L4 - The role of oxygen and sulphur in drug molecules
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
what happens to the lone pair of electrons on oxygen atoms due to the higher electronegativity
its less likely to be protonated that those on a nitrogen atom
oxygen an its orbital hybrids
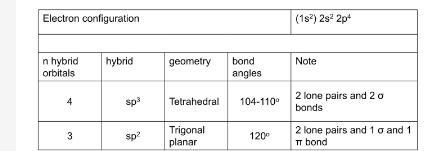
how can biological activity be lost
with the loss of an amino group
does a loss of alcohol function negate biological activity
no
why does a loss of alcohol function not negate biological activity whereas the loss of an amino group does result in loss of biological activity
a loss of alchol means that the molecule might still be active even thoguh it is weaker, yet a loss of amino group abolishes biological activity beccause it destroys key binding interactions
oh groups are polar and can form hydrogen bonds and bond to water and protiens, but its not essensial for binding to a receptor or enzyme. even if lost, it could still fit in using van der waals or hydrophobic forces, while amino groups are ONLY required for biological activity as they are key essensial pharmacophores.
why are ethers less polar than alcohols
no hydrogen bond doner
what are cyclic ethers known as
epoxides
why are 3 memebered ring epoxides highly reactive
due to torsional strain
why are aldehydes less commonlyly found in drug molecules
due to their higher reactivity towards nucleophiles
why are carboxylic acids so acidic
due to the effecient resonance of the negative charge of the carboxylate anions
how can electronic effects affect the acidity of carboxylic acids
electron withdrawing groups increase acidity by charge delocalisation
electron donating groups decrease acidicity by charge localisation
how can hydrogen bonding affect acidicity
hydrogen bonding contributes to the charge delocalisation of the conjugate base of salicliyic acid.
what can increase the aqeous solubility of drugs with carboxylic functions
formation of salts with alkali, its limited by the size and lipophilicity of thte carboxylate anion
why are thiols more acidic than alcohols
the larger sulphur atom is better at delocalising charge than oxygen
how do thiols form -s-s- bridges
by cysteine residues