Honors Algebra 2 Final Review
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
polynomials
an expression of more than 2 algebraic terms.
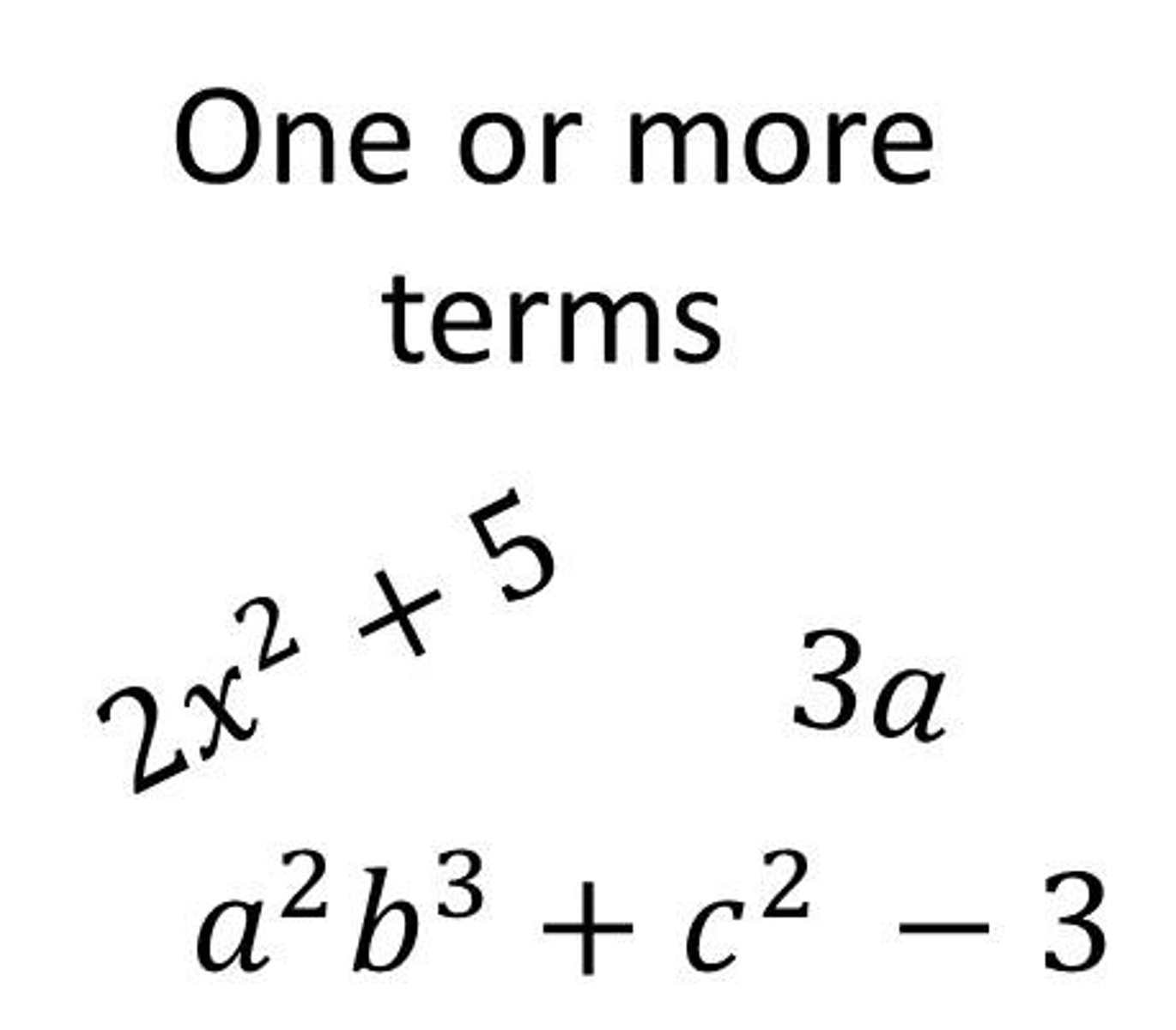
square a number
...to multiply a number by itself or to raise it to the power of 2
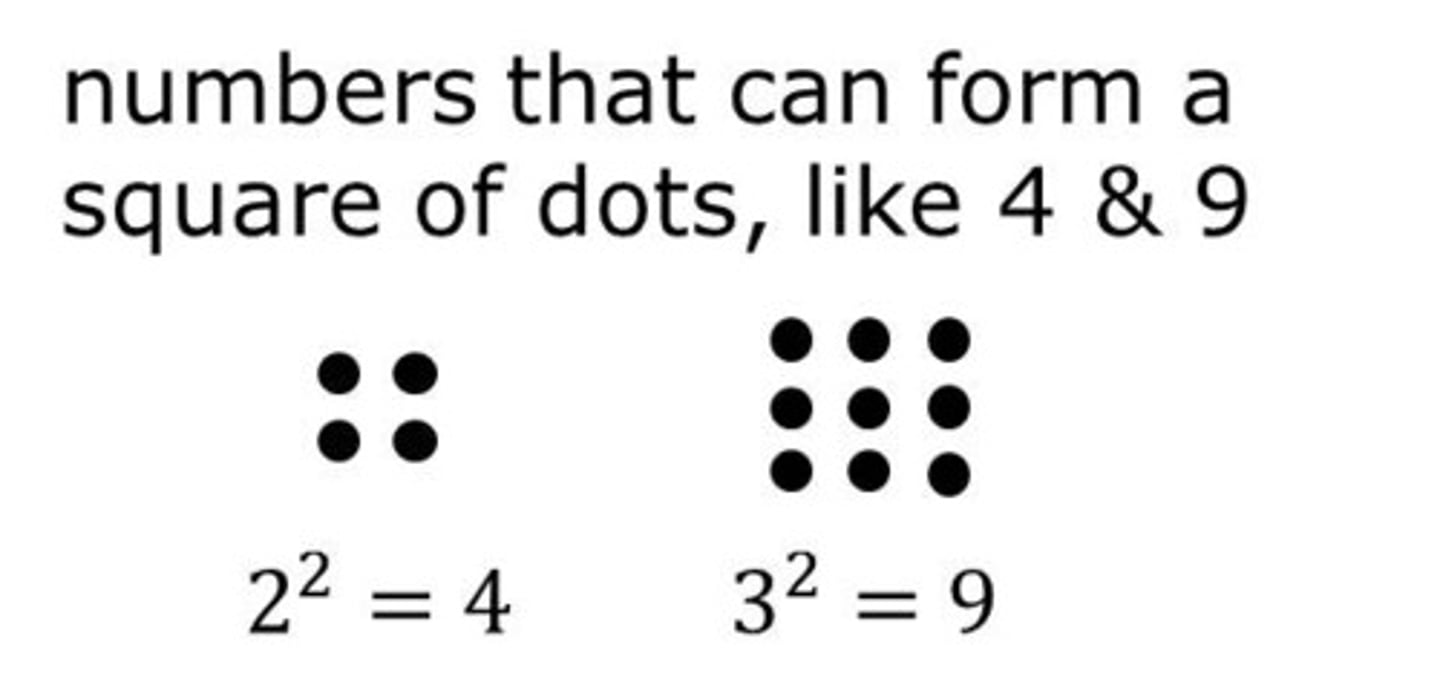
first difference
Values obtained by subtracting each term in a sequence from its successive term.
second difference
Differences that are found by subtracting consecutive first differences from one another.
quadratic equation
is an equation that can be written in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a is not zero.
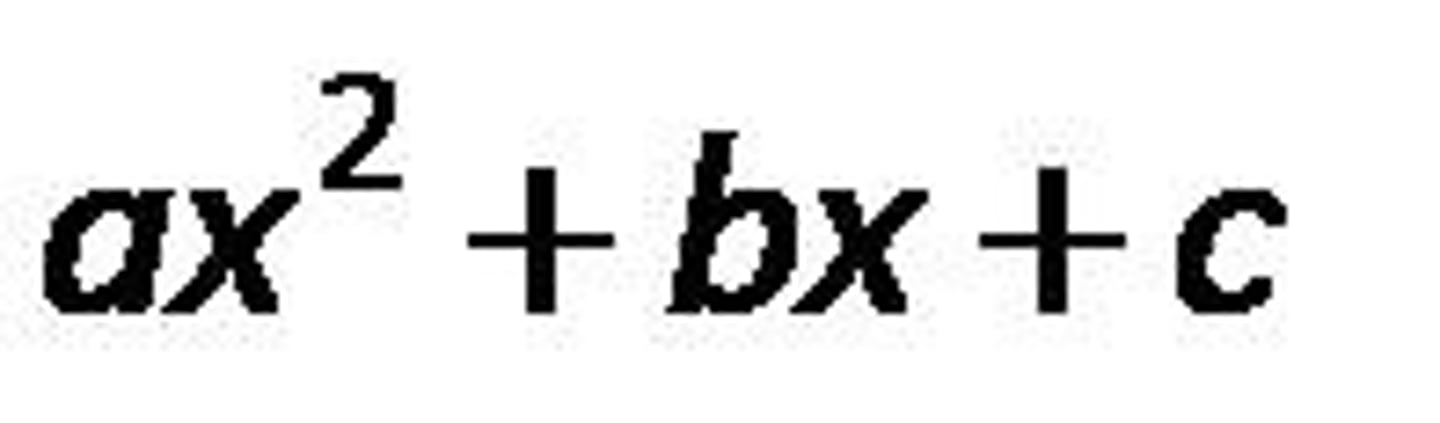
Numerical Expression
An expression that contains only numbers and operations
Monomial
1 term
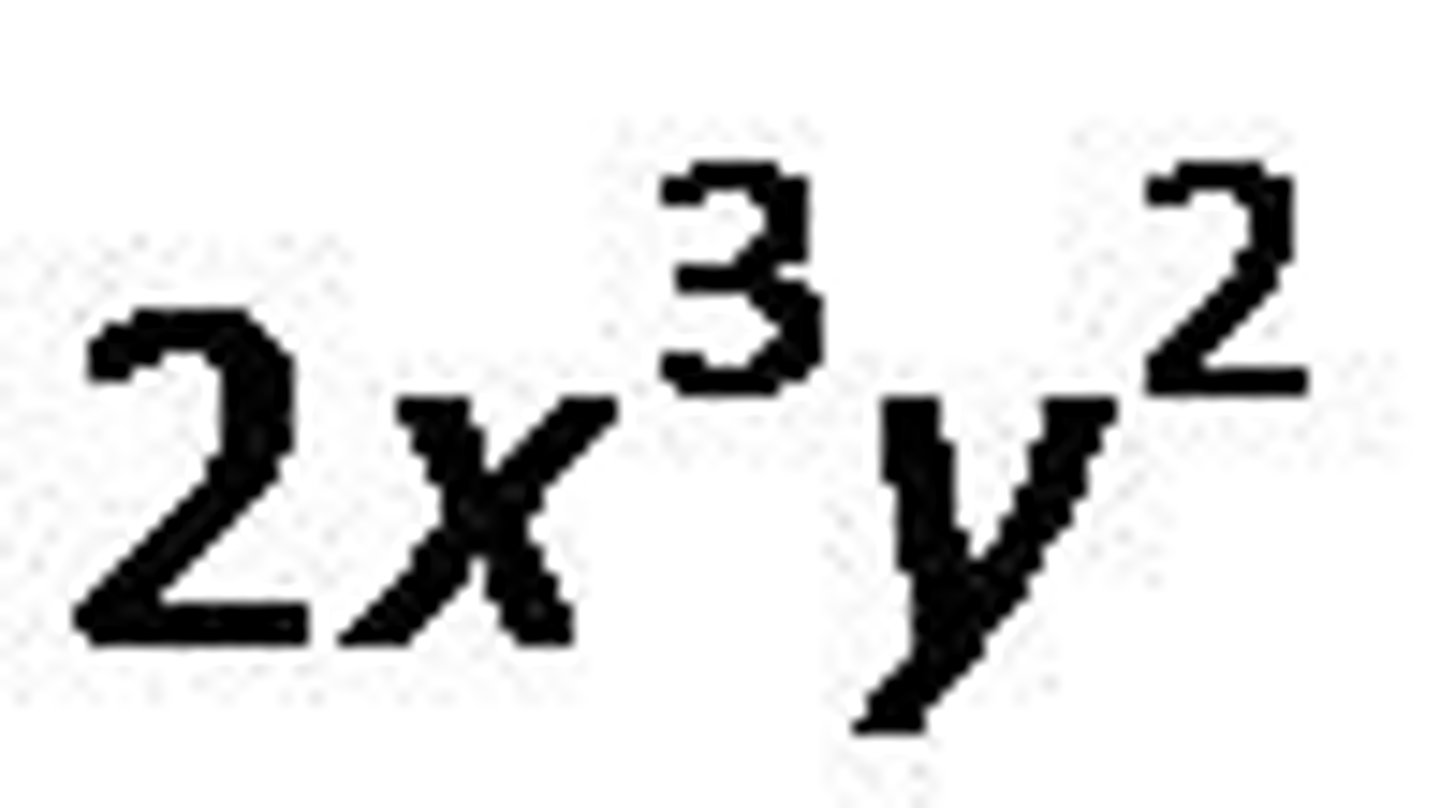
binomials
A polynomial with two terms.
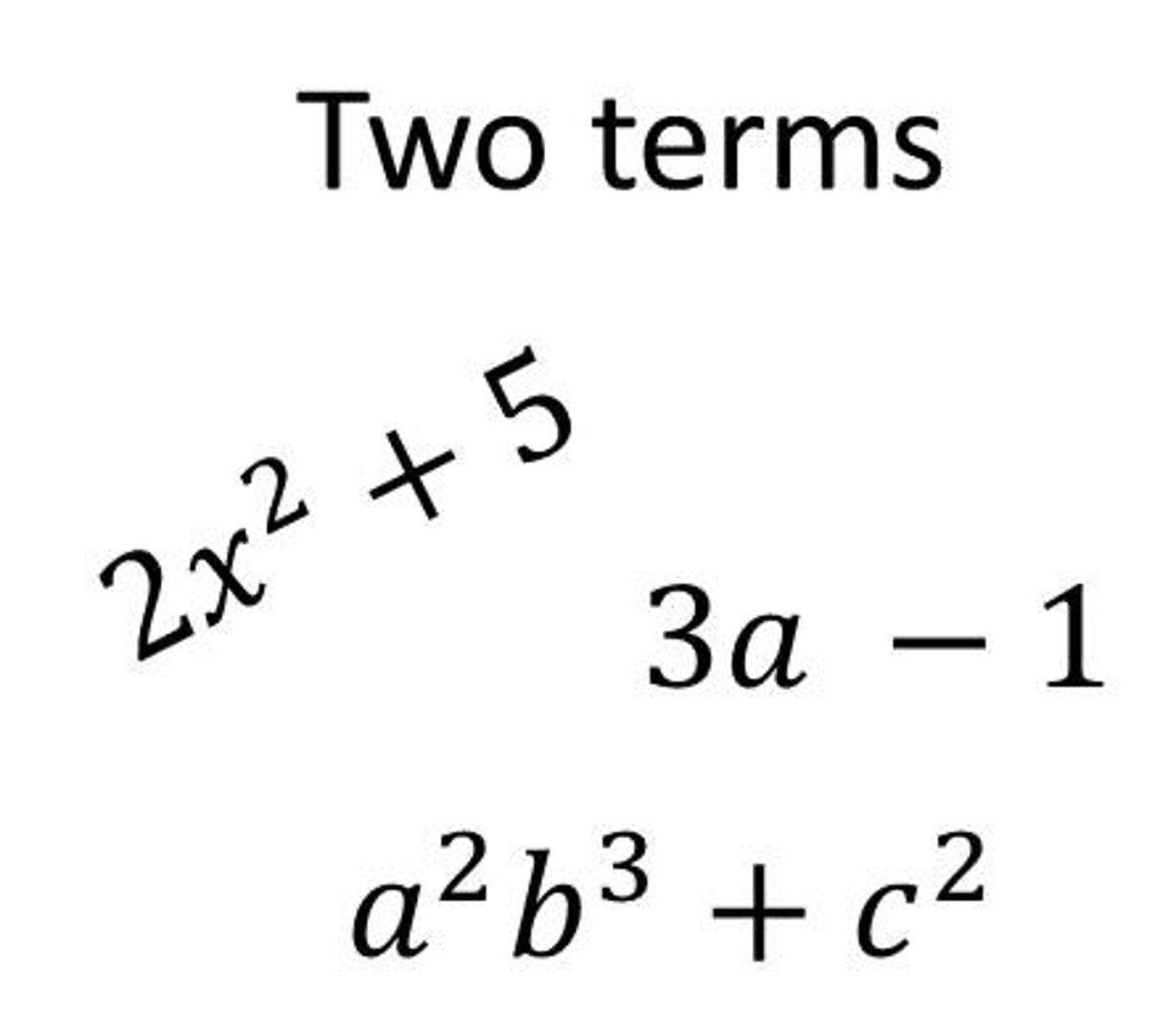
polynomial expressions
2,3, or more unlike terms combined by a addition and or subtraction sign
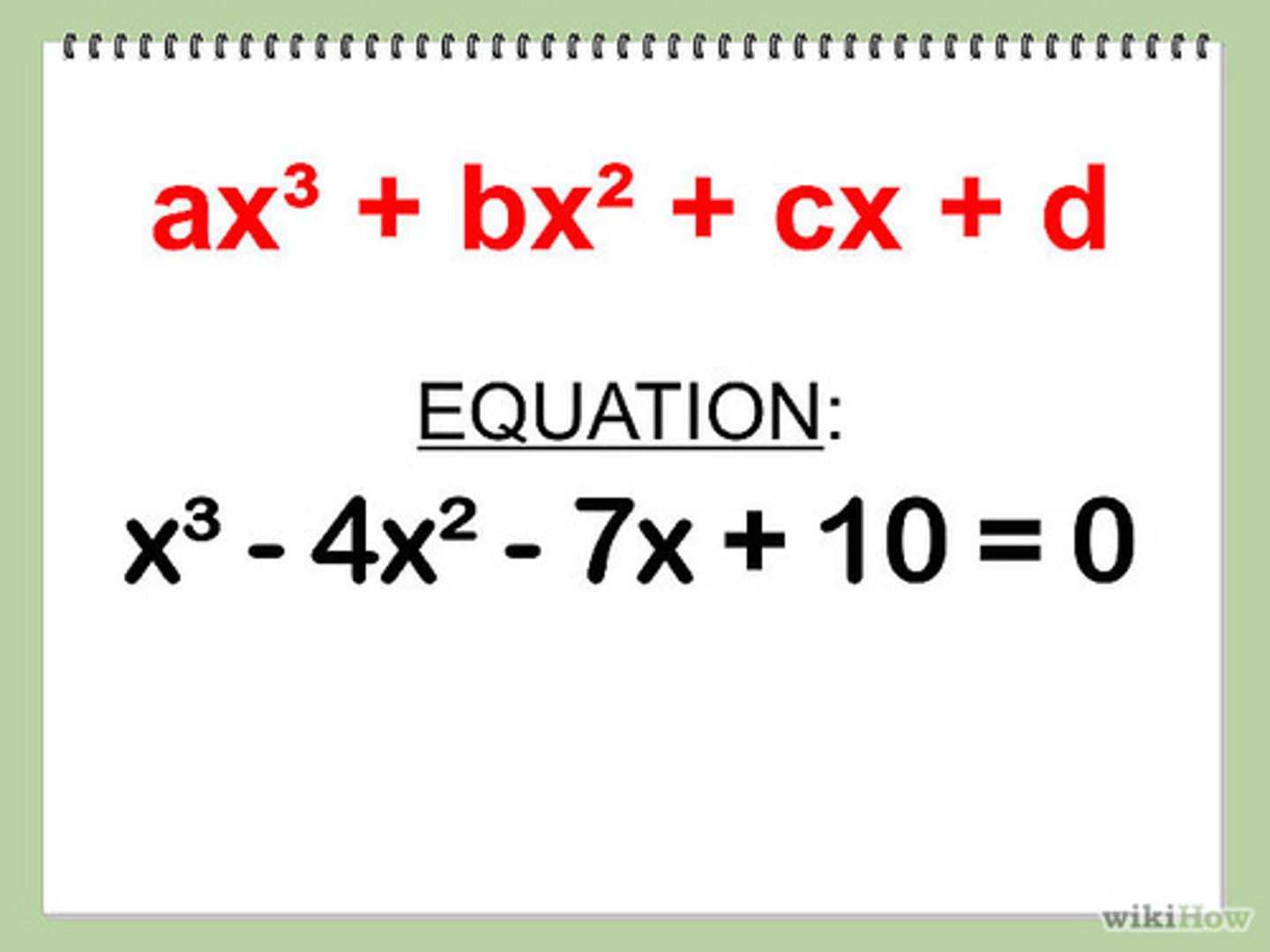
polynomial identity
A polynomial identity is a statement that two polynomial expressions are equivalent. For example, (x+3)^2=x^2+6x+9 for any real number x is a polynomial identity.
Coefficient of a monomial
The coefficient of a monomial is the value of the numerical expression found by substituting the number 1 into all the variable symbols in the monomial. The coefficient of 3x^2 is 3, and the coefficient of the monomial (3xyz)⋅4 is 12.
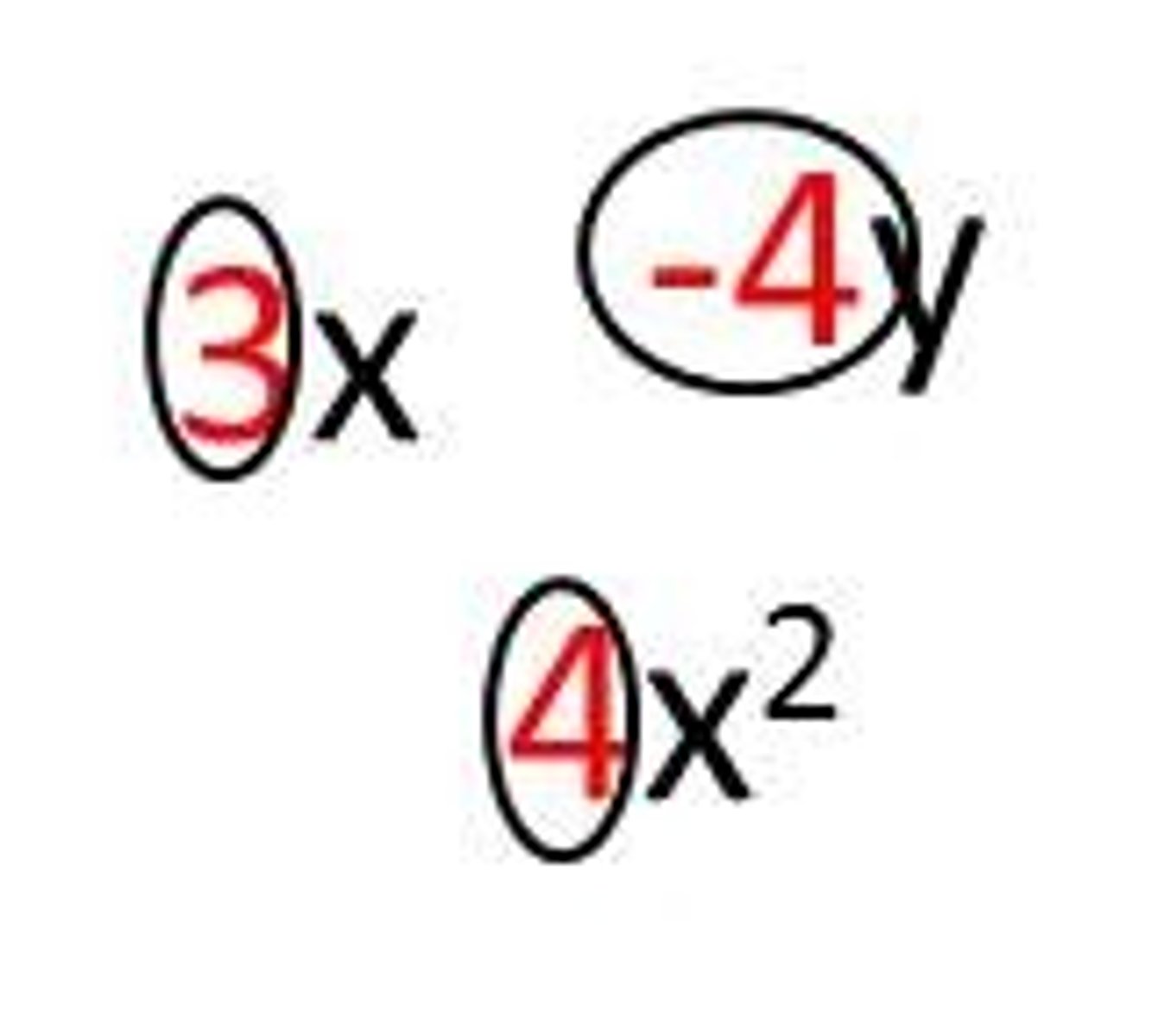
like terms of a polynomial
Two terms of a polynomial that have the same variable symbols each raised to the same power are called like terms.
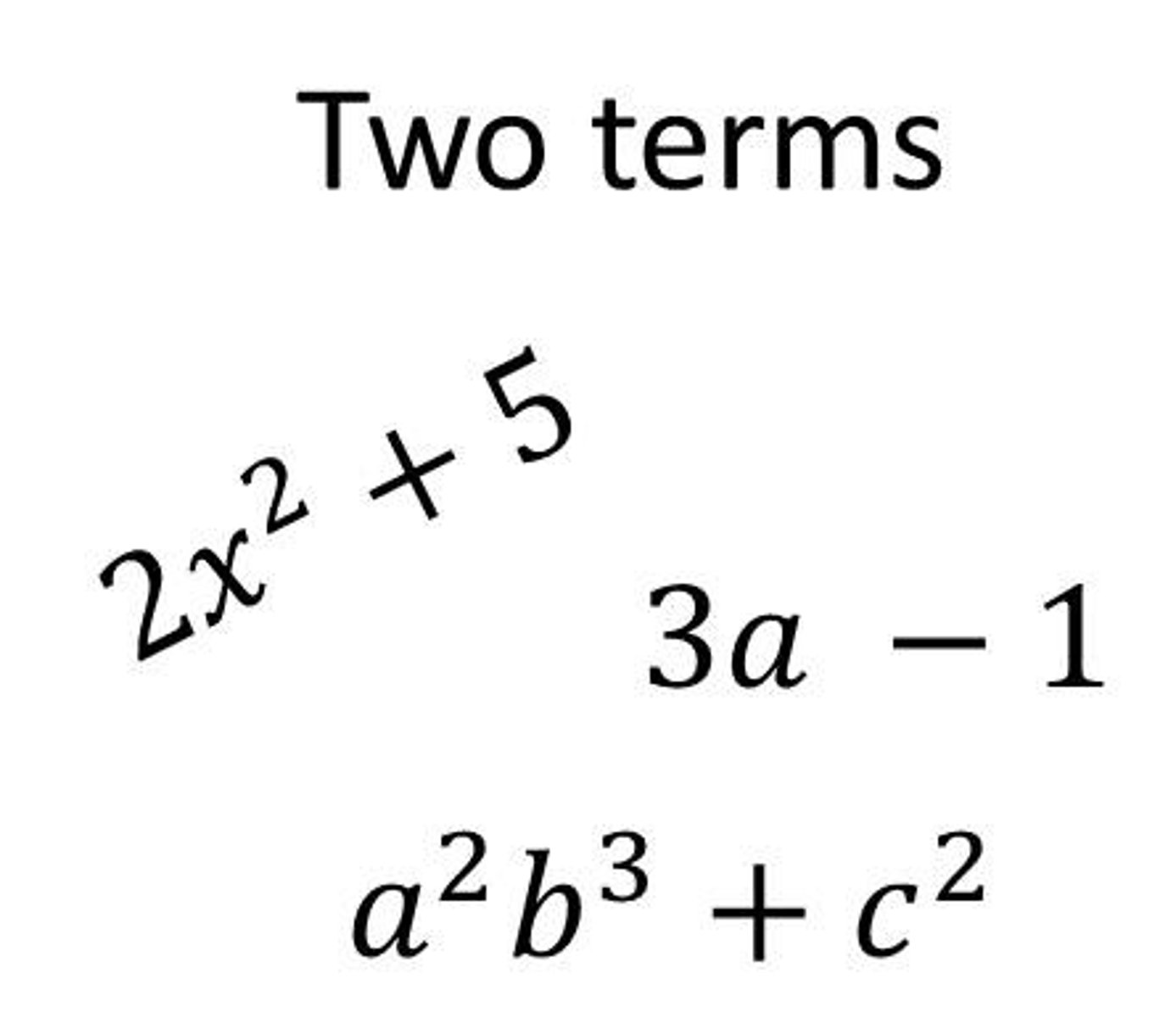
standard form of a polynomial in one variable
The form of a polynomial that places the terms in descending order by degree.
degree of a polynomial
The degree of the term of the polynomial with the greatest degree
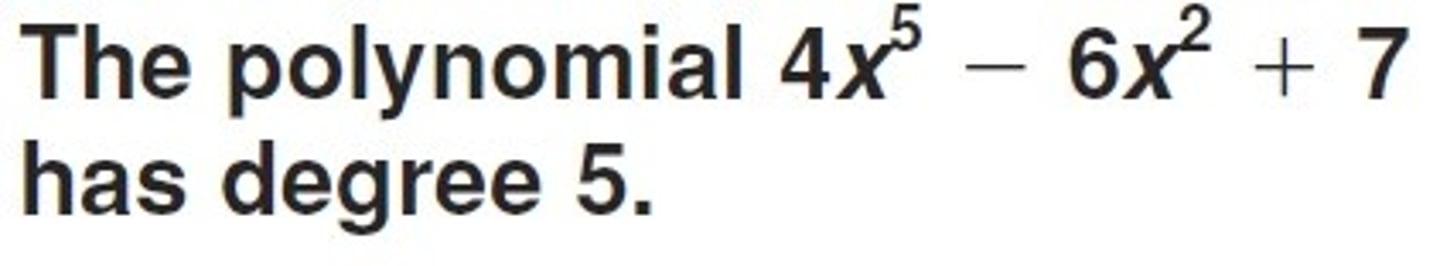
radicals and conjugates
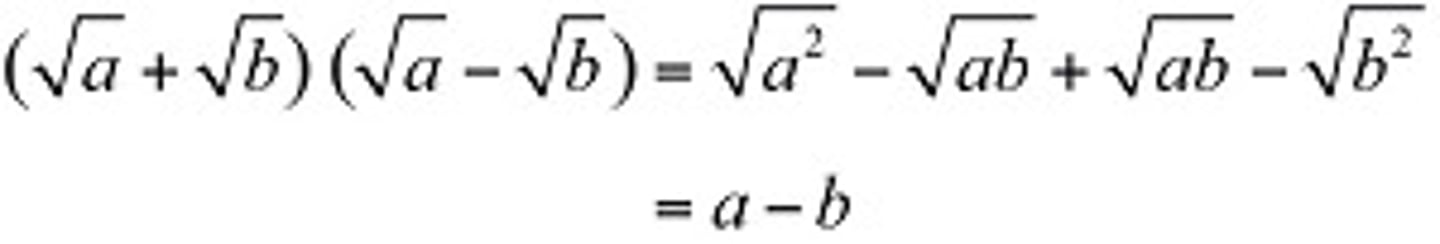
remainder theorem
When we divide a polynomial f(x) by x - c the remainder r equals f(c) ie 2x^2-5x-1 divided by x-3 2(3)^2 - 5(3) -1 = 18 - 15 -1= 2

Pythagorean theorem
a²+b²=c²
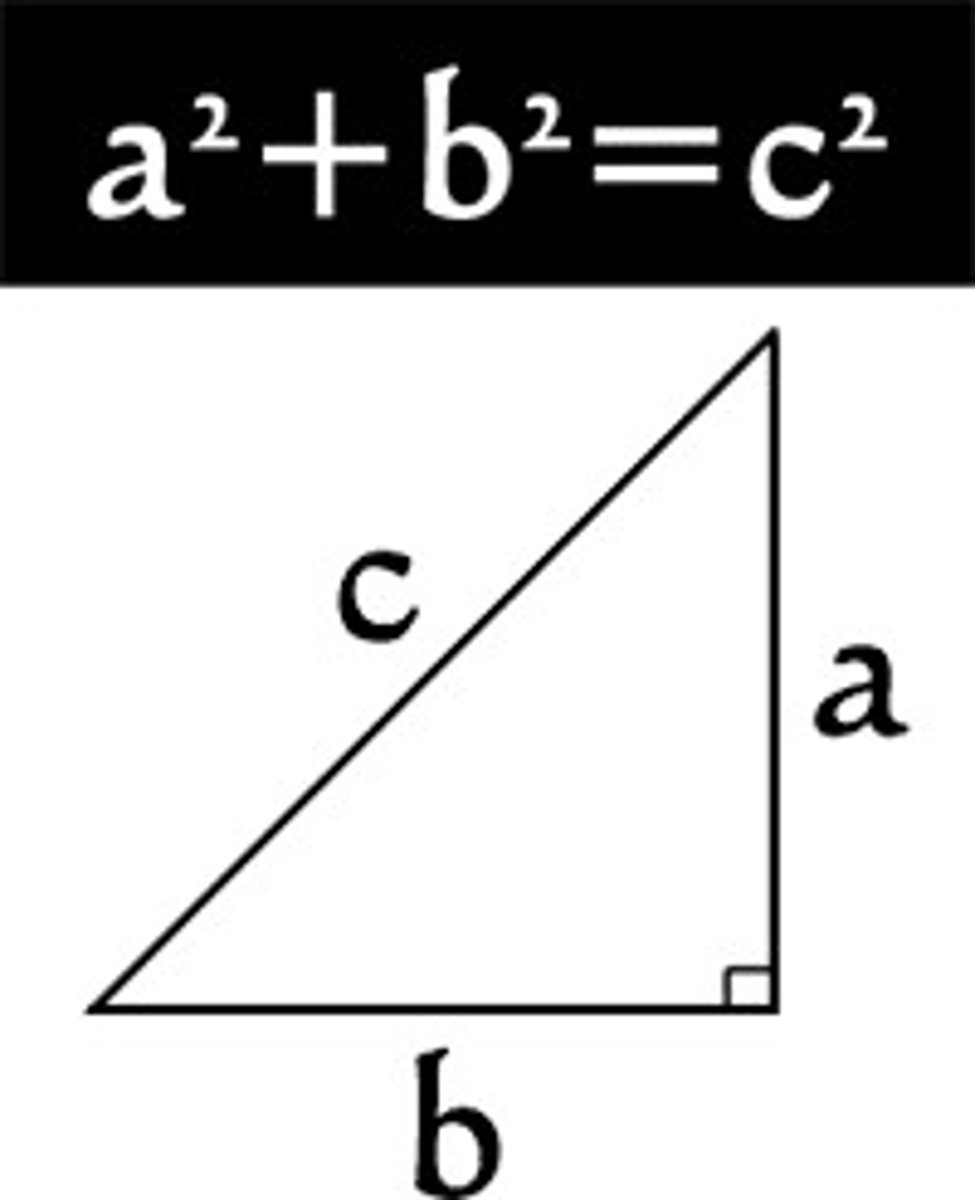
trinomial
A polynomial with three terms
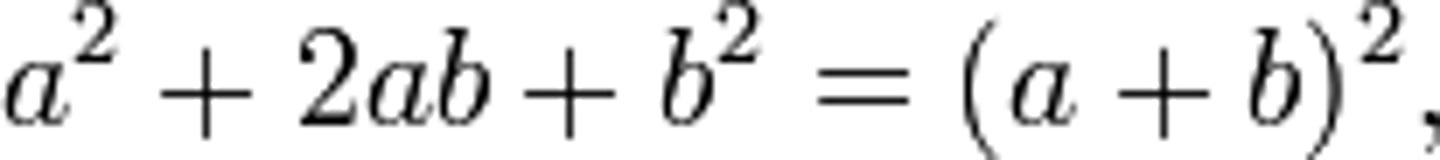
Arithmetic sequence
a sequence in which each term is found by adding the same number to the previous term

numerical symbol
A numerical symbol is a symbol that represents a specific number. Examples: 1,2,3,4,π,-3.2.
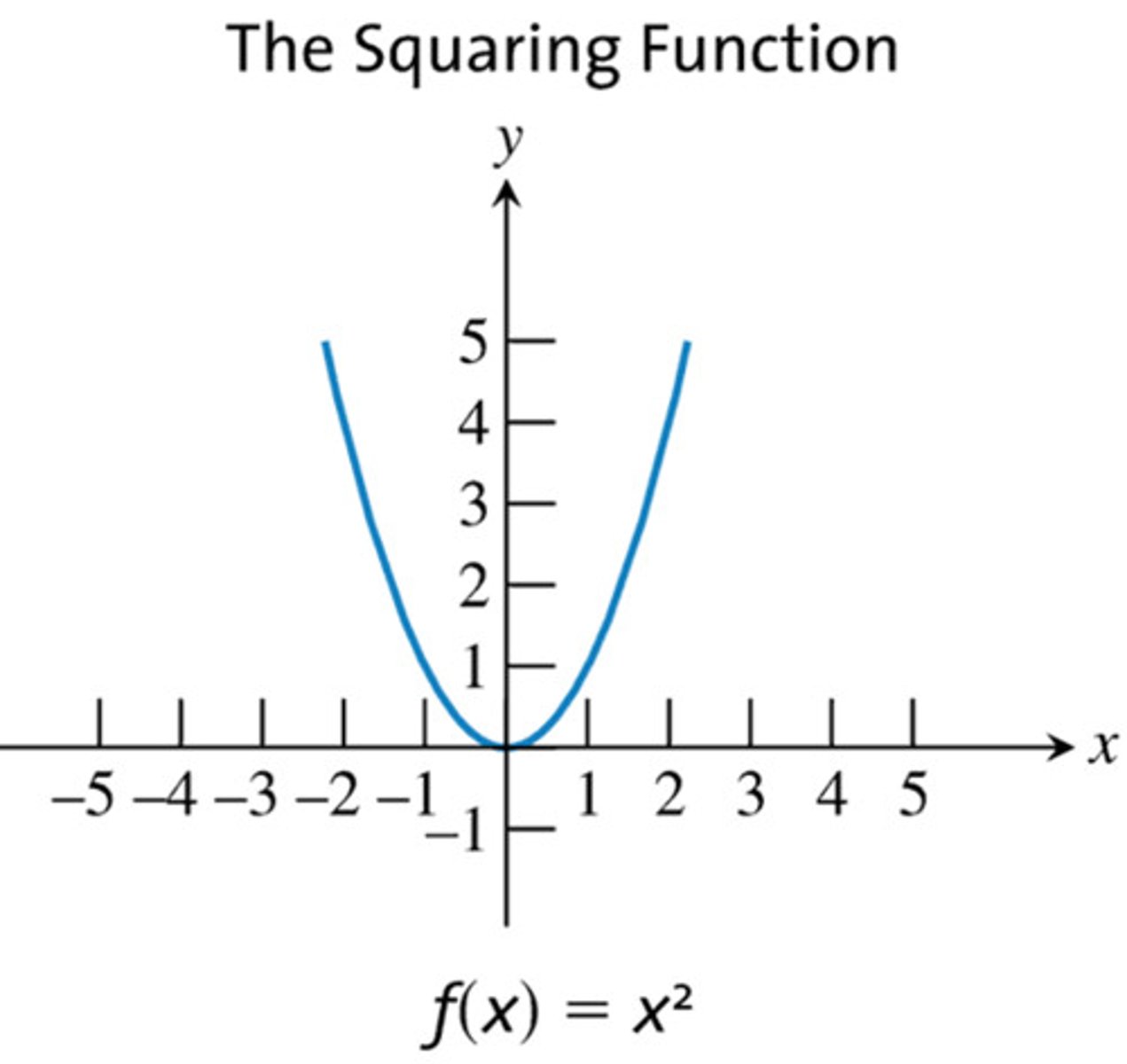
function
is a correspondence between two sets, X and Y, which each element of x is assigned to one and only one element of y. Ex f(x) = x^2
constant function
A function like f(x) = y = 5 that is the same regardless of the independent variable; graph is horizontal line.
linear function
a function in which the graph of the solutions forms a line
quadratic function
A function that can be written in the form f(x) = ax2+bx+c, where a,b,and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0
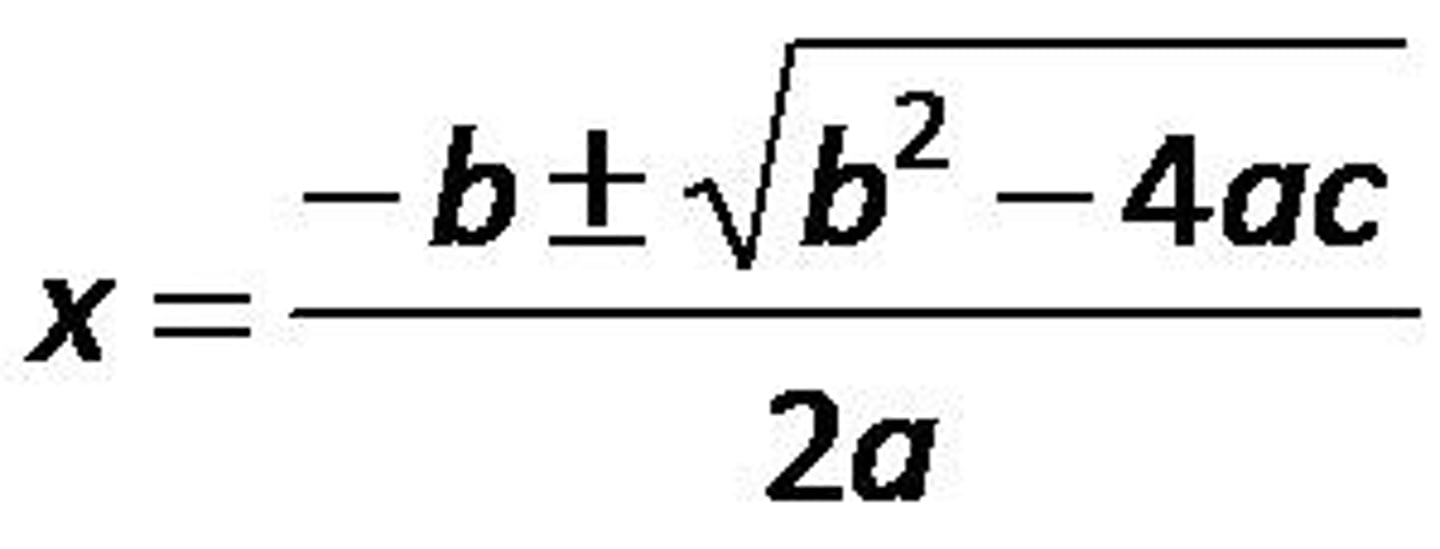
cubic function
a function to the 3d power f(x) ax^3 + bx^2 +cx +d, for constants a,b,c,d, with a not equal to zero.
Zero or Roots of a function
a zero (or root) of a function f(x) = 0 A zero us a function in an element in the solution set of the equation f(x) =0
factoring
To express a polynomial as the product of monomials and polynomials
multiplicity
how many times does a particular root occur in a function. ie f(x)= (x-2)the root is and the multiplicity 3
intercepts
points where a line crosses the x-axis and y-axis
increasing
Cumulative
When f '(x) is positive, f(x) is
decreasing
When f '(x) is negative, f(x) is

relative maximum
A point on the graph of a function where no other nearby points have a greater y-coordinate.
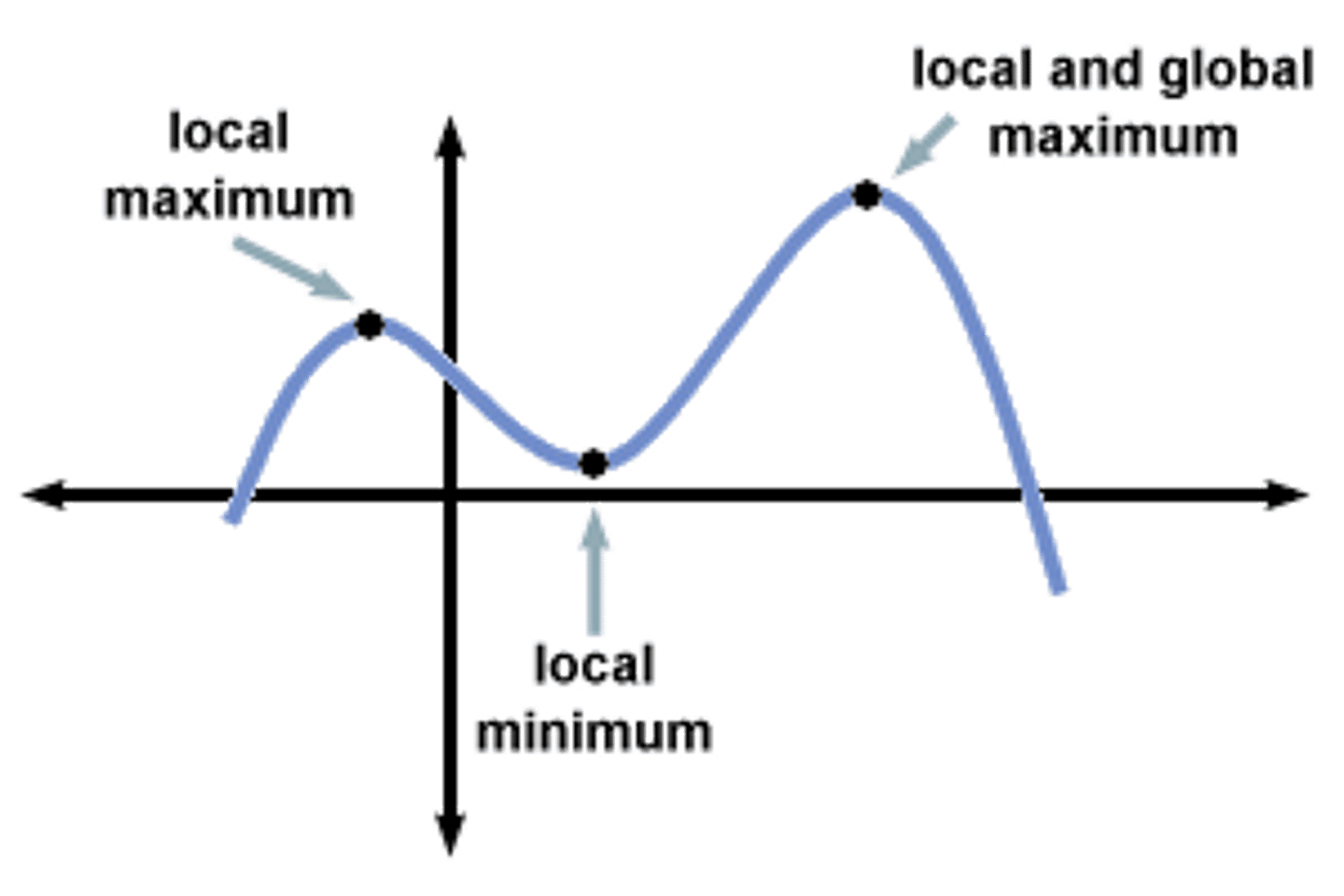
graph of f
If it's above 0, function is increasing. If it's below 0, function is decreasing. Where it hits 0
Pythagorean triple
a set of 3 positive integers that satisfy the Pythagorean theorem
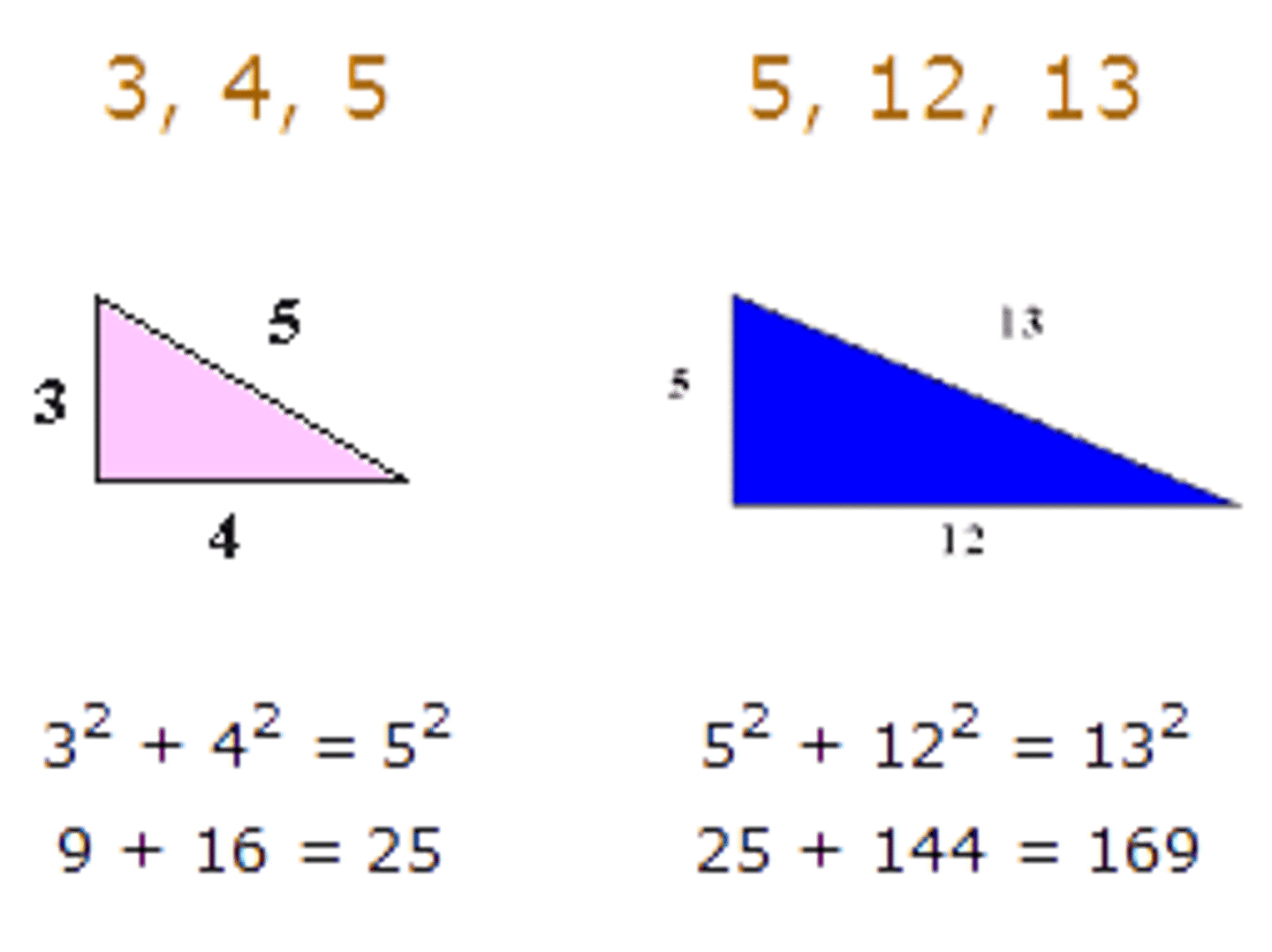
conjecture
An inference based upon guesswork; a supposition

Function
Domain
All of the input or x values in a function (xy)
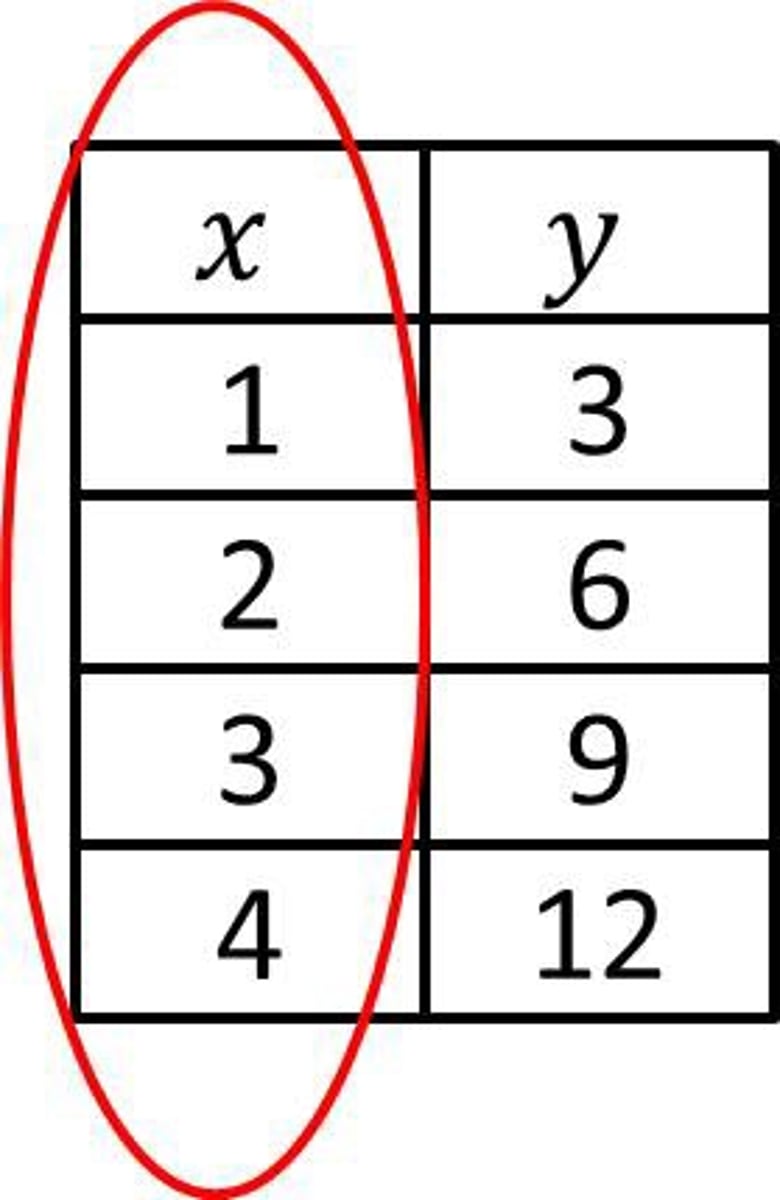
Range
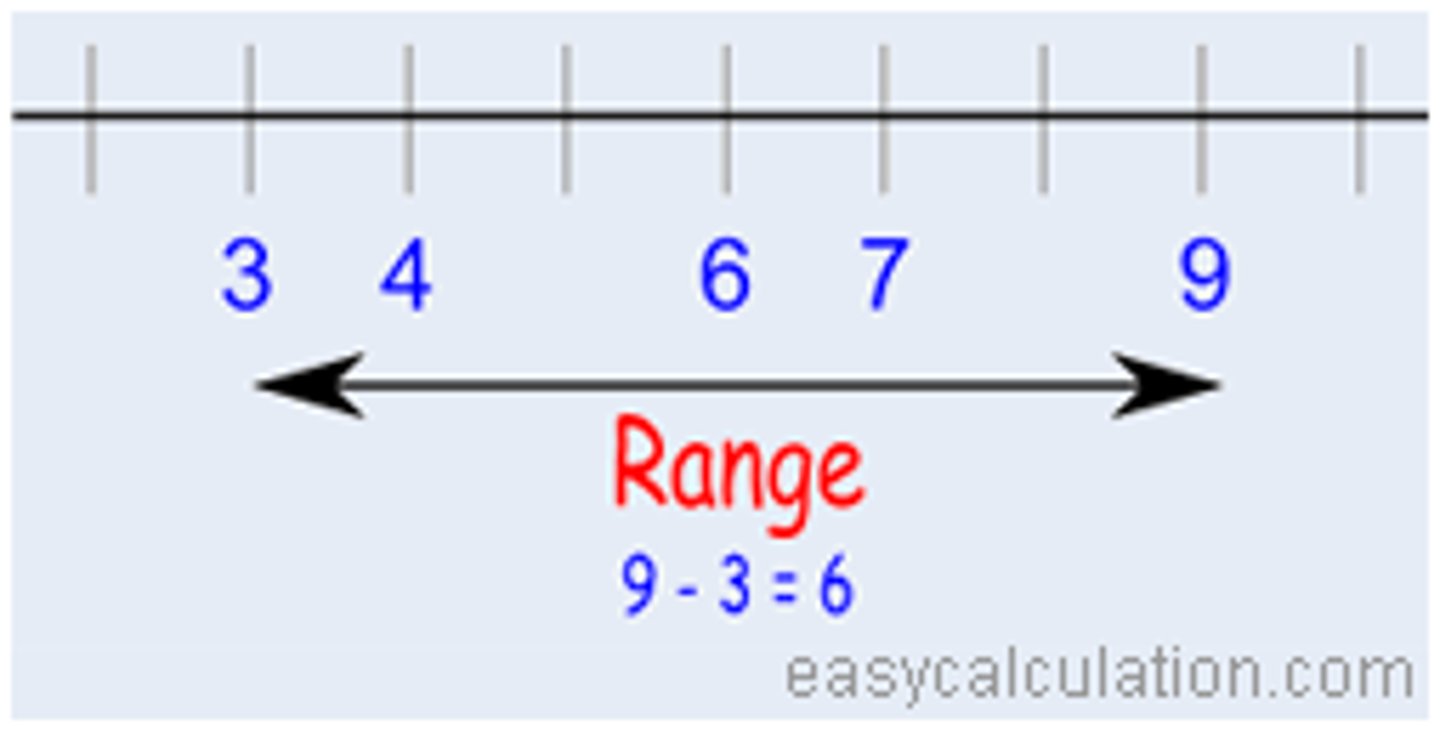
All of the input or y values in a function. Or the y value in an ordered pair. (xy)
interval notation
include the use of three special symbols: parentheses, brackets, and infinity.
Interval notation is a simplified form of writing intervals by using parenthesis and brackets to show whether the endpoints are included. The inequality x < 3 written in interval notation is (- ∞,3) whereas the inequality x£ 3 written in interval notation is (- ∞,3].
![<p>include the use of three special symbols: parentheses, brackets, and infinity.</p><p>Interval notation is a simplified form of writing intervals by using parenthesis and brackets to show whether the endpoints are included. The inequality x < 3 written in interval notation is (- ∞,3) whereas the inequality x£ 3 written in interval notation is (- ∞,3].</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bab4ff30-a92f-4692-94b9-fb673a3d306b.jpg)
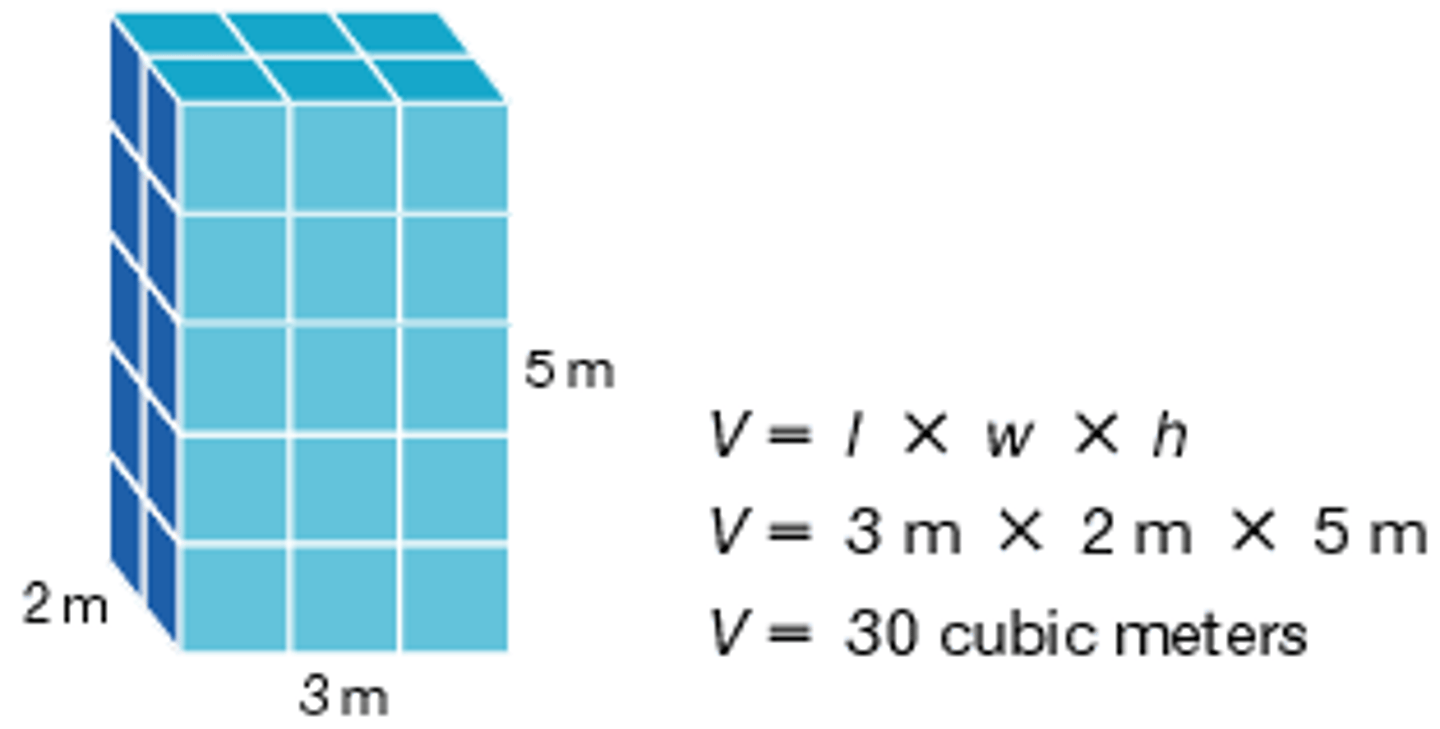
volume
A measure of the size of a body or region in three-dimensional space l x w x h
vector
A quantity that has magnitude and direction
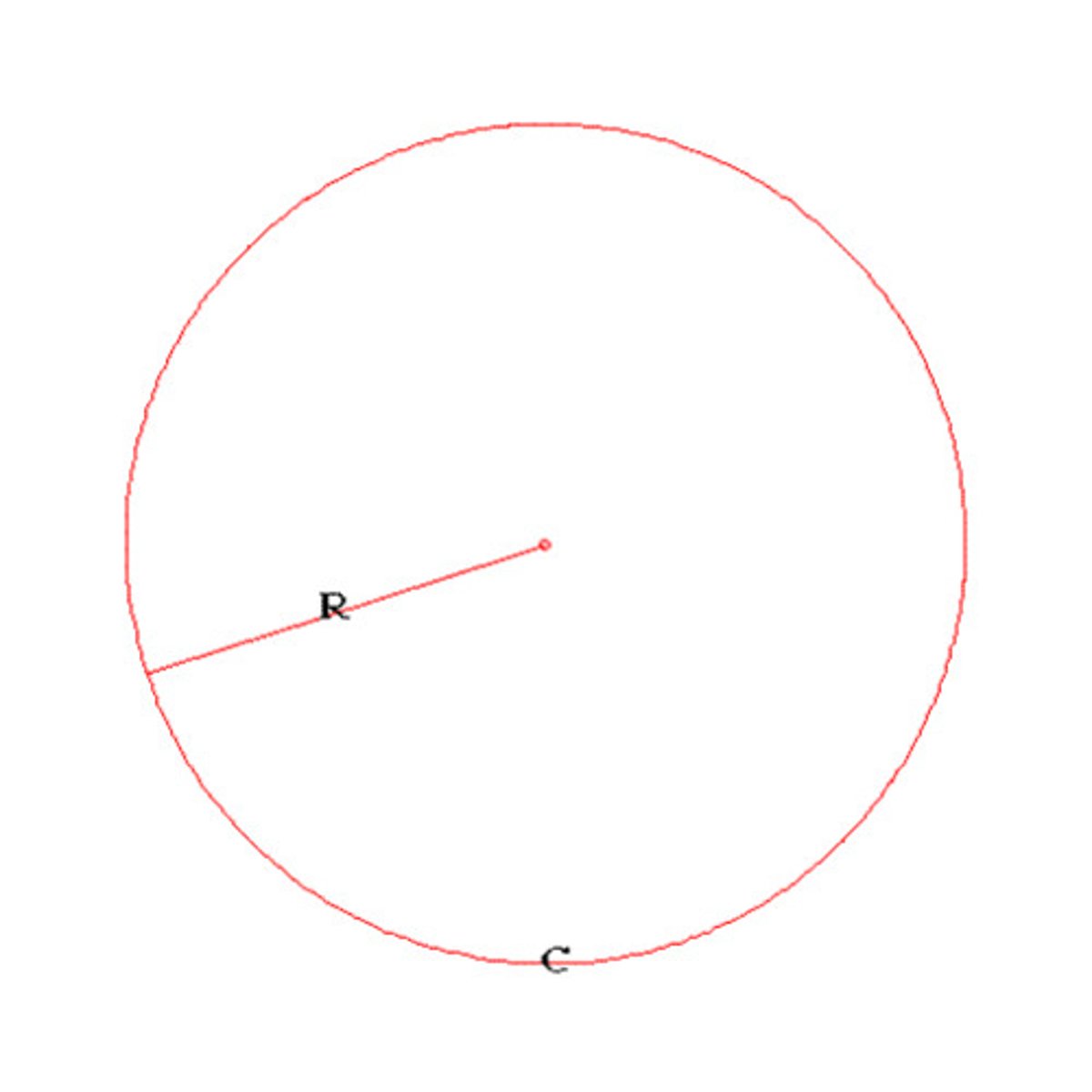
radius
A straight line from the center to the circumference of a circle or sphere.
Flow rate
The volume of fluid that moves through a system in a given period of time.

Riverbed
the ground at the bottom of a river

Cross-Section
a two -dimensional view of a slice through an object

Discriminant
b²-4ac
is the expression under the radical sign in the quadratic formula.
Conjugate
a pair of complex numbers . a + bi and a - bi, where a and b are real numbers and
i is imaginary.
Complex
Pertaining to or using complex numbers: complex method; complex vector space.