Pathophysiology and Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease: Dopamine Neurodegeneration and Motor Impact
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What are the primary symptoms of Parkinson's Disease?
Bradykinesia, tremor, cogwheel rigidity, and shuffling gait.
What is the role of a-synuclein in Parkinson's Disease?
It is involved in neurotransmitter release, dopamine release, membrane stabilization, and mitochondrial regulation.
What are Lewy bodies and what are they composed of?
Lewy bodies are aggregates formed from a-synuclein protein.
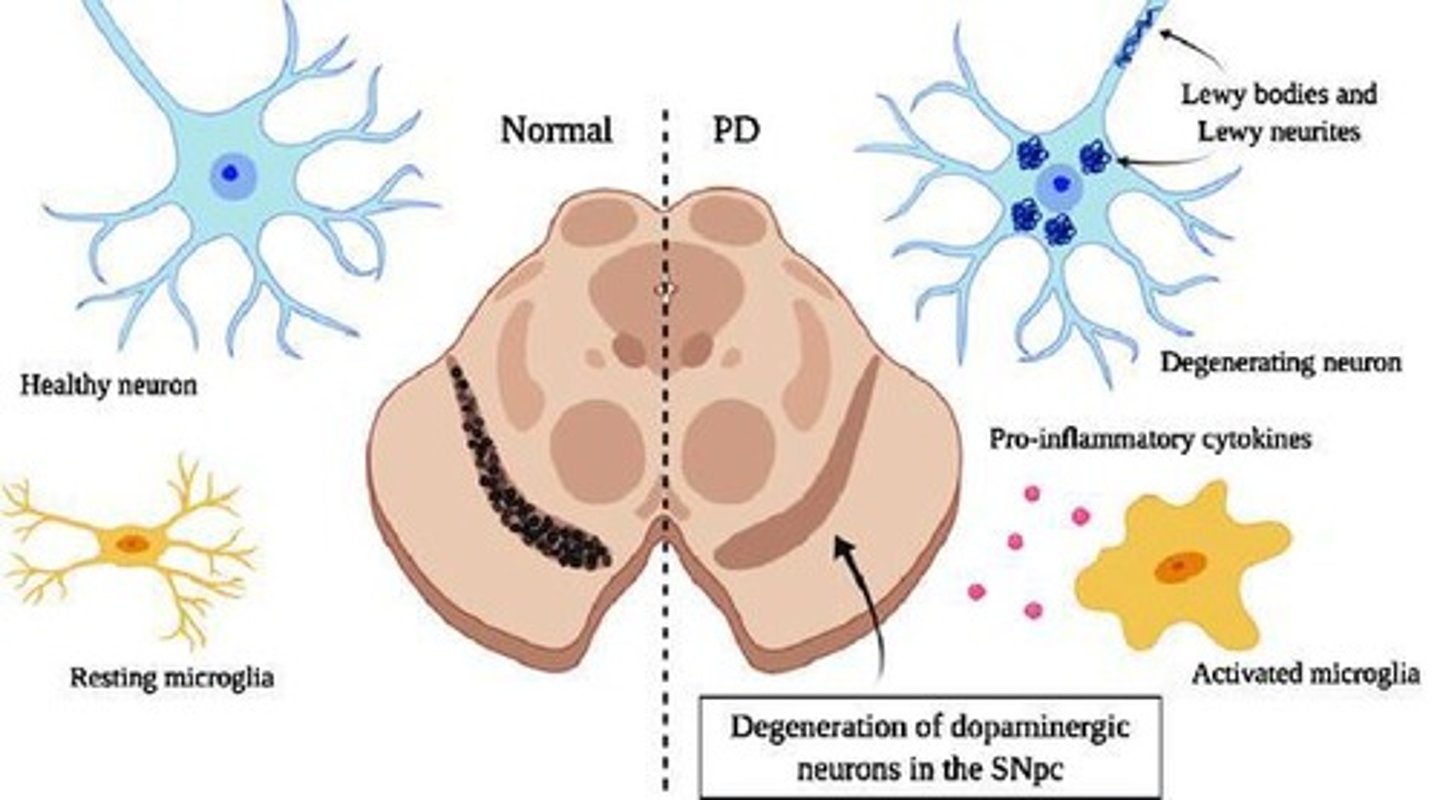
What percentage of dopamine neurons are lost before Parkinson's symptoms appear?
70-80% loss of dopamine neurons occurs before symptoms present clinically.
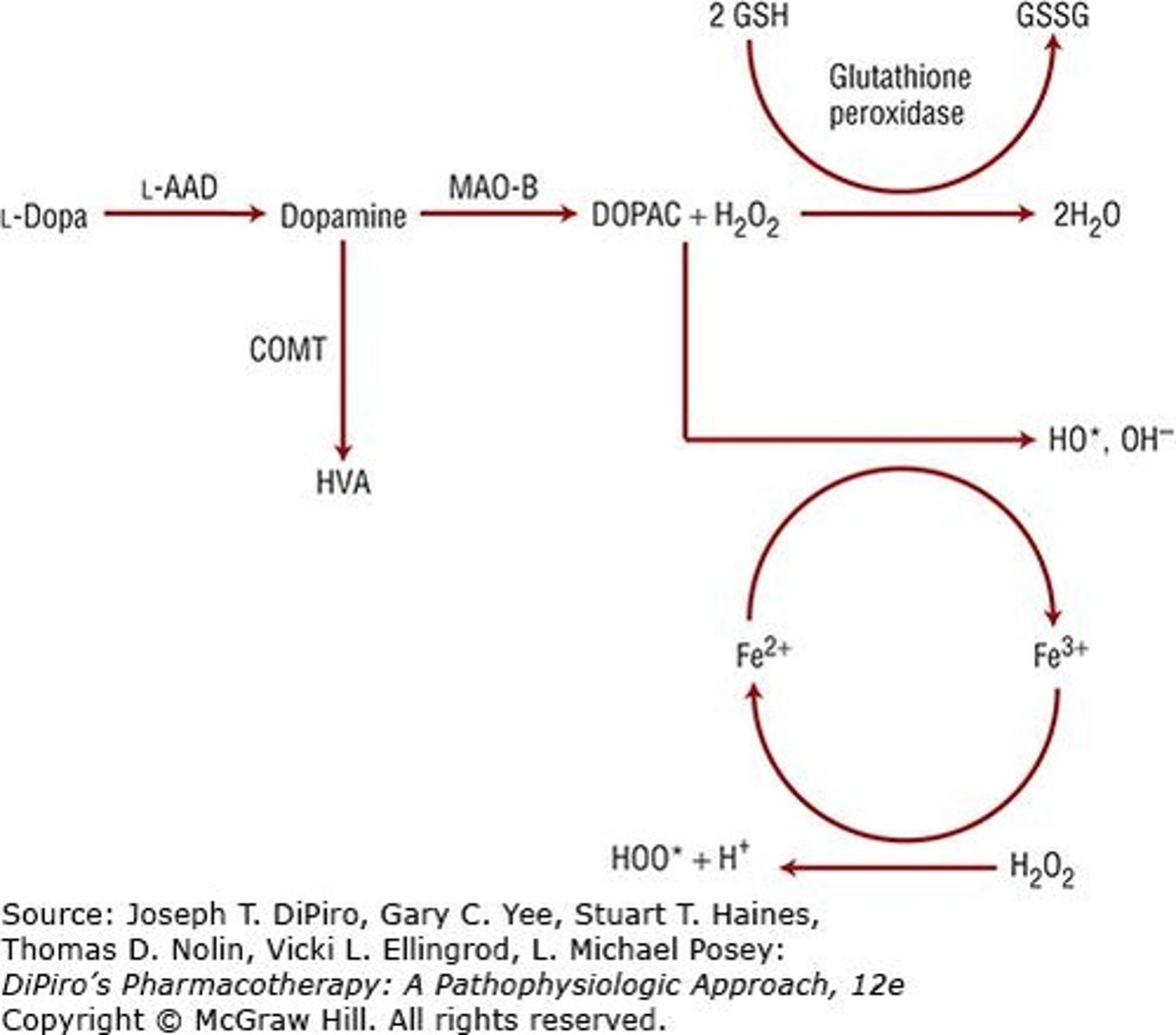
Why are dopamine neurons particularly susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson's Disease?
Increased dopamine metabolism leads to higher free radical production, which contributes to neuronal degeneration.
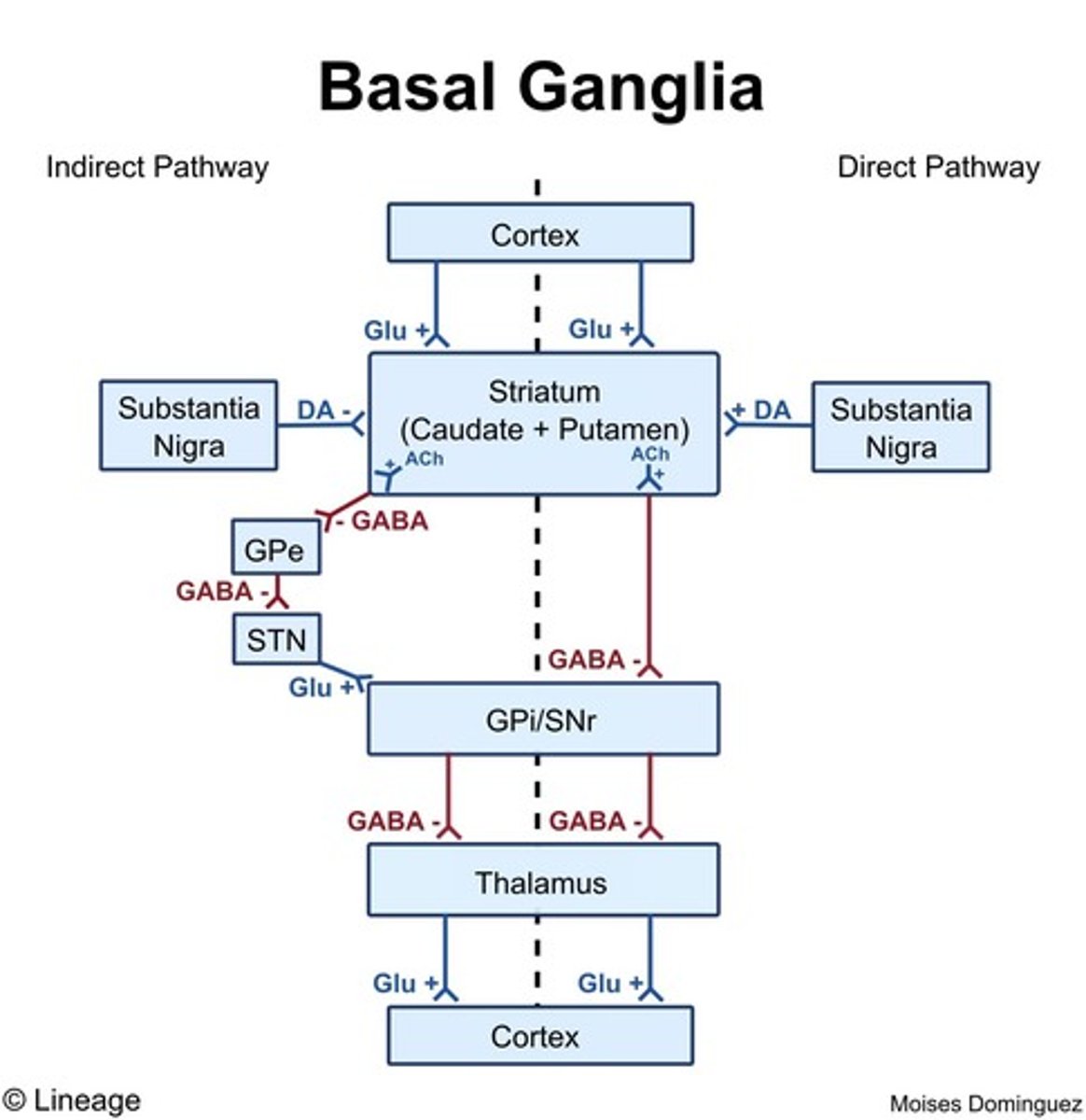
What is the impact of dopamine neurodegeneration on movement?
It results in decreased stimulation of the direct pathway and disinhibition of the indirect pathway in the thalamus.
What is bradykinesia?
A symptom of Parkinson's Disease characterized by slowness of movement.
What is cogwheel rigidity?
A symptom of Parkinson's Disease where muscle stiffness occurs with a ratchet-like resistance to passive movement.
What is the significance of the nigrostriatal tract in Parkinson's Disease?
It is the pathway where dopamine neurons degenerate, affecting motor control.
How does a-synuclein affect neurotransmitter release?
It helps regulate the release of neurotransmitters at presynaptic terminals.
What role does a-synuclein play in mitochondrial regulation?
It may regulate mitochondrial functions, including fusion and the electron transport chain.
What is the shuffling gait in Parkinson's Disease?
A symptom characterized by a slow, dragging walk with small steps.
What is the relationship between dopamine and free radicals in Parkinson's Disease?
Increased dopamine metabolism leads to higher production of free radicals, contributing to neuronal damage.