longitudinal and transverse waves
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what do waves transfer
transfer energy from one place to another not matter
how do waves transfer
they oscillate
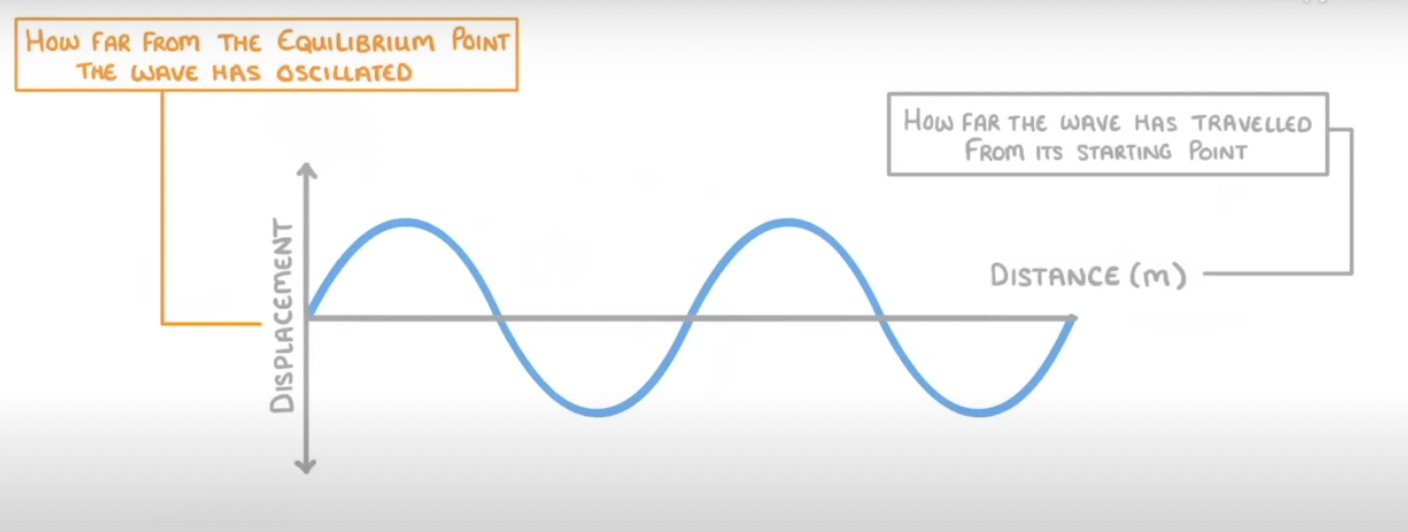
what are the two axis labelled on wave graph
distance or time on x axis
displacement on y axis
Transverse Waves
oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
transverse waves examples
electromagnetic
ripple waves
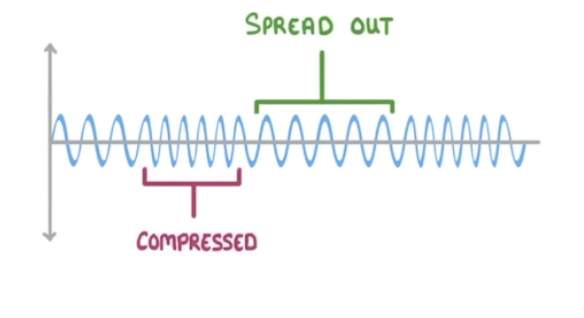
Longitudinal Waves
oscillations that are parallel to energy transfers
examples of longitudinal waves
sound waves
seismic P waves
Compression
Region in longitudinal waves where particles are close together.
Rarefaction
Region in longitudinal waves where particles are spread apart.
Amplitude
Maximum displacement from undisturbed position in a wave.
Wavelength
Distance between equivalent points on adjacent waves.
Frequency
Number of waves passing a point per second.
frequency equation for graph
frequency=1/T
period, T , in seconds, s
frequency, f , in hertz, Hz
Wave Speed Equation
wave speed =frequency ×wavelength
wave speed, v , in metres per second, m/s
frequency, f , in hertz, Hz
wavelength, λ , in metres, m
Time Period
time taken for one entire oscillation of a wave
Wave Speed
Speed at which energy is transferred through a medium.
Electromagnetic Waves
Transverse waves that transfer energy through space.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Continuous spectrum of electromagnetic waves by wavelength.
Radio Waves
Lowest frequency electromagnetic waves used in communication.
Microwaves
Electromagnetic waves used in cooking and satellite communication.
Infrared Waves
Waves used in heating and night vision technologies.
Visible Light
Electromagnetic waves detectable by the human eye.
Ultraviolet Waves
Waves that can cause skin tanning and damage.
X-rays
High-energy waves used in medical imaging.
Gamma Rays
Highest frequency waves, often produced by radioactive decay.