Acid-Base Equilibrium
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:35 AM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
acid
**ARRHENIUS DEFINITIONS:**
Substances that __ionize__ in water to produce hydrogen ions, **H+(aq)**.
Substances that __ionize__ in water to produce hydrogen ions, **H+(aq)**.
2
New cards
base
**ARRHENIUS DEFINITIONS:**
Substances that __dissociate__ in water to produce hydroxide ions, **OH-(aq)**.
Substances that __dissociate__ in water to produce hydroxide ions, **OH-(aq)**.
3
New cards
acid
**BRONSTED-LOWRY DEFINITIONS:**
The proton, H+(aq), **donor** in a reaction.
* e.g. hydrofluoric acid + water
The proton, H+(aq), **donor** in a reaction.
* e.g. hydrofluoric acid + water
4
New cards
base
**BRONSTED-LOWRY DEFINITIONS:**
The proton, H+(aq), **acceptor** in a reaction.
* ammonia + water
The proton, H+(aq), **acceptor** in a reaction.
* ammonia + water
5
New cards
amphoteric substance
Substances that can act as either an acid or a base.
* Water acts as a **base** with hydrofluoric acid, but as an **acid** with ammonia.
* Water acts as a **base** with hydrofluoric acid, but as an **acid** with ammonia.
6
New cards
strong acid
Completely ionizes in water.
7
New cards
weak acid
Only a fraction of the molecules ionize in water.
8
New cards
conjugate acid-base pair
Molecules or ions related by the **transfer of a proton**. An acid becomes a conjugate base when a proton is removed, and a base becomes a conjugate acid when a proton added.
9
New cards
ion-product constant
\
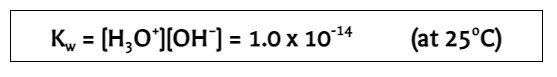
10
New cards
percent ionization
The **ratio** of the concentration of ionized molecules at equilibrium, to the initial concentration of the weak acid, expressed as a percent:
* A **strong acid** almost completely ionizes in water to form hydrogen ions, and its **% ionization > 99%**.
* A **weak acid** partially ionizes in water to form hydrogen ions, and most have a **% ionization < 50%**.
* A **strong acid** almost completely ionizes in water to form hydrogen ions, and its **% ionization > 99%**.
* A **weak acid** partially ionizes in water to form hydrogen ions, and most have a **% ionization < 50%**.

11
New cards
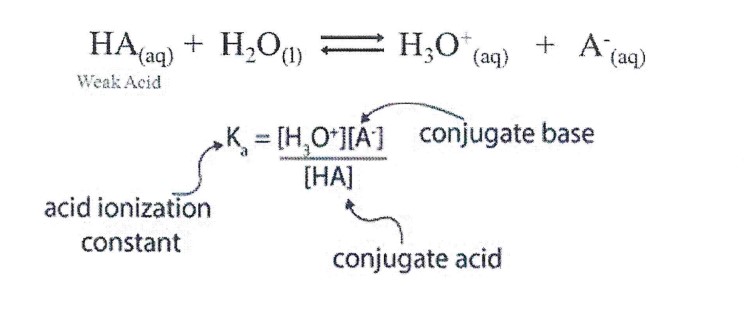
acid ionization constant
**Ka**
A **weak acid** partially ionizes, donating protons in water. At **equilibrium**, there will be **BOTH** the **weak acid**, HA, and its **conjugate base**, A-, in the solution.
A **weak acid** partially ionizes, donating protons in water. At **equilibrium**, there will be **BOTH** the **weak acid**, HA, and its **conjugate base**, A-, in the solution.
12
New cards
monoprotic acid
Has **one** ionizable hydrogen atom.
* e.g. HCl (aq), HNO3 (aq), HClO (aq)
* e.g. HCl (aq), HNO3 (aq), HClO (aq)
13
New cards
polyprotic acid
Has **more than one** ionizable hydrogen atom.
* e.g. H2SO4 (aq), H3PO4 (aq)
\
With the __exception of sulfuric acid__, all of these acids are **weak**. They __*do not ionize completely in one step*__, but rather __*in two or more steps*__. Each step has an ionization constant: Ka1, Ka2, Ka3, etc.
* e.g. H2SO4 (aq), H3PO4 (aq)
\
With the __exception of sulfuric acid__, all of these acids are **weak**. They __*do not ionize completely in one step*__, but rather __*in two or more steps*__. Each step has an ionization constant: Ka1, Ka2, Ka3, etc.
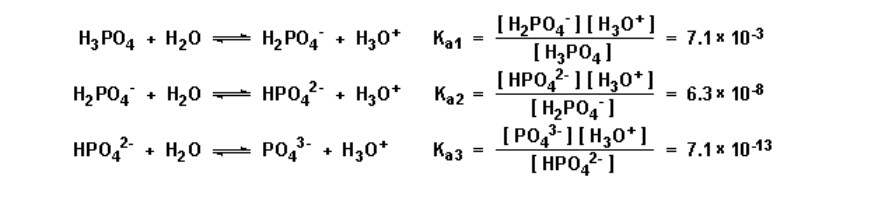
14
New cards
base ionization constant
**Kb**
A **weak base** partially ionizes, accepting protons in water. There are two main categories:
1. **Neutral substances** with an atom that has a nonbonding pair of electrons that can accept H+ (e.g. ammonia and the amines).
2. **Anions** of weak acids (conjugate base).
At **equilibrium**, there will be **BOTH** the **weak base**, B, and its **conjugate acid**, BH+, in solution.
A **weak base** partially ionizes, accepting protons in water. There are two main categories:
1. **Neutral substances** with an atom that has a nonbonding pair of electrons that can accept H+ (e.g. ammonia and the amines).
2. **Anions** of weak acids (conjugate base).
At **equilibrium**, there will be **BOTH** the **weak base**, B, and its **conjugate acid**, BH+, in solution.
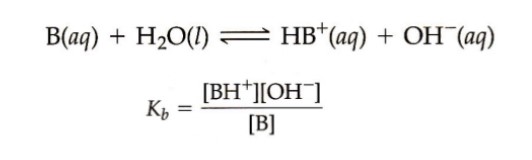
15
New cards
weak base
Partially ionizes, accepting protons in water.
16
New cards
salt
An ionic compound that forms during a **neutralization** reaction between an **acid** and a **base**. The **cation** (positive ion) comes from the **base**, and the **anion** (negative ion) comes from the **acid**.
17
New cards
hydrolysis
**A reaction in which one of the ions from a salt reacts with water, forming either an acidic or basic solution.**
Different salts will produce __various pH ranges__ in an aqueous solution depending on how the ions of the salt react with water to produce either H3O+ or OH- ions.
We can use the strengths of the “parent” acid and base to help us predict the pH of the salt solution.
We need to look at the **salt** and ask:
1. Which “parent” acid and base **reacted** to form the salt?
2. If the “parent” **acid/base** strong or weak?
* __***If it is a strong acid/base:**__ ***fully ionize in water, salt ion will NOT hydrolyze with water (acts as pH-neutral)***
* __***If it is a weak acid/base:**__ ***partially ionize in water, salt ion WILL hydrolyze with water (acts as weak base/acid)***
Different salts will produce __various pH ranges__ in an aqueous solution depending on how the ions of the salt react with water to produce either H3O+ or OH- ions.
We can use the strengths of the “parent” acid and base to help us predict the pH of the salt solution.
We need to look at the **salt** and ask:
1. Which “parent” acid and base **reacted** to form the salt?
2. If the “parent” **acid/base** strong or weak?
* __***If it is a strong acid/base:**__ ***fully ionize in water, salt ion will NOT hydrolyze with water (acts as pH-neutral)***
* __***If it is a weak acid/base:**__ ***partially ionize in water, salt ion WILL hydrolyze with water (acts as weak base/acid)***
18
New cards
titration
Used to determine the **molar mass**, **concentration**, or **pH** of one of the compounds in a neutralization reaction.
19
New cards
equivalence point
Point in a titration when the acid and base that are present **completely react** with each other (**n(a) = n(b)**).
* Located in the middle of steep rise of titration curve.
* Located in the middle of steep rise of titration curve.
20
New cards
endpoint
Point in titration where indicator **changes colour**.
* **pH = pKa** of the indicator (logKa)
* Pick an indicator that changes colour close to the equivalence point so there is **negligible volume** difference.
* **pH = pKa** of the indicator (logKa)
* Pick an indicator that changes colour close to the equivalence point so there is **negligible volume** difference.