Skull Baselines
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are some pathologic Indications?
Skull fractures
Gunshot wounds
Neoplasm (cancerous growth)
Multiple myeloma (cancer in bone marrow)
Pituitary Adenoma (tumor)
Paget’s Disease (fragile, misshapen bones)
What is the degree difference between the glabellomeatal line and the OML
8°
What is the degree difference between the OML and the IOML
7°
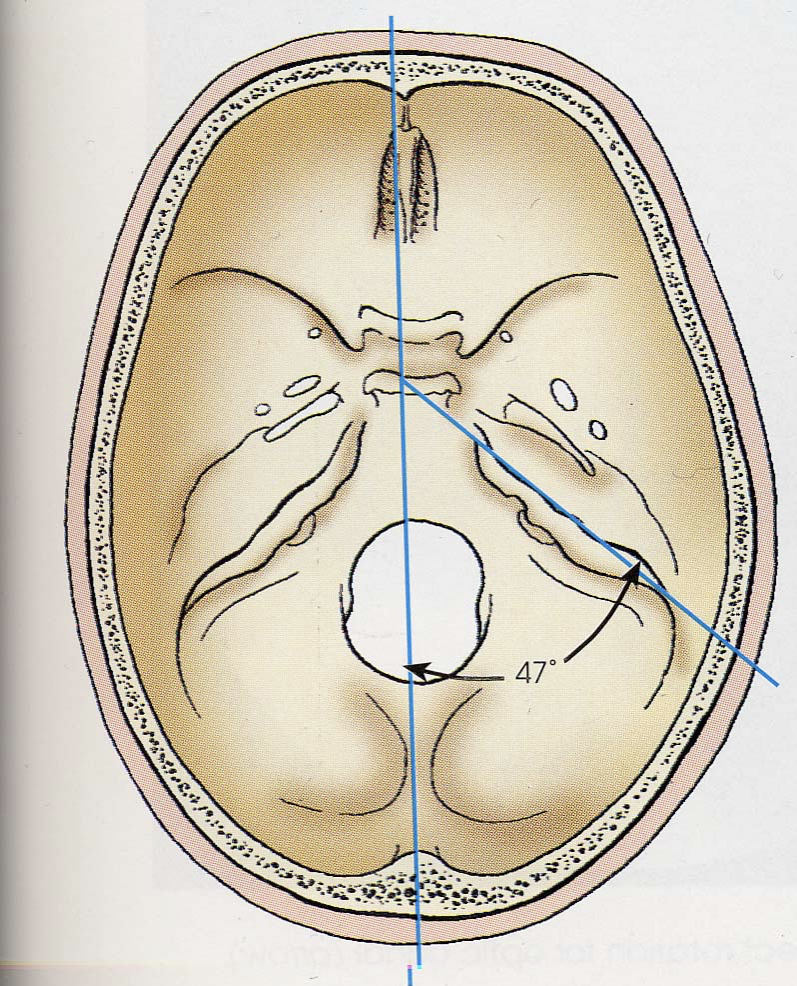
MESOCEPHALIC
Typical shape
Petrous pyramids are 47° from MSP
Petrous pyramids are at the base of the cranium
Optic foramina are 37° open anterior to MSP
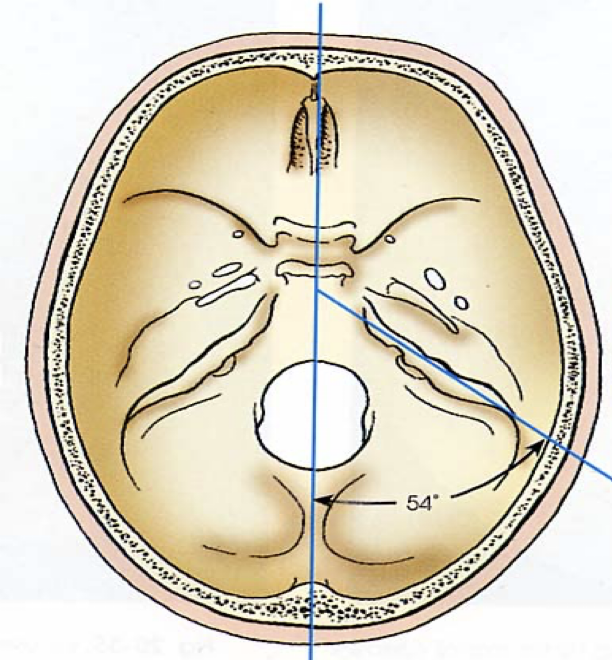
BRADYCEPHALIC
Short front to back
Broad side to side
Shallow vertex to base
Petrous pyramids are 54° from MSP
Internal structures higher
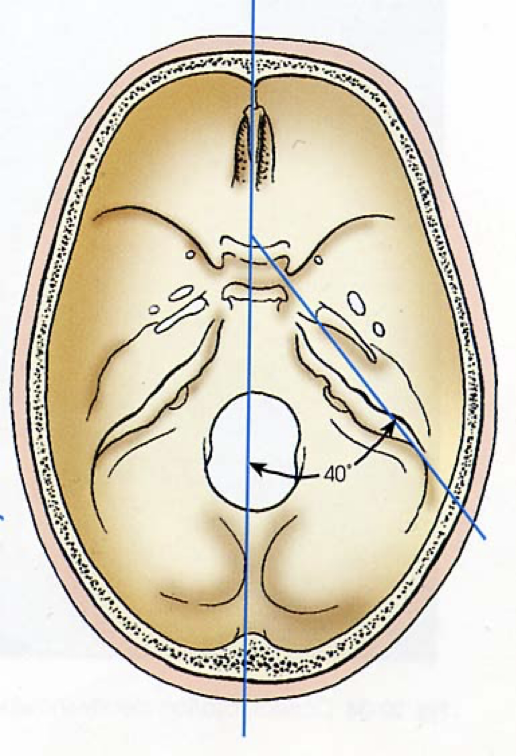
DOLICEPHALIC
Long front to back
Narrow side to side
Deep vertex to base
Petrous pyramids 40° from MSP
Internal structures lower
Why should we consider general body position when we are positioning for skull radiographs?
The head is attached to the body.
Poor and uncomfortable body positions causes difficulty in getting the head positioned, resulting in rotation or other motion and repeats.
Inability to hold position because of muscle strain
Name some key points when positioning the body for skull
Align patient’s body with table
Support any elevated part
Hyposthenic patients may need chest elevated
Hypersthenic patients may need head elevated
View patient on most appropriate plane and get an eye level view
What are 5 common positioning errors
Rotation
Tilt
Excessive Flexion
Excessive Extension
Incorrect CR angle
What are some cleanliness rules
Clean area with disinfectant before and after positioning
Hair & face are naturally oily and leave a residue
Which is worse when the pt is sick
Hair, mouth, nose & eyes come in contact with IR, bucky, and table
May place a cloth or paper towel between IR and patient
Name some radiation protection rules
Thyroid, thymus & gonads shielded on infants & children
Best way to protect is by using proper collimation
Ensure patient is properly instructed
Use of immobilization reduces likelihood of having to repeat
What are some patient preparation protocols
Remove all radiopaque artifacts
Eyeglasses
Dentures and partial plates
Hearing aids
Jewelry
Wigs/hairpieces
Hairpins, barrettes, and pony tail holders
False eyes
Rotation of head prevention
Check MSP to IR
Upright or Recumbent
Perpendicular or parallel
Tilt of head prevention
Check MSP to IR
Upright or Recumbent
Perpendicular or parallel
Align long axis (cervical) with midpoint of the foramen magnum
How to provide support
Any elevated part (shoulders/hip with pillows)
Recumbent examinations of hyposthenic or asthenic patients
Elevate patient’s chest
Recumbent examinations of hypersthenic patients
Elevate patient’s head