Chapter 1: The Criminal Justice System(Objective 1-4)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
•Crimes
•Crimes
−Actions that violate laws defined by society
•Mala in se
−Traditionally accepted crimes that are wrong in themselves or by their very nature, like homicide and sexual assault
•Mala prohibita
−Prohibited by law, but some people in society disagree on their harmfulness, like gambling, prostitution, and drug possession
•Doing Justice
−Not just punishing violators but ensuring that the rights of everyone in the criminal justice system are equally protected. This includes victims, suspects, and witnesses.
•Controlling Crime
−Law enforcement officers and prosecutors must act within the confounds of the law in identifying and prosecuting offenders.
•Preventing Crime
−Fair, equitable, and lawful prosecutions and punishments that can serve as an example to society
•Advancing goals: evidence-based practices
−Enacting and enforcing policies based on factual, science-driven data that leads to a policy success
•Federalism
−Power divided between national and state governments
•Two justice systems
−The federal government prosecutes violations of federal law.
−State (and local) governments prosecute violations of state law.
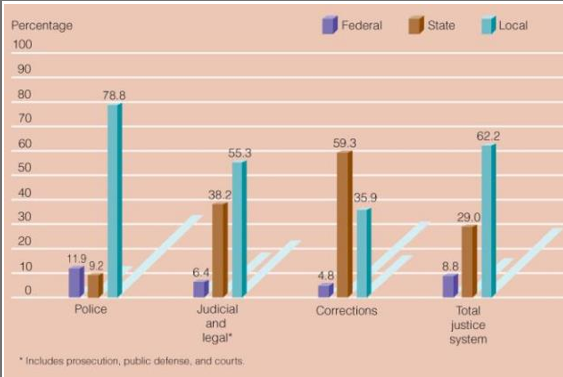
•Percentage (rounded) of criminal justice employees at each level of government
−Most criminal justice employees are state and local officials.
•Expansion of federal involvement
-Since the 1960s. federal law enforcement has taken on more responsibility as more crimes extend beyond just one state’s border. The events of September 11, Internet crimes, computer fraud and schemes, and cyberattacks have increased federal law enforcement agency jurisdictions.
•System
−Complex whole made up of interdependent agencies that each contribute to the system’s function, for example:
Police
Prosecutor’s office
Courts
Corrections
−Each entity relies on the others, and policy changes in one can affect them all.
•Exchange
−Mutual transfer and utilization of resources
−Need to gain the cooperation and assistance from each agency
•Plea bargain
−The accused (defendant) admits guilt to a crime in exchange for consideration for a reduced sentence or reduction in charges.
Discretion
−Official’s authority to make decisions using their own judgment
•Resource dependence
−Agencies depend on other agencies for funding.
•Sequential tasks
−Decisions are made in a specific order.
Filtering
−Screening process that gradually exits people out of the system.