Properties of Amino Acids
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
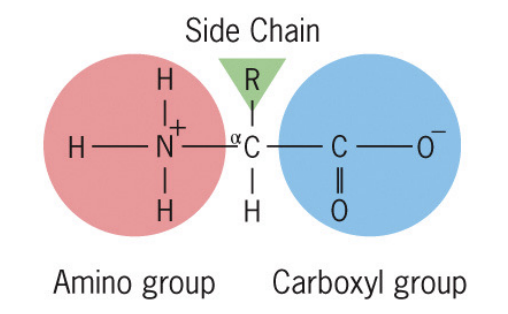
All amino acids have (structure wise — 4 parts)
carboxyl group (pka ~ 10) negatively charged when neutral
amino group (pka ~ 2) positively charged when neutral
single carbon atom (alpa-carbon)
unique side chain, called R group
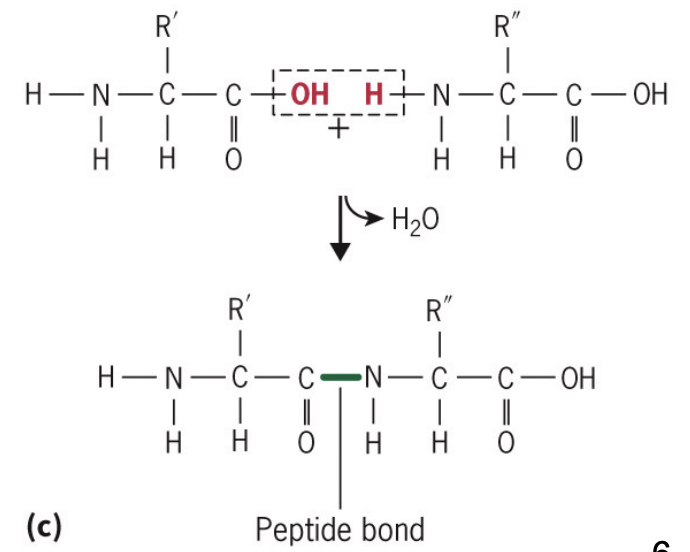
What links Amino acids
peptide bonds via hydration reactions between amino acids
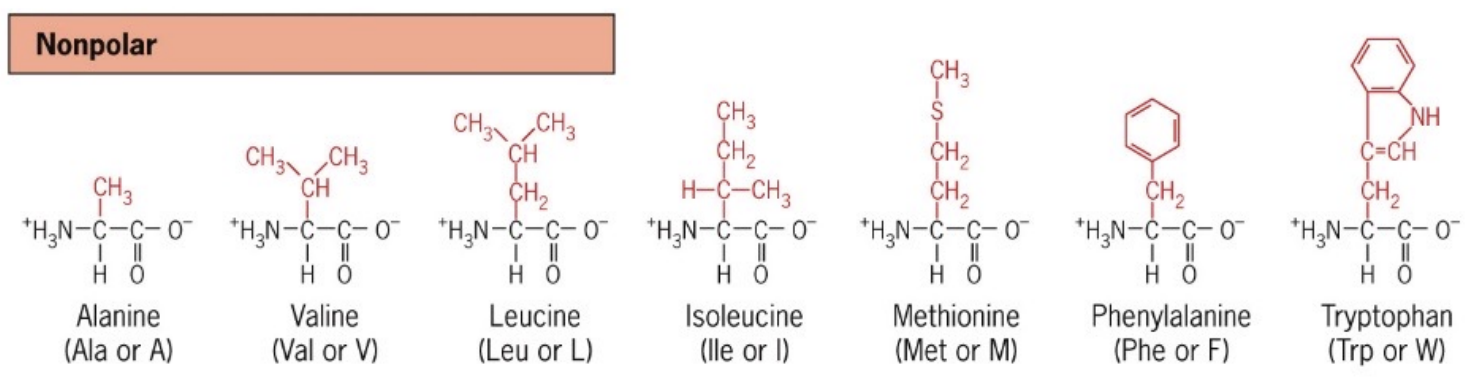
List non-polar Amino Acids
Amino acids with hydrophobic side chains such as alanine(A), valine(V), leucine(L), isoleucine(I), methionine(M), phenylalanine(F), and tryptophan(W)
Great for hydrophobic interactions and van der waals forces
C-H
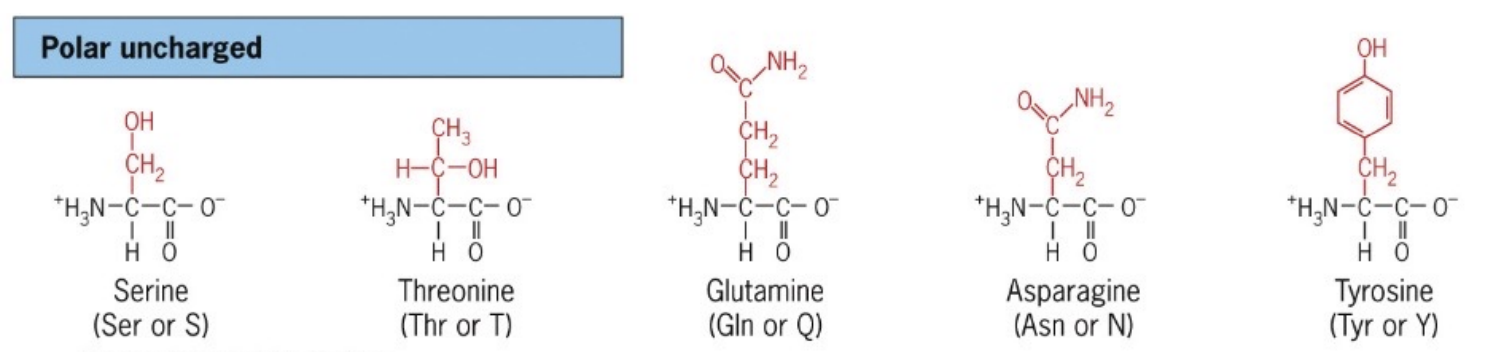
List polar uncharged Amino Acids
Amino acids with polar side chains that do not carry a charge, such as serine (S), threonine (T), tyrosine (Y), asparagine (N), and glutamine (Q).
These amino acids are involved in hydrogen bonding and can interact with water.
hydrophilic
partial + and - charge
S,T, Y → phosphorylated
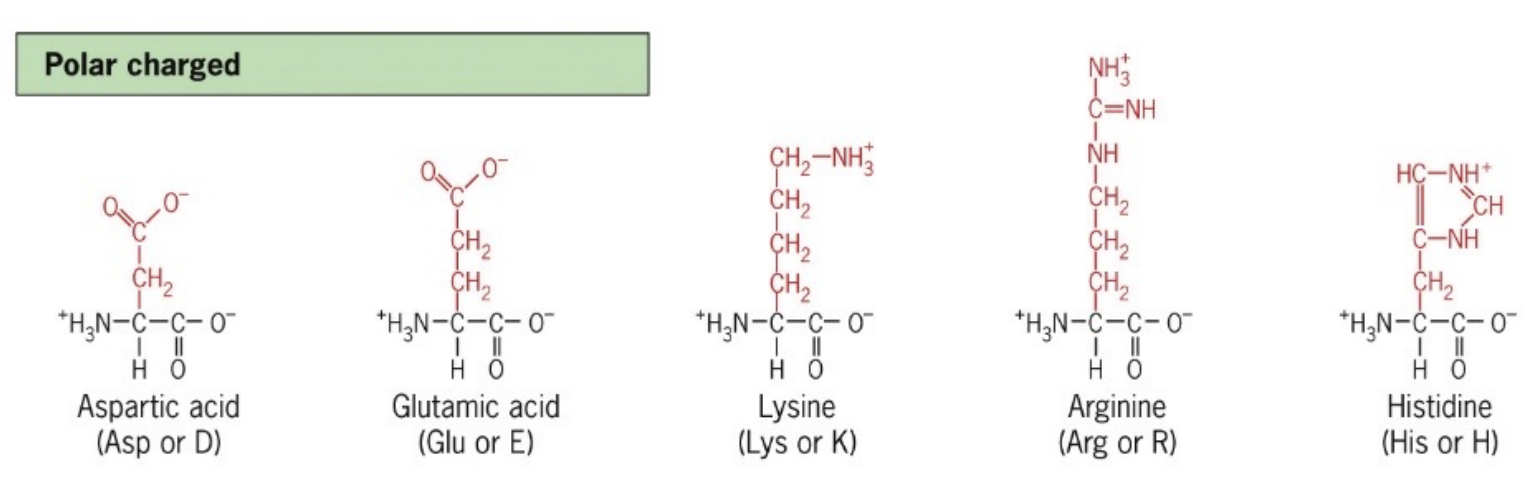
List polar charged Amino Acids
Amino acids with side chains that carry a positive or negative charge, such as aspartate (D), glutamate (E), lysine (K), arginine (R), and histidine (H).
These amino acids are highly hydrophilic and participate in ionic interactions
fully + and - charges
Acidic Amino Acids
Amino acids with negatively charged side chains at physiological pH, primarily aspartate (D) and glutamate (E). These play crucial roles in enzyme activity and neurotransmission.
Basic Amino Acids
Amino acids with positively charged side chains at physiological pH, primarily lysine (K) and arginine (R). These amino acids are essential for protein structure and function, often involved in binding negatively charged molecules.
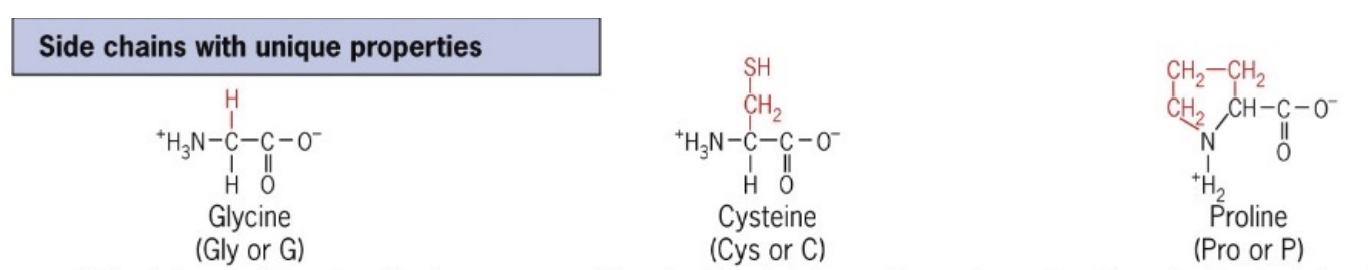
List unique Amino Acids
3 types:
Glycine, flexible and can tightly pack with its one hydrogen atom — small
Proline, with a unique cyclic structure, introduces kinks in protein chains — breaks secondary structure
Cysteine, containing a thiol group (SH), forms disulfide bonds for stabilization
Alanine
Ala
non-polar amino acid with a simple methyl side chain
Valine
Val
non-polar amino acid with a branched isopropyl side chain
Leucine
Leu
non-polar amino acid with a branched isobutyl side chain
Isoleucine
Ile
non-polar amino acid with a branched side chain containing both aliphatic and hydrophobic properties
Methionine
Met
Sulfur-containing non-polar amino acid with a thioether side chain
Phenylalanine
Phe
Aromatic non-polar amino acid with a benzyl side chain
Tryptophan
Trp
Aromatic non-polar amino acid with an indole side chain
Serine
Ser
Polar uncharged amino acid with a hydroxymethyl side chain
Threonine
Thr
Polar uncharged amino acid with a hydroxyl side chain
Glutamine
Gln
Polar uncharged amino acid with an amide side chain
Asparagine
Asn
Polar uncharged amino acid with an amide side chain
Tyrosine
Tyr
Polar uncharged amino acid with a phenolic side chain
Aspartic Acid
Asp
Polar charged acidic amino acid with a carboxylic acid side chain
Glutamic Acid
Glu
Polar charged acidic amino acid with a carboxylic acid side chain
Lysine
Lys
Polar charged basic amino acid with an amino group in its side chain
Arginine
Arg
Polar charged basic amino acid with a guanidinium group in its side chain
Histidine
His
Polar charged basic amino acid with an imidazole side chain
Glycine
Gly
Non-polar, aliphatic (hydrophilic or hydrophobic) amino acid and the simplest amino acid with a hydrogen atom as its side chain.
Cysteine
Cys
Polar, uncharged amino acid known for its thiol side chain capable of forming disulfide bonds.
Proline
Pro
Non-polar, aliphatic amino acid with a unique cyclic structure that influences protein stability and folding.