🤧Infection and Immunology
1/473
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
474 Terms
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
Which gram positive cocci is transmitted by contact, respiratory, and ingestion located in the body as normal flora?
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
Which gram positive cocci has the common disease states:
Impetigo
Folliculitis
Carbuncle
Cellulitis
Erysipelas
Skin Abscess
Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)
Food poisoning (fruit salads, poultry and egg
products, pastries)
Endocarditis, sepsis/septic arthritis (milky joint fluid, especially those who use IV drugs)
Hospital-acquired pneumonia
Septicemia, surgical wound infections
Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
Which S. aureus disease involves fever, rash, hypotension and multiorgan system involvement associated with vaginal and nasal tampons and recent surgery?
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)
Which S. aureus disease involves severe peeling skin with Nikolsky sign, and fever, irritability, poor oral intake in young children <6yo?
IV drug users
Which population is common/concerning for Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infection with endocarditis, sepsis, and osteomyelitis?
Staphylococcus epidermis (S. epi)
Which gram positive cocci located in the body as normal flora likes to grow on plastic and can colonize lines/tubes/catheter with biofilm, transmitted by direct and indirect contact with contaminated people or objects and is a common cause of opportunistic infections like septicemia?
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Which gram positive cocci located in the body as normal GI and vaginal flora is transmitted by direct contact and common cause of uncomplicated UTIs (esp. young sexually active AFABs)?
-Less commonly: acute pyelonephritis, urethritis, epididymitis, prostatitis
Streptococci pyogenes (S. pyogenes)
Which gram positive cocci is Lancefield Group A with normal flora on skin and pharynx transmitted by airborne droplets and hand contact with nasal discharge/contaminated objects?
Streptococci pyogenes (S. pyogenes)
Which gram positive cocci has the common disease states:
Tonsillopharyngitis
Complications:
Scarlet Fever
Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF)
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Acute Glomerulonephritis (Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis)
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
cellulitis, abscess, toxic shock syndrome
necrotizing fasciitis
Scarlet fever
Which S. pyogenes disease involves ‘sandpaper skin’ with erythema that blanches to pressure and strawberry tongue and increases risk for acute rheumatic fever (ARF)?
acute rheumatic fever (ARF)
Which S. pyogenes disease involves fever, arthritis, carditis and CNS involvement, usually 2-3 weeks after pharyngitis?
rheumatic heart disease
Which S. pyogenes disease occurs as a complication of acute rheumatic fever 10-20 years after original illness with mitral regurgitation leading to mitral stenosis?
acute glomerulonephritis
Which S. pyogenes disease occurs as an immune response attacking kidneys in children 5-12 yo with edema, hypertension, tea/rust colored urine (hematuria) and can lead to renal failure?
necrotizing faciitis
Which S. pyogenes infection involves the deep soft tissues and destruction of muscle fascia and overlying subcutaneous fat?
Streptococci agalactiae (S. agalactiae)
Which Group B gram positive cocci is Lancefield Group B with normal flora on skin and vaginal is transmitted by pregnancy and delivery, most concerning to neonates for infection with bacterial sepsis and meningitis?
Enterococcus faecalis and faecium
Which Lancefield Group D gram positive cocci with normal flora in gut, distal GU tract and skin is transmitted by direct or indirect contact with contaminated objects, materials, foods, hands of medical professionals causing UTI, endocarditis, peritonitis, bacteremia, nosocomial infections?
Streptococci pneumoniae (S. pneumo)
Which gram positive diplococci located in the body as normal flora in the nasopharynx is transmitted by droplets and has routine childhood vaccination and adult booster >65yo and causes otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis?
Viridans group Streptococci
Which gram positive cocci group located in oropharynx as normal flora is transmitted by breaches in mucosa includes S. mutans and is a common cause of endocarditis?
intestinal tract
Streptotoccus gallolyticus is normal flora in the _____ of animals and human.
Streptococcus gallolyticus
Which gram positive diplococci is normal flora of the intestinal tract transmitted by direct/in animals and humans is an uncommon cause of endocarditis and bacteremia, and associated with colon cancer?
Bacillus anthracis (B. anthracis)
Which gram positive bacilli (rods/spores) causes disseminated disease through:
GI infection: spores in grasses → undercooked meat → hemorrhagic mesenteric adenitis
Skin infection: spores under the skin → eschar (marked edema and tissue necrosis)
Respiratory infection (inhalation): spores reach terminal bronchioles and alveoli → spread to mediastinal lymph → hemorrhagic mediastinitis
Bacillus cereus (B. cereus)
Which gram positive bacilli is found in soil and transmitted through consumption of contaminated food - reheated fried rice is classic presentation
Clostridium tetani (C. tetani)
Which gram positive bacilli (spores) is found in soil and transmitted through break in skin (deep inoculation and causes tetanus (uninhibited muscle contractions + lockjaw)?
Clostridium tetani (C. tetani)
Which gram positive bacilli (spores) causes tetanus and has routine childhood vaccination and adult boosters ~10 years?
Clostridium botulinum (C. botulinum)
Which gram positive bacilli is ubiquitous on surface of vegetables, fruits, seafoods, soil and marine and transmitted through ingestion of spores?
Clostridium botulinum (C. botulinum)
Ingesting the spores of which gram positive bacilli causes flaccid descending paralysis including:
infant botulism with raw honey (possible contamination)
pre-formed toxin in improperly canned foods
introduction of bacteria to deep wound
Clostridium perfringens (C. perfringens)
Which gram positive bacilli is common in soil and normal flora of the large bowel and causes food poisoning and wound infections?
Clostridium perfringens (C. perfringens)
Which gram positive bacilli causes:
food poisoning: beef, poultry, legumes, gravies
wound infections of bowel (bullet wound) or through skin (higher risk in poorly vascularized tissue/delay in wound care)?
gas gangrene
What condition is caused by C. perfringens alpha toxin passing along the muscles and causing necrosis?
Clostridioides difficile (C. diff)
Which gram positive bacilli (spores/rods) is part of normal intestinal flora but can be suppressed by broad-spectrum antibiotics?
pseudomembranous colitis
What condition occurs when normal intestinal flora is suppressed by broad-spectrum antibiotics, causing C. diff spores to produce bacteria that secrete toxins (A,B)?
hospital patient
Which population is common/concerning for C. diff infection through person-to person transmission?
skin
Where is Corynebacterium sp located in the body as part of normal flora?
Corynebacterium diphtheriae (C. diphtheriae)
Which gram positive bacilli causes diphtheria and a grey and white pseudomembrane that adheres tightly to the throat and oropharynx?
Corynebacterium diphtheriae (C. diphtheriae)
Which gram positive bacilli causes diphtheria and involves routine childhood vaccination and boosters during pregnancy and adults working around infants?
Corynebacterium diphtheriae (C. diphtheriae)
Which gram positive bacilli is transmitted by direct contact with infected secretions or airborne?
Listeria monocytogenes
Which gram positive bacilli causes listeriosis that presents in:
immunocompetent patients: self-limited acute febrile gastroenteritis
immunocompromised patients: invasive infection like sepsis and meningitis
vertical transmission: can cause pregnancy loss, preterm labor → sepsis and meningitis in neonates
Listeria monocytogenes
Which gram positive bacilli is transmitted through ingestion of contaminated foods or through vertical transmission (mother to fetus)?
classically unpasteurized soft cheeses, unheated deli meats (cold cuts), premade deli salads, pates
neonates/fetuses and immunosuppressed
Which population is common/concerning for Listeria monocytogenes infection with sepsis and meningitis?
Gardnerella vaginalis
Which gram positive bacilli is part of vaginal normal flora but can cause bacterial vaginosis (BV) due to changes in vaginal flora and subsequent overgrowth of bacteria?
Malassezia furfur
Which fungus is normal flora of the skin, is not contagious (benign) and cause of non-pruritic pityriasis versicolor (tinea versicolor)?
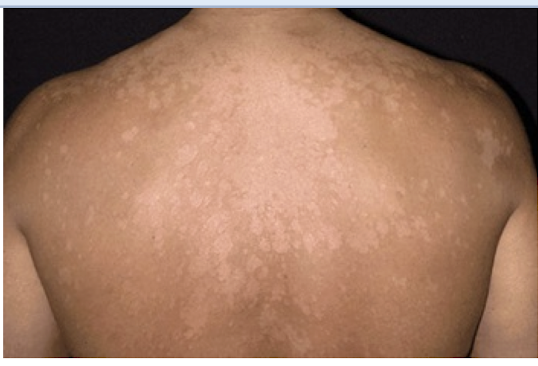
Dermatophytes
Which fungi are transmitted by infected skin scales (human-to-human), animals (pets) and contaminated surfaces and causes itching, scaling skin patches that become inflamed and weep?
over 20 species of tineas
Sporothrix schenckii
Which fungus is transmitted by traumatic lacerations/puncture wounds from contaminated soil/decaying vegetation and causes sporotrichosis and erythema nodosum?
rose gardener’s disease: occupational hazard
infects epidermis, can spread along lymphatic system to subcutaneous tissue and bone or CNS
no person-to-person transmission
Coccidioides immitis
Which fungus is transmitted by inhalation of mold in soil in Southwestern US, Central and South America and causes coccidiomycosis (Valley Fever) with flu-like symptoms?
causes 15-30% of community-acquired pneumonia
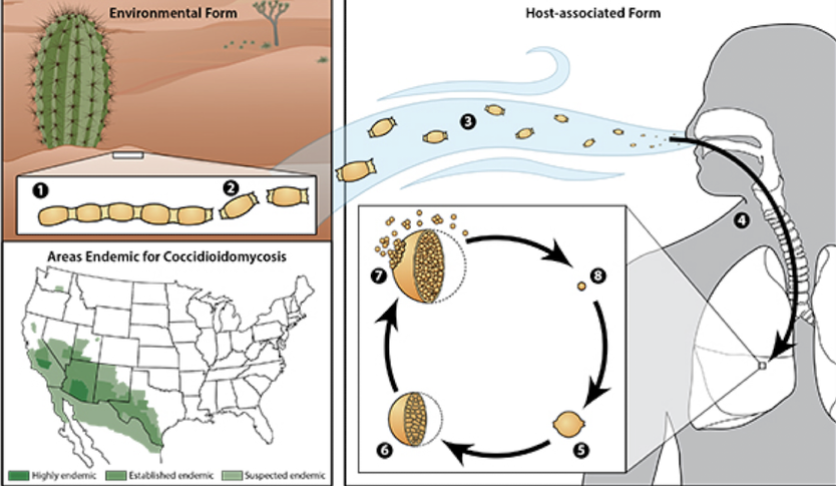
people working in soils/construction
Which populations are common/concerning for Coccidioides immitis infection with coccidiomycosis (Valley Fever) in Southwestern US, Central and South America?
Histoplasma capsulatum
Which fungus is transmitted by inhalation of soil contaminated with bird/bat droppings prevalent in Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys and causes histoplasmosis with flu-like symptoms?
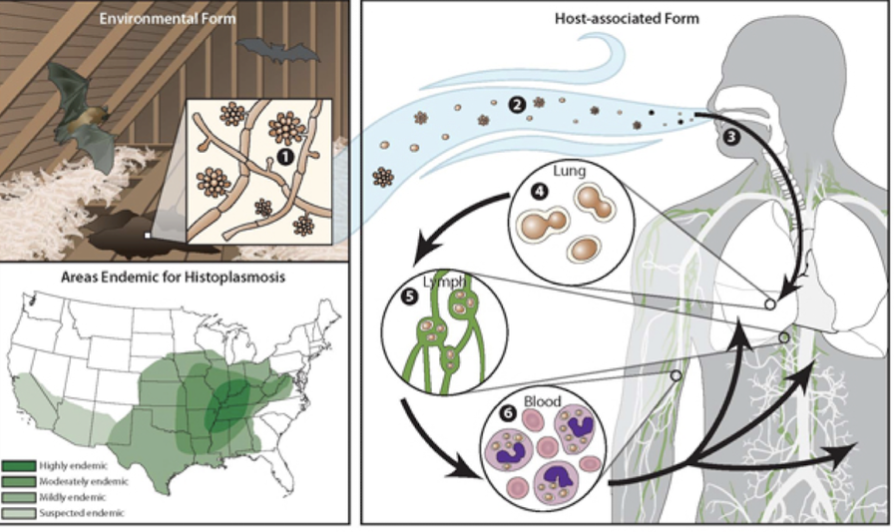
people renovating old houses/barns
Which populations are common/concerning for Histoplasma capsulatum infection with histoplasmosis in Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys?
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Which fungus is transmitted by inhalation of decaying wood and soil and causes blastomycosis in South Central and Southeastern US?
flu-like symptoms, possible dissemination to skin, bones, joints
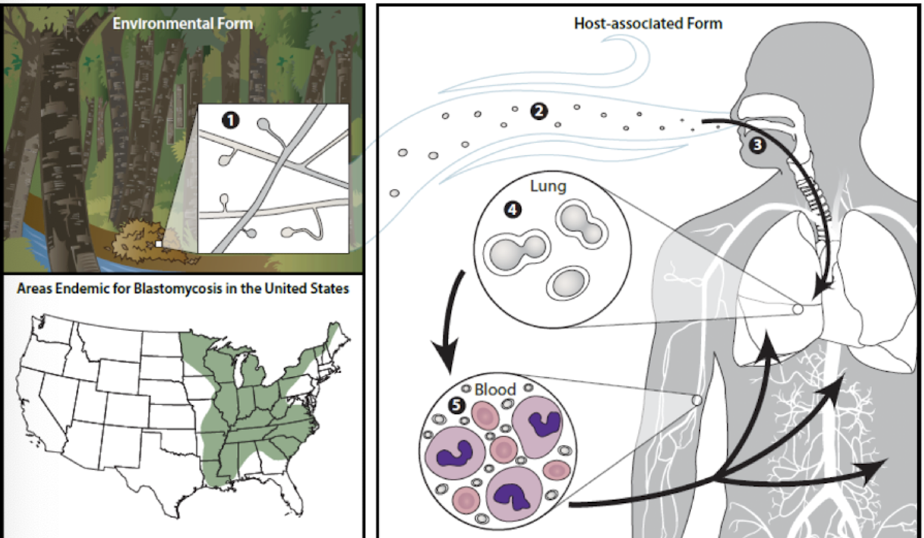
people working in excavation/construction
Which populations are common/concerning for Blastomyces dermatitidis infection with blastomycosis in South Central and Southeastern US?
Candida albicans
Which fungus flourishes when competing bacterial flora are eliminated and causes candidiasis?
cutaneous infections
oral thrush
vulvovaginal vaginitis or vulvitis
diaper rash in infants
Immunocompromised: causes invasive systemic infections (esophageal, systemic into GI tract, kidneys, liver, spleen, blood)
Candida albicans
Which fungus is normal flora of the skin, mouth, vagina, and intestines?
immunocompromised patients with low CD4 counts
Which population is common and concerning for Candida albicans infection with candidiasis?
Cryptococcus neoformans
Which fungus is transmitted by inhalation of soil rich in bird droppings (esp. pigeons) and causes:
causes mild lung infection in healthy patients
immunocompromised: cryptococcal meningitis (disseminates to brain and meninges)

Aspergillus
Which fungus is transmitted by inhalation of dust soil and mold spores in the air and causes aspergillosis?
construction workers at higher risk
produces mycotoxins → liver damage/liver cancer
can disseminate from lung to GI, brain, other organs
symptoms range from allergic reaction to bloody cough and fatigue
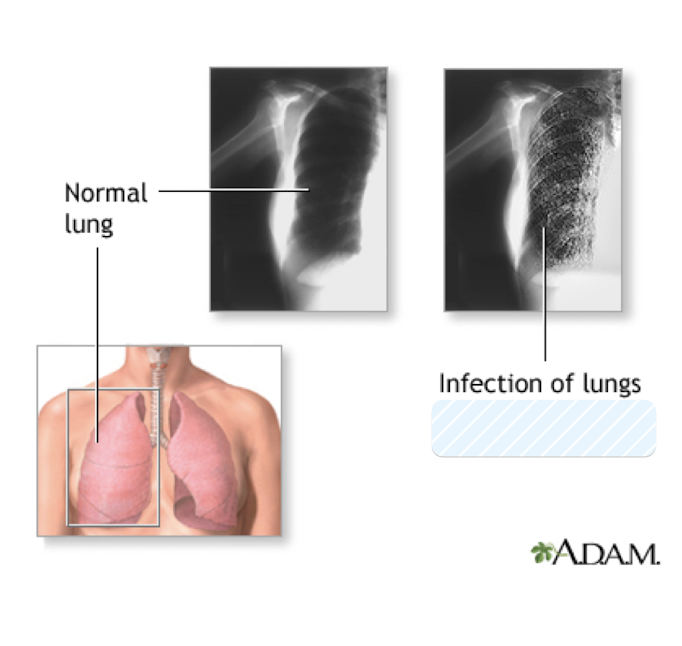
Pneumocystis jiroveci
Which fungus is transmitted airborne person-to-person and causes Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)?
almost 100% fatal if untreated
common disease in AIDS patients/immunocompromised
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)
Which fungal infection presents like a virus on chest x-ray and is successfully treated with an antibiotic (TMP/SMX- Bactrim)?
almost 100% fatal if untreated
common disease in AIDS patients/immunocompromised
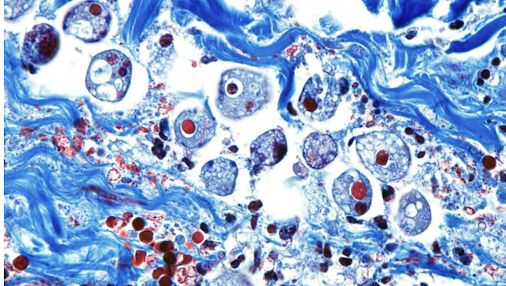
Entamoeba histolytica
Which intestinal protozoa is transmitted via ingestion of food or water containing contaminated cysts and causes:
amebiasis (diarrhea)
amebic dysentery (bloody diarrhea and fever)
common in tropical areas with poor sanitary conditions
rarely can disseminate to liver (forms abscess), lungs/brain
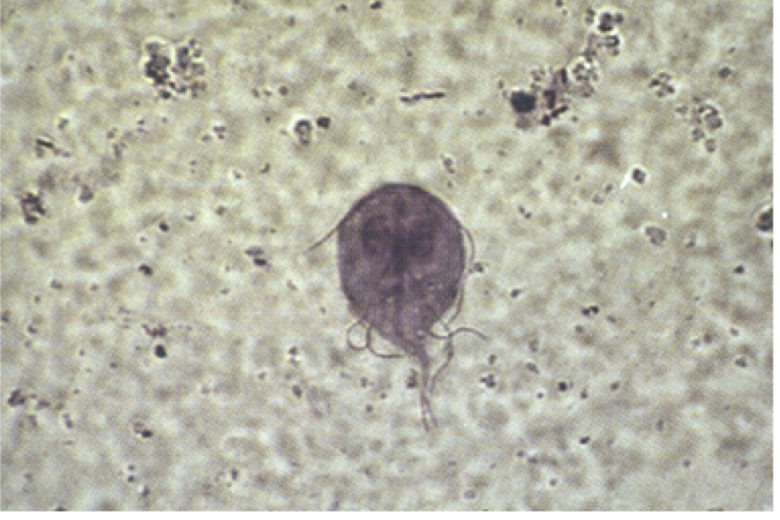
Giardia lamblia
Which intestinal protozoa is transmitted by waterborne, food-borne, fecal-oral routes and causes giardiasis (foul smelling, fatty, watery diarrhea)?
most commonly diagnosed parasitic intestinal disease in US (hikers)
ingestion of raw/undercooked food contaminated with cysts or via food contaminated after cooking
person-to-person transmission in childcare settings
Cryptosporidium species
Which intestinal protozoa is transmitted fecal-oral by ingestion of contaminated recreational water, drinking water, or food, or contact with infected persons or animals and causes Cryptosporidiosis?
Cryptosporidiosis: profuse, watery diarrhea that can last up to 3 weeks in immunocompetent patients
immunocompromised: can lead to life-threatening malnutrition and wasting

cryptosporidiosis
The intestinal protozoa Cryptosporidium species causes which infection involving:
profuse, watery diarrhea that can last up to 3 weeks (immunocompetent)
life-threatening malnutrition and wasting (immunocompromised)

Trichomonas vaginalis
Which urogenital protozoa is transmitted by sexual contact and causes trichomoniasis?
the most common protozoal urogenital tract infection of humans
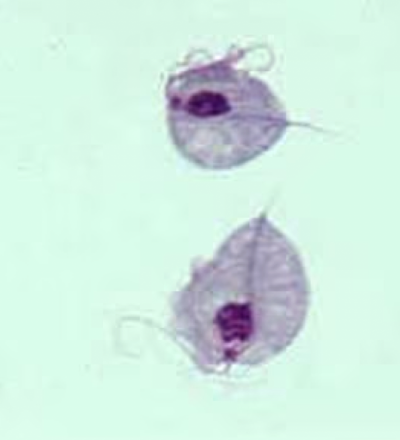
trichomoniasis
Which infection involves these symptoms?
AFAB (more commonly symptomatic)
Inflammation of mucosal tissue of vagina, vulva, cervix
Copious, yellowish/greenish or white frothy, malodorous vaginal discharge
AMAB (less commonly symptomatic)
Infects urethra, prostate and seminal vesicles
Commonly asymptomatic
Whitish penile discharge
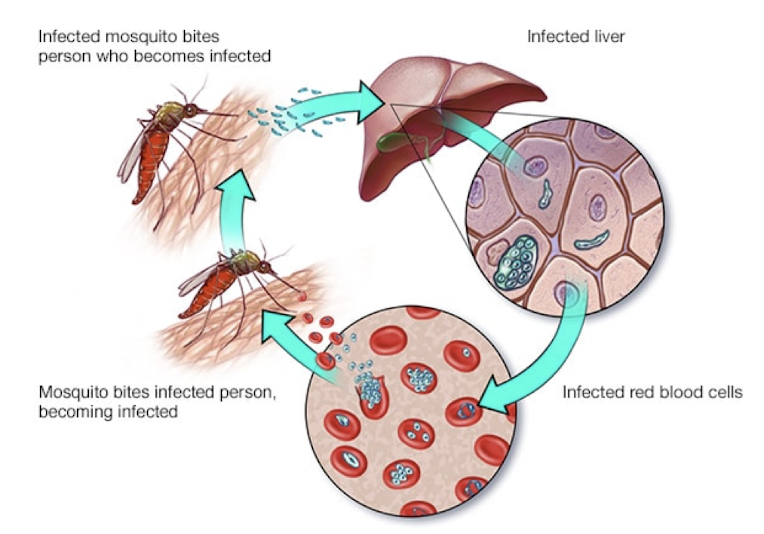
Plasmodium falciparum
Which urogenital protozoa is transmitted by infected mosquito bite or contaminated needle and causes malaria?
fever, chills, shaking, vomiting, joint aches, fatigue, diarrhea
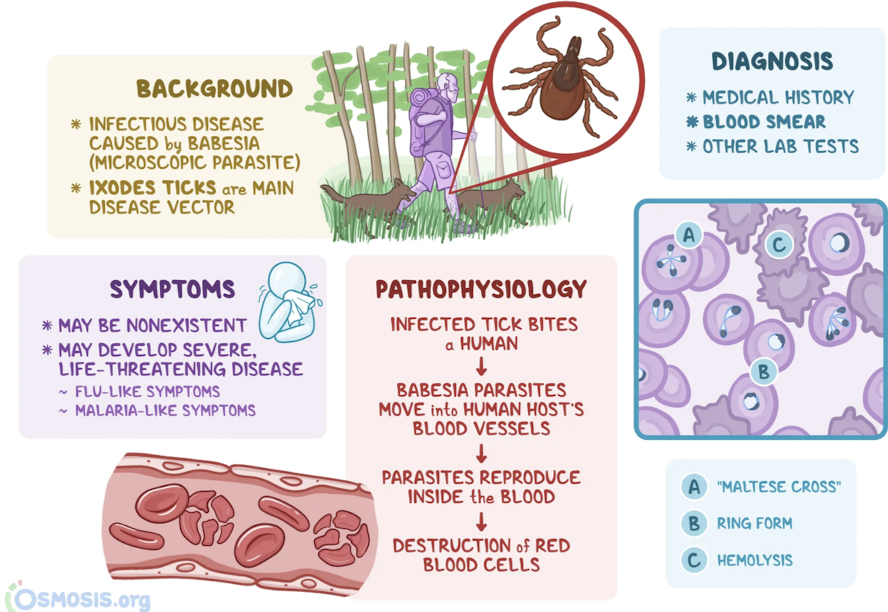
Babesia sp.
Which urogenital protozoa is transmitted by infected tick bites and causes Babesiosis?
flu-like symptoms
can cause to hemolytic anemia (multiplies in red blood cells and ultimately lysing cells) and severe disease
Toxoplasma gondii
Which urogenital protozoa is transmitted by ingestion of infected cat feces, raw or undercooked meat, and vertical transmission and causes toxoplasmosis?
from asymptomatic or mild flu-like symptoms to severe encephalitis (pregnancy)
leading cause of death from food-borne illness in US

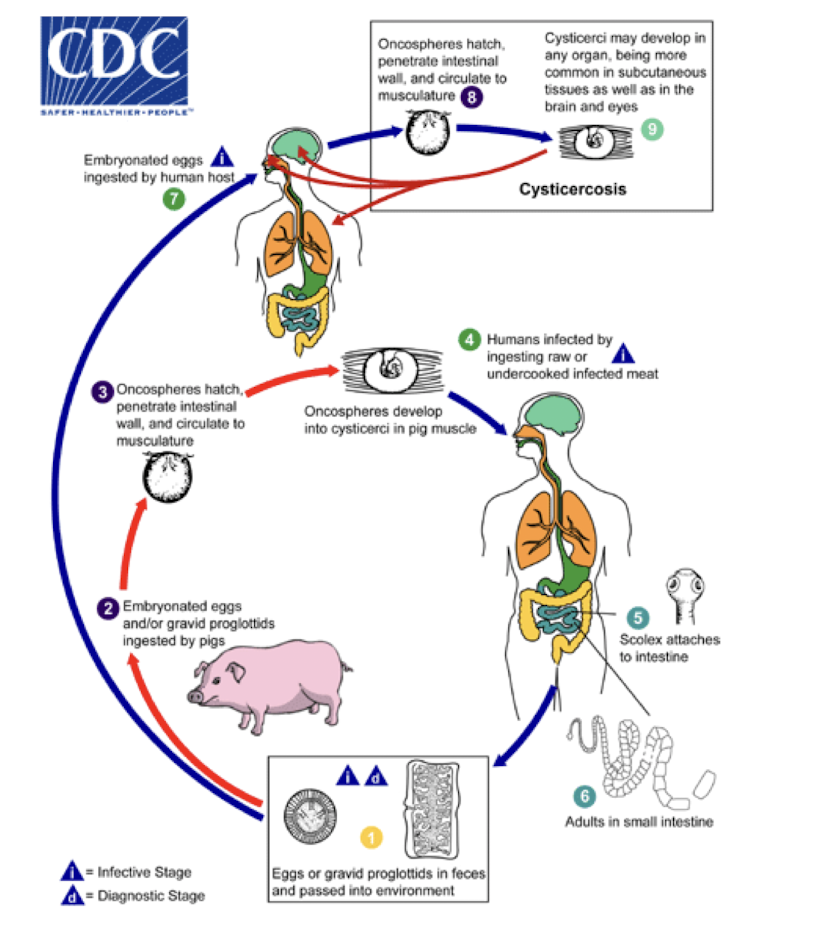
Cestodes
Which helminths are tapeworms transmitted via ingestion of undercooked meat containing larvae or eggs (pork, beef) and fecal-oral route causing many symptoms including cysticercus/cysticercosis?
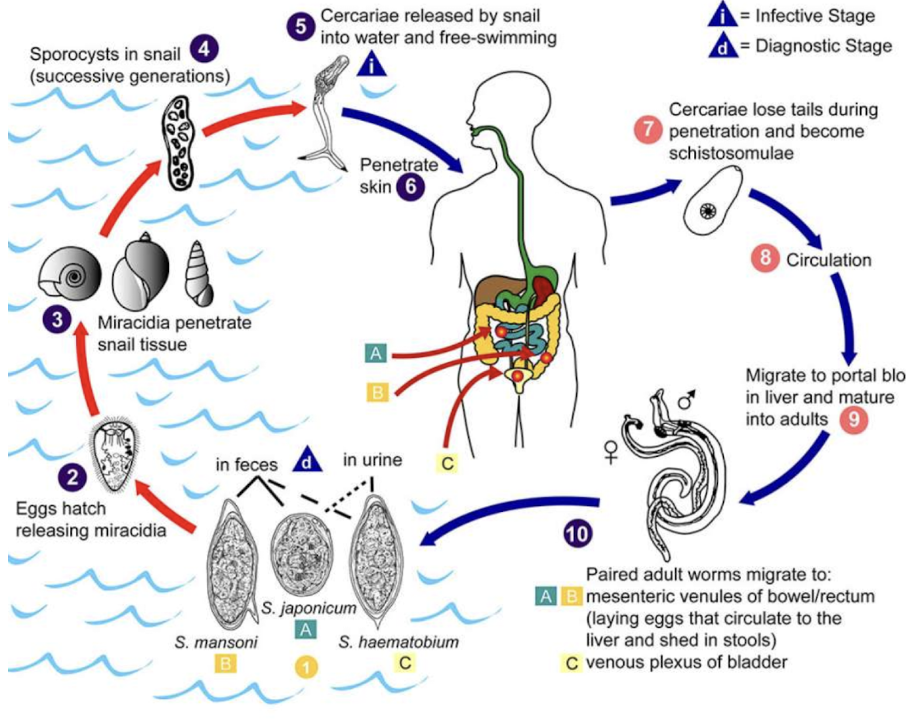
Trematodes
Which helminths are flukes transmitted via snails in contaminated freshwater by absorbing into human skin and causing Schistosomal infection?
rash, fever, chills, cough
can invade bladder and liver
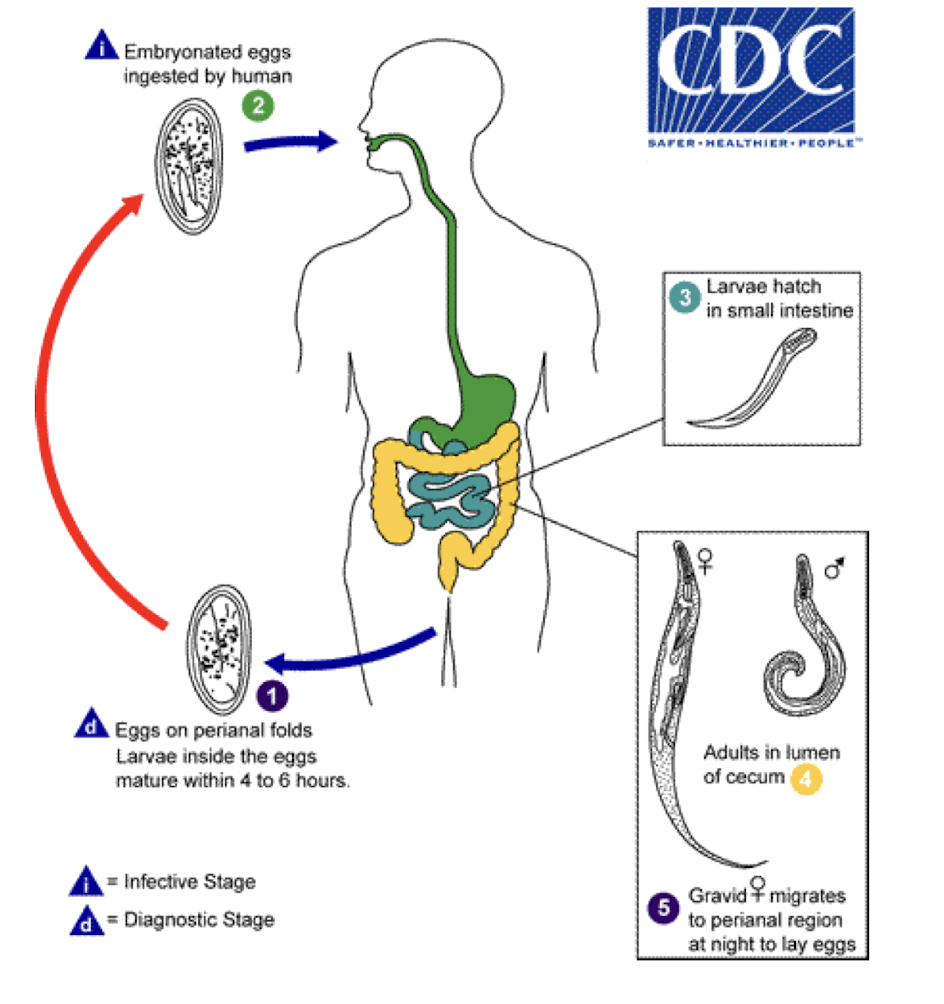
Nematodes
Which group of helminths are Pinworms (roundworms) that cause enterobiasis (perianal itching) transmitted by:
ingestion (contaminated foods/drinks, touching fomites)
inhaled if eggs become airborne
direct penetration of skin
Cimex species
Which parasites are transmitted by contact with infested surface (not transmitted person-to-person) and bites cause itching and loss of sleep?
bed bugs
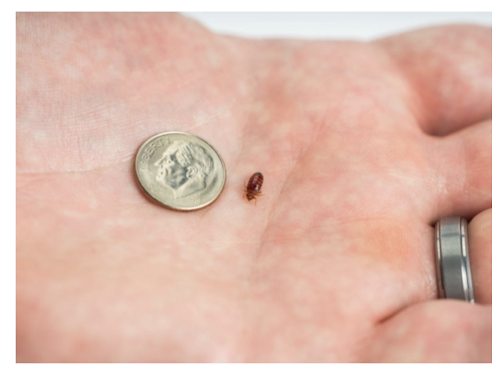
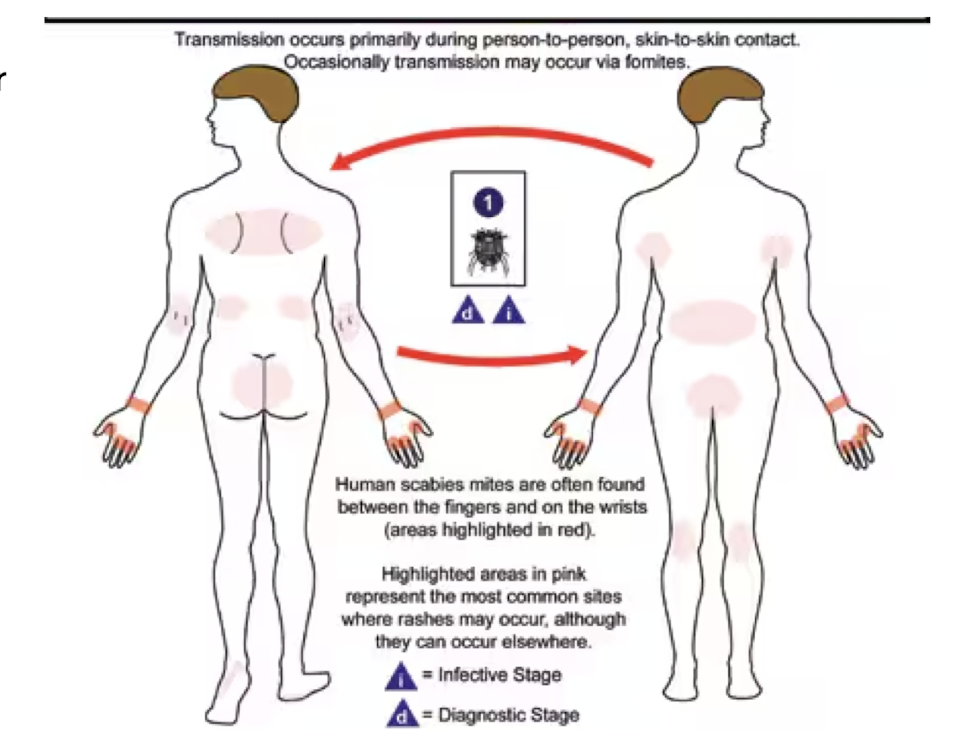
Sarcoptes scabiei
Which parasites are transmitted by direct contact with fomites and cause scabies?
intensely pruritic papular rash with possible burrows
usually not on head
crowded conditions increase risk
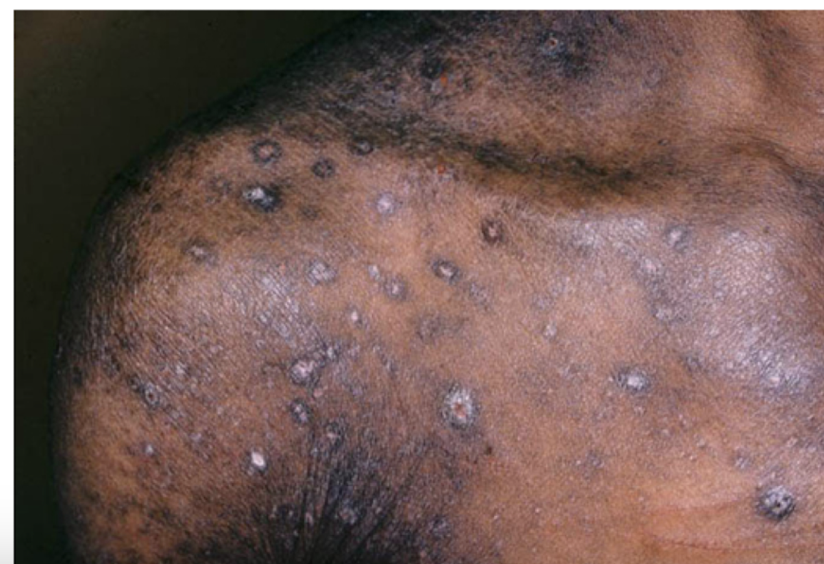
Pediculus humanus capitis
Which parasites are transmitted by head to head contact or via fomites (debatable) causing pediculosis capitis?
scalp pruritus occurs as an allergic reaction to head lice saliva injected during feeding
lice do not jump, fly, or use pets as vectors

Pediculus humanus humanus
Which parasites are transmitted by direct contact and via fomites causing pediculosis coporis?
widespread body pruritus as an allergic reaction to body lice saliva injected during feeding
primarily resides in clothing rather than on skin or hair
often involving the trunk areas
prions
What is the causative agent of TSE (transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, including dementia and behavioral changes?
Unconventional infectious agents
Can cause brain tissue destruction
prions
What do these characteristics describe?
Do not trigger an immune or inflammatory response
Some can be inherited and cause disease, unlike conventional infectious diseases
Extremely resistant to UV light, x-rays, chemical agents that typically inactivate viruses and bacteria
Invariably fatal
Herpes simplex viruses types 1 & 2 (HSV)
Which DNA Herpesviruses is transmitted by direct inoculation of mucocutaneous surfaces and causes oral/genital herpes, herpetic whitlow, encephalitis?
herpetic whitlow
What condition is caused by herpes simplex viruses types 1 & 2 (HSV) and involves herpes infection on the hands/fingers, and is a possible occupational hazard (dentistry)?
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
Which DNA Herpesviruses is transmitted by respiratory droplet and direct contact with lesions and causes varicella (chickenpox) → recurrent infection causes zoster (shingles)?
Vaccination available
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Which DNA Herpesviruses is transmitted by vertical (placenta), saliva, sexual, blood transfusion and causes asymptomatic infection (most common) but also congenital disease and CMV mononucleosis-like syndrome?
80% of population have antibodies
immunocompromised at higher risk
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
Which DNA Herpesviruses is transmitted by saliva exchange and causes mononucleosis?
mononucleosis
What condition is caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) usually in younger individuals and involves:
pharyngitis (posterior cervical chain lymph nodes)
fever
lymphadenopathy
splenomegaly (athletes need to avoid contact sports due to splenic rupture)
Human herpesvirus 6
Which DNA Herpesviruses is transmitted by saliva exchange and causes roseola?
roseola
What condition is caused by Human herpesvirus 6 usually in young children and involves high fever (fever of unknown origin w/o other symptoms) followed by classic rash?
also called 6th disease
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV)
Which DNA Poxvirus is transmitted by close personal contact and causes molluscum contagiosum?
molluscum contagiosum
What condition is caused by Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) usually in young children, with flesh colored umbilicated lesions that appear all at once, starting on face and palms?
Mpox virus
Which DNA Poxvirus is transmitted by person-to-person, vertical, sexual contact and causes rash, fever, headache and fatigue?
Vaccination available
Mpox rash
Which Poxvirus rash involves vesicles or pustules that are deep-seated, firm or hard, well-circumscribed, lesions may umbilicate or become confluent and progress over time to scabs?
Human papilloma virus (HPV)
Which DNA virus is transmitted by sexual contact and skin-to-skin and causes genital warts and can cause cancer (cervical, anal, oropharyngeal, vulvar, penile)?
Vaccination available
Parvovirus B19
Which DNA virus is transmitted by respiratory route and causes Erythema infectiosum?
Erythema infectiosum
Which Parvovirus B19 condition involves “slapped cheek” erythema usually in children several days after a fever, runny nose, and headache?
also fifth disease, Slapped Cheek Disease
Hepatitis B virus
Which DNA virus is transmitted by blood, sexual, vertical contact and causes acute hepatitis?
Vaccination available
additionally fulminant hepatitis and chronic hepatitis are possible
also co-infection with possible Hepatitis C or D possible
the most common blood-borne infection worldwide
Complications
hepatocellular carcinoma
cirrhosis (liver scarring)
acute hepatitis
Which Hepatitis B and D condition involves jaundice (icterus) fever, malaise?
fulminant hepatitis
Which Hepatitis B and D condition involves rapid (days to weeks) and massive necrosis of liver parenchyma and decrease in liver size?
Adenoviruses
Which DNA viruses are transmitted by aerosol droplet and fecal-oral and causes the common cold (upper respiratory infection) and diarrhea (enteric form) especially in children?
upper respiratory infection (URI)
What condition involves coughing, sneezing, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, sore throat?
caused by adenoviruses, parainfluenza viruses, RSV, coronavirus, rhinovirus
Coxsackie viruses A & B
Which RNA viruses are transmitted by fecal-oral and cause:
A virus: hand, food, mouth disease (HFMD) and herpangina (mouth blisters)
B virus: pleurodynia, myocarditis/pericarditis
Poliovirus
Which RNA virus is transmitted fecal-oral and causes paralytic poliomyelitis (paralysis of muscles when RNA virus enters the CNS)?
Vaccination available
Hepatitis A virus (and Hep E)
Which RNA viruses are transmitted fecal-oral and cause fever, jaundice, and hepatomegaly?
Vaccination available for Hepatitis A
Hepatitis D virus
Which RNA virus is transmitted by blood, sexual and vertical contact (only by people with hepatitis B infection) and causes a more severe form of acute hepatitis?
Hepatitis B vaccination provides protection against both
Hepatitis C virus
Which RNA virus is transmitted by blood, vertical and sexual (less common) contact and causes acute and chronic hepatitis, can be asymptomatic?
IV drug users, incarcerated populations
What populations are common/concerning for Hepatitis C virus infection?