3.1: Motion
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Speed
A scalar quantity
Total ground covered
Displacement
Vector quantity
Measures distance travelled in a particular direction
Speed equation
Distance travelled/time
Displacement equation
Total displacement/time
Distance (compare and contrast)
How much ground is covered in total
Displacement (compare and contrast)
The shortest possible distance between two points
Point of instantaneous velocity
To overcome the fact that average speed doesn’t tell you whether speed changes over the total time period
Instantaneous Velocity/Speed
Velocity/Speed of an object measured over a very short period of time
How instantaneous velocity works
V=Δs/Δt
If it keeps getting smaller you get speed at an instant
How to find instantaneous velocity
Use a tangent to find the gradient of a graph at a point
Acceleration Definition
The rate of change of velocity
What type of quantity is acceleration
Acceleration is a vector quantity
Units of acceleration
ms-2
Equation for acceleration
(final velocity - initial velocity) / time
Δv / Δt
Objects with high acceleration
Rockets
F1 cars
Falling objects
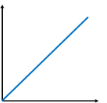
Distance-time graph
Distance on y-axis
Time on x-axis
Gradient is speed
Stationary objects represented with horizontal line
Objects moving with a constant speed are represented with a straight line with a constant gradient
Displacement-time graph
Displacement on y axis
Time on x-axis
Gradient is velocity
Stationary objects represented by a horizontal line
Moving objects represented by a sloping line
Velocity-time graph
Time on x-axis
Velocity on y-axis
Gradient is acceleration
Area under graph is displacement
S.U.V.A.T equation without displacement
v=u+at
S.U.V.A.T equation without final velocity
s=ut + 1 / 2at2
S.U.V.A.T equation without acceleration
s=1 / 2(u+v)t
S.U.V.A.T equation without time
v2=u2+2as
When do we use S.U.V.A.T equations?
When objects are moving at a constant acceleration with a changing velocity
When is an object in free fall?
When an object is accelerating under gravity with no other forces acting on it
What is the acceleration of free fall?
9.81ms-2
What is an electromagnet
Electromagnet holds a small steel ball above a trap door
When current is switched off, timer is triggered and electromagnet demagnetises causing the ball to drop
When the ball hits the trap door, electrical contact is broken and timer stops
Method for determining the acceleration of free fall (electromagnet)
Measure height of fall with a ruler
Record time of fall using timer
Use s=ut+1 / 2at2 where s=h, v=0ms-1 and a=g to calculate acceleration of free fall
What is a light gate?
Two light beams one above another, with detectors connected to a timer. When ball falls through the first beam, it interrupts the signal and the timer starts. When the ball falls through the second beam, a known distance below, the timer stops
Method for determining the acceleration of free fall (light gates)
Measure the height of fall with a ruler
Record the time of fall using the stop clock
Use s=ut+1 / 2at2 where s=h, u=0ms-1 and a=g to calculate acceleration of free fall
Picture method for determining the acceleration of free fall
Drop a small metal ball from rest next to a metre ruler
Its fall is recorded on video with a camera in rapid fire, repeating mode
Camera shutter is held open, which produces a photograph with multiple images of the falling ball
The position of the ball at regular intervals is then determined by examining the recording
Graphical method for determining the acceleration of free fall
Measure the height of fall with a ruler
Record the time of fall with a stop clock
Plot a graph with height on y-axis and t2 on x-axis
Use y=mx+c analysis to find g
Thinking Distance
Distance vehicle travels in the time that it takes for a driver to react to a situation
Thinking distance=speed x reaction time
Factors affecting thinking distance
Condition of the driver (which affect reaction time like alcohol levels):
Alcohol
Tiredness
Drugs
Distractions
Braking distance
The distance a vehicle travels whilst the brakes are applied and the vehicle is decelerating to a stop
Braking distance= (speed)-2/-2 x deceleration
Factors affecting braking distance
Condition of vehicle and road:
Road surface conditions
Worn tyres
Brakes conditions
Larger mass vehicles
Stopping distance
The sum of the thinking and braking distances
Horizontal and vertical forces in projectile motion
The vertical and horizontal components are independent of each other
Projectile motion, assuming no air resistance
Vertical velocity changes due to the acceleration of freefall
Vertical displacement and time of flight can be calculated with SUVAT equations
Horizontal velocity remains constant
Key points on projectiles fired at an angle to the vertical
Only Vy is affected by acceleration of freefall so this continually changes
Vv= maximum at take off and just before it lands= -maximum
Vv= 0 at maximum height
The time taken to reach max height is half the total time of flight
Vy and Vx components of velocity (projectiles fired at an angle to the vertical)
Vertical component= Vy = Vsinθ
Horizontal component= Vx = Vcosθ
Steps to solve distance travelled (projectiles fired at angle to the vertical)
Draw vector triangle, find vx and vy components
Calculate time for max height
Multiply by 2 to get total time
Use s=d/t to find distance travelled