UPTP INGRESO 2023
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Ley del Seno
proporción existente entre los lados y senos de los ángulos de un triángulo.
a/sen(a) = b/send(b) = c/sen(c)
Ley del coseno
el cuadrado de un lado es igual a la suma de los cuadrados de los lados restantes menos el cos del lado elegido por el producto de los lados restantes.
a²=c²+b²-2cos(a)×c×b
Seno de suma o resta de ángulos
sen(a+b) = sen(a)cos(b) + sen(b)cos(a)
Coseno de suma o resta de angulos
cos(a±b) = cos(a)cos(b) -/+ sen(b)sen(a)
Suma a multiplicacion de senos
sen(a) + sen(b) = 2sen((a+b)/2)cos((a-b)/2)
Resta a multiplicacion de Senos
sen(a) - sen(b) = 2sen((a-b)/2)cos((a+b)/2)
Suma a multiplicacion de cosenos
cos(a) + cos(b) = 2cos(a+b/2)cos(a-b/2)
Resta de cosenos a multiplicacion
cos(a) - cos(b) = -2sen(a+b/2)sen(a-b/2)
Multiplicacion a suma de seno por coseno
sen(a)cos(b) = ½(sen(a+b) + sen(a-b))
Multiplicación a suma de seno por seno
sen(a)sen(b) = ½(cos(a+b) - cos(a-b))
Multiplicación a suma de coseno por coseno
cos(a)cos(b) = ½(cos(a+b) + cos(a-b))
Summ of arithmetic sequence
S = n(a1 + an)/2
Summ of geometric sequence
S = a1(r^n - 1)/r-1
Heron's formula
√(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)) where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, and a, b and c being the corresponding sides.
sen(π/3)
√3/2
Send(π/6)
½
Sen(π/4)
√2/2
Sen(0)
0
Send(π/2)
1
Cos(π/3)
½
Cos(π/6)
√3/2
Cos(π/4)
√2/2
Cos(0)
1
Cos(π/2)
0
Tg(π/3)
√3
Tg(π/6)
√3/3
Tg(0)
0
Tg(π/2)
Indefinido.
Log(2)
0.301
Log(3)
0.477
√2
1,41
√3
1,73
√5
2,23
Limacons
a ± b(sen(a))
a ± b(cos(a))
Circles
r = a
r = asen(x)
r = acos(x)
Trigonometric equations
a(sen(k(x-h)) or cos
Where a is the amplitude, w is the speed, and h is the horizontal shift.
t = 2π/k (π/k for tg), where t is the period (f = 1/t)
Amplitude (shifted vertically)
(Max value + |min value|) /2
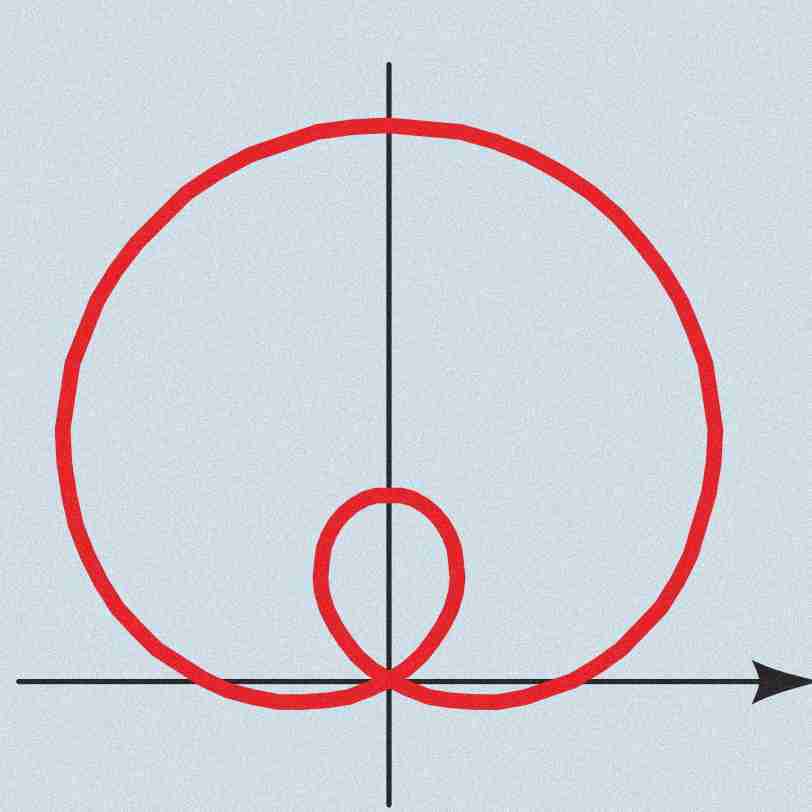
Limacon with inner loop
a ± bsen(x) where a < b
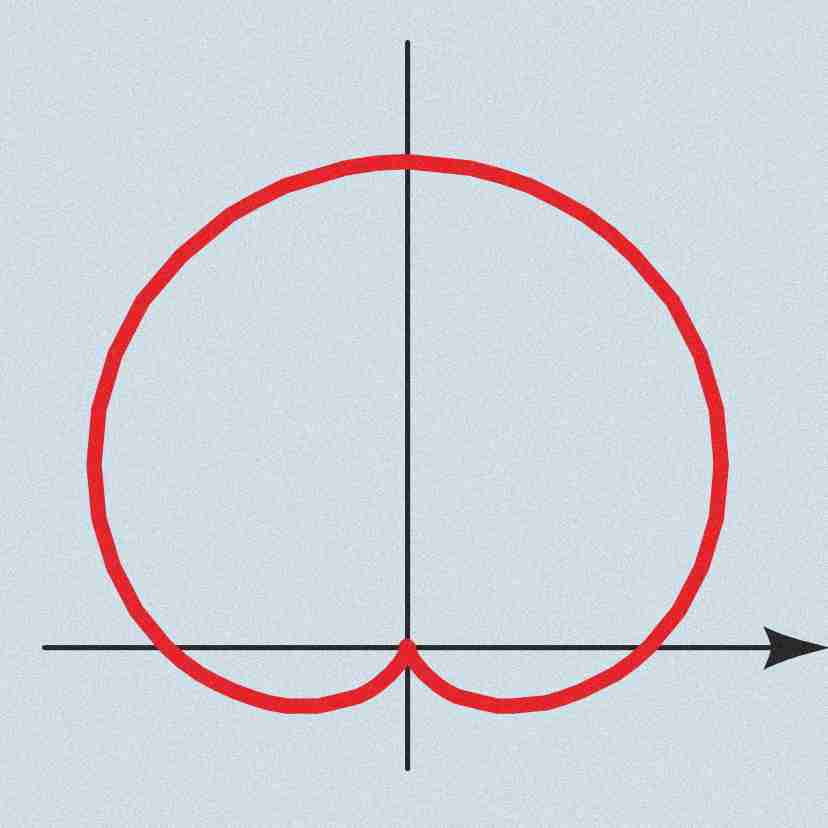
Cardiod
a ± bsen(x) where a = b
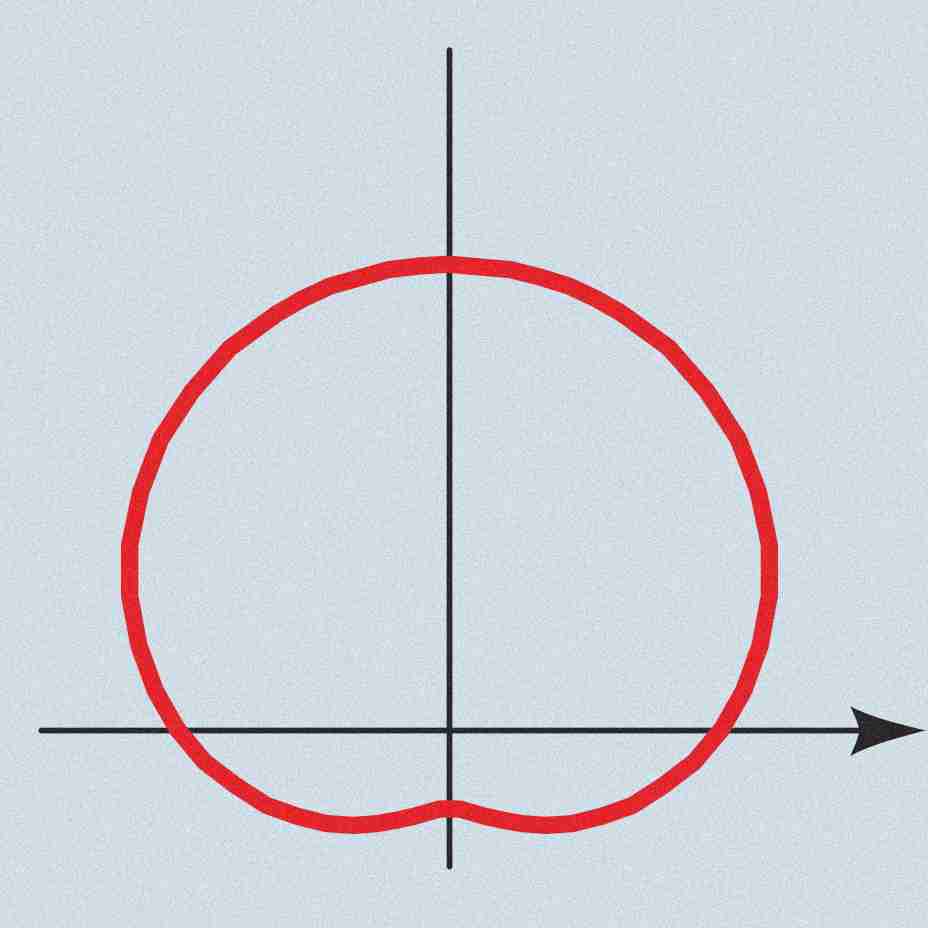
Dumped limacon
a ± bsen(x) where a > b
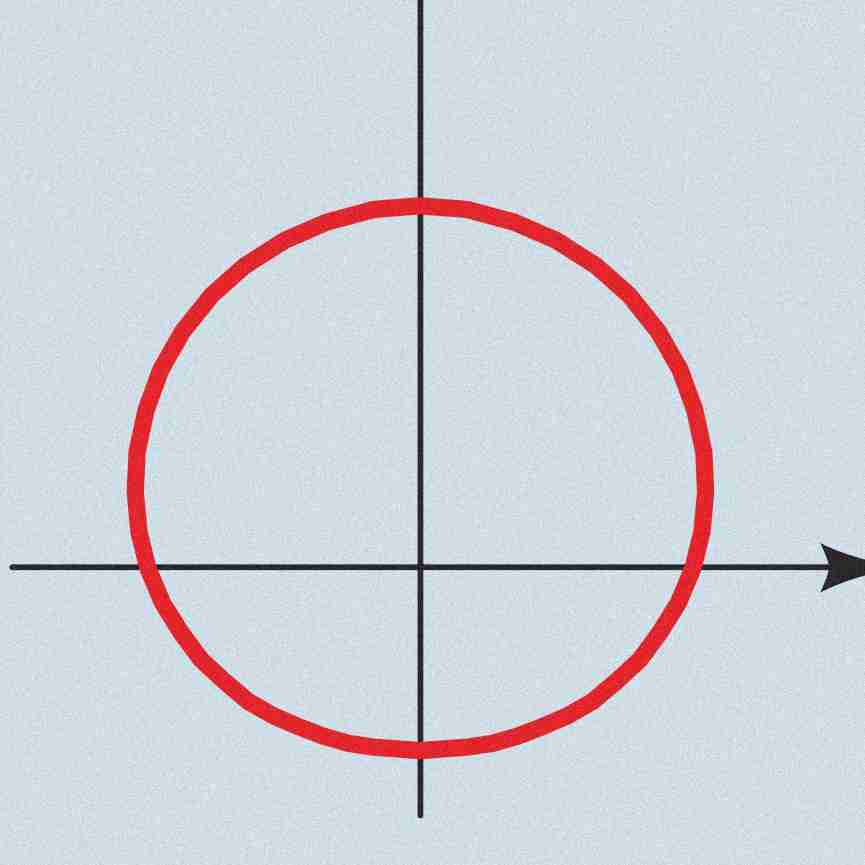
Convex limacon
a ± bsen(x) where a >= 2b
Spiral
r = aΩ
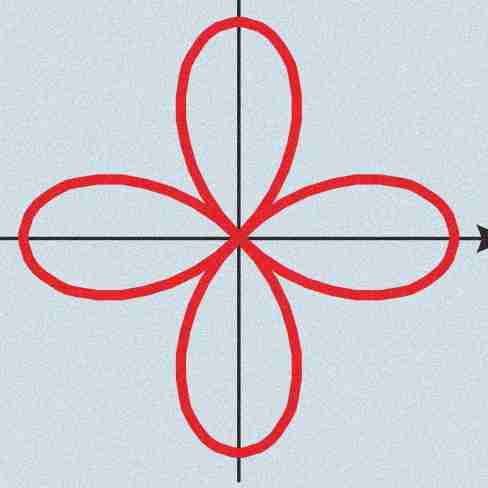
Rose with even amount of leaves
a(sen(nΩ)) where n is even and there's 2n petals
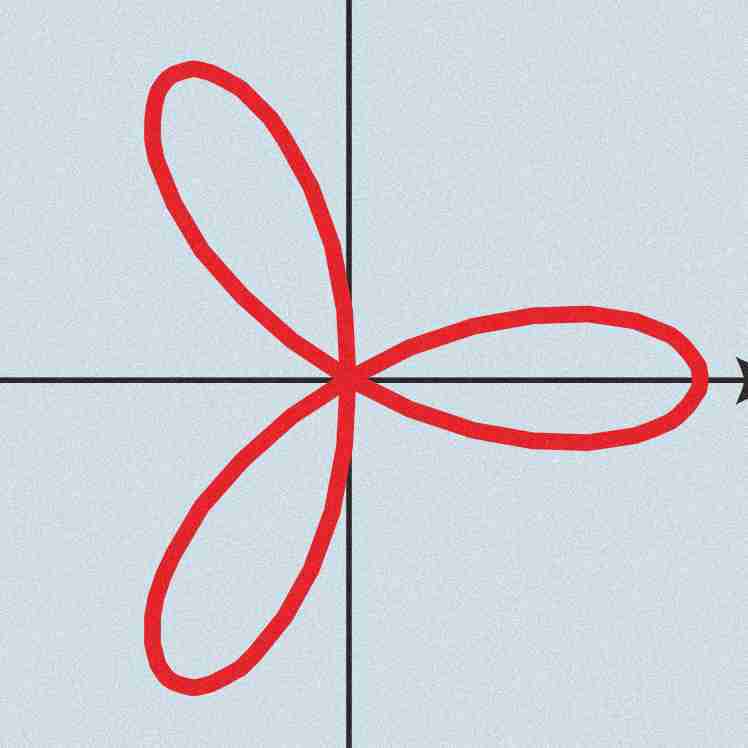
Rose with odd amount of petals
a(sen(nΩ)) where n is odd, and there's n petals
Dot product
a•b = |a||b|cos(θ)
Cross product
a×b = |a||b|sen(θ)
Moivre´s theorem
zn = rn (cos(rθ) + sin(rθ)i), where r is the module of z, and θ is the angle that z creates with x and y (tg-1(y/x)
z1/z2
r1/r2(cos(θ1-θ2) + sen(θ1-θ2))
z1*z2
r1*r2(cos(θ1+θ2) + sen(θ1+θ2))
Projection of U onto V
(A•V/|V|2)* V
Sen(π+x)
-sen(x)
Sen(π/2 + x)
Cos(x)
Sen(π/2 - x)
Cos(x)
Cos(π+x)
-cos(x)
Tg(π+x)
Tg(x)
Cos(π/2 + x)
-sin(x)
Cos(π/2 - x)
Sin(x)
Tg(π/2+x)
-cotg(x)
Tg(π/2 - x)
Cotg(x)
Sin(-x)
-sin(x)
Cos(-x)
cos (x)
tg(-x)
-tg(x)
Suma o resta de ángulos en tangente
tg(a+b) = tga ± tgb / 1 ± tga*tgb
Medio ángulo de seno
√(1-cos/2)
Medio ángulo de coseno
√(1+cos/2)
Medio ángulo de tg
sin(x)/1+Cos(x) = 1-cos(x)/sin(x)
y > |x|
espacio chiquito
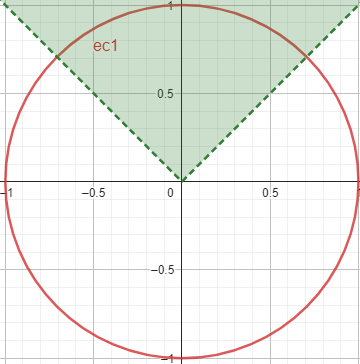
x > |y|
espacio chiquito
range of sin-1
− π/2 to π/2
range of cos-1
0 to π
range of tg-1
− π/2 to π/2
Binomio cubo
(a±b)3 = a3±3a2b+3ab2±b3
Suma y resta de cubos
a3 ± b3= (a ± b)( a2-/+ ab + b2 )
Infinite geometric progression formula
a1/1-r
Compound interest
A = P(1+r/n)nt where p is inital value, r is interest rate, n is amount of times per year and t is years
Pythagorean identities
Tg2(x)+ 1 = sec2
Cotg(x)2 +1 = csc2(x)
sen2(x)+ cos2(x)= 1
Polar to linear
root(x + y) = r
r*cos(theta) = x
r*sin(theta) = y
y/x = theta
Discriminant of conics
Ax + Bxy + Cy + Dx + Ey + F
if B2- 4AC = 0 Is an parabola
if B2 - 4AC > 0 Hyperbola
If B2 - 4AC < 0 Elipse or circle
Newtons Cooling law
Tf = Ts + (T0 - Ts) e-r/t where Ts is the surrounding temperature, T0 is the initial temperature and -r is the rate of change for the specific material.