DMS 233 - OB General Information - Midterm Practice Questions
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is considered the most common congenital craniofacial anomaly?
Cleft lip with or without palate
A jaw index value below what number is suggestive for micrognathia after 18 weeks?
21
What is strongly associated with chromosomal abnormalities which affect AFP?
Cystic Hygroma
What is considered abnormal for nuchal fold thickness?
> 6mm
What maternal disease is an indication associated with fetal goiters?
Grave’s Disease
What system is abnormal with cystic hygromas?
Lymphatic
Which of the following placental shapes is the rarest variant?
Circumvallate placenta
Normal AFI should be between what range?
5-25cm
Which procedure is performed to examine blood from the fetal umbilical cord to detect fetal abnormalities?
Cordocentesis
At what age is a mother considered advanced maternal age (AMA)?
>35
During a routine exam at 28-weeks, a monochorionic/diamniotic twin pregnancy shows one twin with oligohydramnios and a small, “stuck” appearance against the uterine wall, while the co-twin has polyhydramnios with a visibly enlarged bladder. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS)
A 32-week fetus measures with a HC at the 50th percentile and an AC at the 5th percentile. The BPD is normal. Which of the following the most likely diagnosis?
Asymmetric IUGR
The maternal quad screen includes all of the following except:
- AFP
- hCG
- CVS
- uE3
- inhibin-A
CVS
Which of the following is produced by the yolk sac in early gestation and later in pregnancy by the fetal liver?
AFP
MSAFP levels increase with advancing GA and peak from ___ to ___ weeks of gestation.
15-18
AMA increases the risk for …
Down Syndrome
Miscarriage
Preeclampsia
What age is considered AMA?
35 years old at the time of delivery
What does AMA stand for in high risk pregnancies?
Advanced maternal age
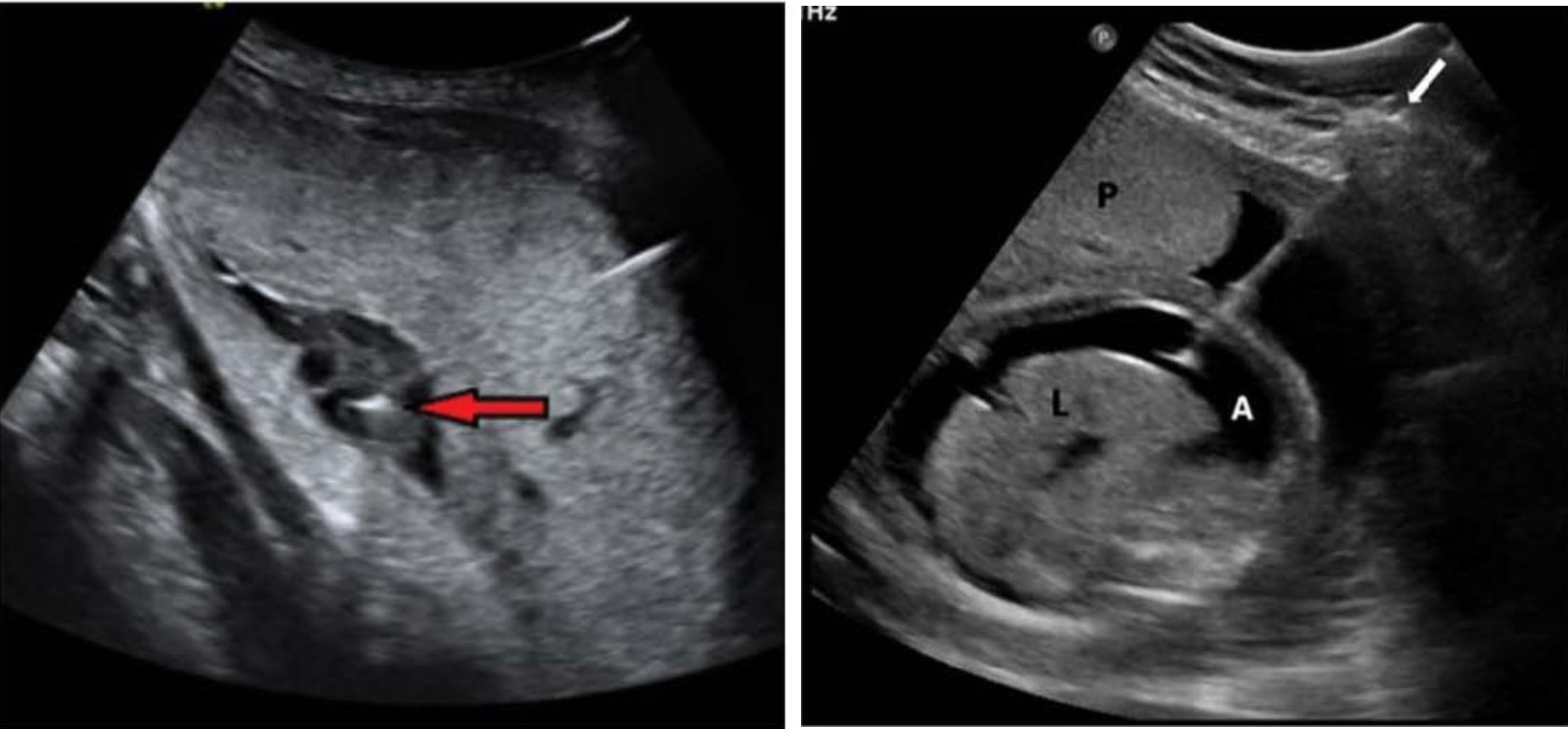
Which image is intravascular and which is intraperitoneal transfusion?
Left is intravascular, right is intraperitoneal
What is the purpose of a cordocentesis?
A blood sample is obtained for the analysis of chromosomes
What is one difference between intraperitoneal and intravascular transfusion?
Intravascular evaluates for RBCs
Ultrasound for for alloimmune thrombocytopenia checks for…
In-utero intracerebral hemorrhage
How is alloimmune thrombocytopenia treated?
Cordocentesis
What is alloimmune thrombocytopenia?
Mother’s immune system develops antibodies against the fetal platelets
How is PROM diagnosed?
Oligohydramnios
Common sign for PROM:
“water breaking”
What is PPROM?
Preterm Premature Rupture of membranes before 37 weeks GA
What is preterm labor defined as?
The onset of labor before 37 weeks of gestation
True or False: Multiple gestations increase the risk for preterm labor
True
What cervical length may indicate preterm labor?
Less than 3 cm
When is an amniocentesis typically done?
15-20 weeks
True or False: An amniocentesis is performed transabdominally
True
What is the purpose of an amniocentesis?
Analyzes fetal chromosomes
Obese women are at an increased risk for all of the following except …
- pregnancy induced hypertension
- Stillbirth
- PROM
- Fetal anomalies
PROM
A fibroid that outgrows its blood supply and undergoes necrosis may cause …
Pain and premature labor
The presence of maternal serum IgG antibody against one of the fetal RBC antigens is a process known as...
Sensitization
____ represents the occurrence of seizures or coma in a preeclamptic patient.
Eclampsia
What is the primary fuel for fetal growth?
Glucose
With systemic lupus erythematosus, the fetal heart must be monitored to rule out...
Congenital Heart Block
How is fetal anemia treated?
Intrauterine transfusion
What is one sonographic sign of fetal anemia?
Hepatomegaly/Splenomegaly
What can fetal anemia lead to?
Fetal hydrops