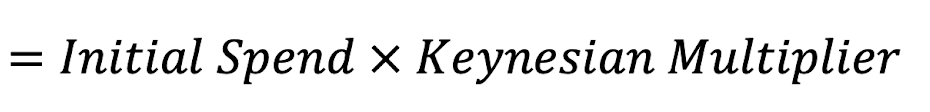IB Economics SL/HL Unit 3 (Macroeconomics)
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All macroeconomics terms, formulas, and diagrams for IB Economics. Includes both SL and HL (HL = Italics). 2022~2029 syllabus. Imported from econinja.net.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
National Income
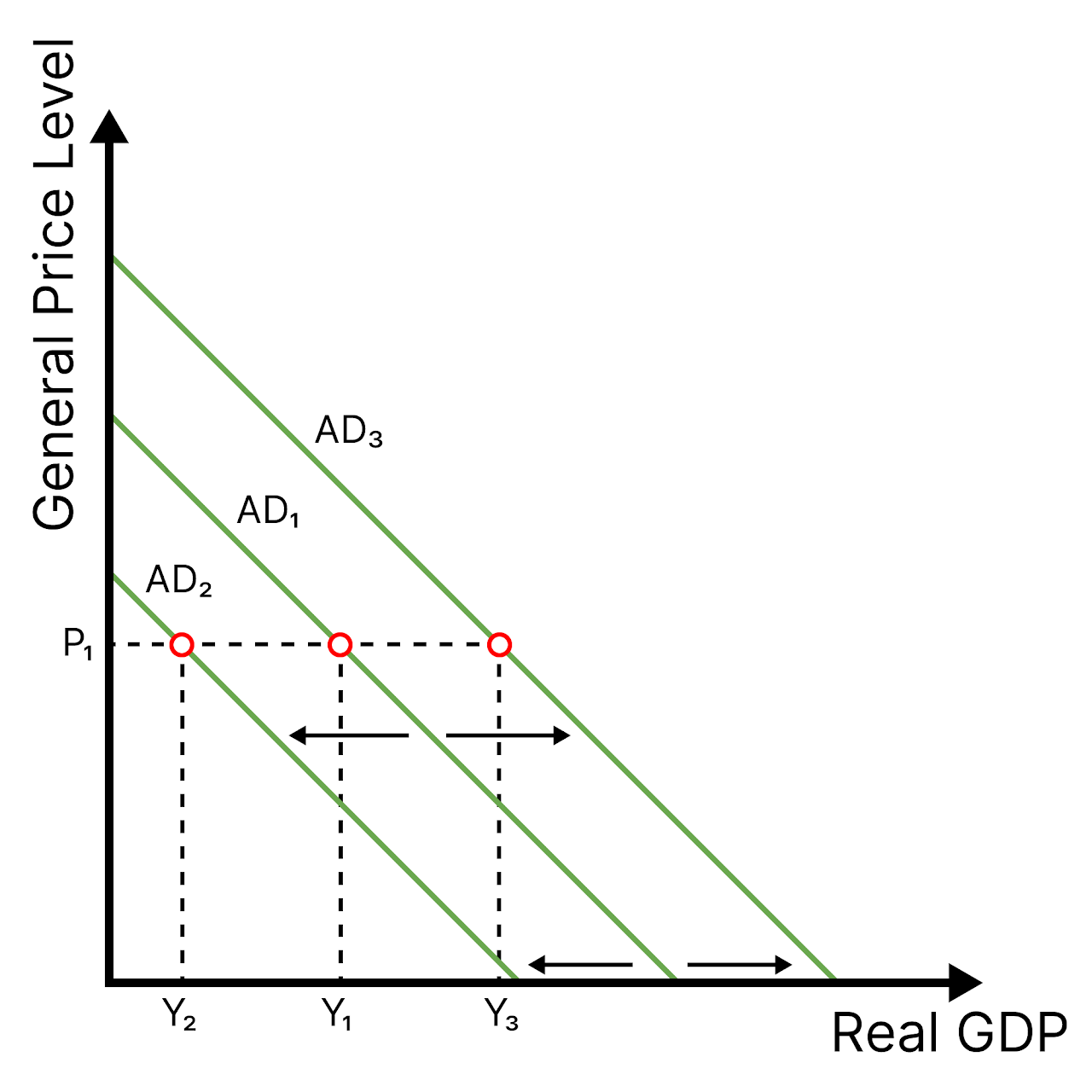
Aggregate Demand
Government/National Debt
Debt Servicing Costs
Credit Rating
Marginal Tax Rate
Monetary Policy
Money Supply
The total amount of money circulating in an economy.
Money Creation
Open Market Operations
Minimum Reserve Requirements
Minimum Lending Rate
Quantitative Easing
Money Demand
Fiscal Policy
Keynesian Multiplier
Crowding Out
Automatic Stabilizers
Supply-Side Policies
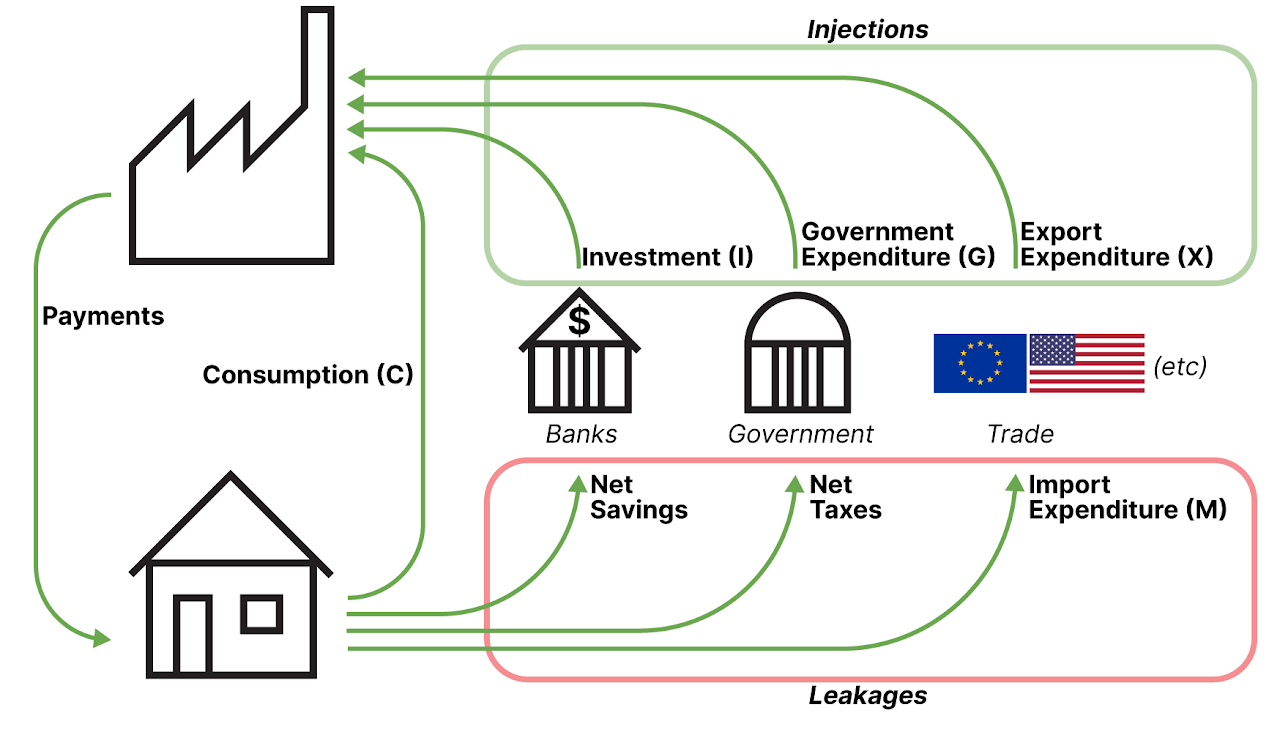
The circular flow of income model
Shows the interactions between decision makers, leakages, and injections
GDP =
= C+I+G+Xn

GNI =
= GDP + Net Income from abroad
Real GDP =
= GDP/Deflator
Real GNI =
= GNI/Deflator
Real GDP Per Capita =
= Real GDP/Population
Real GNI Per Capita =
= Real GNI/Population
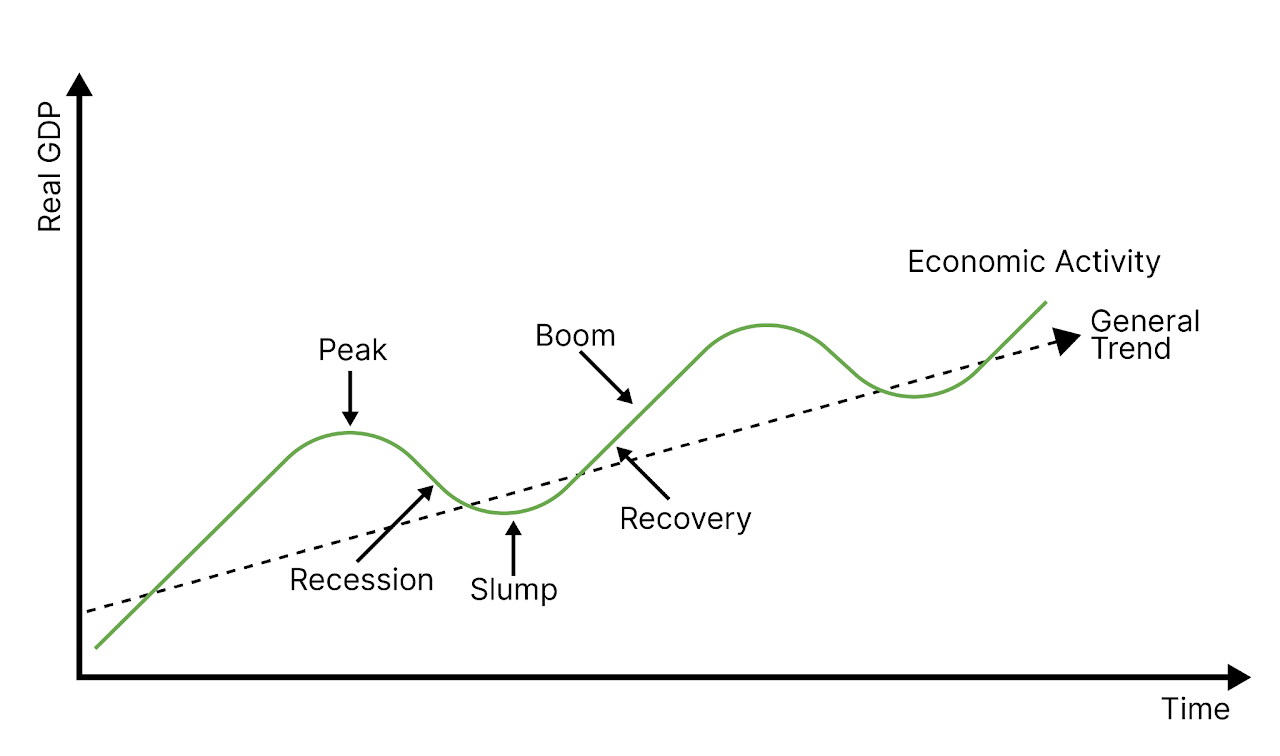
The business cycle
Shows short-term fluctuations and the long-term growth trend.
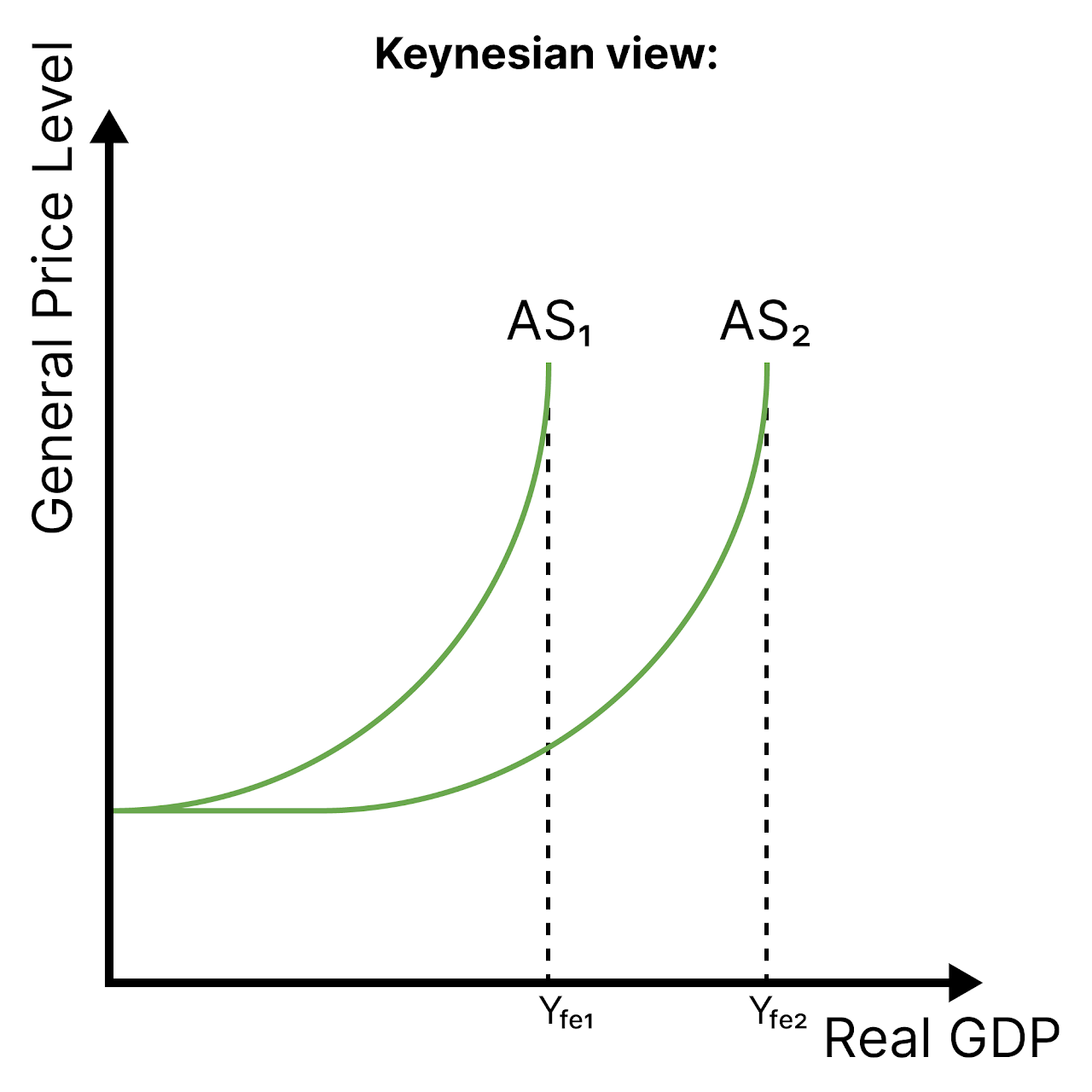
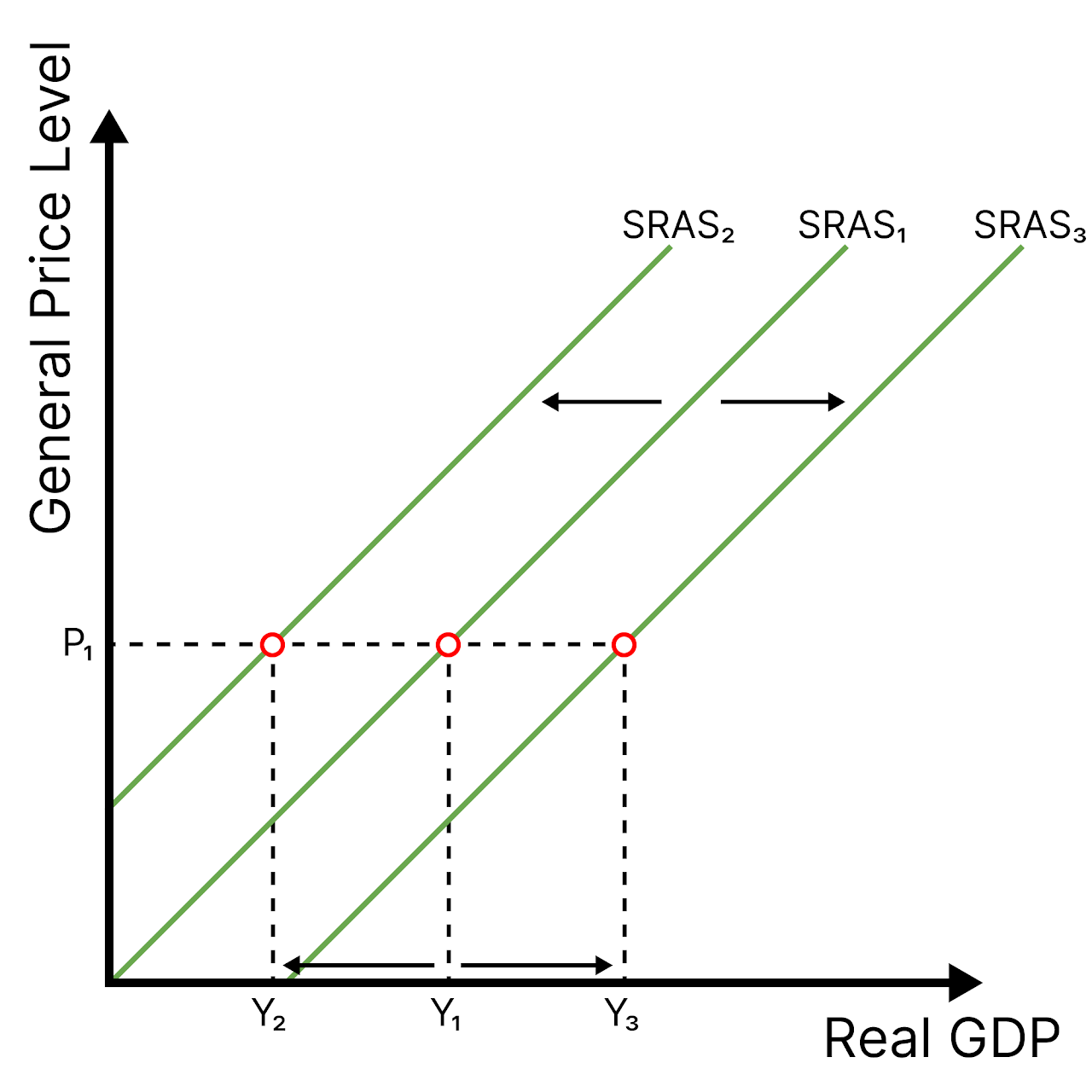
SRAS
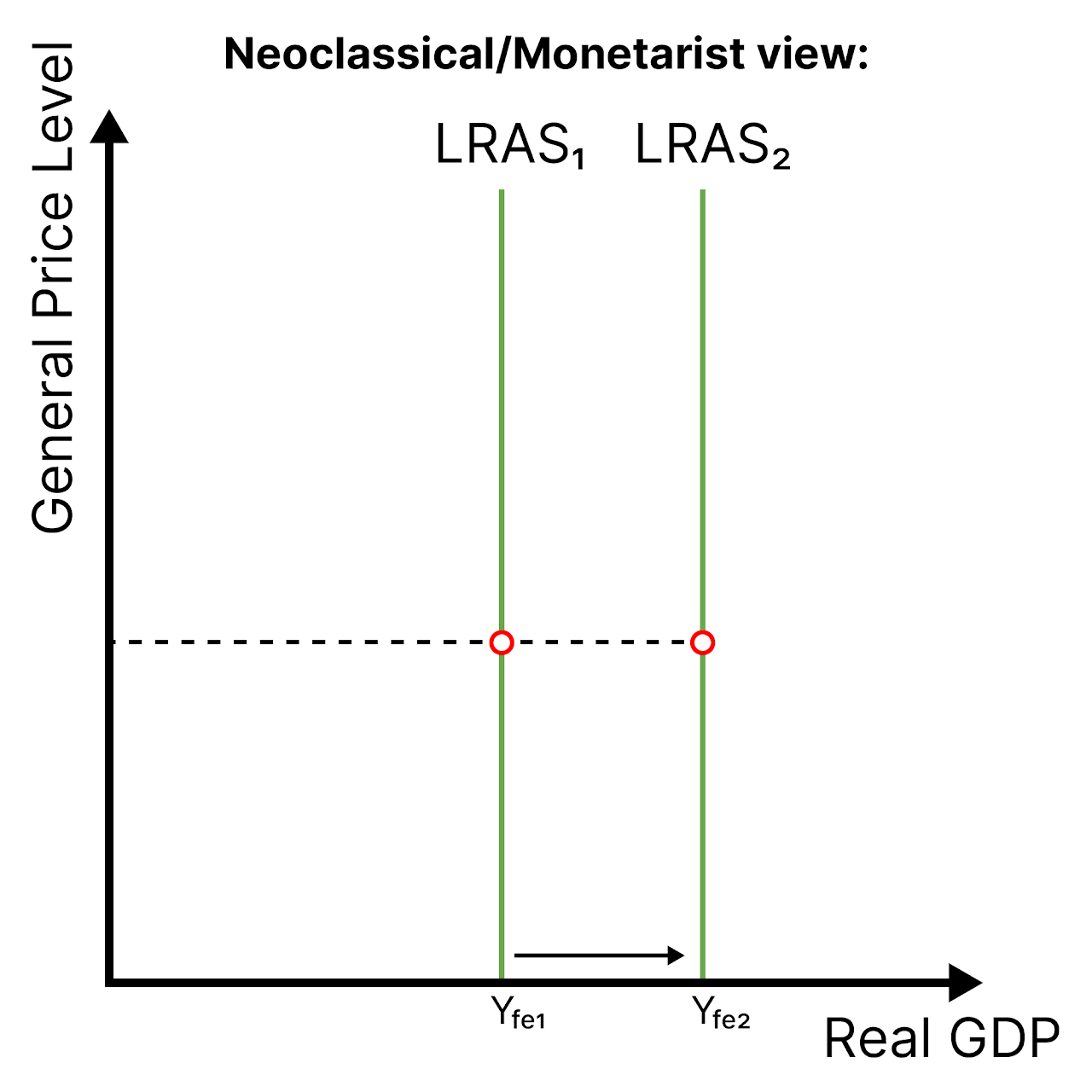
LRAS
Growth (%) =
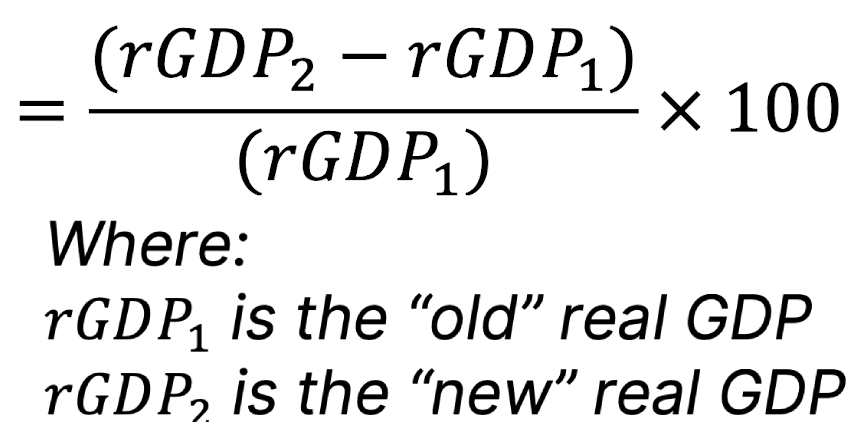
Unemployment (%) =
= 100(Unemployed people/Labor Force)
Weighted Price Index =
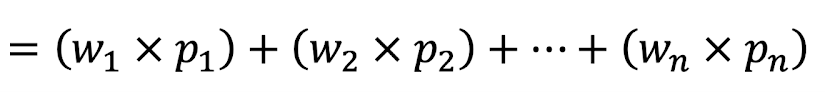
Inflation Rate (%) =
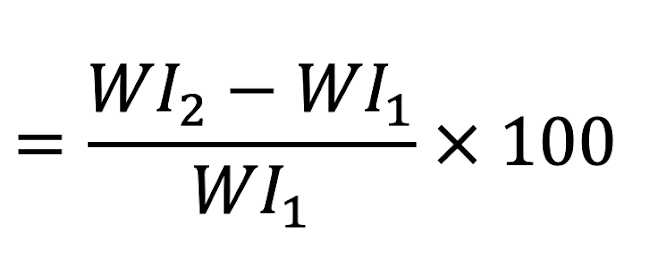
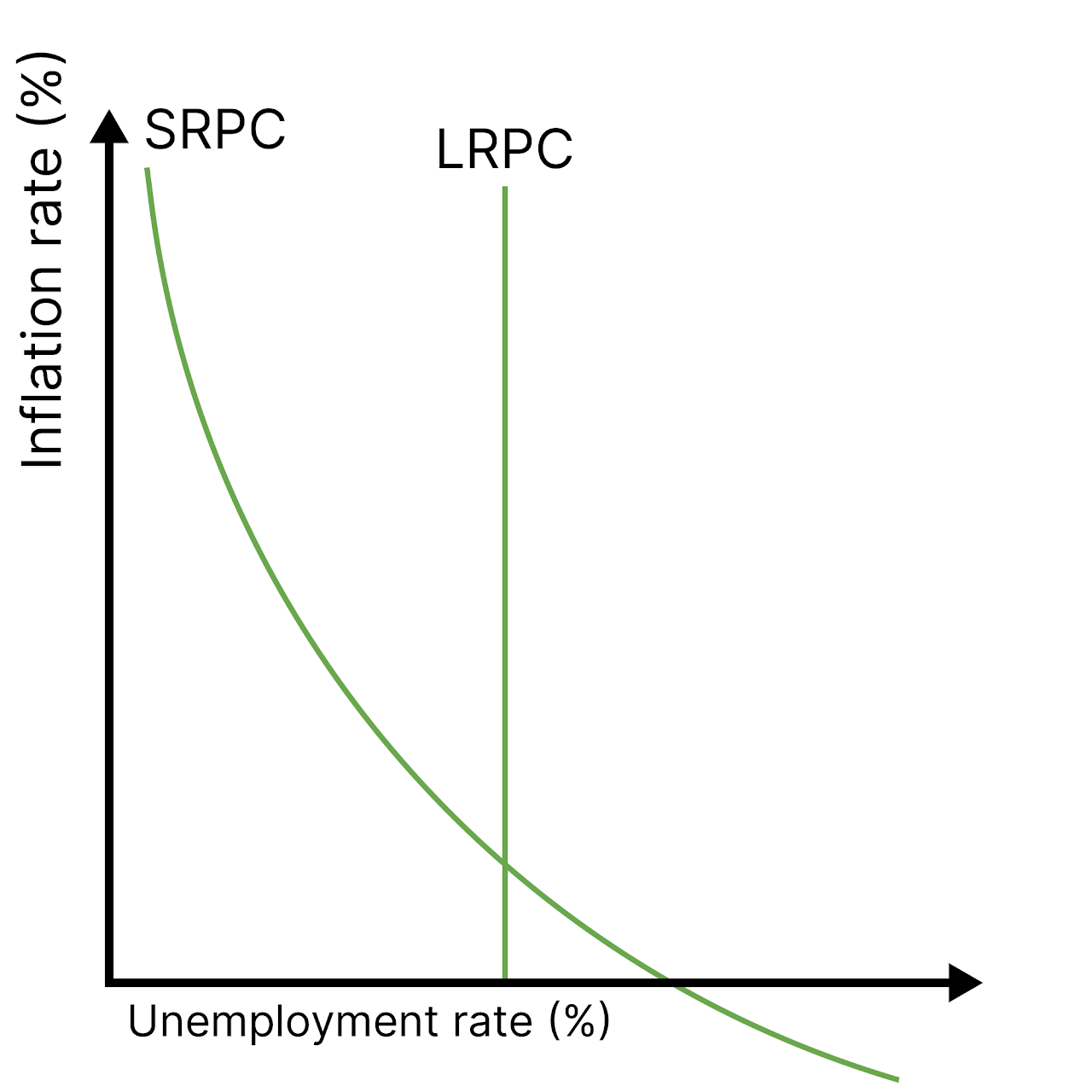
Phillips Curve
Shows the short-run and long-run relationship between inflation and unemployment.
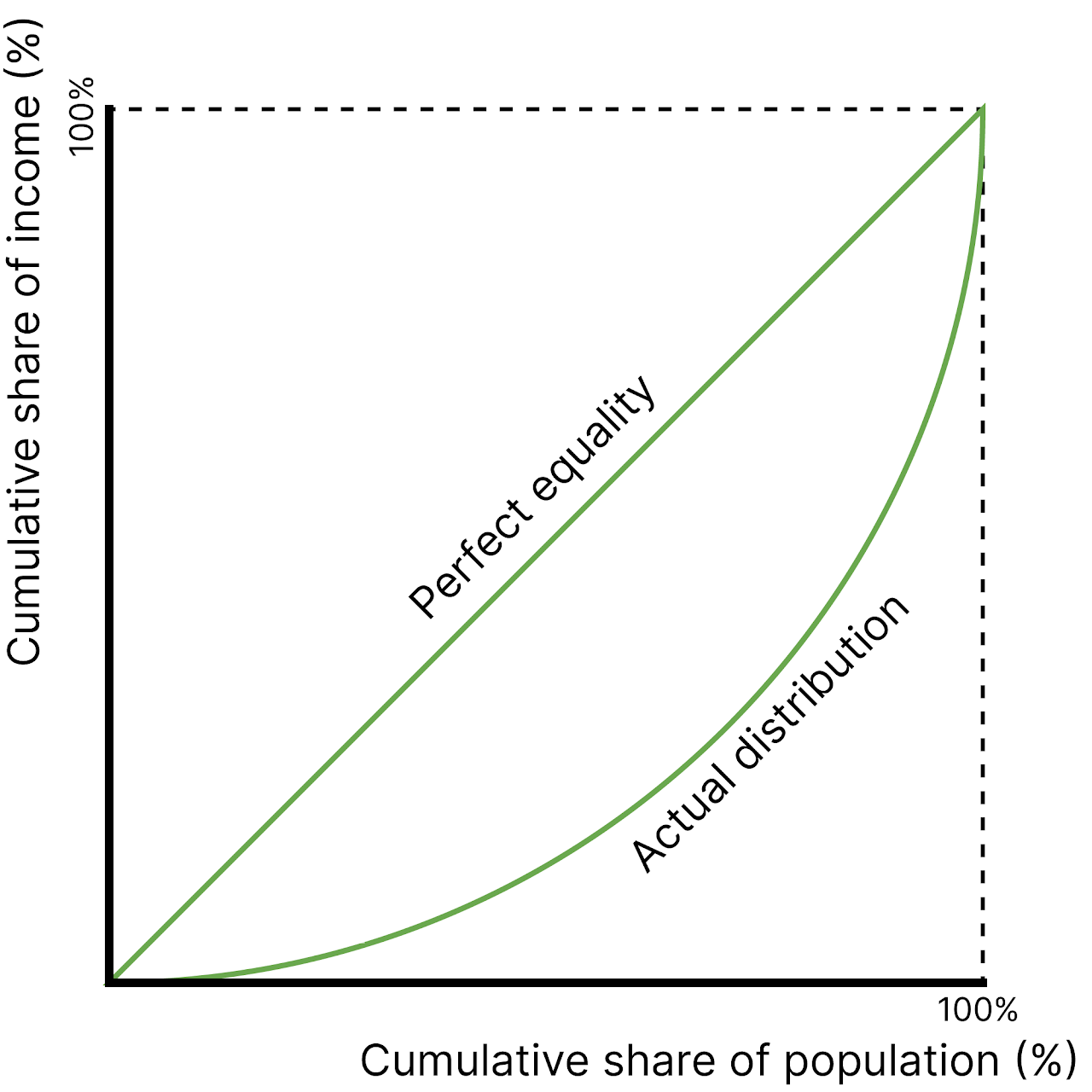
Lorenz Curve
Shows the distribution of income and possible changes in the distribution of income.
Pre Tax Item Cost =
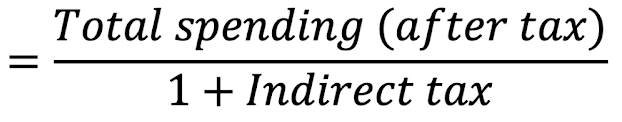
Indirect Tax Paid =
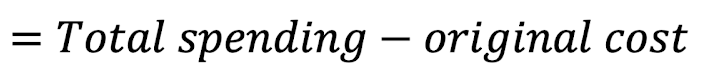
Keynsian Multiplier =
Where:
MPS is the marginal propensity to save (for each $ you earn, how much will you save)
MPM is the marginal propensity to import (for each $ you earn, how much goes to imports)
MPT is the marginal propensity to tax (for each $ you earn, how much goes to tax)
MPC is the marginal propensity to consume (for each $ you earn, how much do you spend)
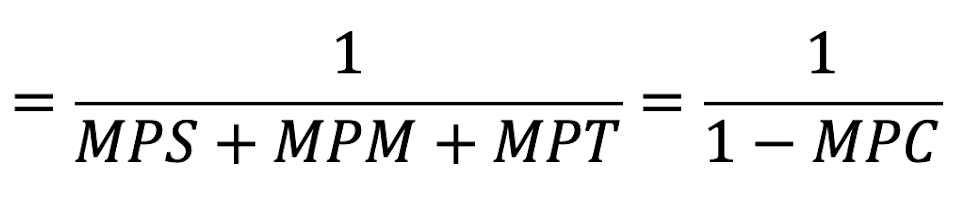
Actual Effect =
The effect on GDP of a change in an injection in investment, government spending or exports, using the Keynesian multiplier