of molecules in a well
As electrophoresis starts, molecules begin to separate by size and charge
As electrophoresis continues, separation increases. Molecules with the same size and charge "run” at the same rate.
If each molecule is visualized, the result is a set of bands
DNA and RNA for electrophoresis
DNA must be cut up (usually by restriction enzymes) before electrophoresis
RNA must be denatured before (and during) electrophoresis
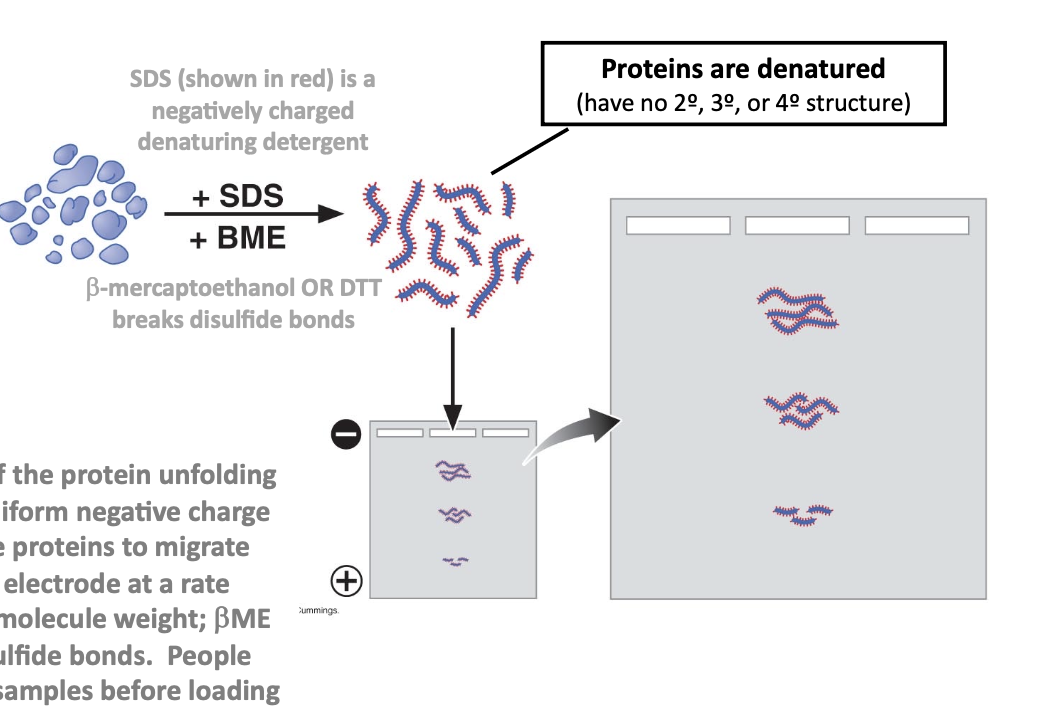
denaturing of molecules
disrupt weak non-covalent bonds but not covalent bonds (peptide bonds or phosphodiester bonds)
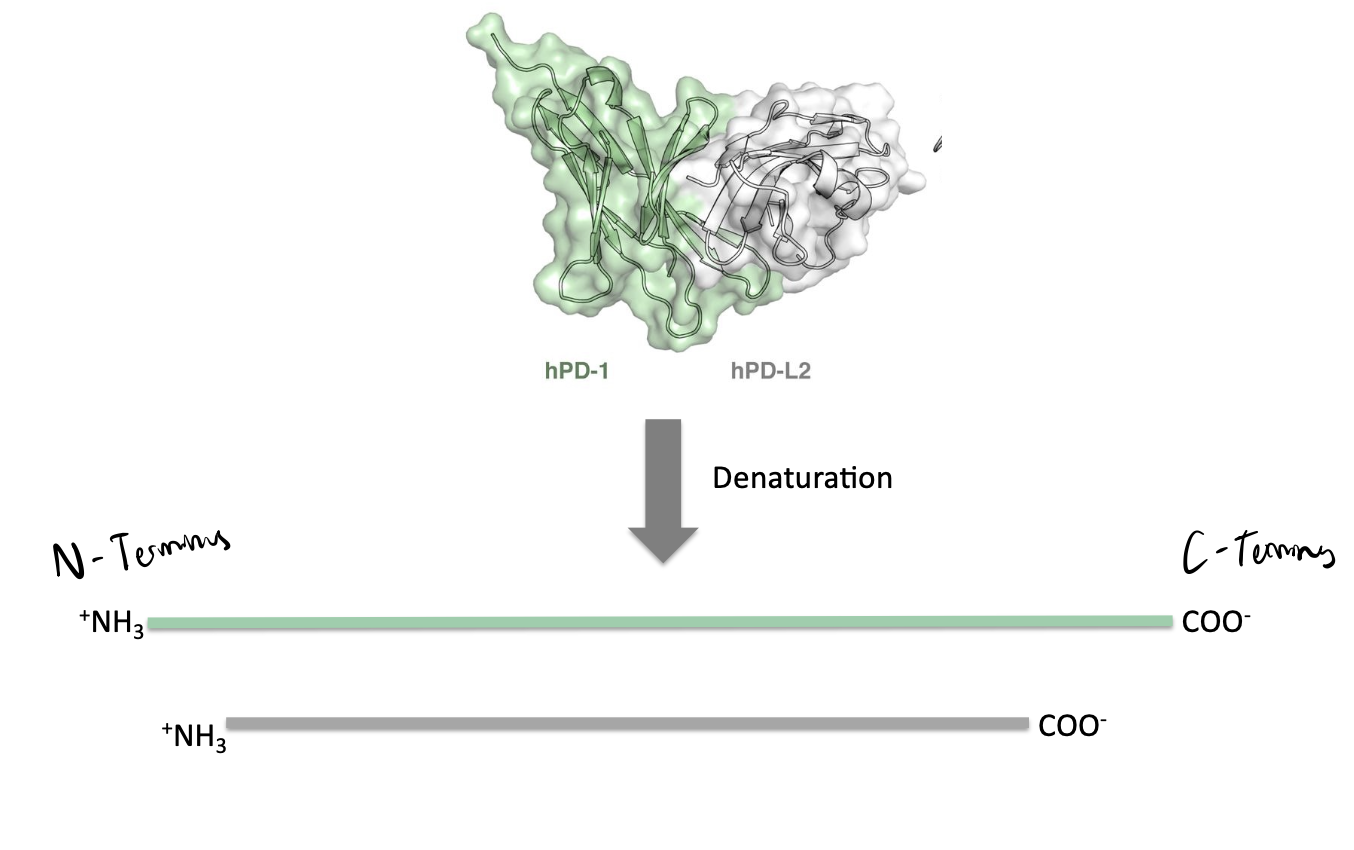
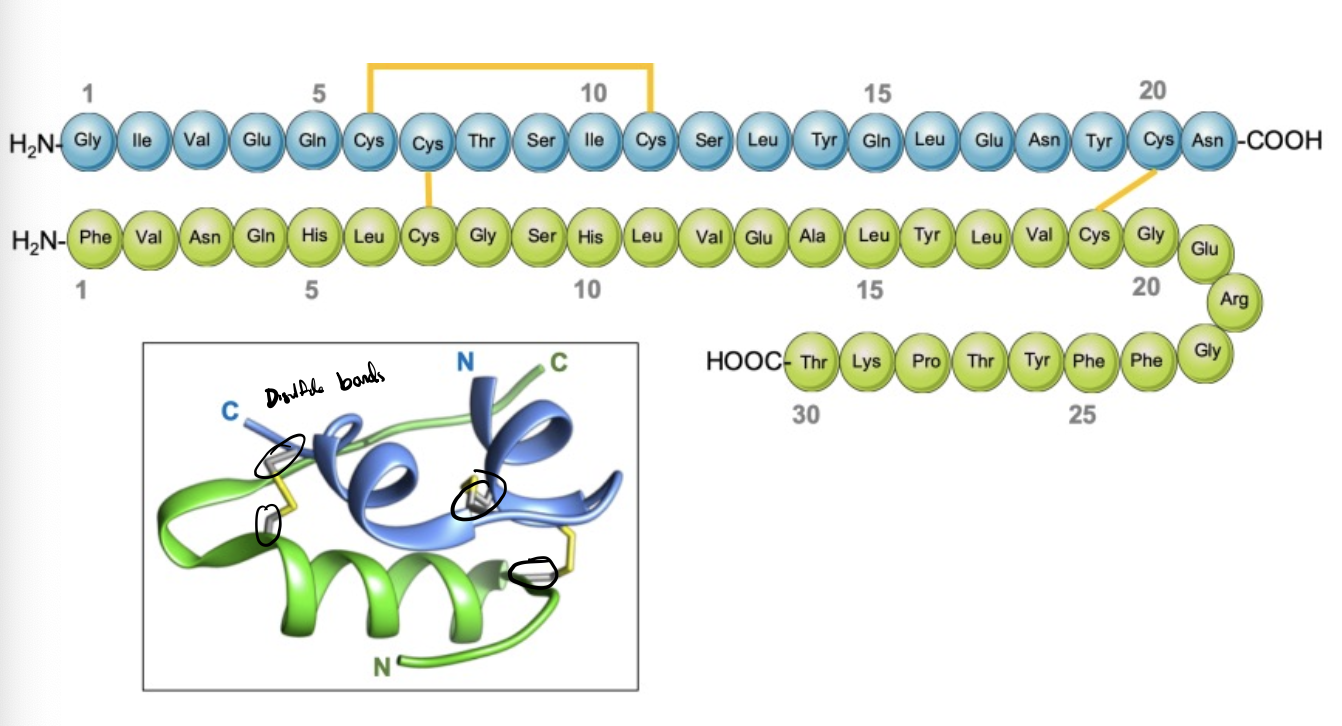
insulin
consists of two polypeptide that are bound by disulfide bonds
SDS-PAGE
electrophoresis of protein samples
sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
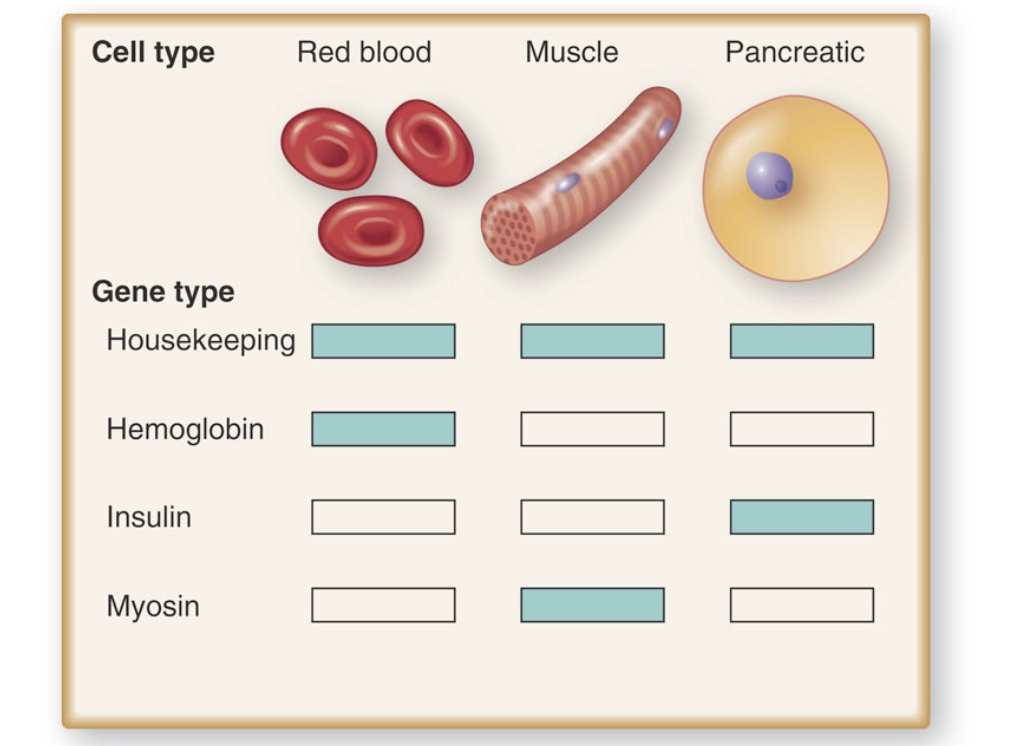
housekeeping gene
one that virtually all cell types express.
they are often used as controls in experiments because their expression levels don’t vary too much from one cell type to another
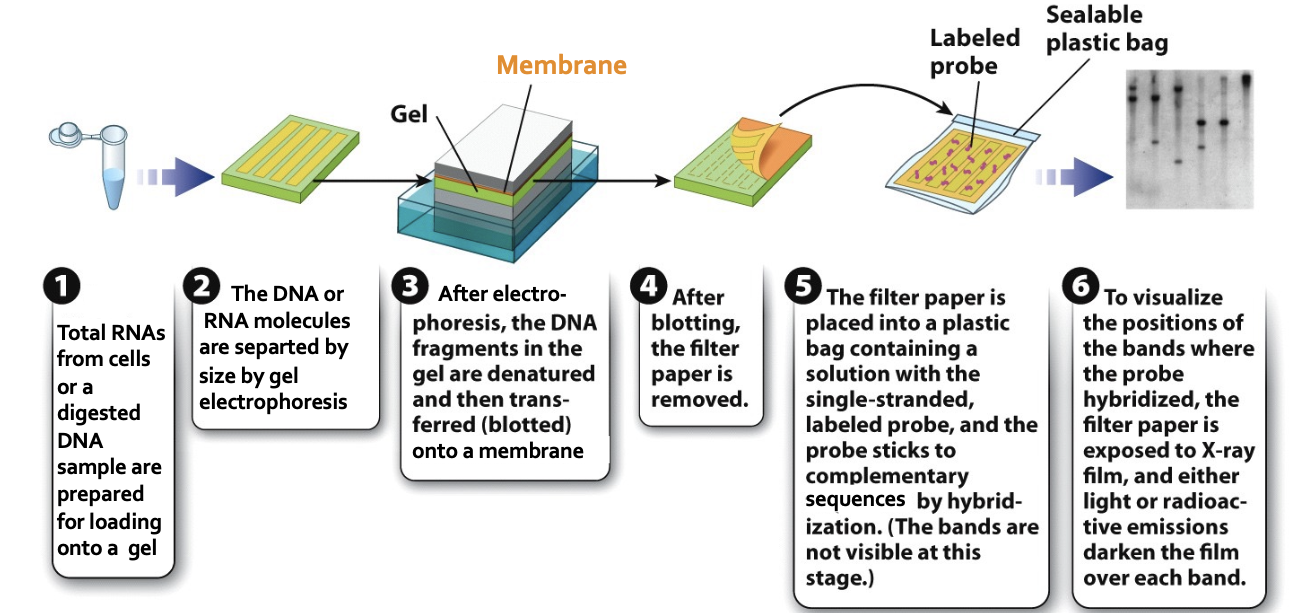
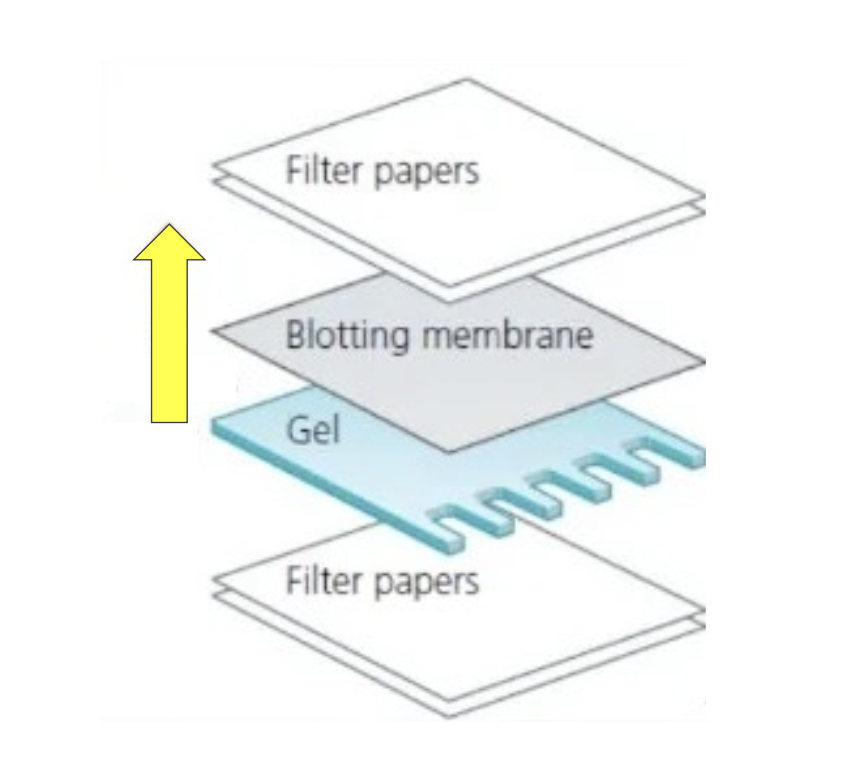
blotting
transfer and virtually irreversible binding of biological molecules to a membrane (“magic paper”). uses probes/antibodies
can be used to detect specific electrophoresed DNA, RNA, or proteins
separate molecules by electrophoresis
transfer molecules to a paper-like membrane
detect specific molecule of interest with a detection molecule
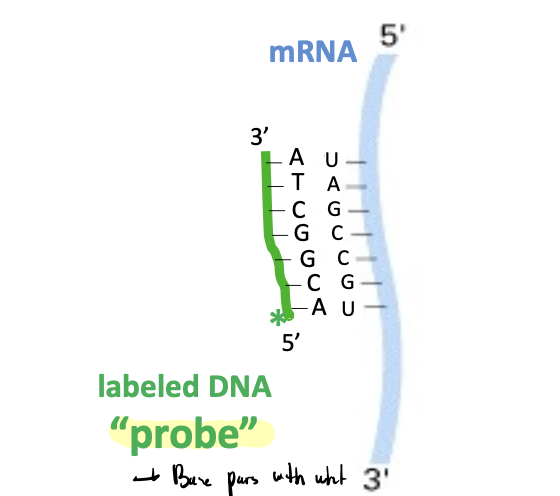
detection of DNA/mRNA
(+) predictable rules for hybridization
(-) mRNA levels do not always correlate directly with protein levels (although they usually do)
uses a DNA probe
DNA probe
using a labeled DNA probe to identify specific DNA sequences within a mixture of DNA fragments
base pairs with what you’re trying to detect
detection of proteins
(+) antibodies allow one to measure the end product of protein-coding genes directly
(-) antibodies are less predictable than nucleic acids and more difficult to obtain
di-sulfide bonds in proteins
antibody
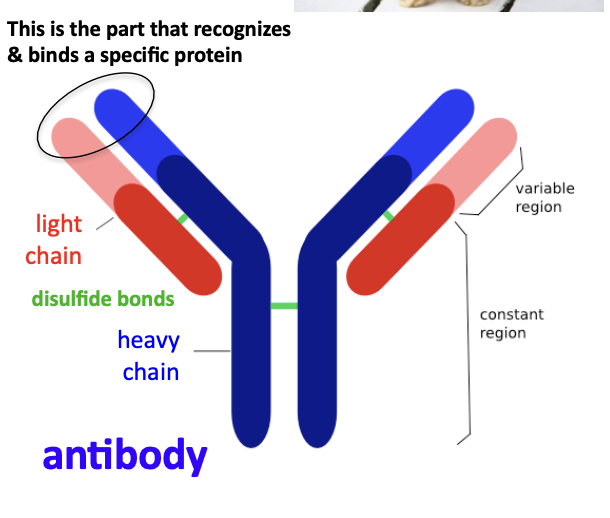
antibody
a protein produced by the immune system to recognize and neutralize foreign substances, like bacteria and viruses, called antigens
used to detect specific protein bands on a blot after electrophoresis
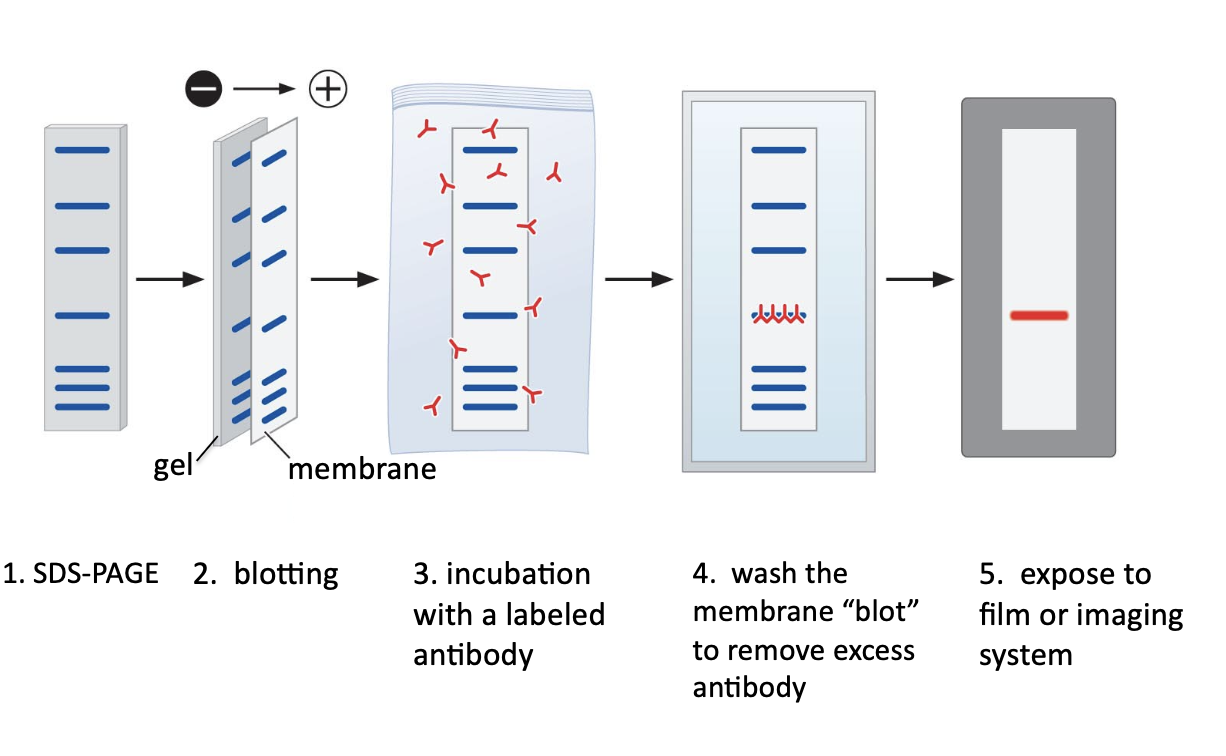
blotting nucleic acids
steps in photo