Instrumentation Questions from Practice Boards
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
Exam 1, Question 35
Which type of collimator should be used for organ counting during a red cell sequestration study?
a) low-energy, high-sensitivity parallel hole
b) low-energy, high-resolution parallel hole
c) pinhole
d) flat field
e) converging
D
Exam 1, Question 47
According to the NRC, Mo-99 contamination in Tc-99m eluate must be measured how often?
a) weekly
b) daily
c) only after the first elution
d) yearly
e) after each elution
C
Exam 1, Question 70
Which of the following exposure rates indicate that a package containing radioactive material must have a category III DOT label?
a) 76 mR/hr at package surface, 5.5 mR/hr at 1 meter
b) 56 mR/hr at package surface, 3.5 mR/hr at 1 meter
c) 22 mR/hr at package surface, 0.9 mR/hr at 1 meter
d) 1.5 mR/hr at package surface, 1.0 mR/hr at 1 meter
e) 0.5 mR/hr at package surface, no detectable radiation at 1 meter
B
Exam 1, Question 71
If a point source produces an exposure rate of 30 mR/hr at a distance of 15 cm, what is the exposure rate at 40 cm from the source?
a) 4.2 mR/hr
b) 8.5 mR/hr
c) 11.2 mR/hr
d) 22 mR/hr
e) 25 mR/hr
A
Exam 1, Question 72
If the half-value layer (HVL) for I-131 in lead is 0.3 cm, what is the minimum thickness of lead that is required to reduce the exposure rate of an I-131 source from 13 mR/hr to less than 2 mR/hr?
a) 0.3 cm
b) 0.6 cm
c) 0.75 cm
d) 0.9 cm
e) 1.2 cm
D
Exam 1, Question 73
A patient receives a unit dosage of Sr-89 chloride intended for another patient. Which of the following statements about this situation is true?
a) Because the patient received only a unit dosage of Sr-89, no report to the NRC is required.
b) According to the NRC, this does not constitute a medical event, but a departmental record should be maintained.
c) The situation describes a medical event that has to be reported only to the nuclear medicine supervisor and the authorized user.
d) No report is necessary since it does not reach the dose threshold for reporting.
e) The situation describes a medical event requiring notification of the NRC.
E
Exam 1, Question 74
According to NRC regulations, the annual occupational dose limit to the eye is:
a) 150 mSv
b) 100 mSv
c) 75 mSv
d) 50 mSv
e) 5 mSv
A
Exam 1, Question 75
A vial of Xe-133 has been decayed in storage for 2 months. When the vial is monitored with a survey meter, the reading is twice the background radiation level. What should the technologist do next?
a) Remove any radiation symbols from the vial, then dispose of it.
b) Perform a wipe check.
c) Return the vial to storage.
d) Vent the radioactivity left in the vial into a fume hood.
e) Dispose of the vial as biohazardous waste.
C
Exam 1, Question 76
According to the NRC, wipe tests of areas where radiopharmaceuticals are prepared or administered must be performed:
a) on a reasonable schedule
b) every day on which radiopharmaceuticals are used
c) weekly
d) only if contamination occurs
e) monthly
A
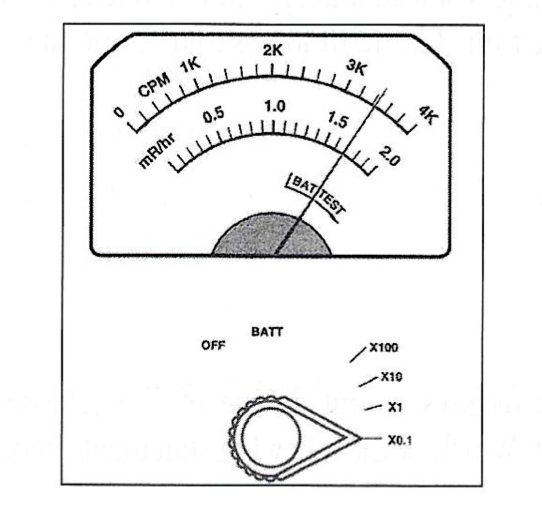
Exam 1, Question 77
What is the measured exposure rate shown on the diagram of the G-M meter depicted here?
a) 0.017 mR/hr
b) 0.17 mR/hr
c) 1.7 mR/hr
d) 17 mR/hr
e) 170 mR/hr
B
Exam 1, Question 78
When opening packages containing radioactive material, which of the following steps should be performed first?
a) Perform a survey using a Geiger counter.
b) Wipe-test the package receiving area.
c) Put on disposable gloves.
d) Wipe-test the package for contamination.
e) Verify the package contents against the packing slip.
C
Exam 1, Question 79
During cleanup of a radioactive spill, decontamination of the area must continue until wipe checks reveal that:
a) The exposure rate of the area is less than 3 mRem/hr.
b) The exposure rate of the area cannot be distinguished from background activity.
c) The contamination is reduced to a small area.
d) No one would receive the maximum allowable total effective dose equivalent (TEDE) if he/she remained in the area.
e) No more contamination can be removed from the area.
E
Exam 1, Question 80
Personnel must wear a radiation monitoring device during work hours if they are:
a) exposed to radiation at any time during work hours
b) exposed to radiation above background levels
c) likely to exceed 10% of the annual maximum allowable occupational exposure
d) likely to exceed the annual maximum allowable occupational exposure
e) a radiologic technologist
C
Exam 1, Question 81
A patient can be released after receiving a therapeutic radiopharmaceutical if no other individual is likely to receive an exposure dose, from being exposed to the patient, exceeding how many Rems?
a) 0.5 Rem
b) 0.7 Rem
c) 2.5 Rem
d) 5.0 Rem
e) 7.0 Rem
A
Exam 1, Question 82
If a source of radioactive contamination produces an exposure rate of 3 mR/hr, how long will it take for the exposure rate to drop to a background exposure rate of 0.05 mR/hr?
a) 5 half-lives
b) 6 half-lives
c) 7 half-lives
d) 8 half-lives
e) 9 half-lives
B
Exam 1, Question 83
According to the NRC, records of surveys must be retained for how many years?
a) as long as the facility’s license is in effect
b) 7 years
c) 5 years
d) 4 years
e) 3 years
E
Exam 1, Question 84
Which of the following materials is recommended for shielding syringes containing the positron-emitting radionuclide?
a) lead
b) tungsten
c) gold
d) steel
e) plastic-lined lead
B
Exam 1, Question 85
If a nuclear medicine technologist needs a diagnostic x-ray, how should this exposure be included in his/her occupational exposure record?
a) The technologist should wear his/her radiation dosimeter during the x-ray examination.
b) The exposure from the x-ray examination must not be included in the occupational exposure record.
c) The RSO will supply a separate dosimeter for the technologist to wear during the x-ray examination.
d) A pocket dosimeter should be used.
e) The RSO will estimate the probable exposure and add it to the technologist’s permanent record.
B
Exam 1, Question 86
According to the standard of practice, if the results of a dose calibrator geometric variation test demonstrate that the measure values exceed the values by 12-15%, the technologist should:
a) Replace the instrument.
b) Use a correction factor to determine true activities.
c) Perform a chi-square analysis.
d) Use the actual dose calibrator activity readings.
e) Have the instrument repaired.
B
Exam 1, Question 87
A technologist measures a Co-57 standard in a dose calibrator on the following settings—Co-57, Tc-99m, I-123, I-131, Xe-133, and Tl-201—and then calculated the percentage difference between the calculated and measured activities. The technologist is assessing:
a) constancy
b) chi-square analysis
c) linearity
d) geometric variation
e) accuracy
A
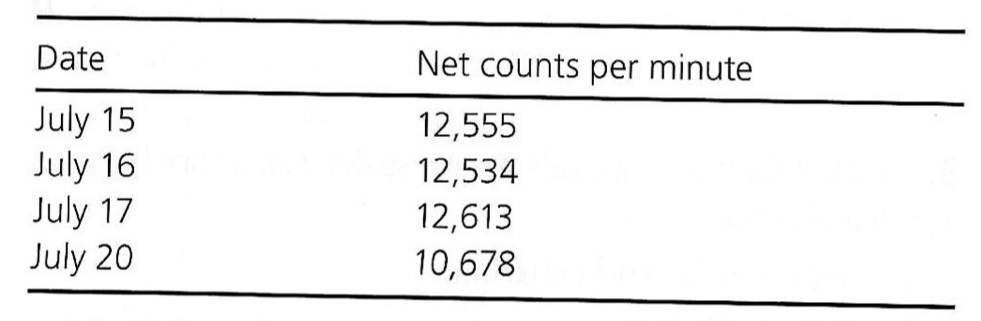
Exam 1, Question 88
A Cs-137 reference standard is counted daily with a scintillation spectrometer, using the same gain, window, and high voltage setting. On the basis of the data above, on July 20, the technologist should:
a) Use the spectrometer for clinical studies.
b) Arrange for repair of the instrument.
c) Change the gain setting.
d) Change the fine gain setting.
e) Recalibrate the operating voltage.
E
Exam 1, Question 89
According to the standard of practice, how often should dose calibrator linearity testing be performed?
a) annually
b) quarterly
c) monthly
d) daily
e) hourly
B
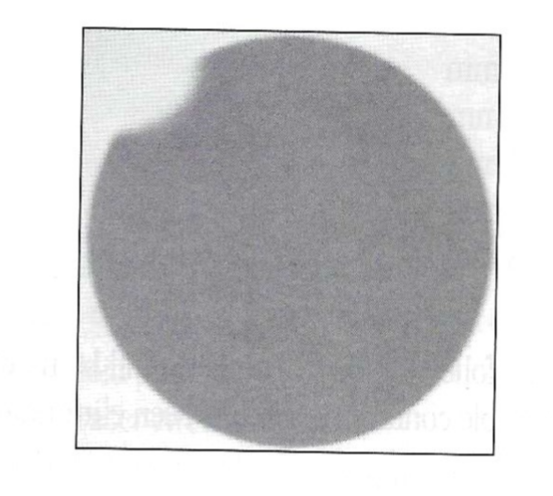
Exam 1, Question 90
To repair the non-uniformity demonstrated on the intrinsic uniformity image shown above, the service engineer will need to:
a) Replace the crystal.
b) Redo the reference map calibration.
c) Repair the collimator.
d) Replace the photomultiplier tube.
e) Replace the x, y localization board.
D
Exam 1, Question 91
Which of the following sources is the most appropriate for assessing dose calibrator constancy?
a) Cs-137
b) Co-57
c) I-125
d) I-131
e) Tc-99m
A
Exam 1, Question 92
Which of the following statements about the effect of the filter-cut-off frequency is true?
a) The lower the cuttoff frequency, the smoother the image.
b) The higher the cuttoff frequency, the noisier the image.
c) Adjusting the cutoff frequency will not affect image appearance.
d) The cutoff frequency cannot be adjusted after the image has been acquired.
e) The lower the cutoff frequency, the noisier the image.
E
Exam 1, Question 93
Temporal resolution is related to which of the following acquisition parameters?
a) percentage energy window
b) matrix size
c) framing rate
d) collimator
e) crystal size
C
Exam 1, Question 94
It would be appropriate to apply temporal smoothing in which of the following studies?
a) gated-equilibrium cardiac function study
b) SPECT study of the brain
c) SPECT study of the liver
d) thyroid image
e) whole-body bone image
A
Exam 1, Question 95
If an image is acquired into a 128 × 128 matrix on a scintillation camera with a 350 mm diameter field of view, what are the dimensions of each pixel?
a) 2.73 × 2.73 mm
b) 3.14 × 3.14 mm
c) 5.92 × 5.92 mm
d) 6.51 × 6.51 mm
e) 7.83 × 7.83 mm
A
Exam 1, Question 96
Which of the following instruments should be used to determine whether all removable contamination has been eliminated?
a) Geiger-Mueller counter
b) well counter
c) dose calibrator
d) uptake probe
e) cutie pie (ionization chamber)
B
Exam 1, Question 97
Which of the following matrix sizes and acquisition modes would be most appropriate for a blood flow study of the feet?
a) 64 × 64 word
b) 64 × 64 byte
c) 256 × 256 byte
d) 256 × 256 word
e) 512 × 512 byte
B
Exam 1, Question 98
A daily uniformity flood for a scintillation camera should contain a minimum of how many counts?
a) 10,000
b) 1-2 million
c) 3-5 million
d) 6-10 million
e) 20-30 million
C
Exam 1, Question 99
As a pinhole collimator is moved farther away from the thyroid, how will it affect the image?
a) The gland will appear larger.
b) The image will be flipped.
c) The gland will appear smaller
d) There is no change in size or orientation.
e) Right and left are reversed.
C
Exam 1, Question 100
During geometric variation testing of a dose calibrator, activity in a 1 mL syringe measures 253 uCi when the expected reading is 212 uCi. Which of the following correction factors should be applied to the measured reading?
a) 23.3
b) 4.1
c) 1.19
d) 0.84
e) 0.51
D
Exam 2, Question 69
Which of the following federal (U.S.) agencies regulates the packaging and transport of radioactive materials?
a) United States Pharmacopeia
b) Environmental Protection Agency
c) Department of Transportation
d) Nuclear Regulatory Commission
e) Food and Drug Administration
C
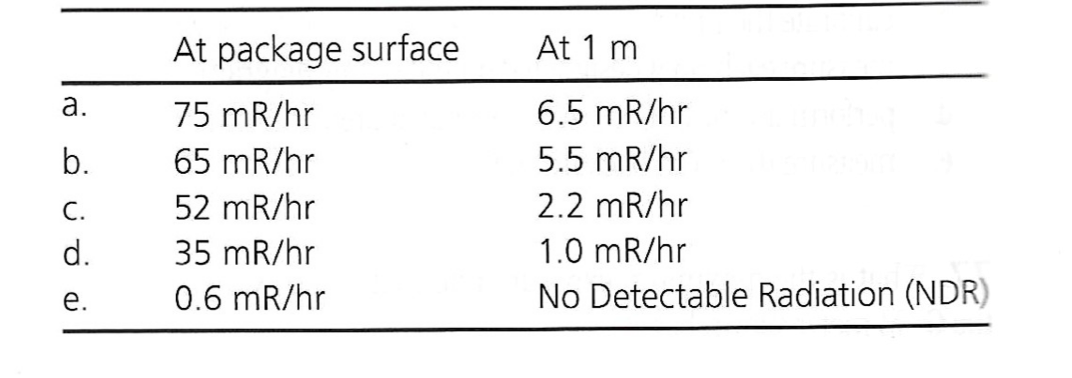
Exam 2, Question 70
Which of the above exposure rates indicate that a package containing radioactive material must be labeled with a Category III DOT label?
D
Exam 2, Question 71
If the radiation intensity of a point source at 0.5 m measures 36 mR/hr, at what distance will the intensity be halved?
a) 7.1 m
b) 5.3 m
c) 2.2 m
d) 1.1 m
e) 0.7 m
E
Exam 2, Question 72
If the HVL of Co-60 in lead is 1.25 cm, what percentage of Co-60 photons is absorbed from a Co-60 source shielded with 2.5 cm of lead?
a) 75%
b) 50%
c) 35%
d) 27.5%
e) 25%
A
Exam 2, Question 73
According to the NRC, a written directive is required for the administration of all the following radiopharmaceuticals except:
a) 35 mCi [I-131] sodium iodide
b) 15 mCi [P-32] sodium chromate
c) 15 mCi [P-32] sodium phosphate
d) 10 mCi [Sr-89] chloride
e) 20 mCi [F-18] FDG
E
Exam 2, Question 74
According to NRC regulations, the annual occupational dose limit for any organ or tissue other than the eye is:
a) 50 mSv
b) 5 mSv
c) 15 Rem
d) 35 Rem
e) 50 Rem
E
Exam 2, Question 75
According to NRC regulations, which of the following cannot be disposed of in the sewage system?
a) unused [I-123] sodium iodide capsules
b) feces from a patient who received [I-131] therapy
c) spit from an aerosol [Tc-99m] pentetate
d) urine from a renal test
e) disposable diaper of a child who has received [Ga-67]
A
Exam 2, Question 76
In performing a room survey with a G-M counter, the technologist should first:
a) perform a battery check on the counter
b) calibrate the unit
c) measure each area designated on the survey diagram
d) perform a wipe test on each designated area
e) measure the room background
A
Exam 2, Question 77
What is the maximum exposure rate that can be measured with the G-M meter shown here?
a) 50,000 mR/hr
b) 5,000 mR/hr
c) 500 mR/hr
d) 50 mR/hr
e) 5 mR/hr
D
Exam 2, Question 78
A technologist monitors the empty carton from a shipment of [I-131] sodium iodide. The container measures 0.08 mR/hr, and room background measures 0.07 mR/hr. The technologist should next:
a) Notify the RSO.
b) Dispose of the container as radioactive waste.
c) Wipe test the container for removable contamination.
d) Obliterate any radiation symbols and dispose of the container in regular trash.
e) Notify the NRC.
D
Exam 2, Question 79
According to NRC regulations, in what areas can radioxenon be administered?
a) in any room that can be closed off with doors
b) only in rooms that have xenon alarm systems
c) only in imaging rooms that can be negatively pressurized
d) in any room where a G-M detector is available to use
e) only in imaging rooms that can be positively pressurized
C
Exam 2, Question 80
When can a decay factor be used to calibrate a unit dosage in place of measuring the dosage in a dose calibrator?
a) A dose calibrator must be used to measure every dosage.
b) only if the same size and type syringe is used
c) only if a unit dosage was not manipulated after preparation and calibration
d) only if the dosage contains less than 1 mCi activity
e) only if the dosage contains Tc-99m
C
Exam 2, Question 81
A patient received 5 mCi of [I-131] sodium iodide for treatment of hyperthyroidism. The patient should adhere to all of the following instructions except:
a) Minimize close contact with others.
b) Remain at home at least 30 days.
c) Use separate personal utensils for first week after therapy.
d) Drink plenty of liquids.
e) Wash hands after using the toilet.
B
Exam 2, Question 82
After a Tc-99m spill, decontamination procedures have not been able to remove all of the spilled material. If the current exposure rate is 32 mR/hr, how long will it take for the exposure rate to drop to 2 mR/hr?
a) 24 hr
b) 18 hr
c) 12 hr
d) 8 hr
e) 4 hr
A
Exam 2, Question 83
If a patient must be hospitalized in isolation after receiving a high activity of I-131, which of the following signs must be placed on the door of the isolation room?
a) “Authorized Personnel Only”
b) “Caution: Airborne Radioactivity”
c) “Reverse Isolation Procedures Required”
d) Length of time a visitor may stay in the room
e) Sign-in sheet to record name and age of each visitor
D
Exam 2, Question 84
How soon after a medical event has occurred must the NRC be notified?
a) written report within 24 hr
b) telephone notification within 72 hour
c) telephone notification no later than following calendar day
d) written report within 30 calendar days
e) written report within 5 regular work days
C
Exam 2, Question 85
According to the NRC, written instruction must be provided to a patient who has received radionuclide therapy when:
a) the patient is a female of childbearing age
b) the patient resides with children younger than 18 years of age
c) the patient is under the age of 18 years old
d) every patient must receive instructions, regardless of dosage
e) another individual may receive an exposure greater than 0.1 Rem (1 mSv) from the patient
E
Exam 2, Question 86
Which of the following statements about the shielding method of performing a dose calibrator linearity test is true?
a) The linearity check must be done over a 24 hour period.
b) Only a few microcuries of radioactivity are needed to perform the test.
c) Linearity must be tested more frequently if this method is used.
d) A different source activity is required for each shield combination.
e) When the shields are first used, the decay method must be used to confirm their accuracy.
E
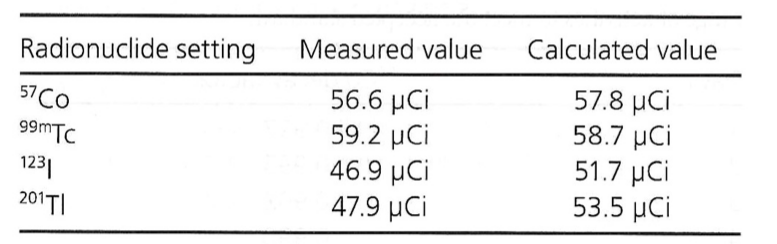
Exam 2, Question 87
The above dose calibrator constancy test results were obtained with a Co-57 reference source. Which of the following measured values fall within the limits according to the standard of practice?
a) Co-57, Tc-99m, I-123
b) Co-57, Tl-201
c) Tc-99m, I-123, Tl-201
d) Co-57, Tc-99m
e) Co-57, Tc-99m, I-123, Tl-201
A
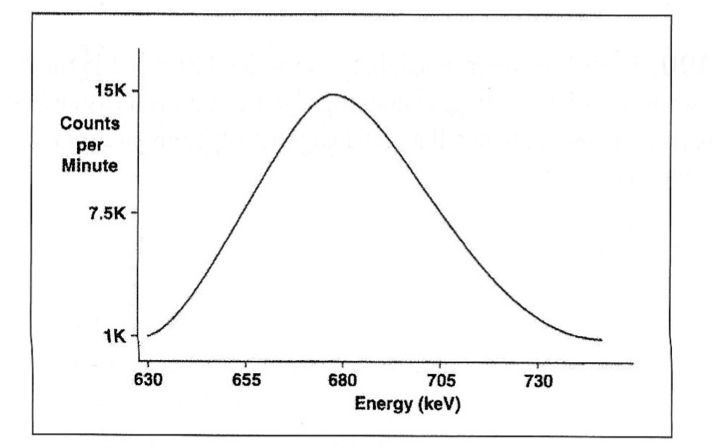
Exam 2, Question 88
Based on the graph shown above, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) is:
a) 2500 cpm
b) 680 keV
c) 7500 cpm
d) 50 keV
e) 500 cpm
D
Exam 2, Question 89
To perform a constancy test on a dose calibrator that is being used in a general nuclear medicine imaging department, the best choice of radionuclide settings on which to count the reference standard would include which of the following?
a) I-123, I-125, I-131
b) I-125, Co-57, Cs-137
c) Tc-99m, Tl-201, Cs-137
d) Co-57, Cs-137, I-131
e) Tc-99m, Tl-201, I-123
E
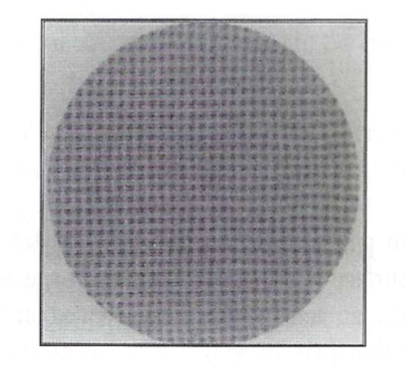
Exam 2, Question 90
The scintillation camera quality control image shown above was obtained with which of the following transmission phantoms?
a) 4-quadrant bar
b) orthogonal hole
c) Moiré phantom
d) parallel-line equal-space (PLES)
e) Hine-Duley
B
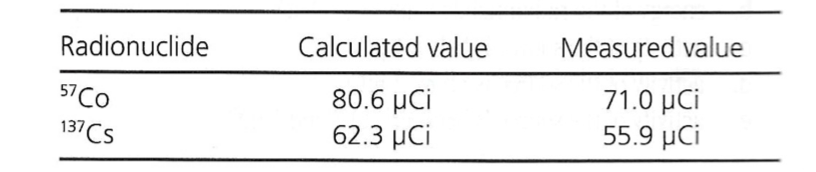
Exam 2, Question 91
The above data were obtained during a dose calibrator accuracy test. On the basis of these results, which of the following statements is true?
a) The wrong radionuclides were used to perform this test.
b) The instrument should be repaired or replaced
c) Too much radioactivity was used to perform this test.
d) The instrument accurately measures radionuclides of different energies.
e) Insufficient radioactivity was used to perform this test.
B
Exam 2, Question 92
Which of the following is a high-pass filter?
a) Ramp
b) Hanning
c) Parzen
d) Newcomer
e) Butterworth
A
Exam 2, Question 93
In quantitating scintillation camera detector uniformity, the central field of view (CFOV) is defined as the diameter of the useful field of view (UFOV) times:
a) 0.95
b) 0.75
c) 0.33
d) 0.25
e) 0.15
B
Exam 2, Question 95
To perform pixel calibration, two capillary sources are placed on the camera surface 15 cm apart. From an image acquired using a 128 × 128 matrix, an activity profile is generated on the computer. If the profile shows that there are 45 pixels between the two activity peaks, the pixel size is:
a) 0.02 cm
b) 0.12 cm
c) 0.20 cm
d) 0.33 cm
e) 0.42 cm
D
Exam 2, Question 96
Coincidence loss is likely to occur when using a well counter if the:
a) energy of the radionuclide is below 50 keV
b) energy of the radionuclide is above 300 keV
c) activity of the source is below 1 uCi
d) activity of the source is above 2 mCi
e) activity of the source is between 1 uCi and 1 mCi
D
Exam 2, Question 97
To assure a maximum error of 2% at the 95% confidence level, all samples that are measured in a well counter should be counted for a time interval that produces at least:
a) 7,500 counts
b) 5,000 counts
c) 1,000 cpm
d) 500 cpm
e) 10,000 counts
E
Exam 2, Question 98
If a Cs-137 source used to determine constancy of a dose calibrator was originally calibrated to contain 200 uCi on June 1, 1998, what would be the expected activity of the source on June 1, 2002 (1 year decay factor of 0.977; 2 year decay of 0.955)?
a) 182.4 uCi
b) 185.0 uCi
c) 186.6 uCi
d) 191.0 uCi
e) 195.4 uCi
A
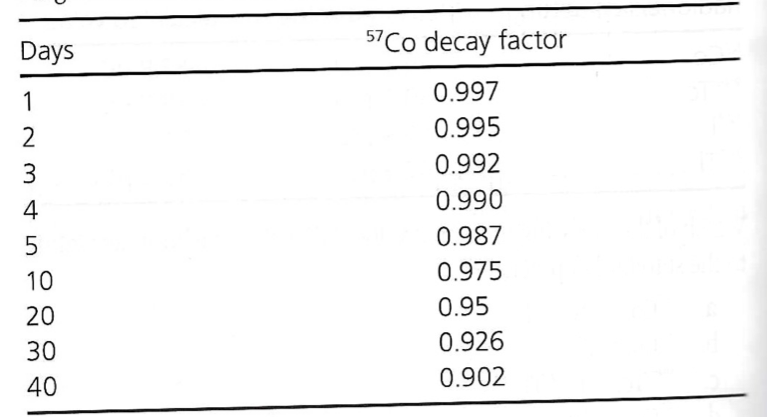
Exam 2, Question 99
A Co-57 source used to determine dose calibrator constancy was originally calibrated to contain 325.8 uCi 35 days ago. If the source is measured today, the dose calibrator reading must fall within what range of activities to meet the accepted standard?
a) 238.2-357 uCi
b) 258.0-337.6 uCi
c) 268.0-327.6 uCi
d) 280.3-342.7 uCi
e) 271.5-331.9 uCi
C
Exam 2, Question 100
It has been determined that a correction factor of 1.15 must be used when a 5 mL syringe containing about 25 mCi is measured in a particular dose calibrator. If a unit dosage activity reads 26.2 mCi, what is the true activity?
a) 22.7 mCi
b) 25.1 mCi
c) 30.1 mCi
d) 40.1 mCi
e) 47.4 mCi
C
Exam 3, Question 68
According to NRC regulations, which of the following signs should be posted on the door of a radiopharmacy laboratory in which radiation levels have been measured to be 7.5 mR/hr?
a) “Caution: Radiation Area”
b) “Caution: Radioactive Materials”
c) No posting is required.
d) “Caution: High Radiation Area”
e) “Caution: Very High Radiation Area”
A
Exam 3, Question 69
To determine the transportation index for a package containing radioactive material, the package must be monitored at:
a) the surface of the package
b) 6 in from the surface
c) 1 m from the surface
d) 2 m from the surface
e) 3 m from the surface
C
Exam 3, Question 70
To comply with NRC regulations, personnel radiation exposure records must be maintained:
a) for 3 years
b) indefinitely
c) for 5 years
d) for 5 years
e) for 7 years
B
Exam 3, Question 71
If a point source produces an exposure rate of 50 mR/hr at a distance of 1 foot, at what distance from the source will the exposure rate be reduced to 2 mR/hr?
a) 5.5 ft
b) 5 ft
c) 10 ft
d) 25 ft
e) 50 ft
B
Exam 3, Question 72
An occupationally exposed worker who is required to wear a personal radiation monitor must wear it at work except when:
a) leaving the nuclear medicine department
b) radiation exposure results from patients who had radioactive materials administered at another facility
c) badge readings are likely to exceed allowable limits
d) personally undergoing a radiographic or nuclear medicine procedure
e) calibrating equipment
D
Exam 3, Question 73
According to the NRC, a written directive for the administration of 15 mCi of [I-131] sodium iodide must include the following information:
a) patient’s thyroid uptake value
b) dosage
c) patient’s birth date
d) lot number of the radiopharmaceutical
e) patient’s name
B
Exam 3, Question 74
According to the NRC, the annual radiation exposure to members of the general public must be limited to no more than:
a) 500 mRem
b) 2 mRem
c) 50 mRem
d) 100 mRem
e) 1 mRem
D
Exam 3, Question 75
Which of the following materials is the best choice for shielding P-32?
a) lead
b) aluminum
c) plastic
d) No shielding is required for P-32.
e) tungsten
C
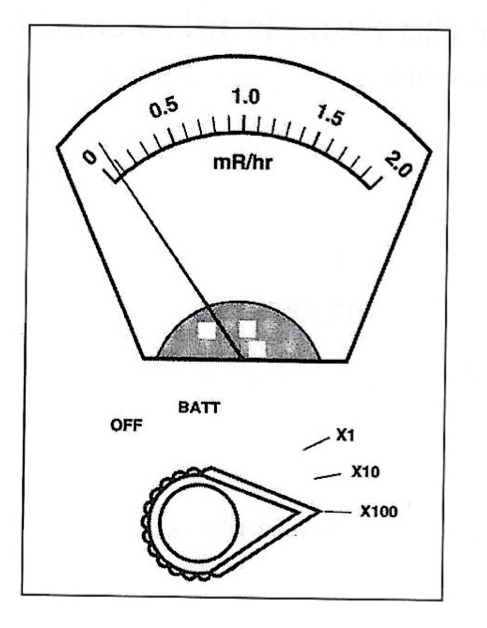
Exam 3, Question 76
A technologist is measuring room background with an end-window G-M survey meter. The meter shows the above reading. What should the technologist do next?
a) Adjust the scale of the meter.
b) Record the meter reading as room background.
c) Choose another area of the room to measure background.
d) Recalibrate the survey meter.
e) Check the probe for contamination.
A
Exam 3, Question 77
During a routine room survey for radioactive contamination, a technologist identifies an area on the floor that exceeds the trigger level. Which of the following should the technologist do next?
a) Determine the identity of the radionuclide present in the contaminated area.
b) Ascertain the source of the contamination.
c) Perform a dose calibrator background determination.
d) Cover the area until it has decayed to background level.
e) Perform a wipe test to determine if the contamination is removable.
E
Exam 3, Question 78
In the case of a radioactive spill that involves contamination and life-threatening injuries to personnel, which of the following actions should be given priority?
a) decontamination of the victim
b) medical treatment of the seriously injured
c) confinement of the radioactive spill
d) notification of the radiation safety officer
e) establishment of hot and cold zones
B
Exam 3, Question 79
Nurses caring for I-131 therapy patients who require isolation should be advised that the major sources of contamination include the patient’s:
a) feces, urine, and blood
b) urine, saliva, and perspiration
c) blood and urine
d) sputum and blood
e) feces and blood
B
Exam 3, Question 80
According to NRC regulations, a technologist cannot use a diagnostic dosage that exceeds 20% of the dosage prescribed by the authorized user unless:
a) There is no other radiopharmaceutical available.
b) The patient weighs more than 20% over the standard reference weight.
c) The authorized user approves the individual dosage.
d) The patient’s physician approves the individual dosage.
e) The radiologist or nuclear medicine physician approves the individual dosage.
C
Exam 3, Question 81
If a woman who is breast-feeding needs I-131 therapy for treatment of thyroid cancer, how long must she suspend breast-feeding?
a) 48 hr
b) 1 week
c) She may not resume it with this child.
d) Suspension of breast-feeding is not necessary in this case.
e) 72 hr
C
Exam 3, Question 82
According to the NRC, wipe-test results must be reported as:
a) cpm
b) mR/hr
c) dpm
d) mRem/hr
e) mCi/mL
C
Exam 3, Question 83
15 mRem is equivalent to how many mSv?
a) 0.15
b) 0.015
c) 0.0015
d) 1.5
e) 15
A
Exam 3, Question 84
A package containing radiopharmaceuticals is delivered before the nuclear medicine department opens. According to the NRC, the package must be checked in and monitored:
a) as soon as the department opens
b) within 3 hr after the department opens
c) within 6 hr after the department opens
d) within 24 hr of the time of delivery
e) within 48 hr of the time of delivery
B
Exam 3, Question 85
On the basis of these data:
Wipe test count: 375 cpm
Background count: 120 cpm
and a well counter efficiency of 45%, the results of the wipe test in dpm are:
a) 49 dpm
b) 115 dpm
c) 255 dpm
d) 423 dpm
e) 567 dpm
E
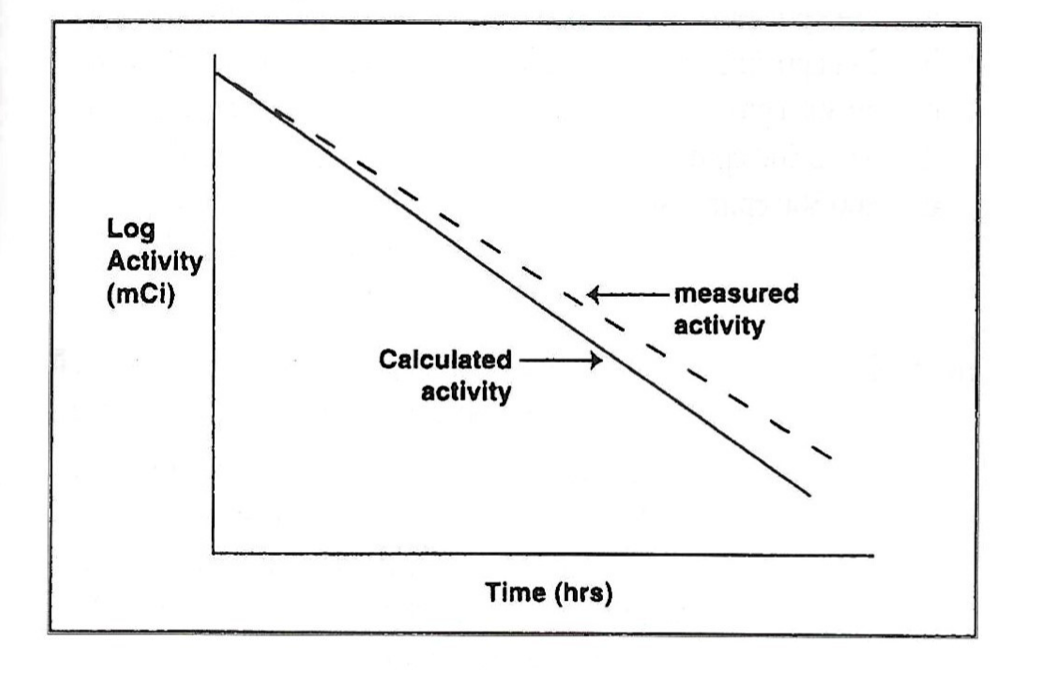
Exam 3, Question 86
On the basis of the graph above, the dose calibrator linearity test results demonstrate that:
a) The instrument consistently give higher readings than expected.
b) Lower activities are measured as accurately as higher activities.
c) The instrument is operating linearly over the range of activities measured.
d) The instrument should be used to measure only millicurie amounts of radioactivity.
e) The instrument consistently gives lower readings than expected.
A
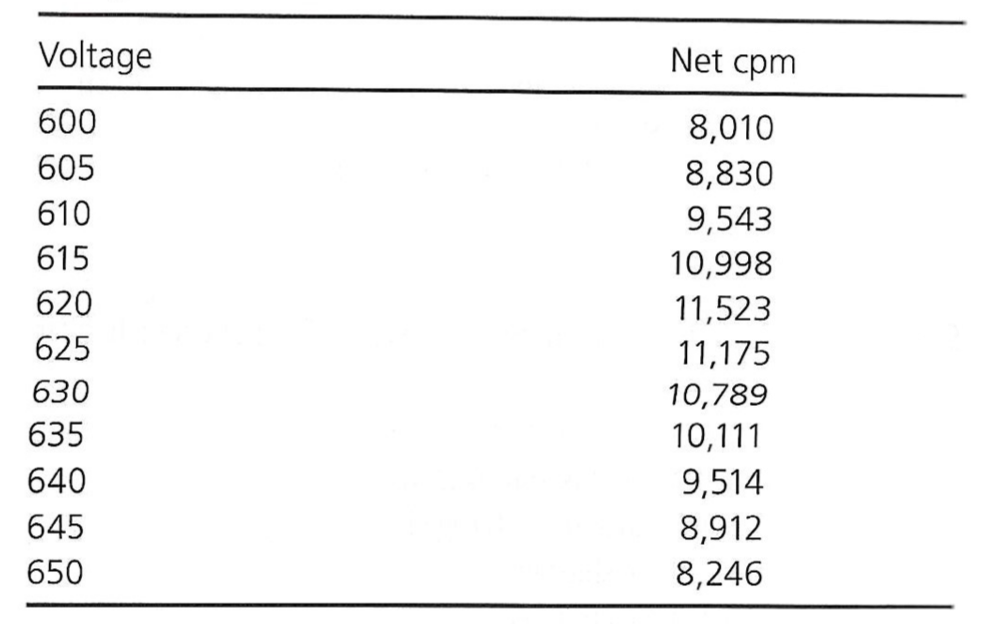
Exam 3, Question 87
The calibration of a scintillation spectrometer yielded the above data. What is the operating voltage of this instrument?
a) 615
b) 625
c) 620
d) 630
e) 635
C
Exam 3, Question 88
An energy resolution test is performed on a scintillation spectrometer using Cs-137. If the full width at half maximum (FWHM) is determined to be 53 keV and the photopeak energy is 662 keV, what is the percent energy resolution of the instrument?
a) 0.08%
b) 12.5%
c) 1.3%
d) 8%
e) 25%
D
Exam 3, Question 89
If a dose calibrator linearity test begins by assaying 50 mCi of Tc-99m pertechnetate, for how long should the test be carried out?
a) 24 hr
b) 48 hr
c) 72 hr
d) 66 hr
e) 96 hr
D
Exam 3, Question 90
If a PLES transmission phantom is used, how many images must be acquired to assess linearity over the entire field of view of a scintillation camera?
a) 1
b) 3
c) 2
d) 5
e) 4
C
Exam 3, Question 91
According to the NRC, all dose calibrator quality control results must be retained for:
a) 1 year
b) 5 years
c) the life of the instrument
d) as long as the facility’s license is in effect
e) 3 years
E
Exam 3, Question 92
What is the effect of changing the order of a Butterworth filter from 3 to 5?
a) The image will be smoother.
b) The star artifact will be eliminated.
c) The image will appear unchanged.
d) The image will be sharper.
e) The image will be enlarged.
D
Exam 3, Question 93
A 256 × 256 matrix requires how much more computer memory than a 64 × 64 matrix?
a) 2 times more
b) 16 times more
c) 8 times more
d) 4 times more
e) 32 times more
B
Exam 3, Question 94
Which of the following statements about an image acquired with zoom is true?
a) Image resolution is increased.
b) Background counts are increased.
c) More memory is required.
d) Contrast is decreased.
e) Specificity is increased.
A
Exam 3, Question 95
If a [Tc-99m] medronate bone image and [In-111]-tagged white blood cell image are acquired simultaneously with a 128 × 128-word mode matrix, how much computer memory is required to store the images?
a) 32 kB
b) 16 kB
c) 256 kB
d) 128 kB
e) 64 kB
E
Exam 3, Question 96
An uptake probe would be used for which of the following studies?
a) splenic sequestration
b) red cell mass
c) red cell survival
d) plasma volume test
e) liver sequestration
A
Exam 3, Question 97
How much memory will be needed for a gated-equilibrium cardiac function examination that is acquired in 30 frames with a 128 × 128-byte mode matrix?
a) 3,840 bytes
b) 16,384 bytes
c) 491,520 bytes
d) 546 bytes
e) 256 bytes
C
Exam 3, Question 98
What energies will be accepted by a 15% window placed around a centerline of 159 keV?
a) 135-183 keV
b) 144-174 keV
c) 151-167 keV
d) 147-171 keV
e) 159-189 keV
D
Exam 3, Question 99
A SPECT study is acquired using 60 projections over a 360° rotation. Each projection is acquired for 0.5 min. If the counting rate is 144,000 cpm, how many counts will be collected for the total acquisition?
a) 1,036,800
b) 2,587,300
c) 3,640,000
d) 3,920,000
e) 4,320,000
E
Exam 3, Question 100
Using a 125 uCi source, 30,500 cpm were collected during a camera sensitivity determination. If the background count is 1200 cpm, what is the sensitivity of the instrument?
a) 234 cpm/uCi
b) 244 cpm/uCi
c) 29,300 cpm
d) 3,662,500 cpm
e) 300,500 cpm
A
Exam 4, Question 68
The NRC defines an unrestricted area as one in which an individual will receive less than how many milliRems in an hour?
a) 2 mRem
b) 5 mRem
c) 50 mRem
d) 100 mRem
e) 500 mRem
A
Exam 4, Question 69
A package containing radioactive material is monitored and found to produce 0.4 mR/hr at the surface and no detectable radiation exposure at 1 m from the surface. Which DOT label must be affixed to the outside of the package?
a) “Category I-A”
b) “Category II”
c) “Category III”
d) No DOT label is required
e) “Category I”
E
Exam 4, Question 70
The NRC requires that all of the following information be included in unit dosage measurement records except the:
a) date of measurement
b) time of measurement
c) patient’s name
d) radiopharmaceutical name
e) dose calibrator make and model number
E