Mod 6: intro to articulations
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is the axial skeleton?
it forms the verticle, central axis of the body and includes all bones of the head, neck, chest, and back. It protects the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs and attachment sites that move the upper body
-skull, spinal column, and ribs
what is the appendicular skeleton?
includes all bones of the upper and lower limbs and the bones that attach the limbs to the axial skeleton.
-it attaches to the axial skeleton via two girdles, the pectoral girdle, and pelvic girdle
what is an articulation?
where a bone meets another bone, cartilage, or teeth
-they can vary in stability and mobility
what is an attachment
an area of bone that projects above the surface of the bone. it is the attachment points for tendons and ligaments
what are depressions
grooves where blood vessels and nerves pass on the surface of the bone
what are openings
they allow vessels and nerves to enter the bone or pass through the bone
How are joints classified?
structure and function. The amount of mobility found between the bones
what is synarthrosis
an immobile or nearly immobile joint. Strong union. Low mobility, high stability
ex) hips
What is amphiarthrosis
it is a joint with limited mobility. right in the middle of mobility and stability
ex) some fibrous joints
what is diarthrosis
a freely mobile joint, it is classified as nonaxial (plane joint). High mobility, low stability
ex) synovial joint, shoulder
It is an articulating bone seperated by a fluid filled joint cavity
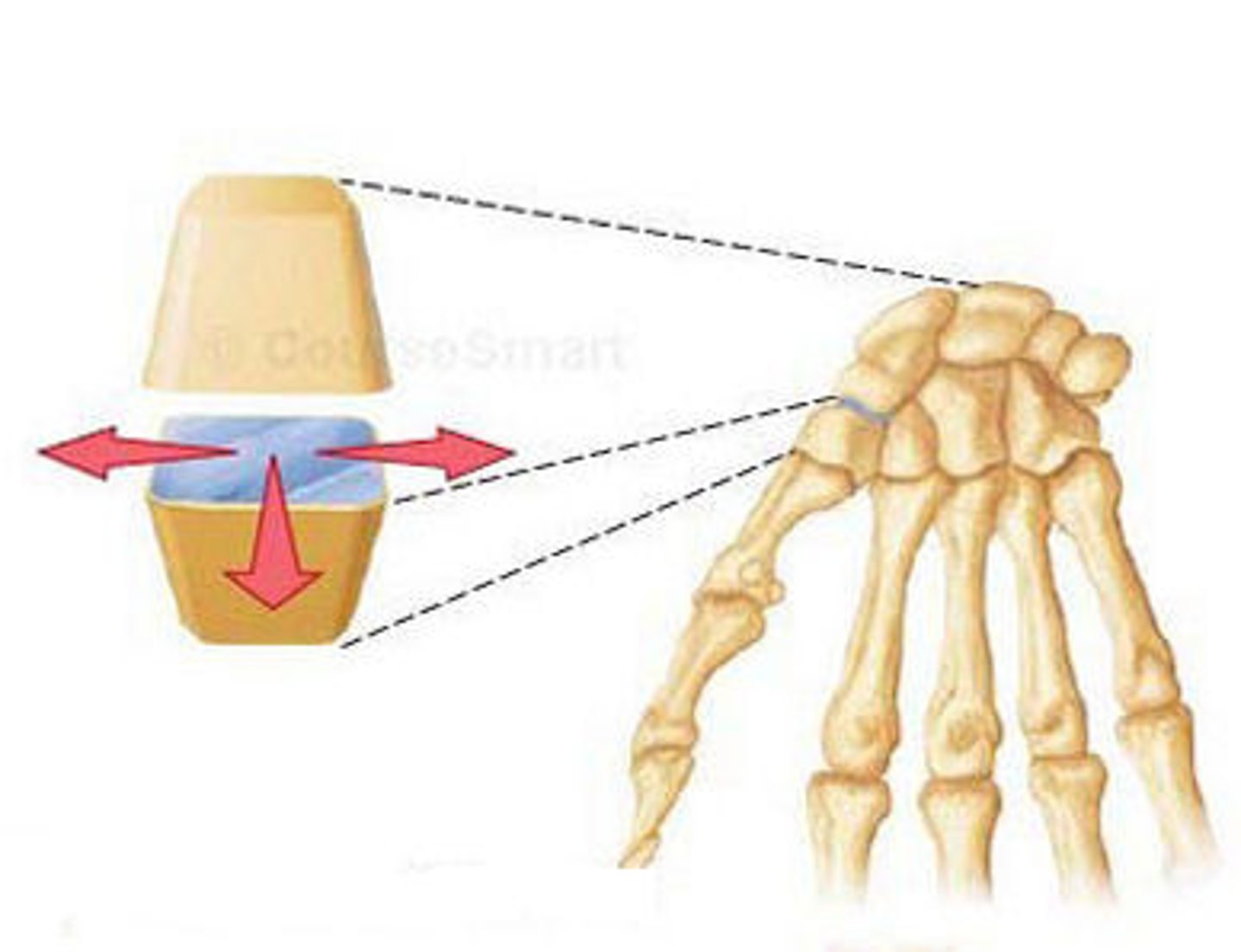
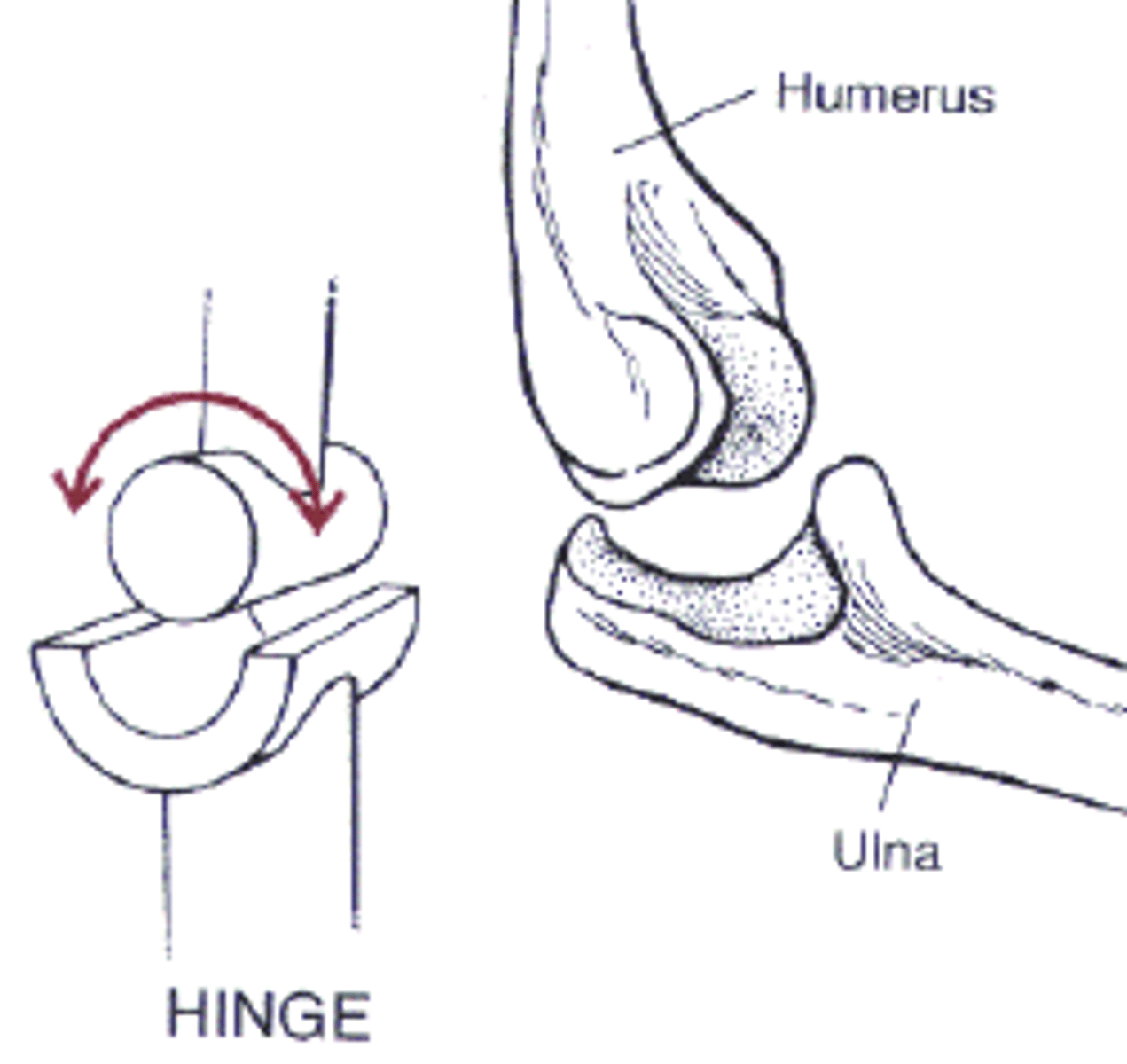
What is a uniaxial joint?
movement in one plane
-pivot joint, hinge joint
ex) elbow
What is a biaxial joint?
movement in two planes ex) knuckle
-saddle joint, condylar joint
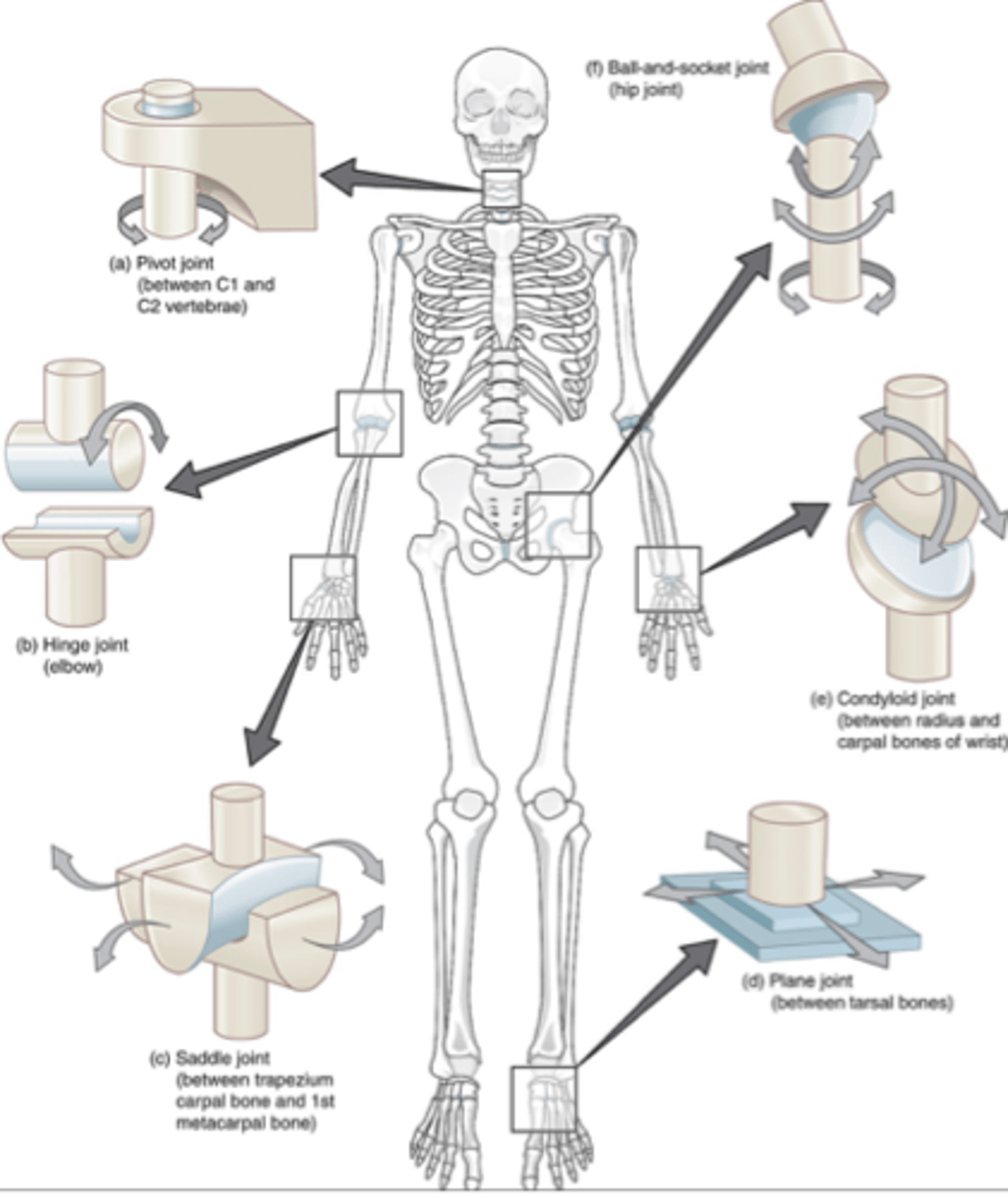
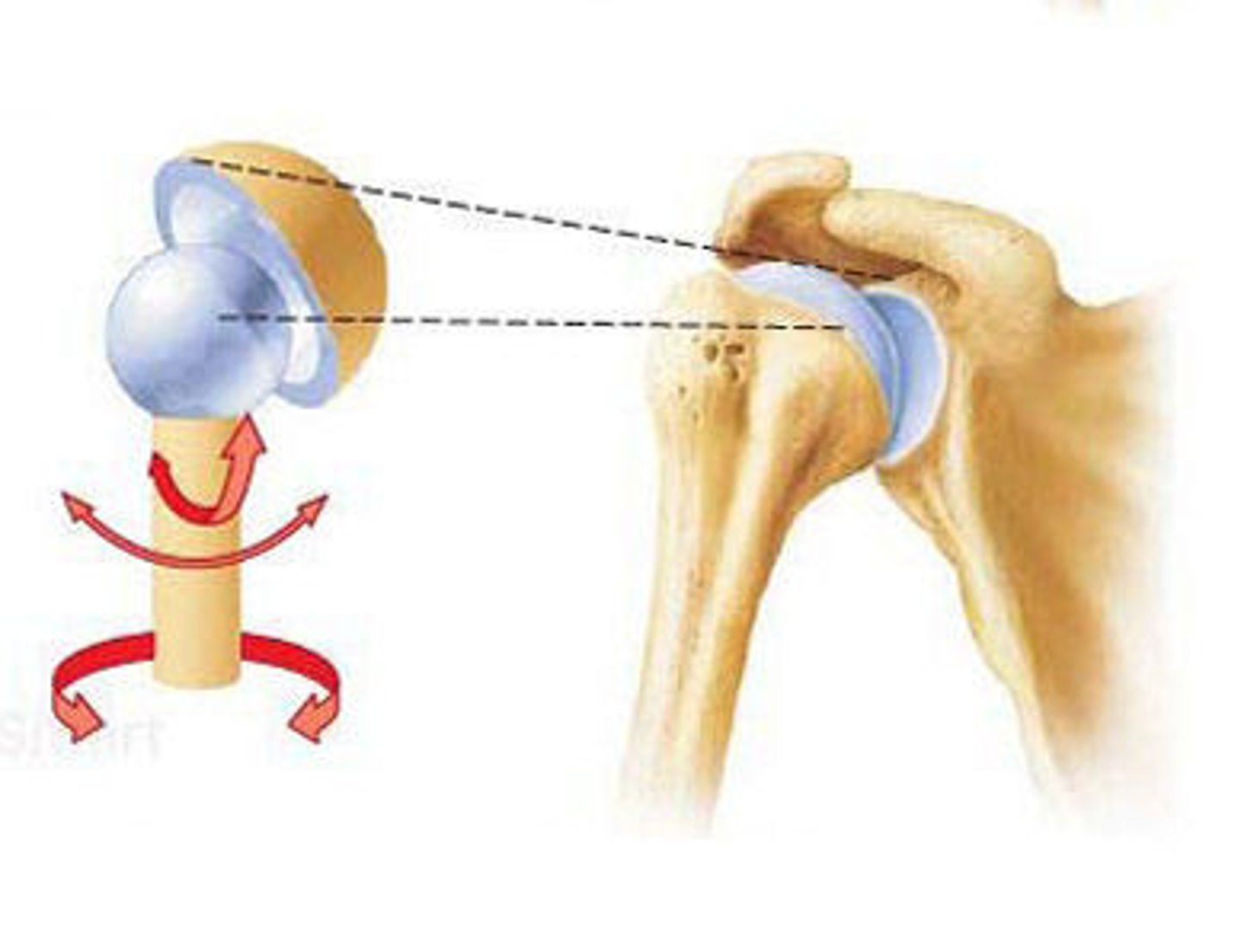
what is a multiaxial joint?
all three planes. shoulder joint has three degrees of freedom or axes of rotation
-ball and socket
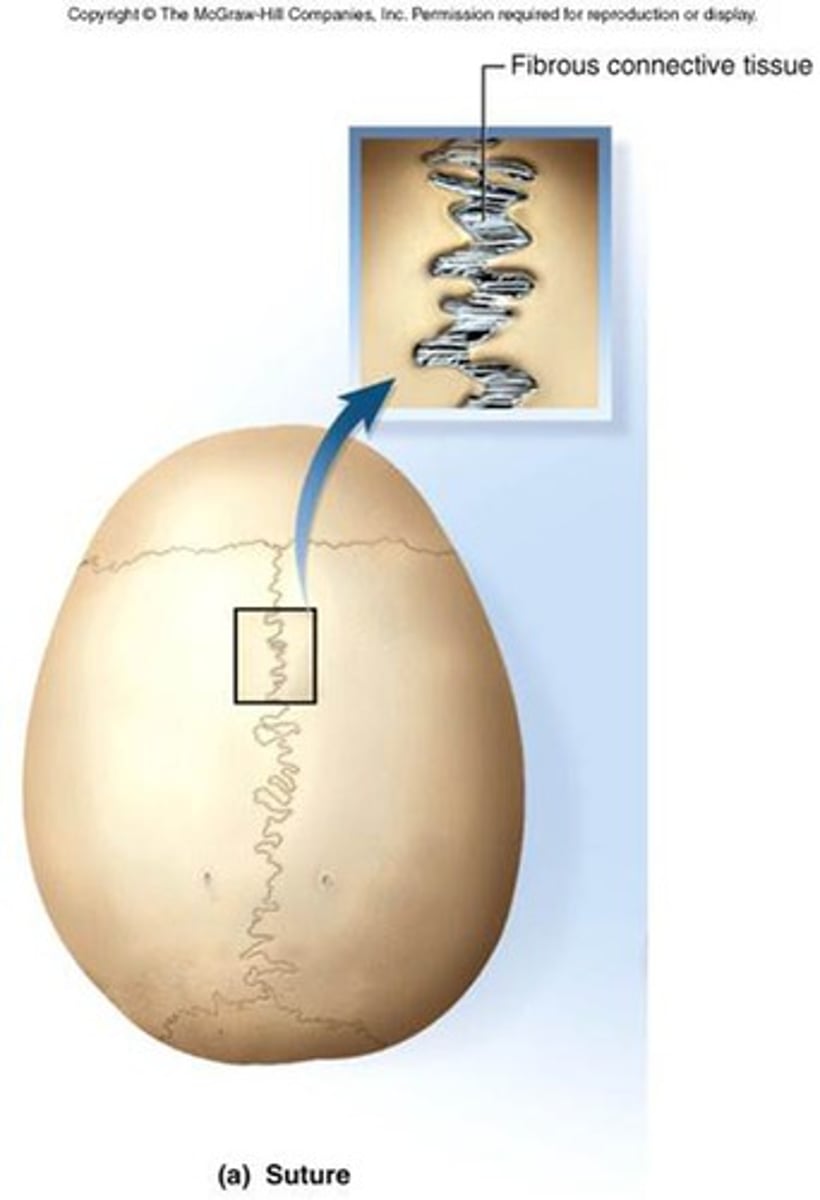
what is a suture
a narrow fibrous joint found between most bones of the skull
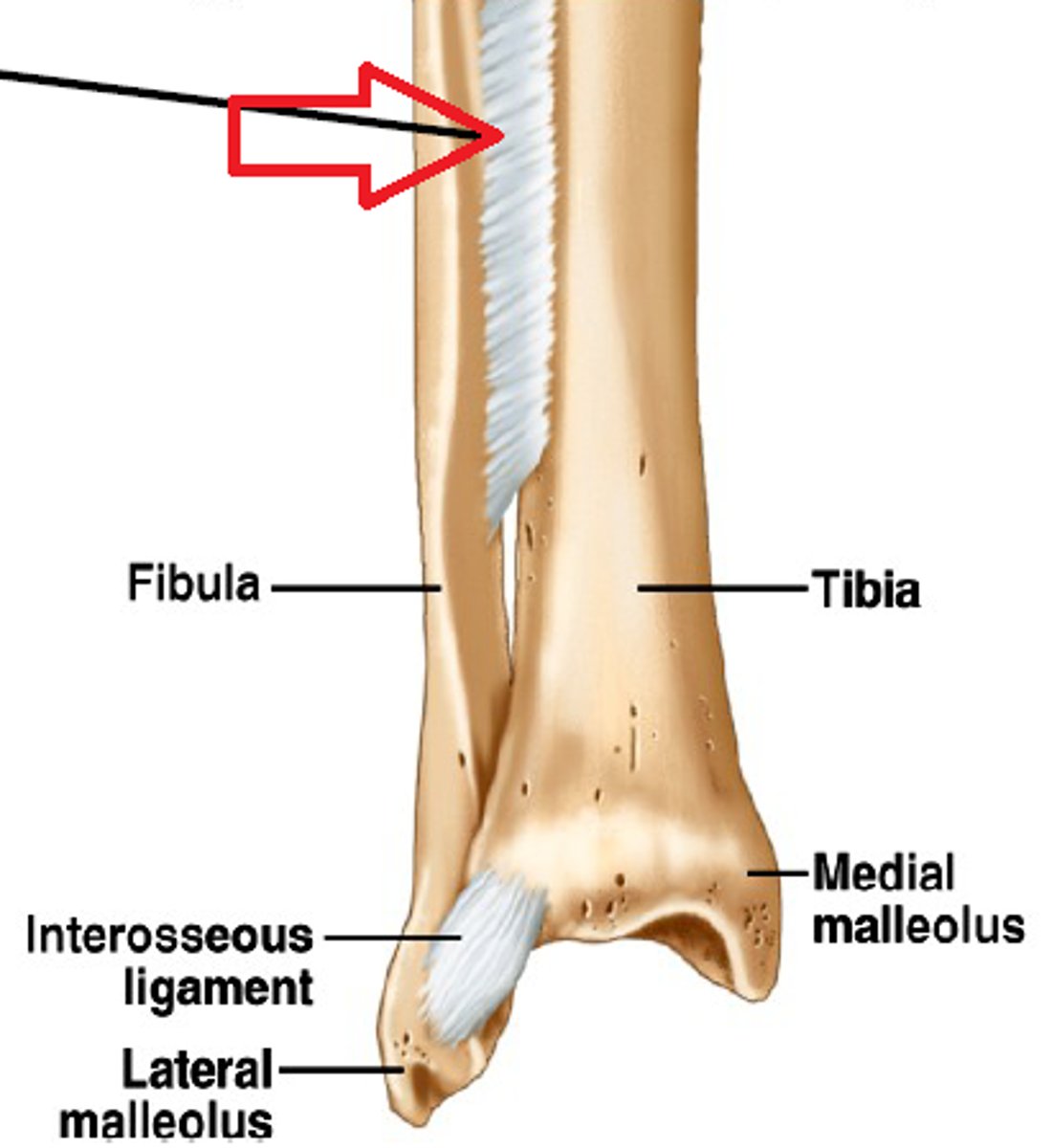
what is syndesmosis
bones widely seperated but held together by narrow band of fibrous CT
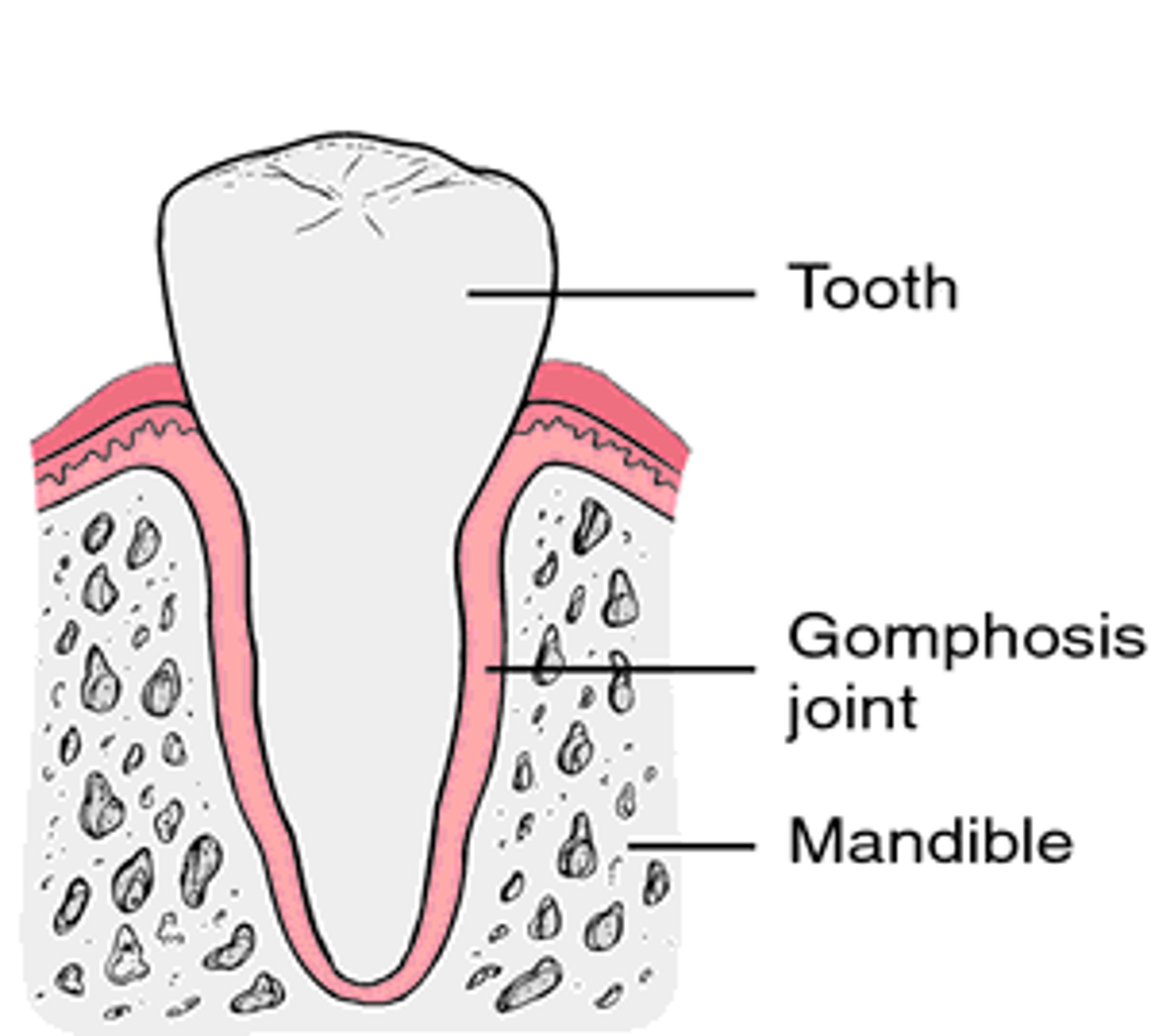
what is gomphosis
narrow fibrous joint between roots of tooth and boney socket in jaw
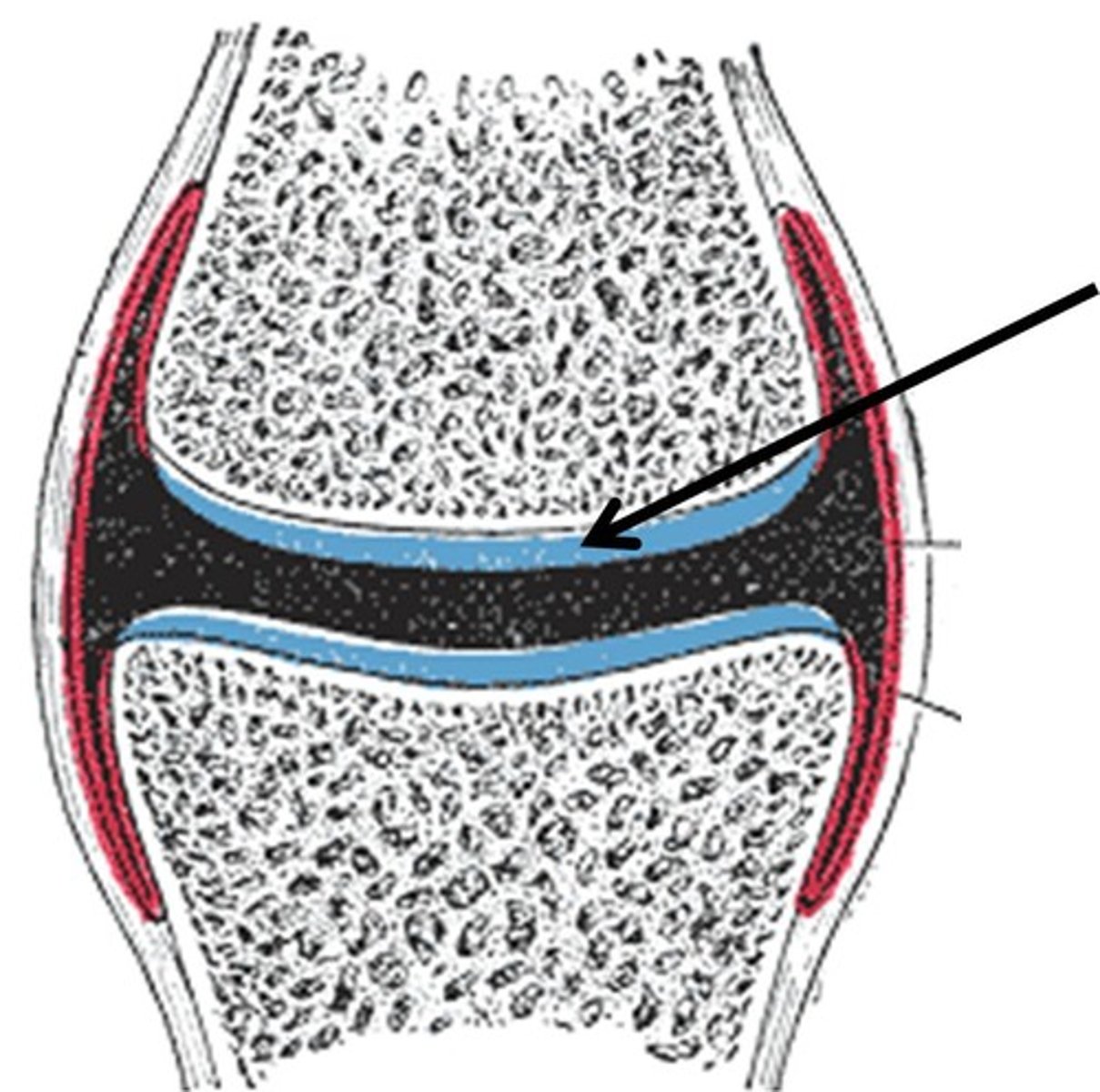
what is a synchrondrosis joint?
it is a cartilage joint where bones are joined by hyaline cartilage
what is a symphysis joint?
it is where bones are joined by fibrocartilage
what is a synovial joint?
most common type in the body, bot seen at fibrous or cartilage joints. it is a fluid filled space which lets bone more freely.
It has articular cartilage which is hyaline cartilage and acts as a shock absorber but is avascular, so will not repair
What are the walls of a synovial joined formed from?
articular capsule which is fibrous CT
what is articular cartilage
it is hyaline cartilage preventing friction
what is a synovial membrane?
it secretes synovial fluid which provides lubrication
what are ligaments?
what bones are also connected by, they are strong bands of dense regular CT. Bones connected to bone
-extrinsic ligament is outside the articular capsule
-intrinsic ligament is inside the articular capsule
-the more ligaments, the stronger and more stable the joint
-inhibits mobility
what is a fat pad
it is what some synovial joints have, it serves as a cushion filling in spaces.
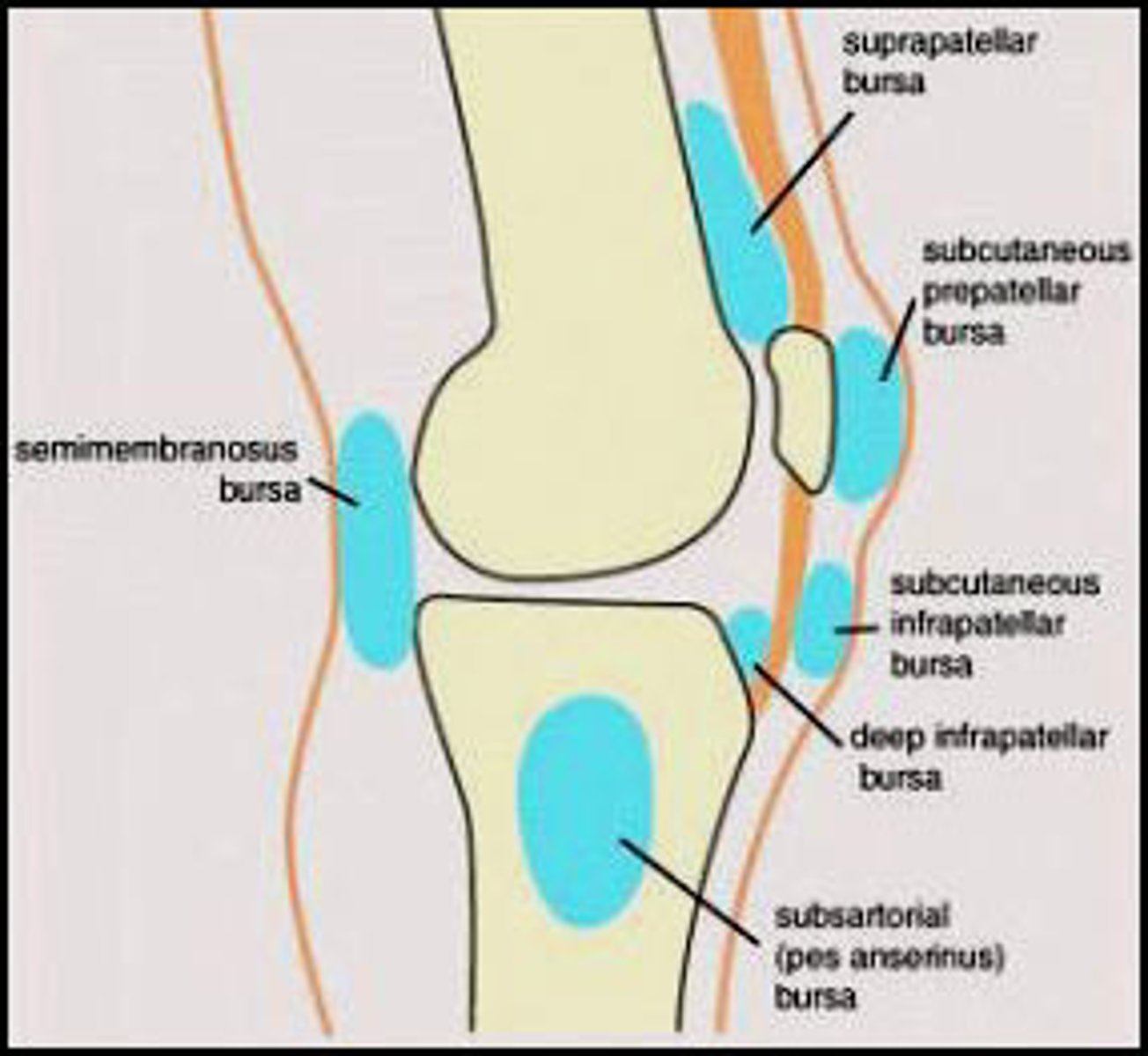
what is a bursae
is it thin CT sac filled with synovial fluid
they reduce friction between tendons passing over JOINTS
what is a tendon sheath
it is an elongated bursae around tendons, reduce friction between tendons passing over BONE
What plane does flexion and extention occur on?
the sagittal (anterior-posterior) plane
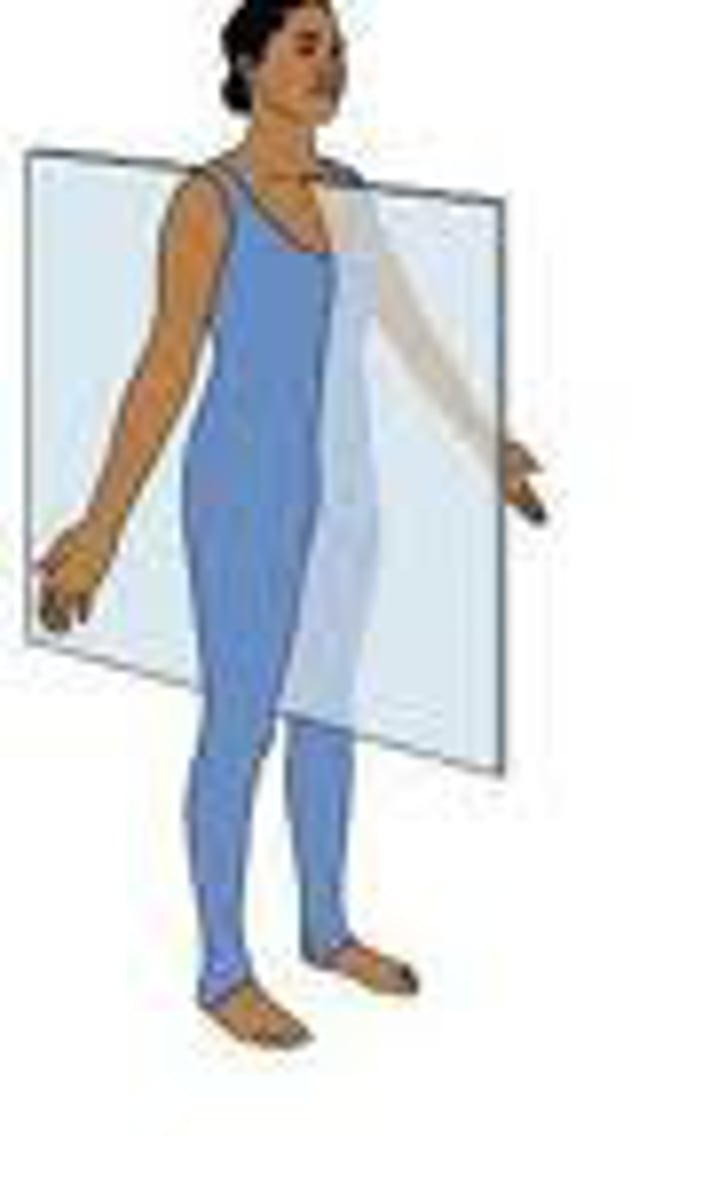
what plane does adduction and abduction occur on?
The coronal (frontal plane)
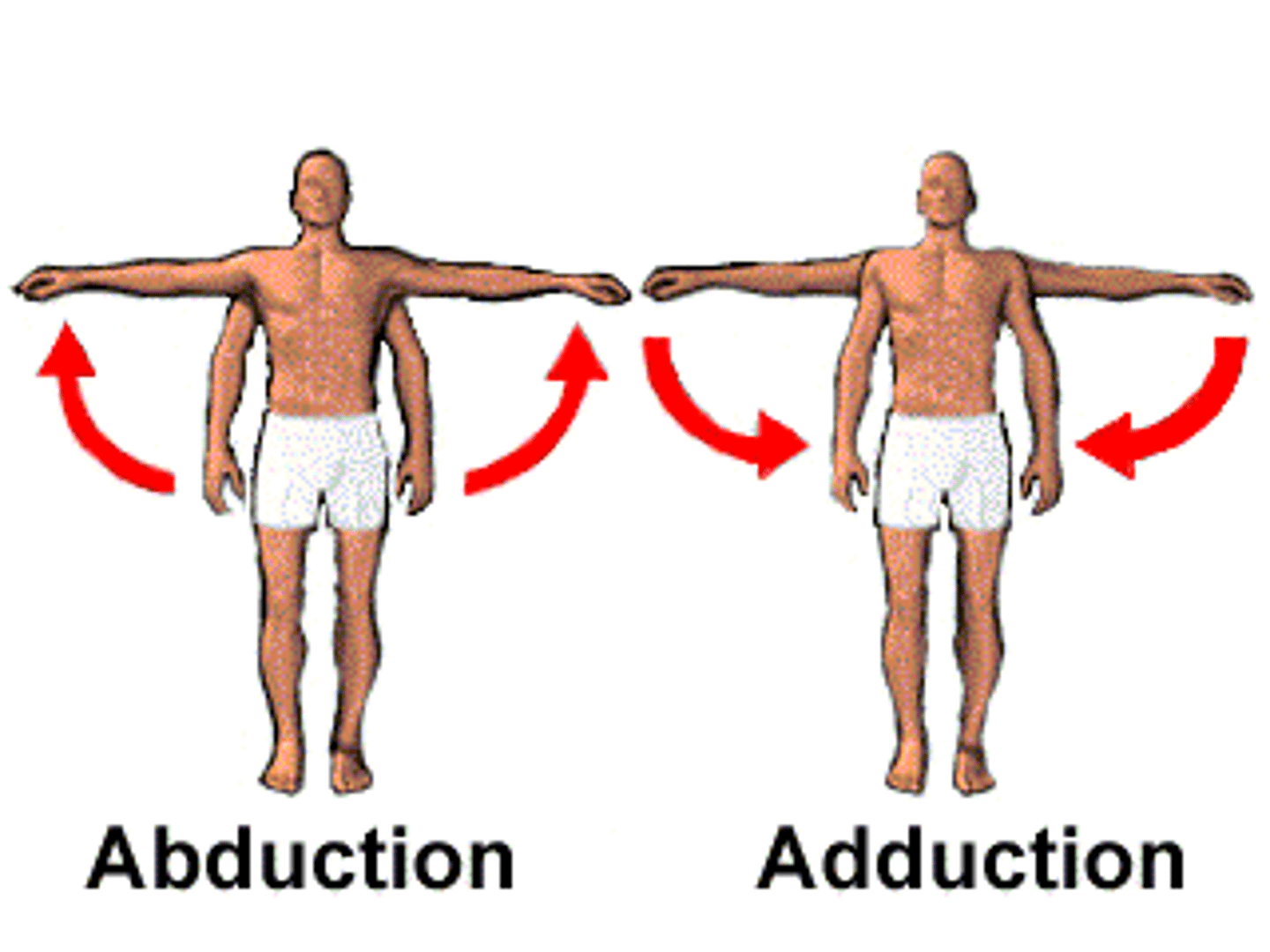
what are factors that influence joint stability?
articular surfaces, ligaments, muscle tone
what are articular surfaces?
shape influences the movements possible and stability
what is muscle tone
it helps stabilize joints by keeping tension on tendons
what are examples of synarthrosis joints?
-some fibrous joints like suture, gomphosis
-some cartilaginous joints like synchondrosis (growth plate)
-NO joint cavity/capsule
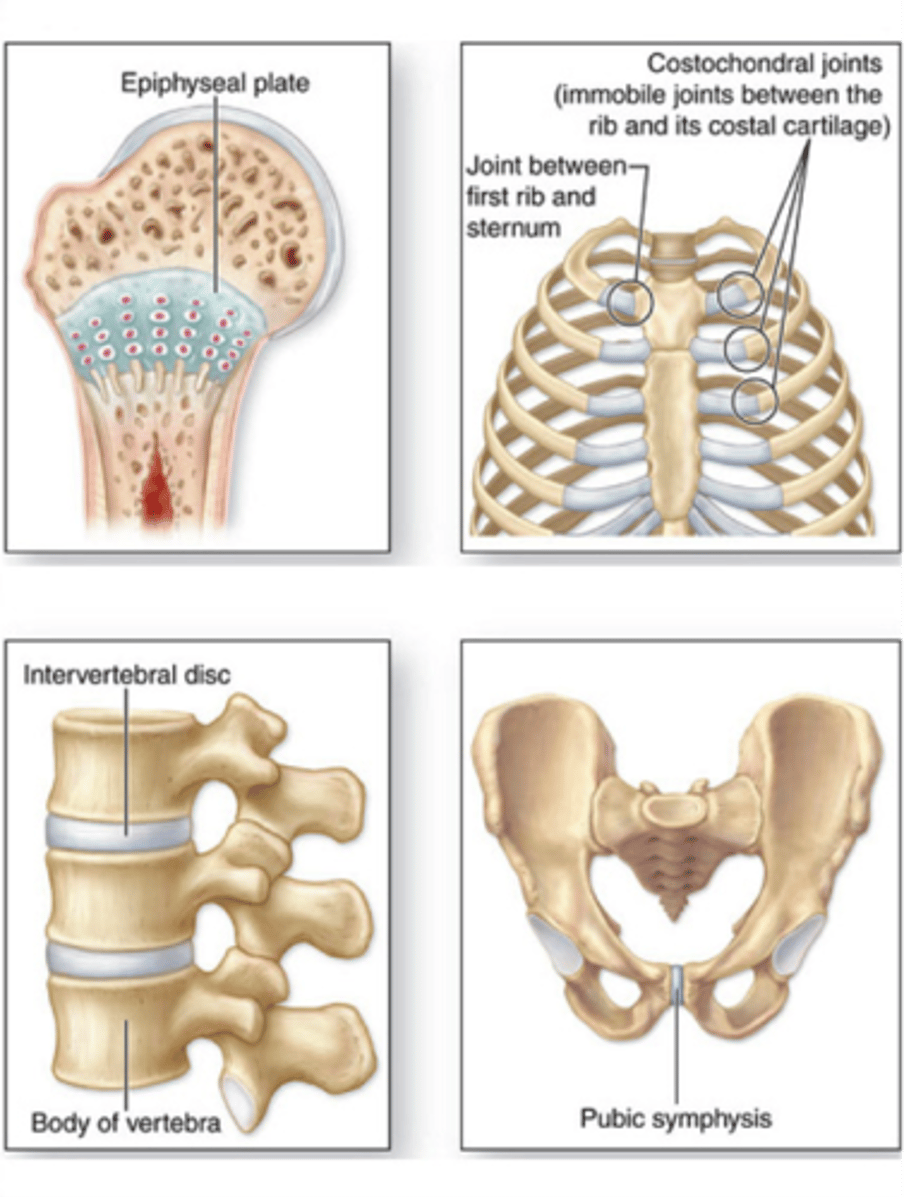
what are examples of amphiarthrosis joints?
-some fibrous joints like syndesmosis
-some cartilaginous joints like symphysis and intervertebral disc
-NO joint cavity, capsule
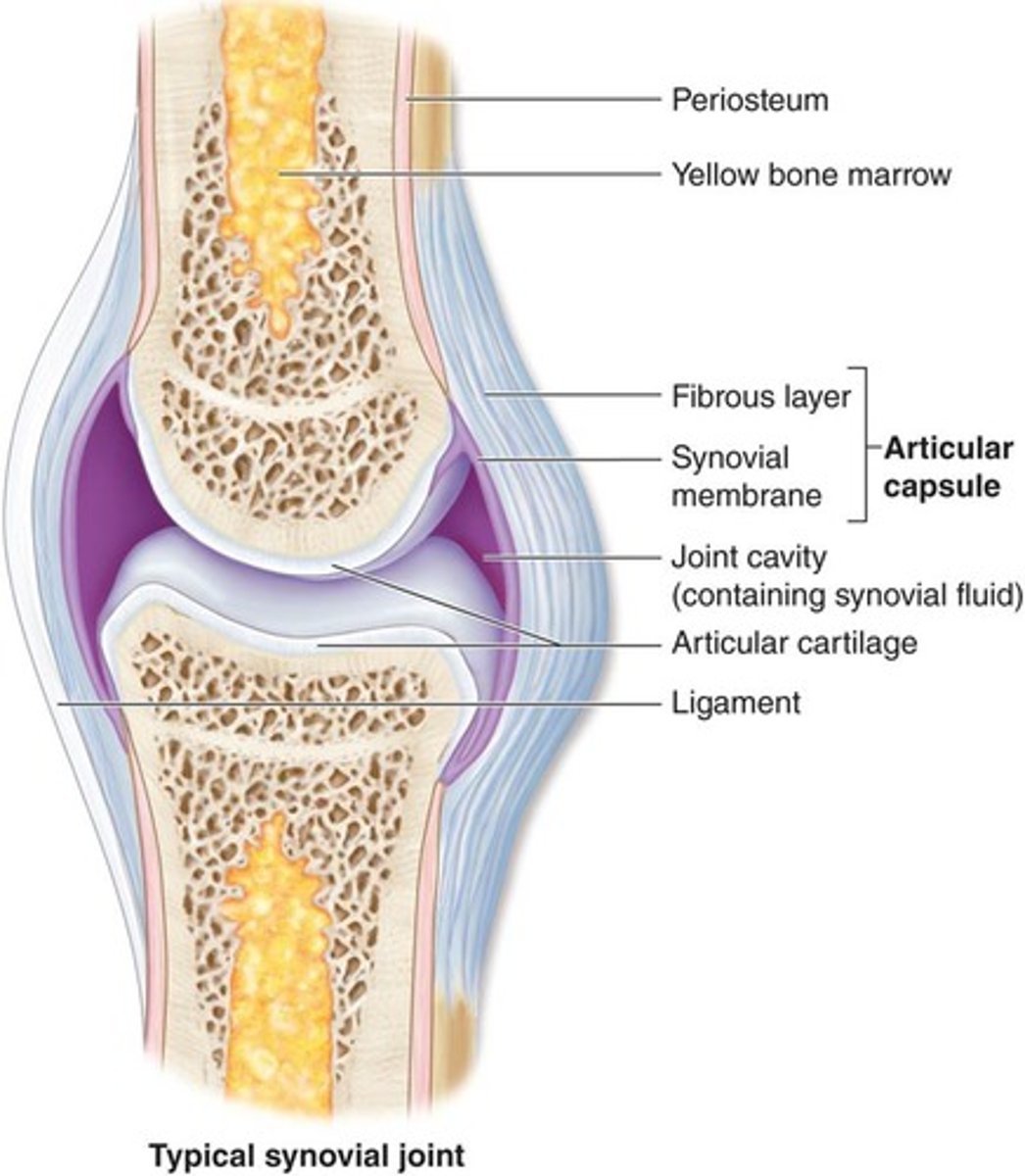
what is the general anatomy of a diarthroses joint?
1. articular capsule which is CT, the most superficial side
2. synovial membrane just deep to articular capsule, secreting synovial fluid that fills the joint cavity
3. joint cavity that has synovial fluid
4. articular cartilage which has poor blood supply so bad if damaged
5. ligaments (intrinsic and extrinsic)
6. nerves and blood vessels
-highly innervated
-blood vessels do not enter into the joint cavity
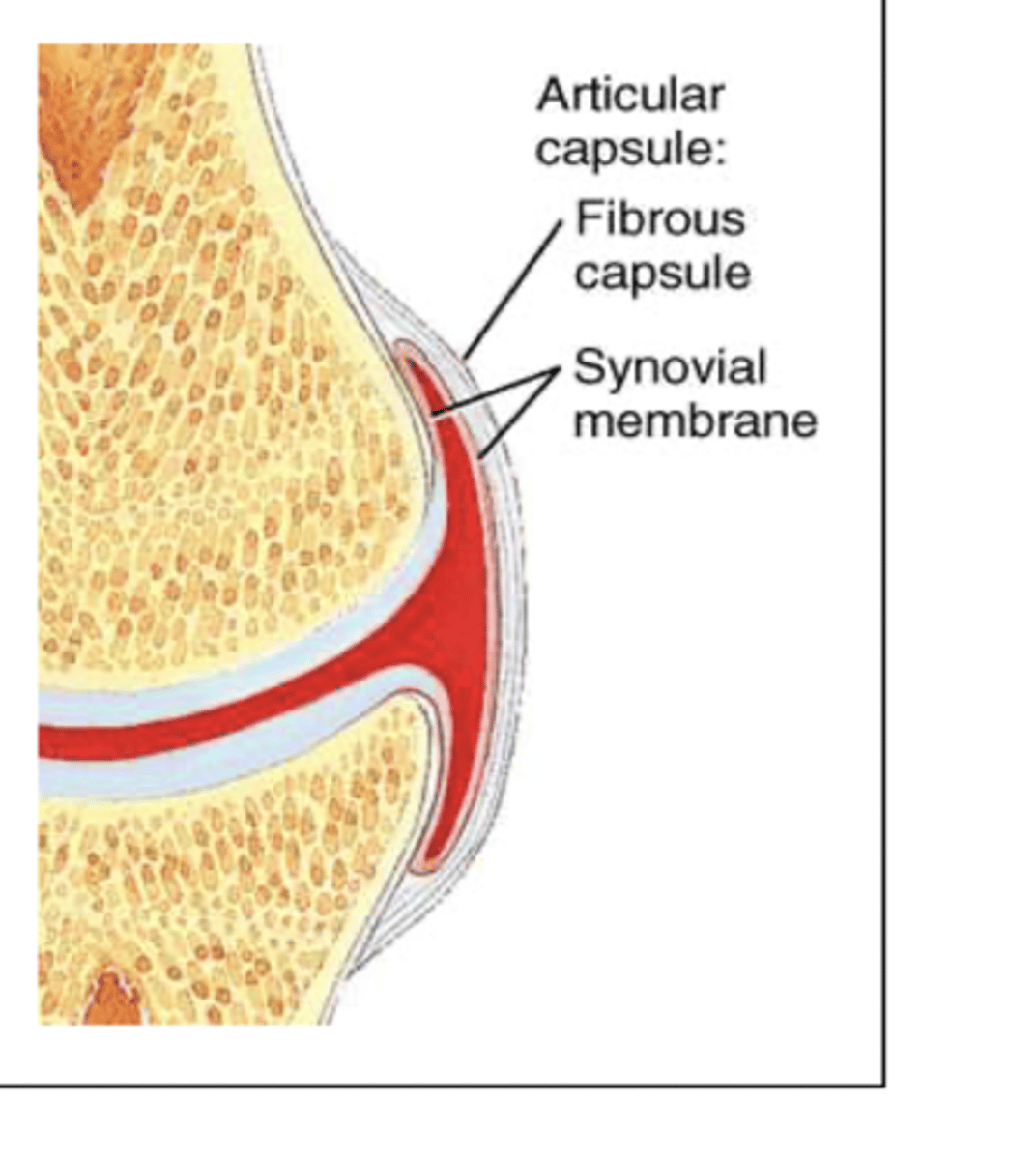
what are the two layers of the synovial joints?
outer fibrous layer made of dense regular CT, providing structural stability
inner synovial membrane that secretes synovial fluid into the joint
What does the joint cavity contain?
synovial fluid which is filtrate of blood which nourishes and lubricates the joint and cartilage
what do synovial joints contain?
sensory nerves that detect pain and moniter how much the capsule is being stretched (mechanoreceptors)
They also have a superficial blood supply from vessels around the joint, they mostly just supply the synovial membrane because it is the metabolically active tissue that secretes the fluid
what are articular disks in the synovial joint?
they are present in some synovial joints like menisci of knee and wrist and occur in joints with articulating bones of different shapes
what axis does the coronal plane correspond with?
anteroposterior axis
what axis does the sagittal plane correspond with?
transverse axis
what axis does the transverse plane correspond with
vertical axis
what are the movements of synovial joints?
gliding, angular movements, rotation, special movements
what are gliding motions
occurs in plane joints
what are angular motions
flexion, extension, abduction (alien, away), adduction (add to the midline of the body), circumduction
what are rotational motions
medial-lateral rotation (toward midline-away)
supination (palm up, holding soup) -pronation
what are special movements?
depression, elevation,
dorsiflexion, plantar flexion,
inversion, eversion,
protraction, retraction
,opposition, reposition