L8: Analyzing Agent-Based Models
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Types of measurements and when to think about them
• Good to know what you want to measure and analyze before you build your model
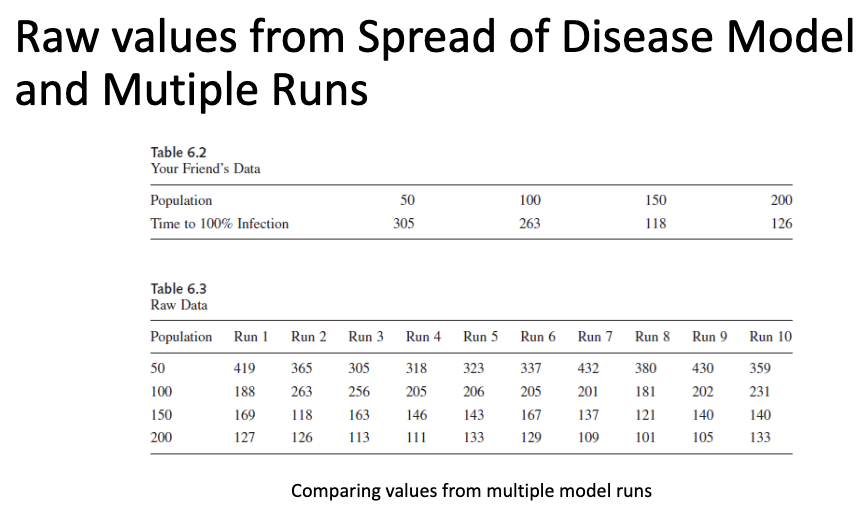
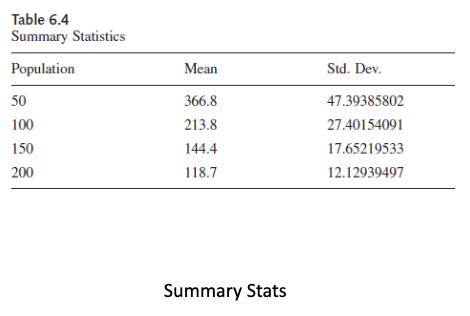
e.g., measuring time to 100% infection in population at various population sizes
traffic throughput, population size, etc.
• Should be clearly linked with a research question or goal
Why do we need multiple runs in AGM?
ABM employs randomness so the measures will vary from one ‘run’ to the next
• Sampling error - we want to be confident that our results are robust
E.g., what is the trend we observed when population increases?
How many runs do we need?
100 - 10,000 - it really depends
• Number of parameters
• Convention
• Variance stability
• Power analysis (detecting effects)
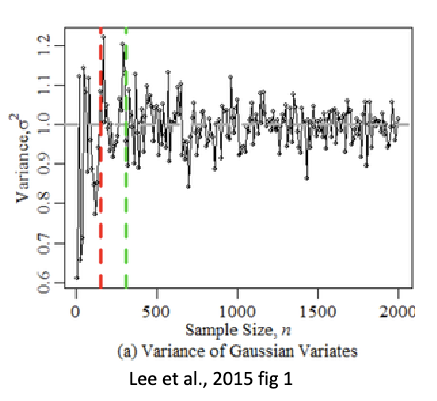
How do you conduct variance stability?
• Look at variance across sample sizes (runs)
• Set a threshold (e.g., E ~ 0.01)
• nmin = coefficient of variation ᵅᵆ = ᵰ/ᵰ (sd/mean) from consecutive sample sizes < E
• e.g., ᵅ ∈ {10, 500, 1000, 5000, 1000} and ᵅᵆ ∈ {.42,.28,.21,.21,.21}
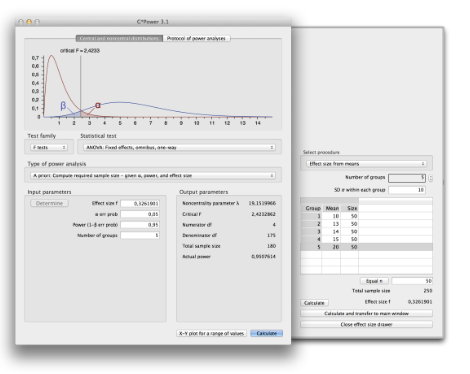
How do you conduct power analysis?
• G*Power
• Need to know what kind of analysis you plan to do, and what size effect you might expect (or a range)
What is Parameter sweeping/sensitivity analysis?
Systematically checking the plausible range of parameter values
Assess the important of parameters on model behavior
Could be the key thing that drives your research question
Levels of a certain parameter
Determine how the other parameters effect the key behavior you observe
What are the 2 statistical analyses of ABM?
Descriptive Statistics
Means, standard deviations, medians, and other methods of analyzing the values of a variable.
Inferential statistics
To compare different models, models with different params, to model patterns in output, etc.

BehaviorSpace tool
What are the 4 Types of data to analyze from ABMS?
• statistical
• graphical
• network-based
• spatial
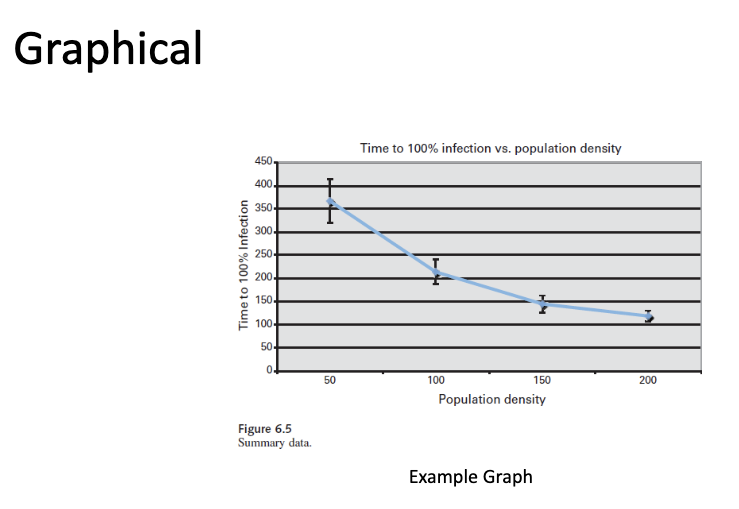
How do you analyze graphical models?
Outgrowth of statistical results
• Transform statistical results into graphs that can be more easily examined by the observer
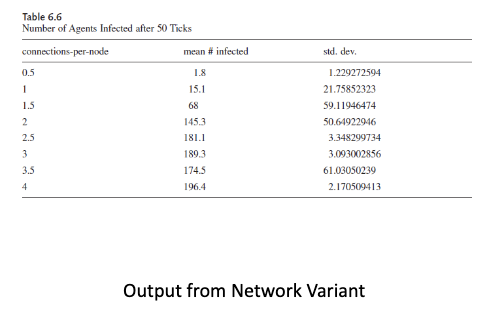
How do you analyze network models?
• Have to reconsider metrics for network model because some options are not viable (e.g., may never reach 100% infection of population with less connected nodes)
Termination criteria for experiments (e.g., fixed time and number of infected)
• Other ideas could be cluster coefficient, path length, node centrality, etc.
Spatial Analysis and Environment
• Analysis of patterns of variables in a one-, two-, or higher-dimensional space, and they frequently address questions regarding the pattern of data in the space (or in interaction with the space)
• See Environmental variant of Spread of Disease model

Describe Validation, verification, and replication
Model validation
• Determine whether the model corresponds to the real-world phenomenon
Model Verification
• Determine whether implemented model corresponds to target conceptual model
Model Replication
• Someone else implements the model and sees if the results are consistent