Human Anatomy
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam #1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
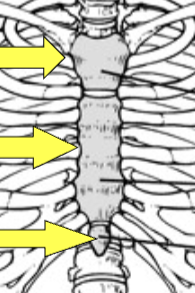
Name the 3 sections of this bone
Sternum -
Manubrium
Gladiolous
Xiphoid
What is an organ made up of?
2+ tissue
Anterior
Towards the front
Posterior / Dorsal
Towards the back
Medial
close to the midline
Lateral
Away from the midline
Superior ( Rostral)
Towards the head
Inferior (Caudle)
Towards the feet
Superficial
close to surface
Deep
Beneath surface
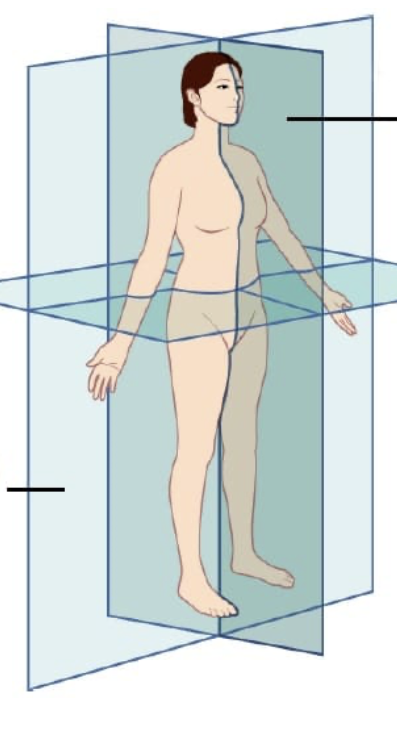
What are the different planes
Coronal, Transverse, Midsagital, Sagital/Parasagital
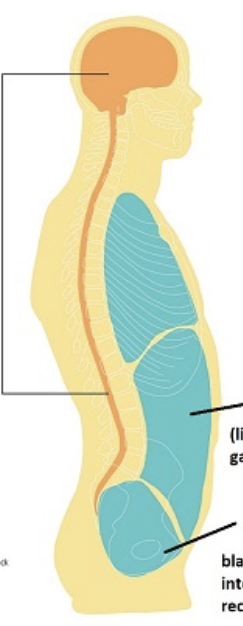
What are the names of these cavities
Dorsal - Brain and Spine
Ventral - All other main organs
Thoracic Cavity
Lungs
Diaphragm
Seperates the lungs and the abdomen
Pericardial Cavity
Houses the Heart
Abdominopelvic cavity
Houses the Stomach
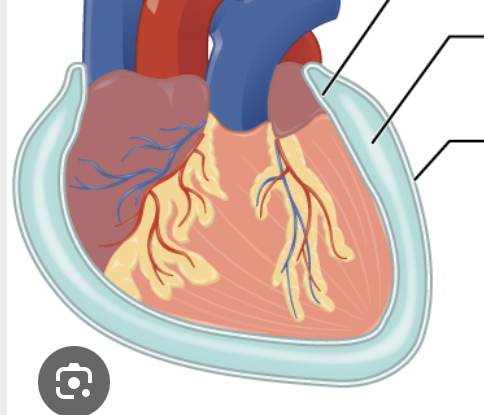
What are the 3 serous membranes
Serous cavity - filled with fluid
Parietal layer - touches body wall on outside
Visceral layer - touches organ inside
What are the (3) types of serous membranes
Pericardial - Heart
Pleural - Lungs
Peritoneum - Guts
Retroperitineal vs intraperitineal
Retropiritineal - In the cavity but not in the parietal peritoneum (ex. Kidneys)
Intraperitineal - Inside of the parietal peritoneum
Head
Caput / Cranial Region
Neck
Cervical Region
Chest
Thorax
Armpit
Axillary region
Lower back
Lumbar region
Belly Button
Umbilical
What might a dark spot around belly button mean
Cullens sign - Potential bleeding
Pelvic Region
Perineal Region
Below Lumbar region
Sacral Region
Natal Cleft
Seperate Glutes
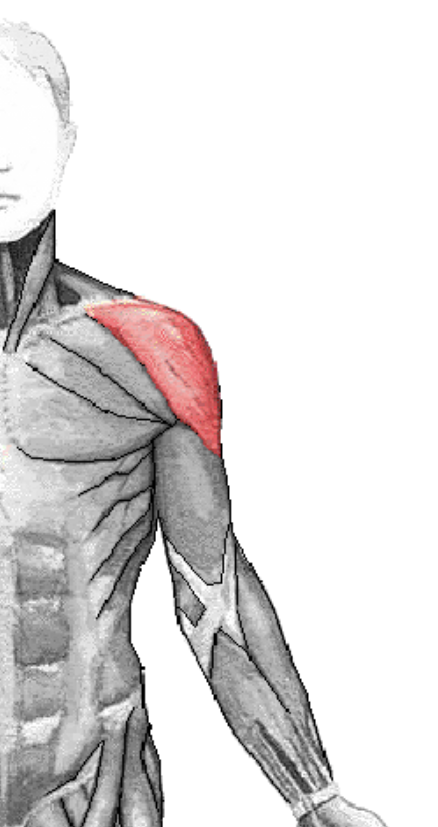
Deltoid Region - site of intramuscular injections
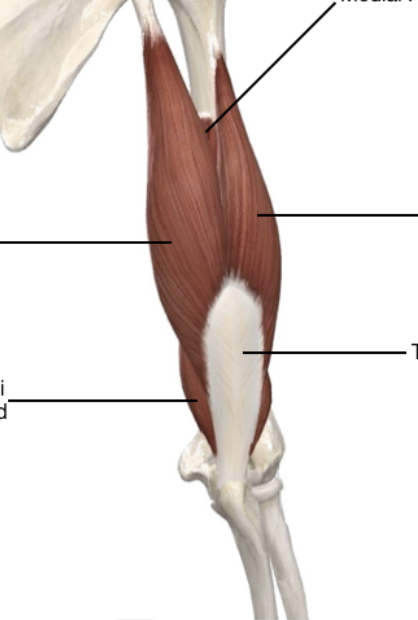
Brachium Region
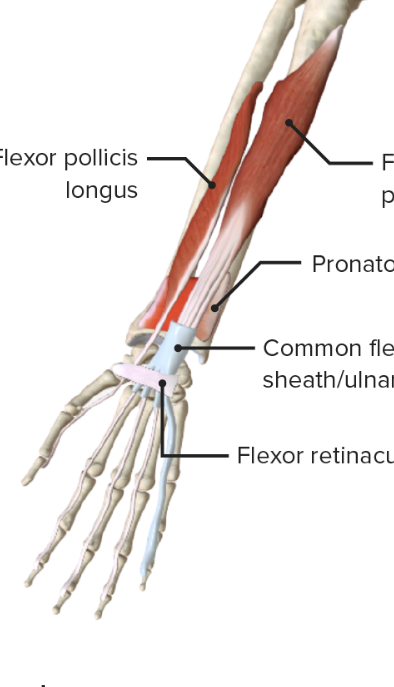
Antebrachium Region
Back of hand
Dorsum of the hand
Palm
Palmar region
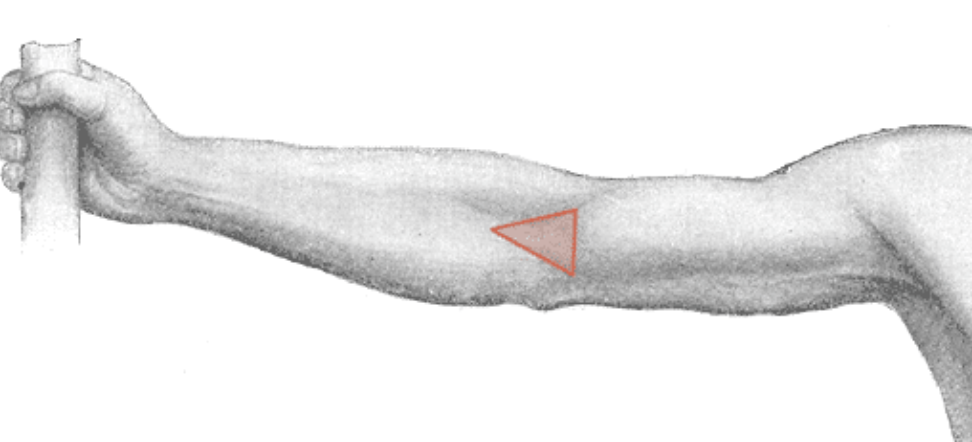
Cubital Fossa
Toes and fingers
digits
Thigh
Femoral Region
Calf
Crural Region
Foot
Pes
Hand
Manus
Knee
Patellar Region
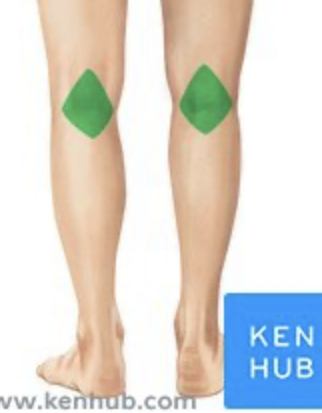
Popliteal Fossa
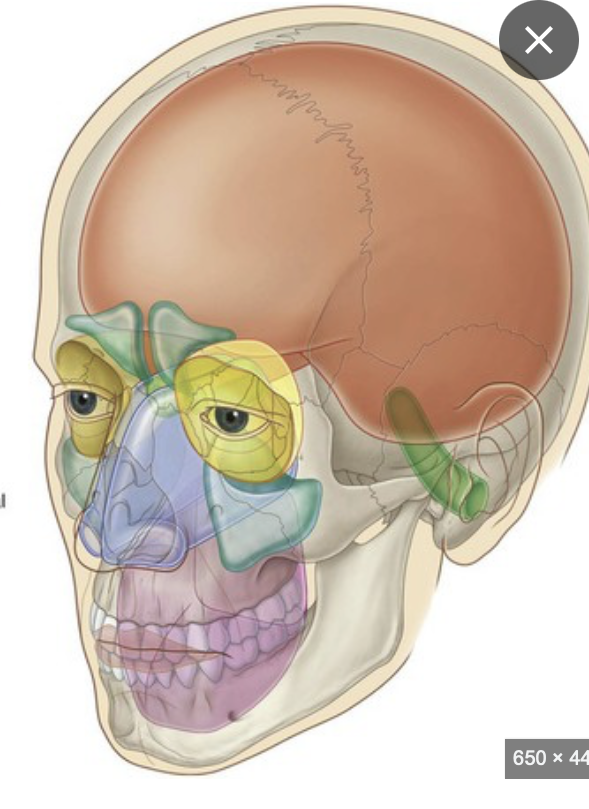
Name these cavities
Orbital Cavity - Eyes
Nasal Cavity - Nose
Cranial Cavity - Brain
Oral Cavity - Mouth
Middle Ear Cavity
Peritoneal Lavage
Detects trauma to abdominal organs within the peritoneal - done by removing fluid
Functions of the integumentary System (6)
Protection
Prevention of Water loss
Temp regulation
Metabolic Regulation
Sensory Reception
Excretion by means of sercretion (sweating)
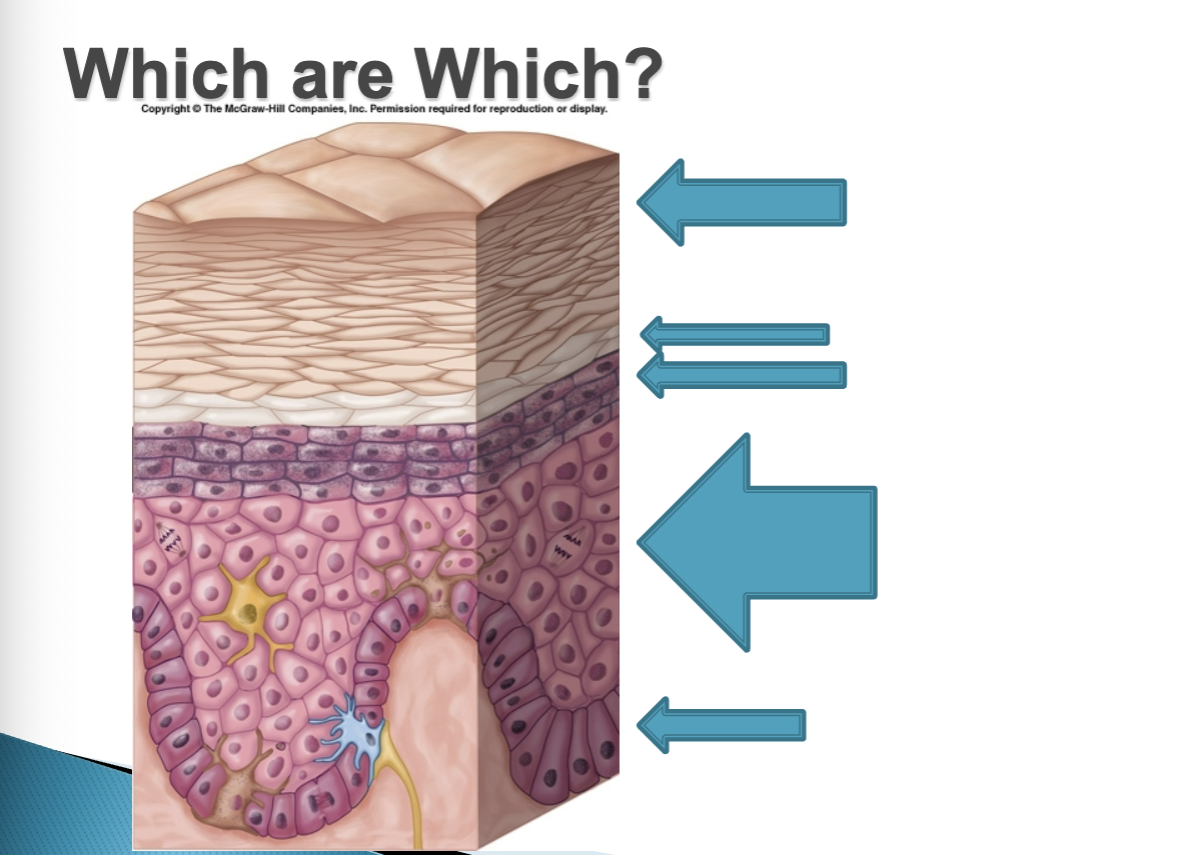
What are the layers of the skin (superficial to deep)
Epidermis → Dermis → Hypodermis
What are the 5 Layers of the epidermis (Deepest to most superficial)
Stratum Basale → Stratum Spinosum → Stratum Granulosum → Stratum Lucidum (only on palms, soles, and lips) → Stratum Corneum
Keratinocytes
Skin cell
Melanocytes
pigment cells
Tactile (Merkel) Cells
Cells that are sensitive to touch
Epidermal Dendritic Cells
Phagocytic cells (cells that swallow other cells for cleaning)
Stratum Basale
Single Cell layer
Contains pigmented Melanocytes (skin color)
Living, reproducing cells (mitotically active)
Contains : Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, and Teactile (Merkel) Cells
Stratum Spinosum
Serveral layers thick
Small mitotic activity
Sharp edged cells
Contains - Keratinocytes & Epidermal Dendritic Cells
Stratum Granulosum
3-5 cell layers thick
Keratinocytes begin to die (fills with keratin which waterproofs skin)
Stratum Lucidum
Only in palms, soles of feet, and lips
Transparent
Flat dead keratinocytes
Stratum Corneum
20-3- cell layers thick
Outside layer
Flake off continually
Dead keratinocytes
Come Let’s Get Sun Burnt!
Hand water wrinkles
occurs from osmosis
What is the purpose of perspiration (sweating)
Cools down body by trying to evaporate water
Vasodilation
Heat expands blood vessels - brings blood to surface to cool it down ( when face goes pink)
Vasoconstriction
Blood vessels constrict when cold
What is synthesized by skin? UV light necessary
Vitamin D
Rickets disease
Bones are soft and bow due to lack of UV light and Vitamin D