Global History Regents (copy)
4.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
1
New cards

Napoleon Bonaparte
The ruler who came into power at the end of the French Revolution who expanded France territory.
He made French people feel pride in their country (nationalism).
Napoleon was then defeated in 1812 for invading Russia during the winter which resulted in the death of his soldiers.
He made French people feel pride in their country (nationalism).
Napoleon was then defeated in 1812 for invading Russia during the winter which resulted in the death of his soldiers.
2
New cards
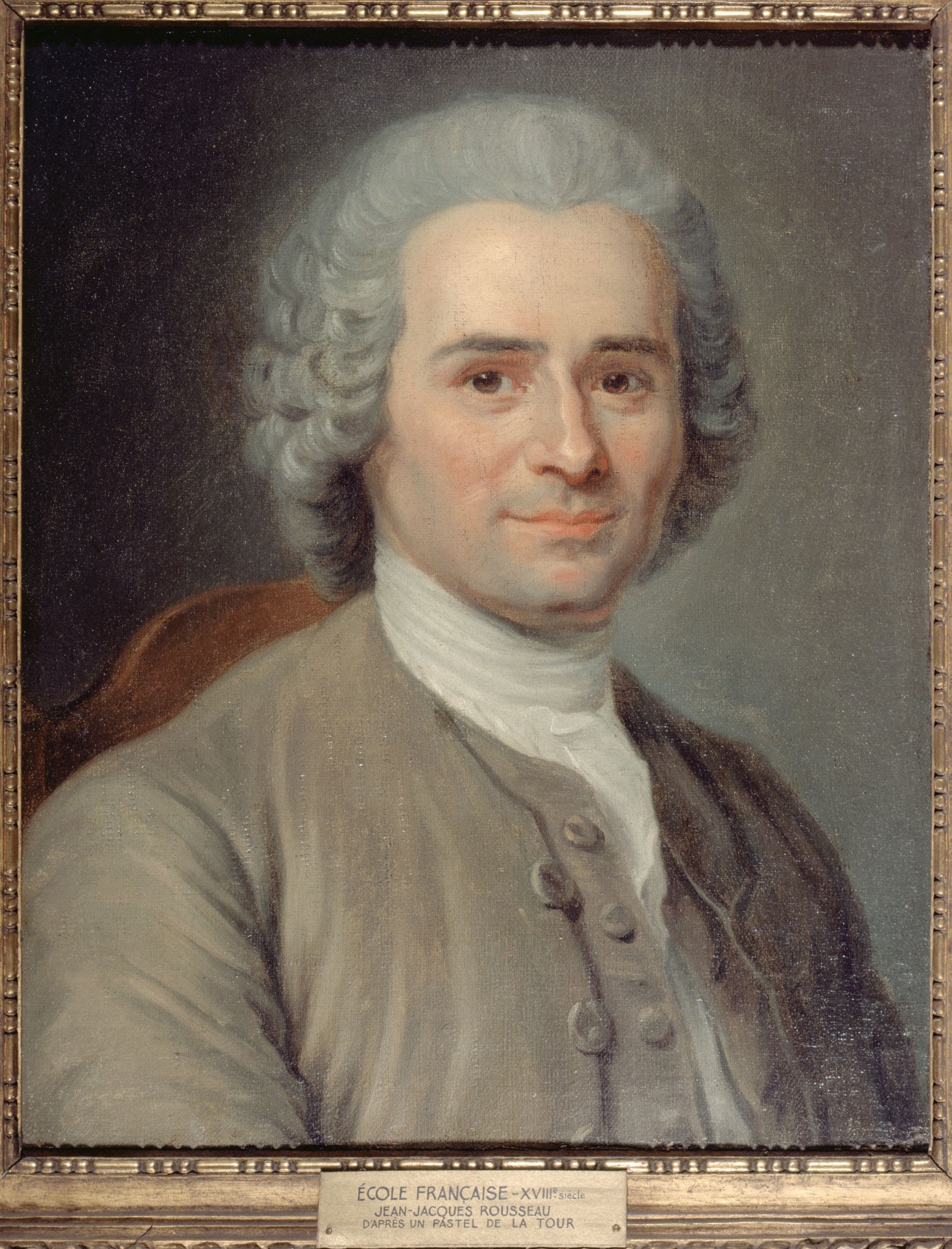

Rousseau
Society is a social contract (Agreement amongst everyone to ensure that theyll work for the greater good)
3
New cards
Enlightened Despots
European kings and queens who believed in Enlightenment ideas and ruled by their principles
4
New cards
Declaration of the Rights of Man
This document gave equal rights to the men of France and created a fair system of taxation
5
New cards
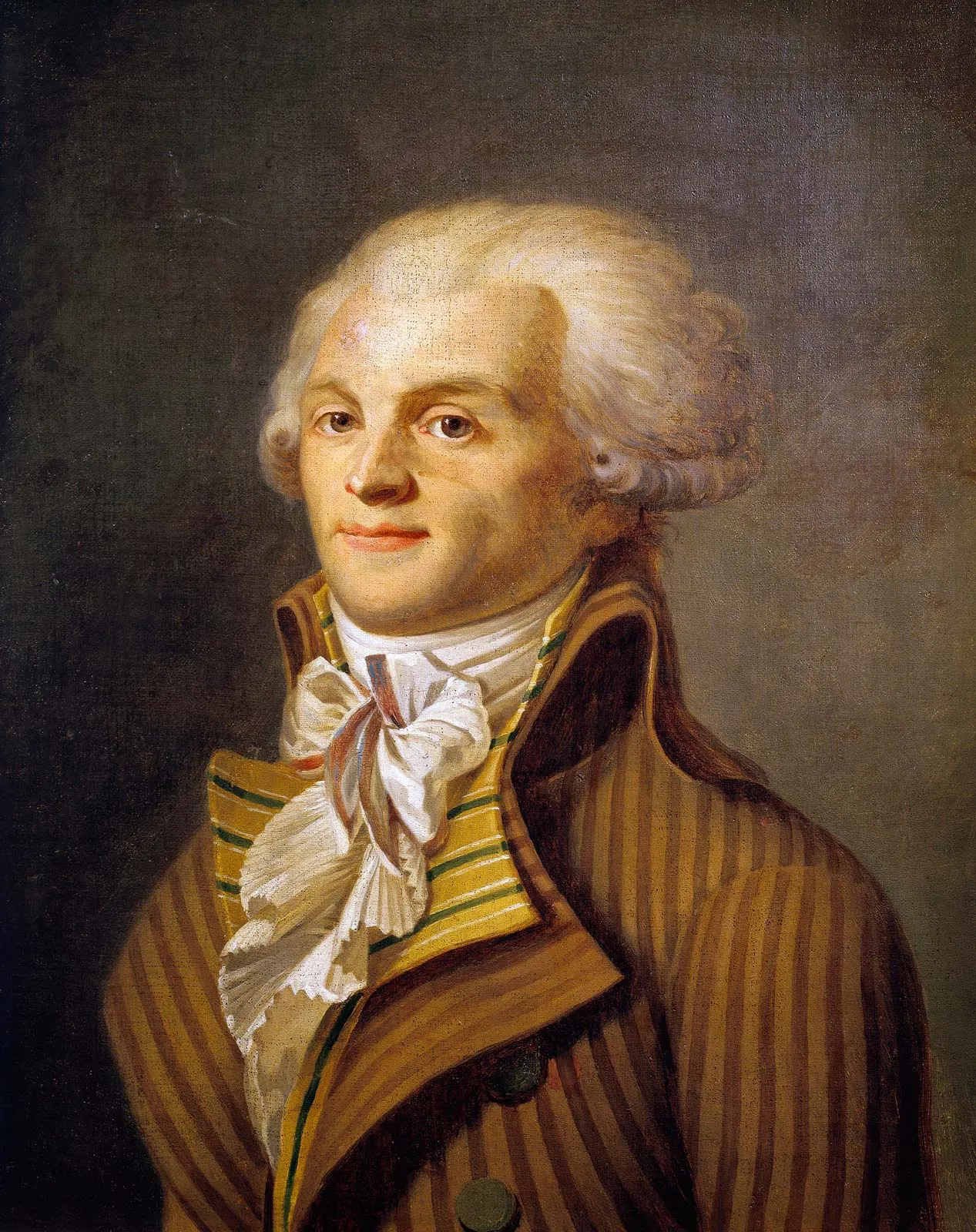
Reign of Terror
The leaders of the French Revolution executed thousands of people that were loyal to the king. The Jacobins (extreme group) led this event and Robespierre was the leader.

6
New cards
Haiti’s Social Class Division
grand blancs, petit blancs, free black people, enslaved people
7
New cards
Boukman Rebellion 1791
slave revolt led by Dutty Boukman, eventually becoming a revolution

8
New cards

Toussaint LOuverture (black Napoleon)
leader of Haitian revolution & military strategist
9
New cards
Industrial Revolution
The change of producing goods by hands to producing goods with machines in factories. It began in Great Britain because there was many natural resources such as coal, iron, tin, lead, and waterways. This led to bad working conditions, formation of the labor union, and laws banning child labor and setting a minimum wage.
10
New cards
Formation of Labor Union
Workers formed labor unions that fought to improve the pay & working conditions of workers
11
New cards
Laissez Faire Capitalism (Market Economy)
This was the economical system used during the industrial revolution based on the ideas that businesses and factories should be owned by individuals instead of the government and the price and decisions should be made by the individuals
12
New cards
Nationalism
Pride for your country. Usually develops in areas where people share a common language, culture, and history.
13
New cards
Unification of Italy
Italy combined their separate states into one nation in 1870
14
New cards
Bad working conditions
Workers in factories worked in risky conditions for a long period of time and low pay
15
New cards
Unification of Germany
Germany combined their separate states into one nation in 1871, all thanks to Otto von Bizmarck who used the "blood and iron" policy to unify German lands.

16
New cards
"White mans Burden"
This racist poem encouraged Europeans to civilize the people they conquered by westernizing them
17
New cards
Social Darwinism
It was natural for powerful countries to take over weaker countries
18
New cards
Scramble for Africa
Over 90% of Africa was conquered by western countries
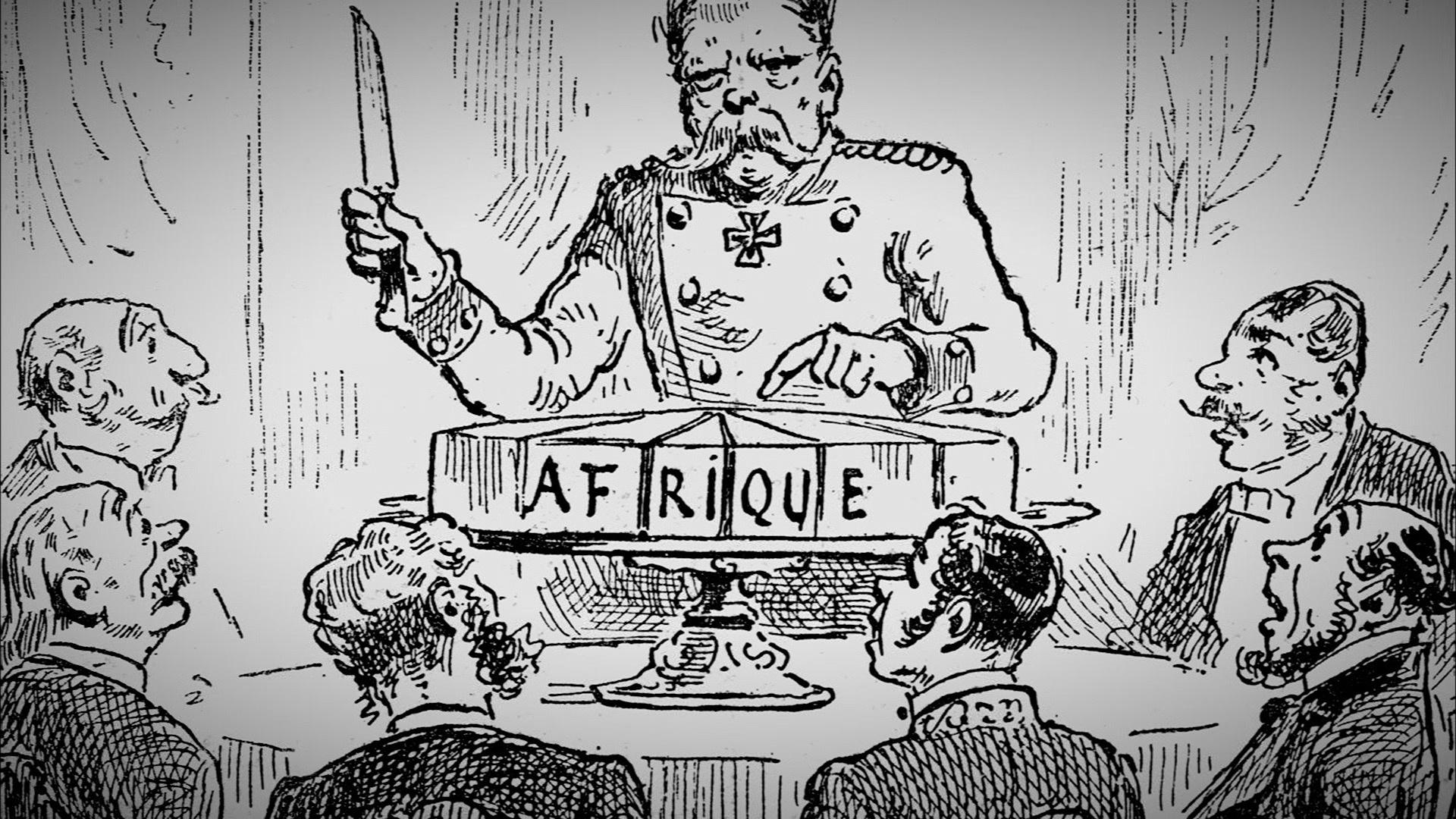
19
New cards
Imperialism in China
The British began to smuggle opium into China, causing China to fight back in the Opium war where they lost and were forced to open up trade markets that were controlled by different European nations
20
New cards
Imperialism in India
India was taken over by Great Britain and ruled for almost 200 years
21
New cards
Sepoy (Indian soldiers in the British army) Mutiny
Rebellion where India tried to gain independence but failed
22
New cards
Japanese imperialism
Japan took over Korea and part of China for natural resources
23
New cards
World War I
Global Military Conflict fought in Europe
24
New cards
Militarism (WWI)
Countries in Europe built up their armies and their supplies in the late 1800s
25
New cards
Alliances (WWI)
Countries in Europe divided themselves into two military alliances (The Triple Alliance and Triple Entente) to prepare for war in Europe
26
New cards
Imperialism (WWI)
Europeans countries competed with each other for colonies in Africa and Asia and the Balkans (Southeastern Europe)
27
New cards
Nationalism (WWI)
Ethnic groups in the Balkans wanted independence from Austria-Hungary and they were willing to fight for it
28
New cards
Treaty of Versailles
This treaty ensured the end of WWI and punished Germany in multiple ways. Germany was forced to accept blame for causing WWI, pay reparations, reduce the size of its military, and forced to give up some of their colonies.
29
New cards
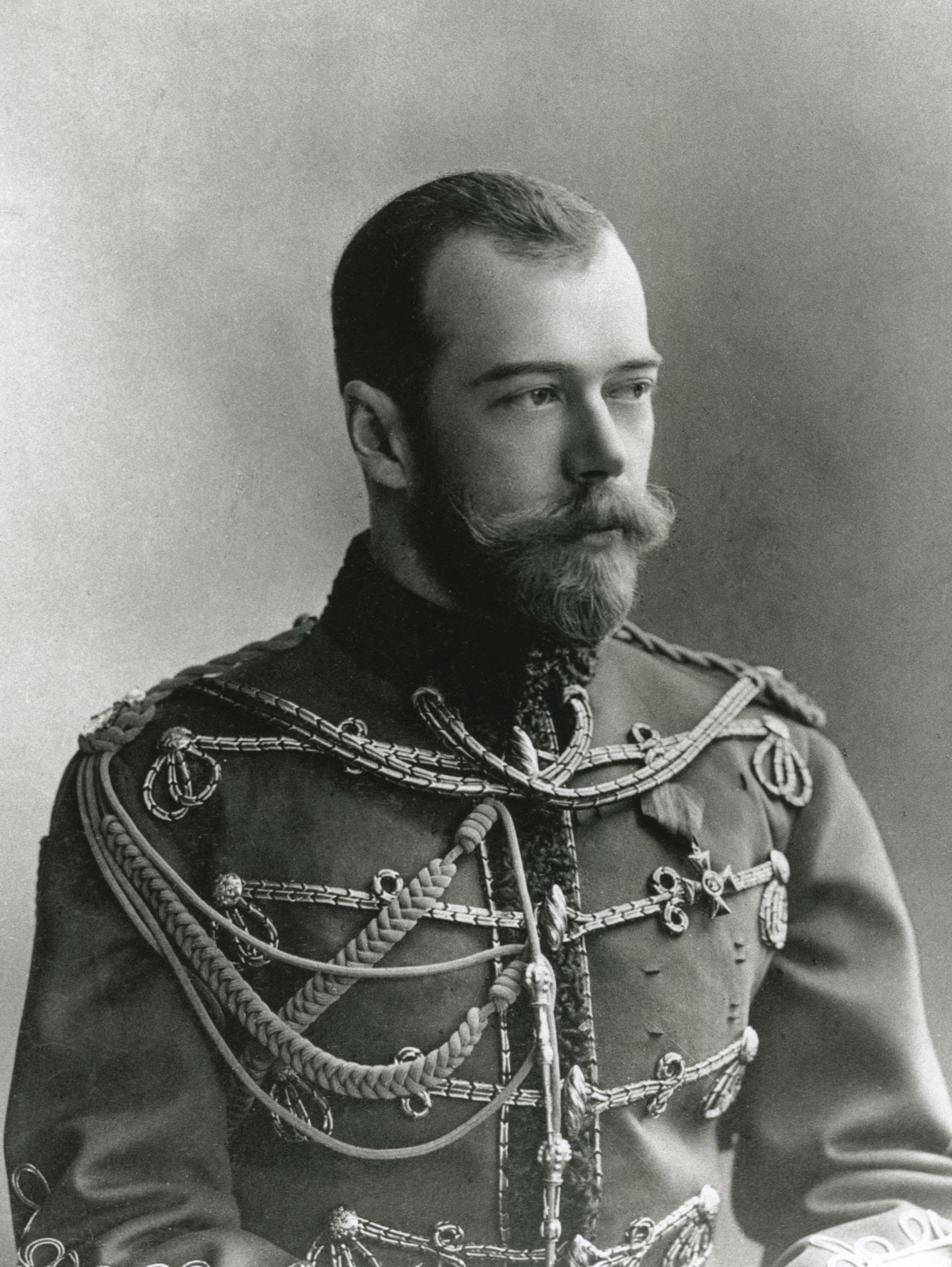

Czar Nicholas II
He abused his power by denying the rights of the people
30
New cards
Bolsheviks
They were a radical group that lead the Russian Revolution. The leader was Vladimir Lenin and they gained support of the Russians by promising to provide “Peace, Land, and Bread.” This meant that Russia would be removed from WW1, given land, and be feed.
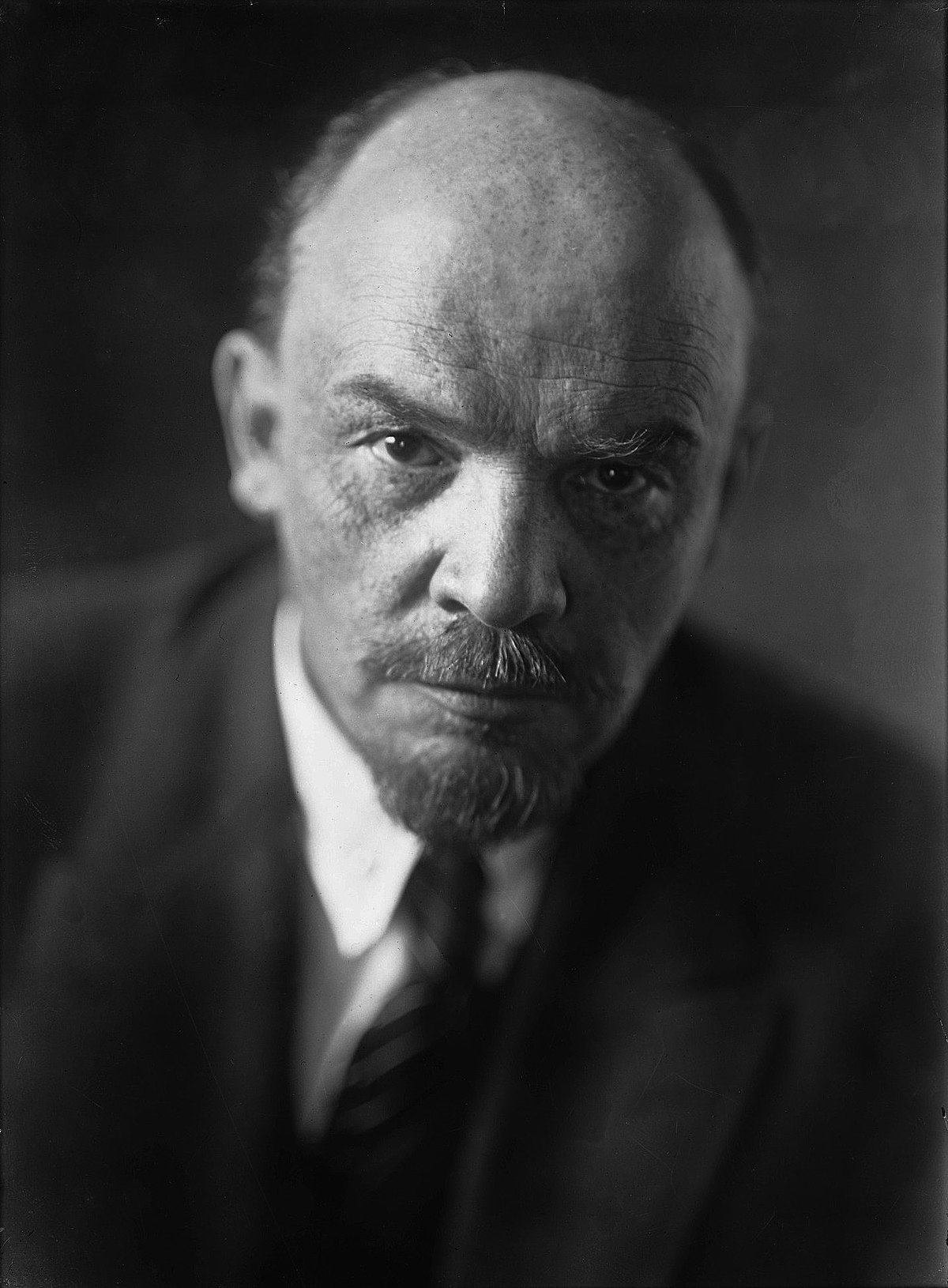
31
New cards
Censorship
Dictators ended freedom of speech, and the governments controlled the media of their nation
32
New cards

Stalins political party
The Communists
33
New cards

Mussolinis political party
The Fascists
34
New cards

Hitlers political party
The Nazis
35
New cards
Five-Year Plan
Stalin tried to modernize the industry and agriculture by setting economic goals every five years
36
New cards
Collectivization
Stalin took over individual farms (private property) and forced people to live on collective farms (large farms) owned by the government
37
New cards
Rape of Nanking
The Japanese raped and killed Chinese civilians in Nanking city
38
New cards
Italian Aggression during WW2
Benito Mussolini of Italy invaded and took over Ethiopia

39
New cards
Germany Aggression during WW2
Adolf Hitler violated the Treaty of Versailles by building up Germany’s military, placing soldiers in Rhineland (Area between Germany and France) and taking over the neighboring country of Austria and Czechoslovakia.
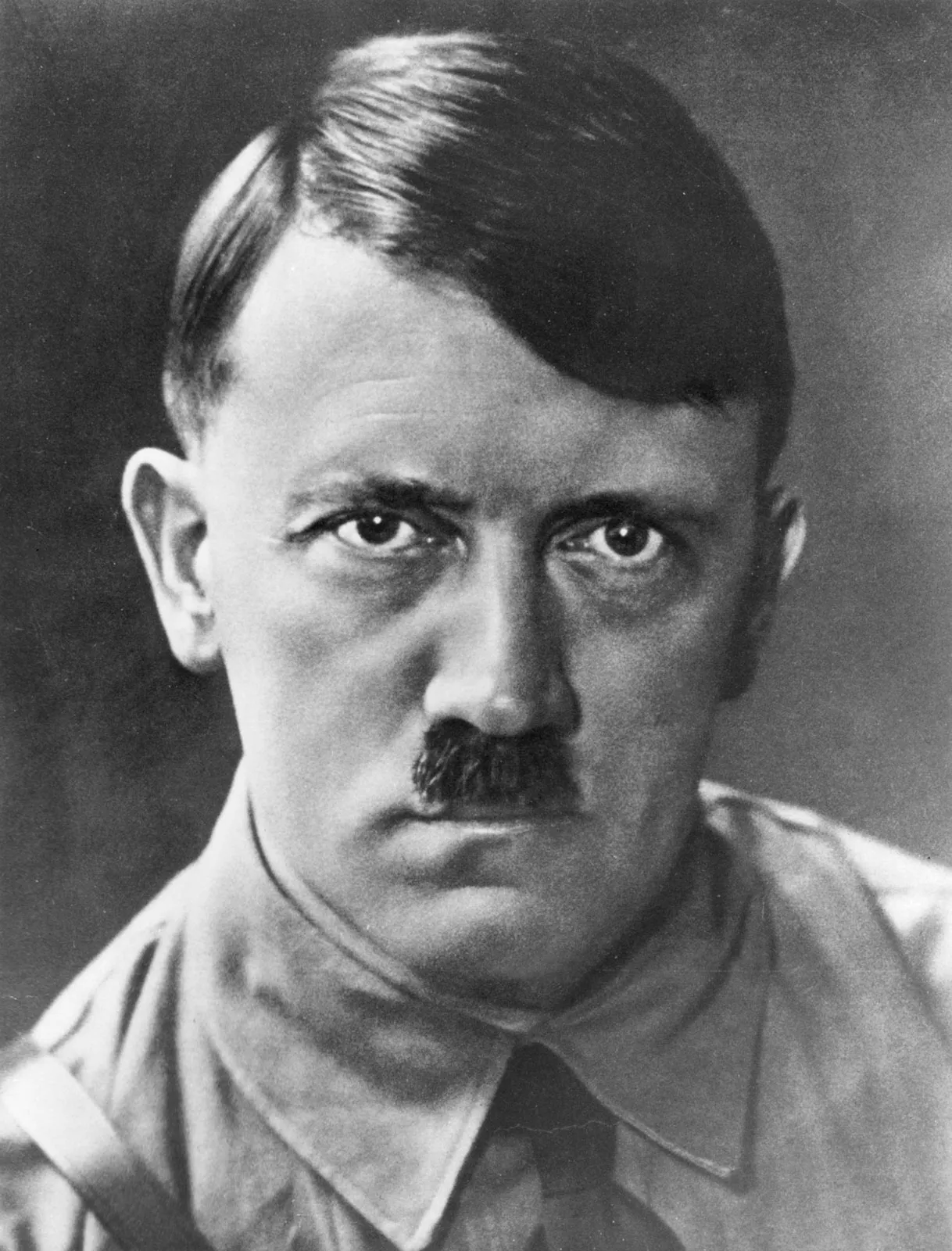

40
New cards
The League of Nations
International organization created after WWI in order to prevent war. It failed to stop Hitler, Mussolini, and Japan.
41
New cards
Appeasement
This is a policy where an aggressive nation is given what they want by other nations to avoid war
42
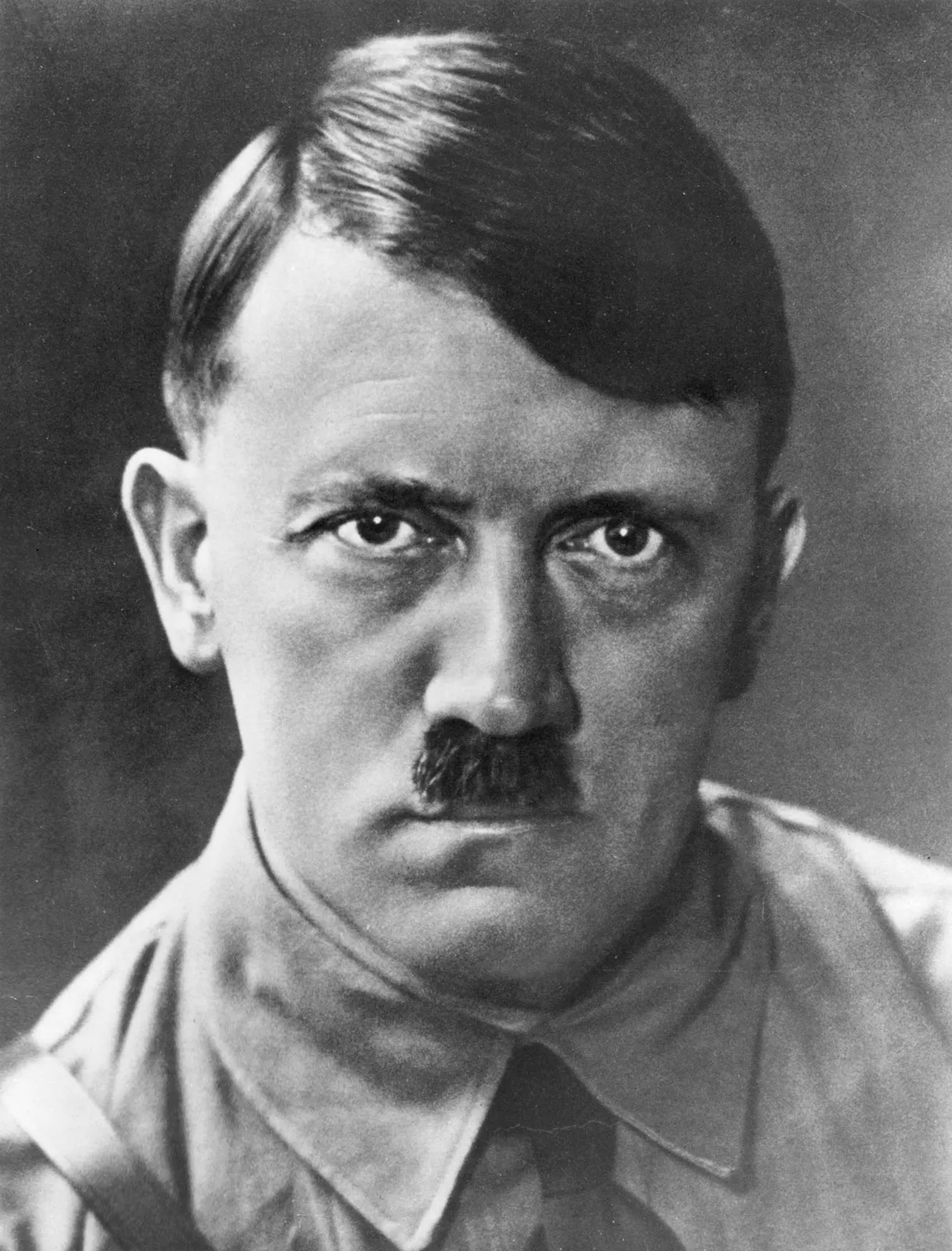
New cards
Munich Conference
Germany, Great Britain appeased Hitler by giving him control over Czechoslovakia. This led Hitler to demand even more land.

43
New cards
Invasion of Poland
This event started WWII. Poland was defeated by Germany because they lacked natural boundaries (they had flat plains, it was east to conquer them)
44
New cards
Pearl Harbor
Japan attacked United States
45
New cards
D-day Invasion
The beginning of the final allied push against Germany which resulted in Germanys defeat
46
New cards
Atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The Final event of World War II. The U.S. bombed Japan which caused Japan to surrender soon after.
47
New cards
The Holocaust
During World War II, Hitler and the Nazis tried to kill all jews. 6 million Jews and 6 million non-Jews were killed.
48
New cards
The Security Council (United Nations main body)
Keeps peace between nations
49
New cards
International Court of Justice (United Nations main body)
Settles disputes between countries
50
New cards
General Assembly (United Nations main body)
Votes on key policies of the United Nations
51
New cards
Secretariat (United Nations main body)
Responsible for day-to-day administration of the United Nations
52
New cards
Declaration of Human Rights
A document created by the United Nations that lists all the rights that all people should have within their nations
53
New cards
Nuremberg Trials
Court case where the surviving Nazis were put on trial. 19 Nazi leaders were executed or sentenced to imprisonment for their crimes against humanity.
The Nuremberg Trial demonstrated that people will be held accountable for their actions.
The Nuremberg Trial demonstrated that people will be held accountable for their actions.
54
New cards
The Cold War
A war between the United States and the Soviet Nation that last 50 years. It was called cold because they didn’t directly fight each other.
55
New cards
Iron Curtain
The imaginary line dividing the democratic countries of Western Europe from the communist countries of Eastern Europe
56
New cards
Containment
The policy where United States attempted to stop the spread of communism
57
New cards
Truman Doctrine
The U.S. gave $400 million in economic and military aid to Greece and Turkey to help them defeat communist groups within their countries
58
New cards
Marshall Plan
The U.S. gave $13 Billion to the countries of Western Europe to help them rebuild after WWII
59
New cards
Berlin Wall
Concrete wall built by the communists to prevent people from East Germany from escaping to West Germany
60
New cards
Berlin Airlift
The U.S., Britain, and France flew in supplies to the people of West Germany after Stalin set up a blockade (Berlin Wall)
61
New cards
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)
A military alliance between the U.S., Canada, and the democratic nations of Western Europe. They agreed if one of the nations involved in this alliance were attacked, they would all be attacked.
62
New cards
Warsaw Pact
A military alliance between the Soviet Union and the other communist nations of Eastern Europe
63
New cards
Hungary Revolution of 1956
When Hungary (a communist satellite) tried to break away from Soviet control, the Soviet Union sent in the army and ended the rebellion.
64
New cards
Arms race
The U.S. and the Soviet Union competed to build up the largest supply of nuclear weapons
65
New cards
Cuban Missile Crisis
The United States found out that the Soviet Union was building missile bases in Cuba (a communist nation) and pointing them at the U.S. and the crisis ended when the Soviet Union agreed to remove them
66
New cards
Decolonization
Nations colonized by western nations finally gain independence
67
New cards
Caste (lower social classes) Systems
Theres discrimination in rural areas since tradition remains strong there and discrimination against the lower class is very severe
68
New cards
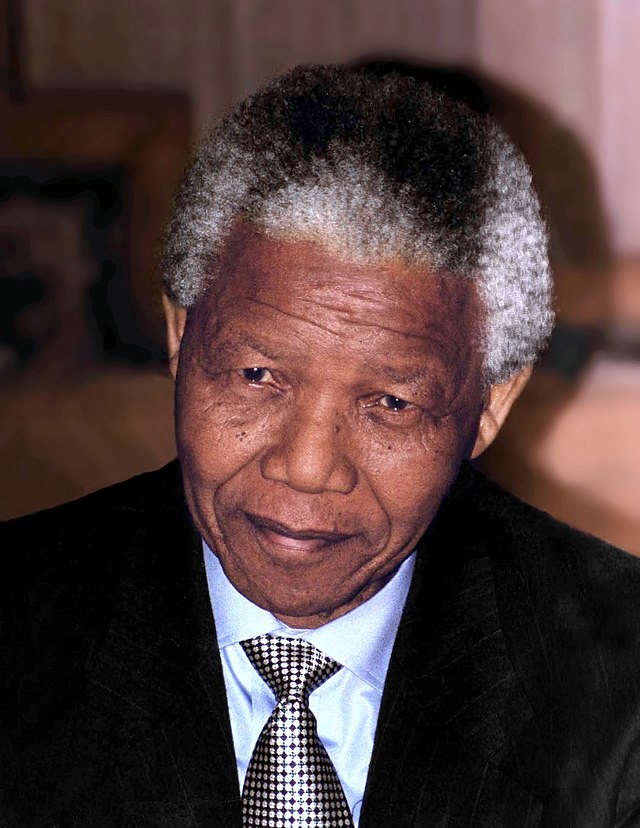

Nelson Mandela
He was a Black South African nationalist leader who fought against Apartheid who was imprisoned by the White South African government for 27 years and later voted to be the first Black South African President after the apartheid came to an end in 1990
69
New cards
Rwandan Genocide (1994)
The Hutus slaughtered 800,000 Tutsis in only a few months
70
New cards
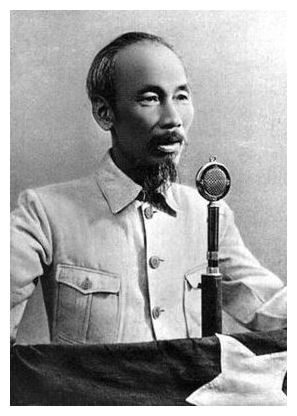
Ho Chi Minh
Vietnamese nationalist leader who led a 8-year war against France to gain independence for Vietnam
71
New cards
Great Leap Forward
This was Maos attempt to modernize the industrial and agricultural production in China by forcing peasants to move onto large government farms (similar to Stalins Five-Year Plan and Collectivization)
72
New cards
Cultural Revolution
Mao used violent young Communist soldiers (Red Guards) to eliminate all of the opposition that he had
73
New cards
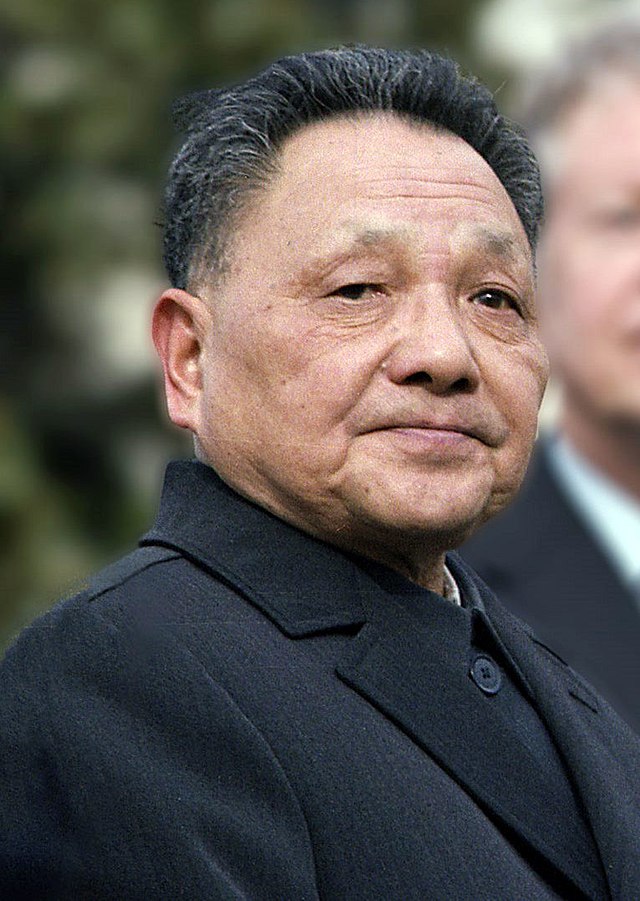

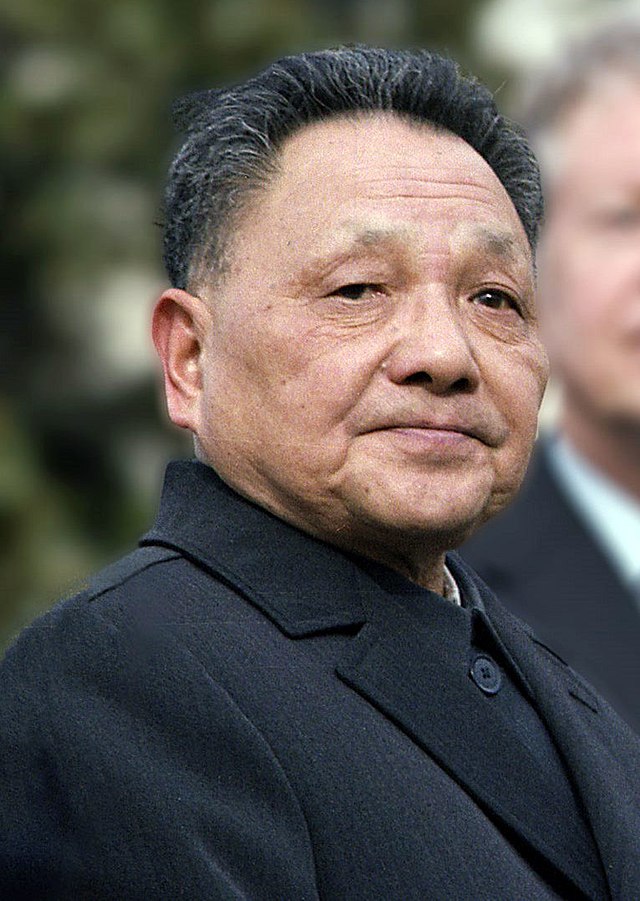
Deng Xiaoping
The capitalist ruler that came after Mao Zedong and changed the economy into a capitalist economy
74
New cards
Tiananmen Square Protest/Massacre 1989
The Chinese peacefully demanded democratic changes (reforms) where they wanted more rights and a say in government. Deng Xiaoping calls in the army to handle the protests and that led to hundreds of Chinese protestors being killed.

75
New cards
Arab Nationalist interested in the Middle East because…
wanted independent states that emerged from the collapse of the Ottoman Empire
76
New cards
European Nationalists interested in the Middle East because…
wanted control of trade routes and resources (mainly oil) from the region
77
New cards
Zionists interested in the Middle East because…
wanted to establish a Jewish homeland
78
New cards
Creation of Israel
Part of the Holy Land was used to create the Jewish nation of Israel
79
New cards
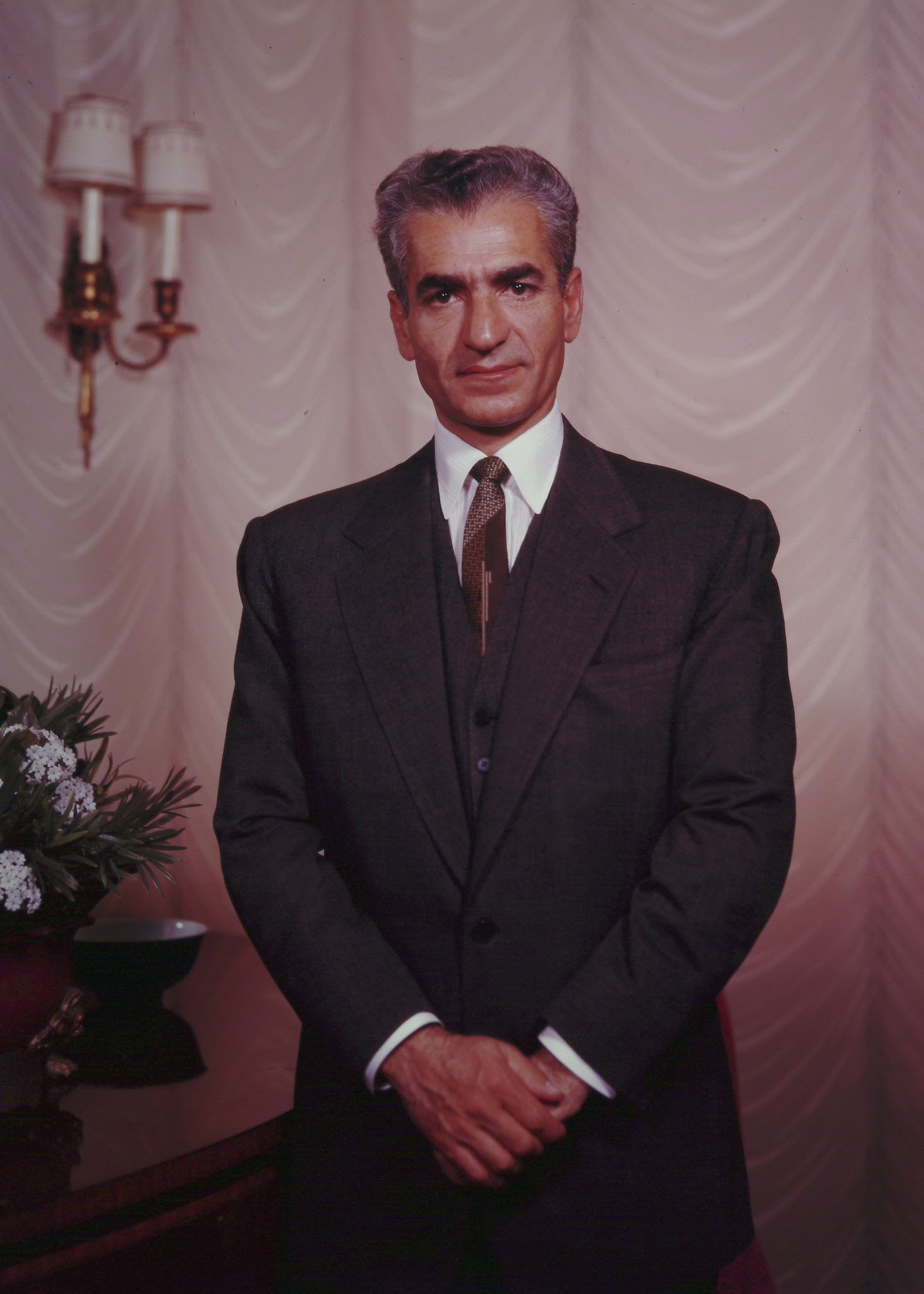

The Shah
He proclaimed himself King after his father and was an absolute monarch who abused his power and wanted to modernize, secularize, and westernize Iran.
80
New cards
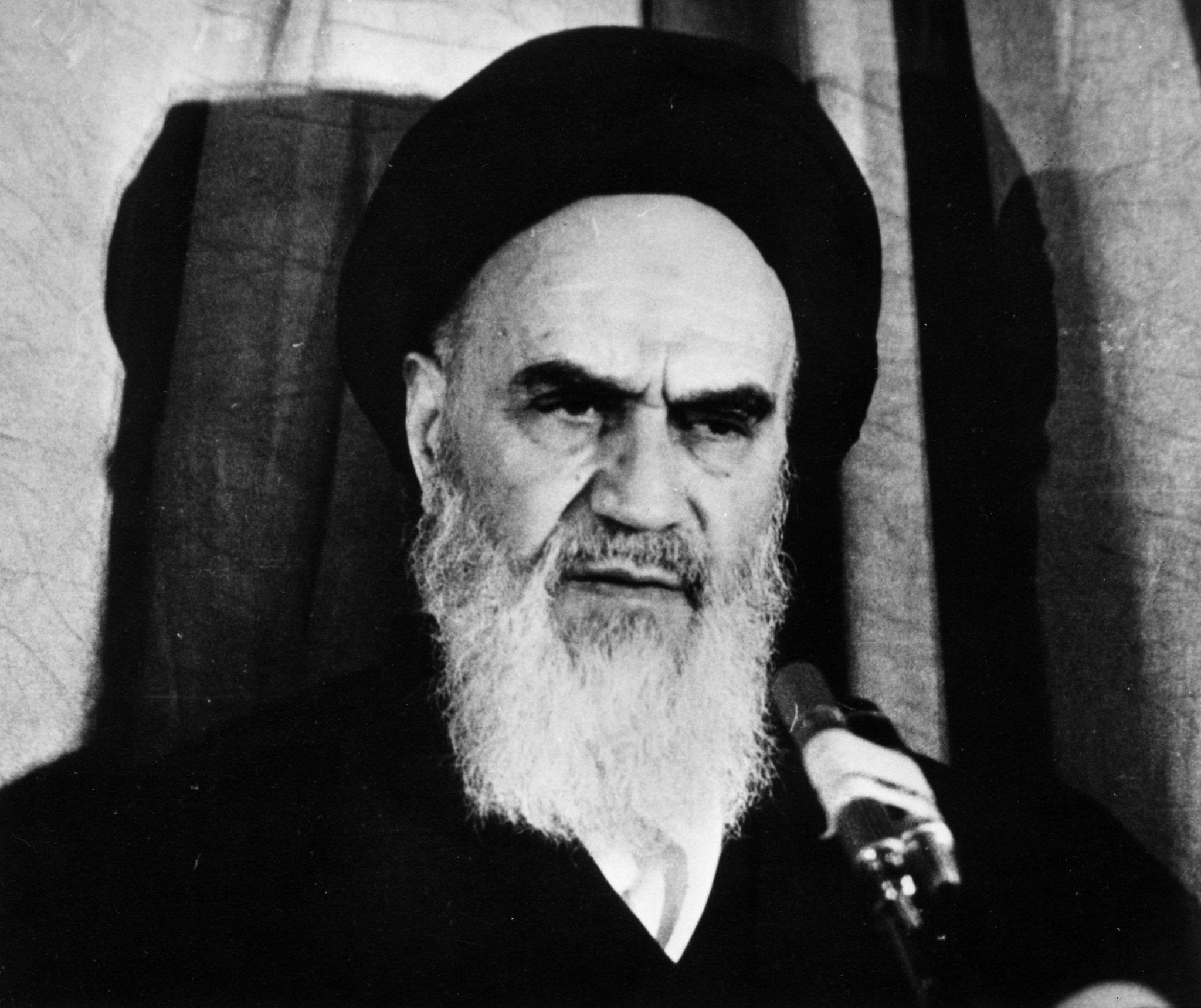

Ayatollah Khomeini
He came to power after the Iranian Revolution and established a Theocracy (Islam) and he wanted to be traditional, nonsecular and not westernized.
81
New cards
Green Revolution (Began 1960s)
The use of technology to increase the food supply by improving irrigation (supply of water), machinery, fertilizer, pesticides, and better seeds and livestock
82
New cards
Genocide
The attempt to exterminate an ethnic group, this is a violation of our human rights.
83
New cards
Armenian Massacre
The Turks of the Ottoman Empire murdered about one million Armenians during WWI that lived in their territory.
84
New cards
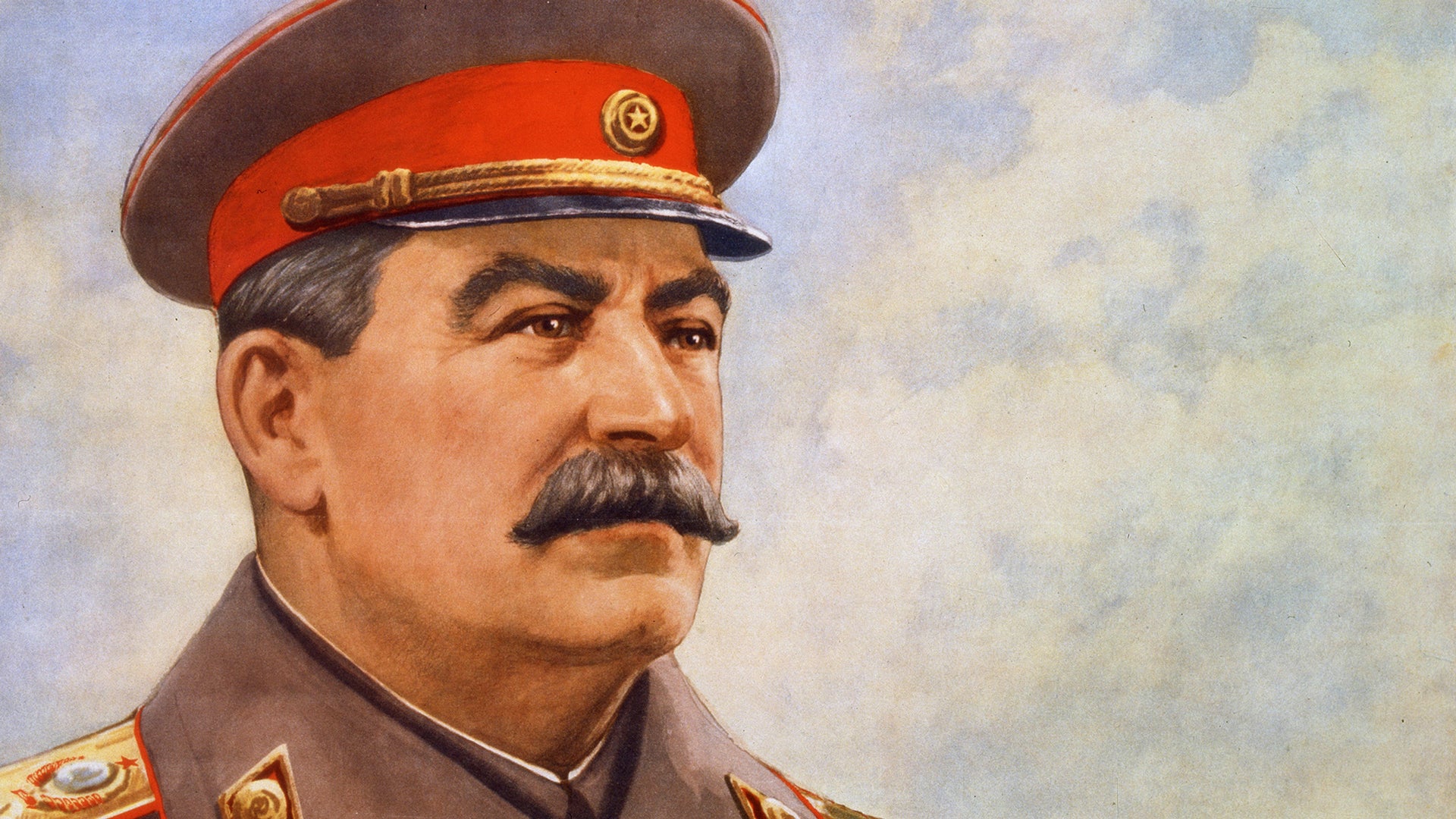
Ukrainian Famine
Joseph Stalin took away food from Ukrainians

85
New cards
Yugoslavia Genocide
Slobodan Milosevic was the Serbian ruler of Yugoslavia who violently attacked non-Serbs (especially Albanians) living in his land
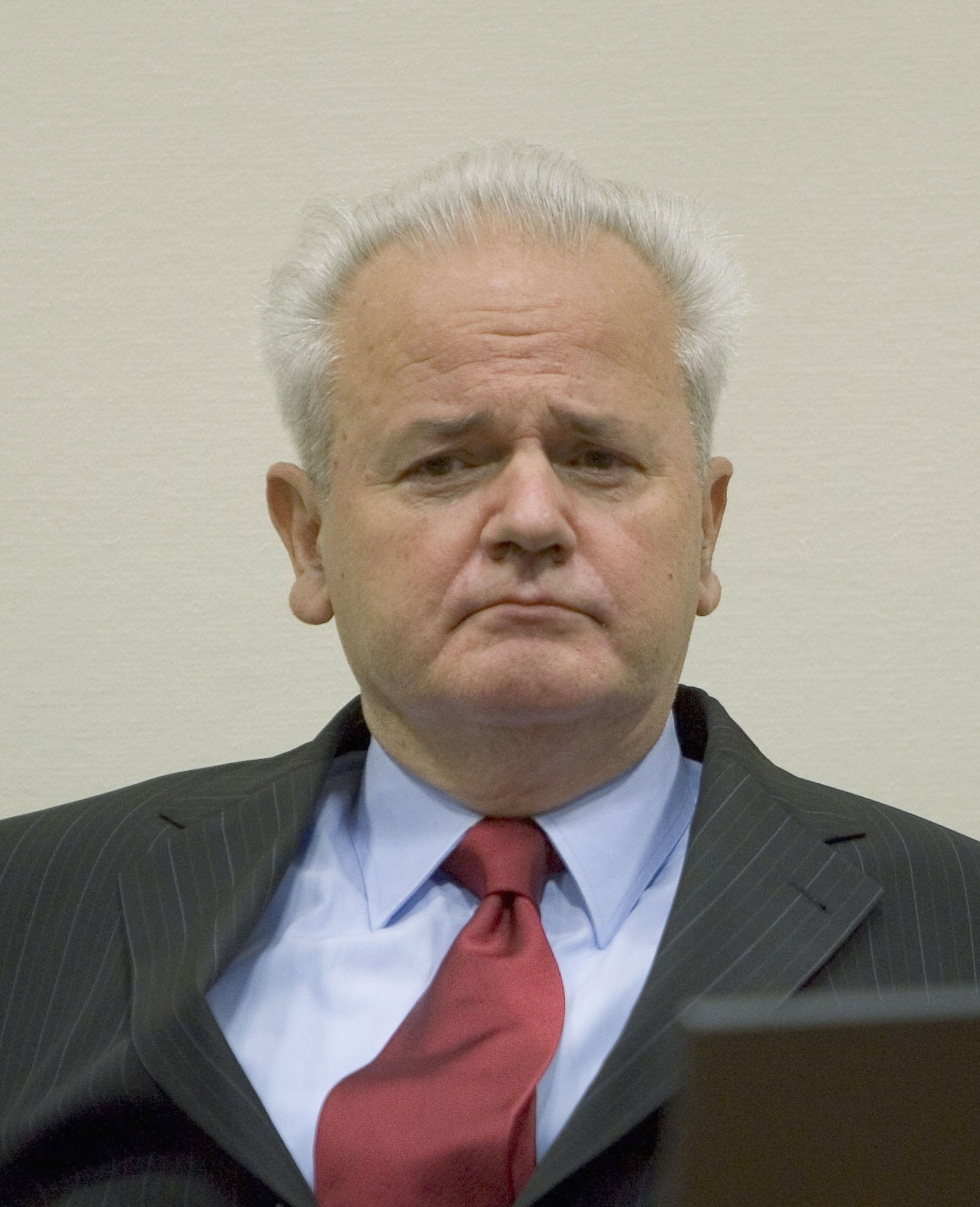

86
New cards
Isreal vs Palestine
Israel had been made in the Holy Land and due to this, Palestinians disliked Israelis because the Palestinians were displaced. They had ongoing tension.
87
New cards
Enlightenment
The period in European history when reasoning (logic) was used to understand and improve society.
88
New cards
Divine Rights
Power was given to those who were chosen by the gods. Enlightenment philosophers believed that governments receive their authority from the people and not from God.
89
New cards
French Revolution
The people of France overthrew King Louis XVI (killed by the Jacobins) and fought for more rights.
* The Third Estate included mostly peasants and they had less rights than the other estates and were taxed the most out of the three.
* France was ruled by absolute monarchs who abused their power and denied the rights of the people.
* France was economically unstable because the kings would spend way too much money and basically put France in debt.
* The middle class of France gained more power & rights.
* The Third Estate included mostly peasants and they had less rights than the other estates and were taxed the most out of the three.
* France was ruled by absolute monarchs who abused their power and denied the rights of the people.
* France was economically unstable because the kings would spend way too much money and basically put France in debt.
* The middle class of France gained more power & rights.
90
New cards
Haiti Revolution
Slaves in the French colony Saint Domingue (Haiti) revolted & fought for their independence.
* France colonized Haiti & used slave labor to get access to the island's natural resources.
* The people there were also mistreated and discriminated against.
* France colonized Haiti & used slave labor to get access to the island's natural resources.
* The people there were also mistreated and discriminated against.
91
New cards
The Latin Revolutions (1800 - 1830)
**They fought for independence from Spain, Portugal, and France.**
* **Governments were controlled by Peninsulares (People from Spain & Portugal) who treated Latinos poorly. Creoles (Europeans born in Latin America), Mestizos (mixed Europeans/Native Americans), Native Americans, and African slaves demanded more rights.**
* **Governments were controlled by Peninsulares (People from Spain & Portugal) who treated Latinos poorly. Creoles (Europeans born in Latin America), Mestizos (mixed Europeans/Native Americans), Native Americans, and African slaves demanded more rights.**
92
New cards
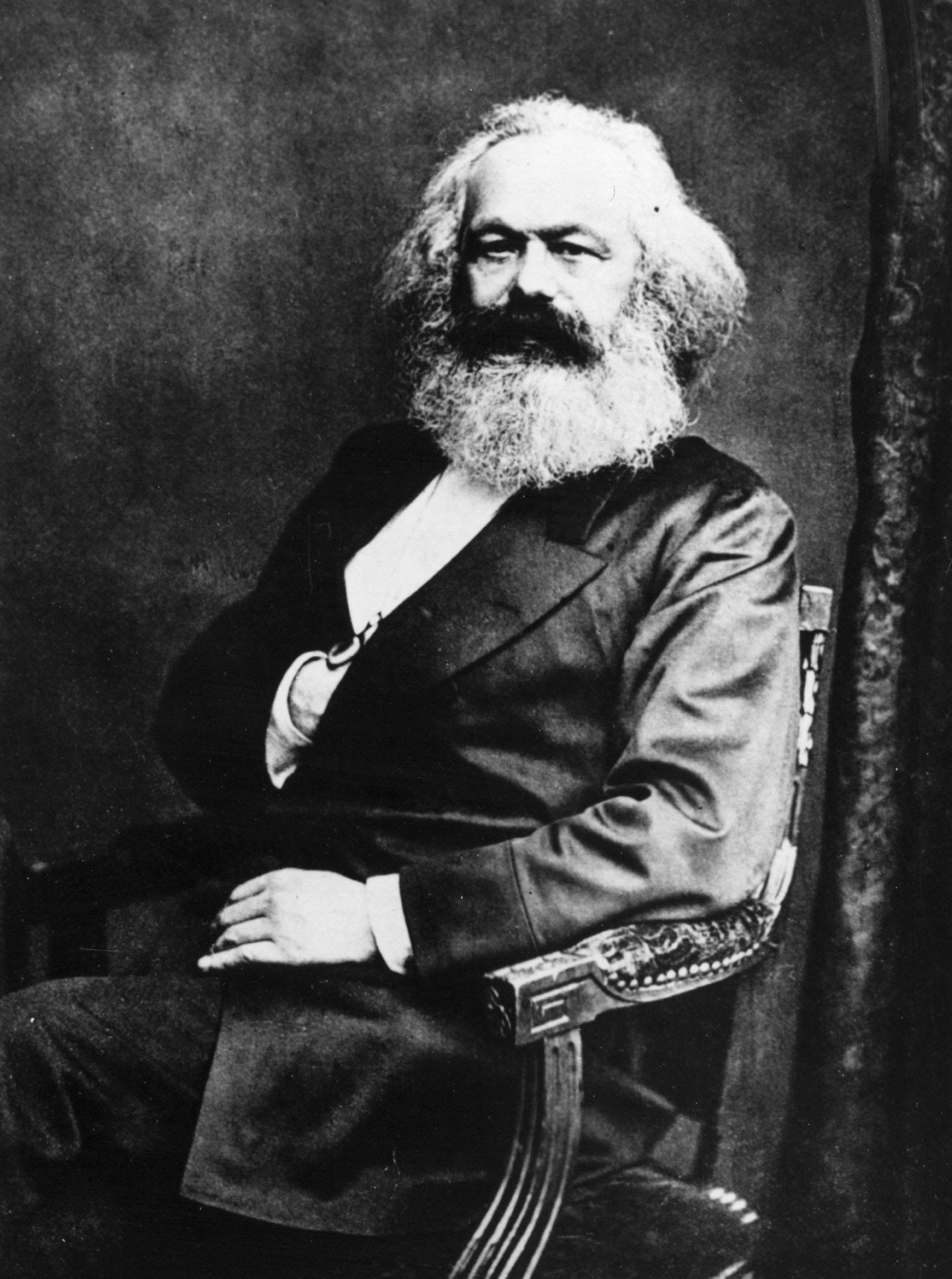

Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels
They believed that capitalism was bad. They thought that it allows factory owners to exploit factory workers. They also wrote a book called the Communist Manifesto that basically states how the Bourgeoisie (wealthy factory owners) would exploit the Proletariat (poor factory workers) to earn more money and they basically wanted the Proletariat to revolt against it and eliminate capitalism.
The idea of Marx & Engels became the foundation of Communism and inspired the Soviet Union and China.
The idea of Marx & Engels became the foundation of Communism and inspired the Soviet Union and China.

93
New cards
Potato famine
(1845 - 1850) About 1 million Irish people died of famine when their potato crops failed to grow because of potato blight. Over 1 million Irish people migrated to the United States to escape the famine & find more opportunities.
94
New cards
Nationalism in Ireland
Due to nationalism, many Irish people didn’t want to be ruled by Great Britain so they fought for independence so Southern Ireland gained independence in 1921.
95
New cards
Meiji Restoration (1868 - 1912)
Japan was ruled by Emperor Meiji and during his ruling, Japan was being modernized, industrialized, and westernized.
During the Meiji period, Japan became a powerful and modernized country and started to colonize other countries.
During the Meiji period, Japan became a powerful and modernized country and started to colonize other countries.
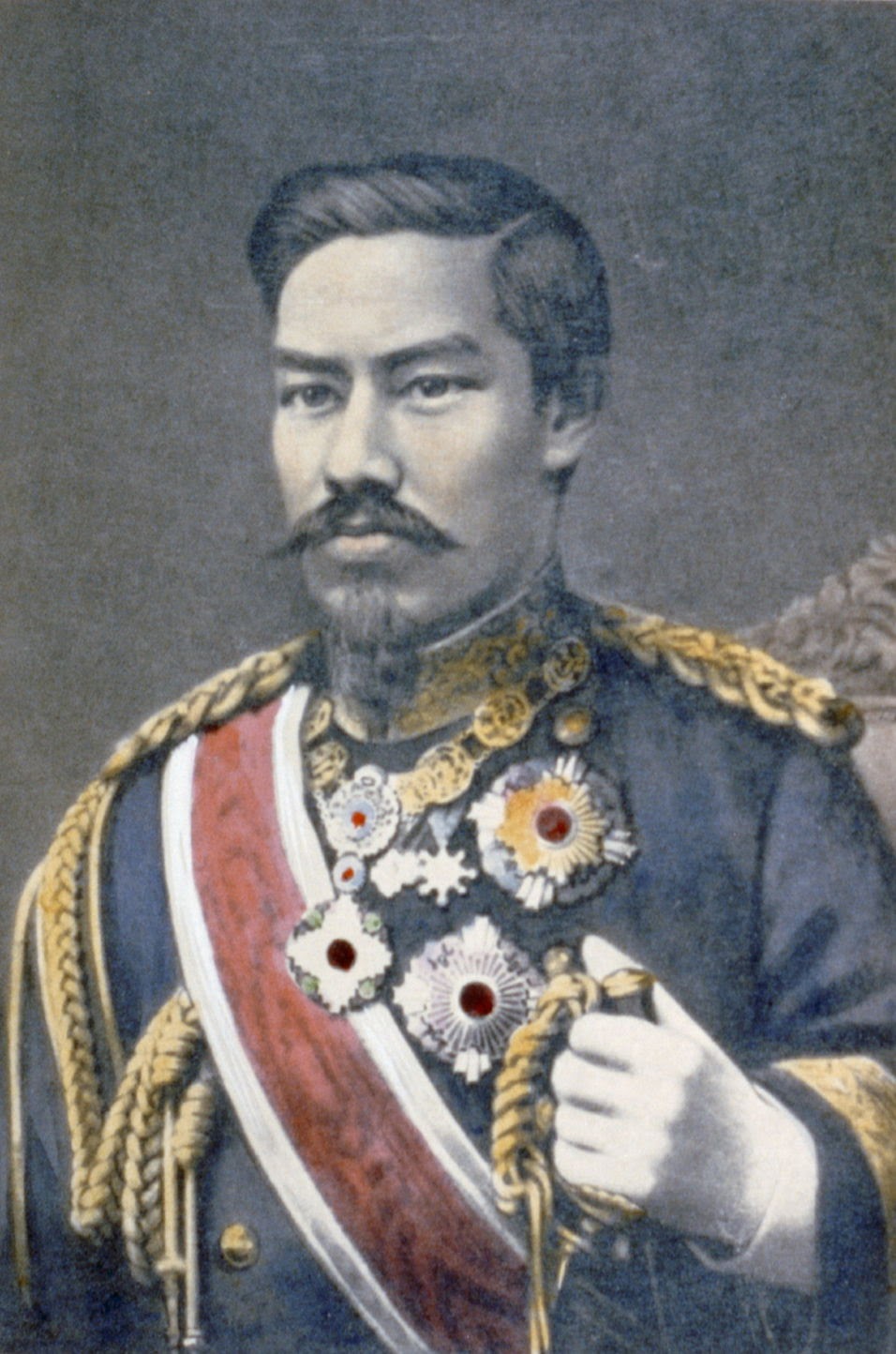

96
New cards
Bolshevik Revolution (1917)
The people of Russia overthrew their Czar (king) and created a new government. Because of WWI, Russians suffered many casualties and WW1 created food shortages at home.
During the revolution:
* Czar Nicholas II was executed.
* Lenin and the Bolsheviks came to power in Russia.
* Russia became a communist nation.
During the revolution:
* Czar Nicholas II was executed.
* Lenin and the Bolsheviks came to power in Russia.
* Russia became a communist nation.
97
New cards
One political party
Only the political party of the dictators was allowed to exist.
98
New cards
Command (Communist) economy
The government owns the businesses, make business decisions, and sets prices.
99
New cards
Battle of the Stalingrad
Hitler fought for Russia but had lost due to the harsh climate and large size of the nation.

100
New cards
United Nation formation
formed to solve international problems and prevent future wars. 191 nations currently belong to the United Nations and they’re made up of 6 main bodies.