Business Economics
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Advanatges of specialisatuion

Disadvantages of specialisation

In the short run,
Some costs are fixed
In the long run,
all costs are variable
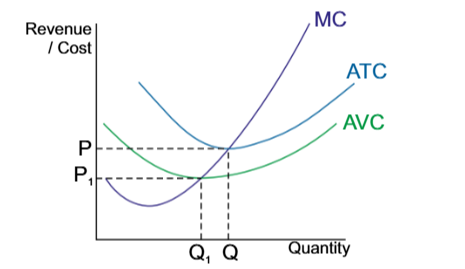
Marginal Cost MC means
The additional cots to produce one more unit of good
Lowest AC occurs when
MC=AC
When AC=MC, the firm
Has reached the point of productive efficiency
What dioes the law of diminishing returns explain?
It explains what happens if all costs stay fixed and only one variable increases. It applies only in the short run
The additional output, which is generated when the firm keeps all factors, apart for one, fixed is called
Marginal product
The firm can be adding up more of one factor, while keeping others fixed, since specialisation is possible, but then
The law of diminishing returns arises, and output begins to decline
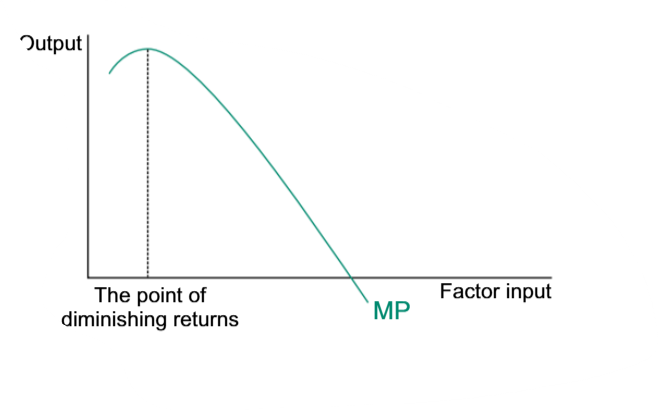
The Law of Diminishing Returns
The Marginal returns curve is
Opposite to the MC curve
Economies of Scale
the cost advantages of production on a large scale
Internal Economies of Scale
Technical economies of scale, purchasing economies of scale, managerial economies of scale, financial economies of scale, risk-bearing economies of scale, marketing economies of scale
technical economies of scale

Purchasing economies of scale

Managerial economies of scale

Financial economies of scale

Risk-bearing economies of scale

Marketing economies of scale

External economies of scale include
External changes
Examples of external economies of scale

Diseconomies of scale
disadvantages of firms being large scale
Internal disadvantages of scale

External disadvantages of scale

What is the best generator of large economies of scale
High fixed costs
Example of high fixed cost, low variable cost industry, preserving large economies of scale

What is the rational reaction of other firms, when one firm starts experiencing the economies of scale in high fixed costs industries?
Replicate the path of the first firm, or exit the market
In the long run, a firm can move into new
Short Run Average Cost curves
The lowest points of SRAC curves are represented by
The LRAC curve entirely
The average costs curves of a firm
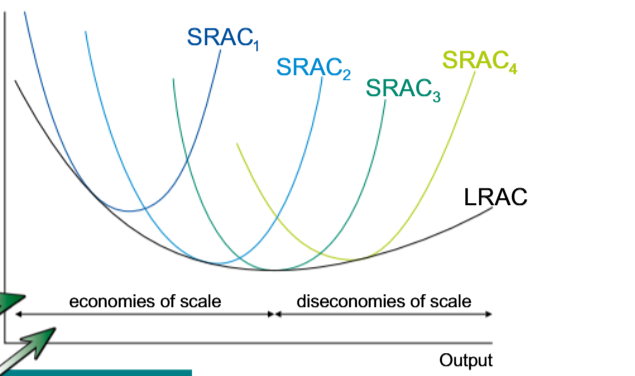
What way can a firm minimize the average costs of production

What way is the shape of the LRAC curve determined
By internal economies and diseconomies of scale
The precise influencers of the shape of LRAC curve


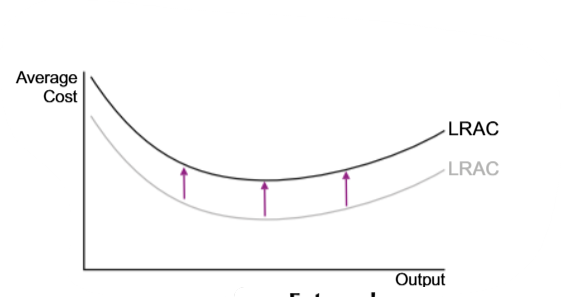
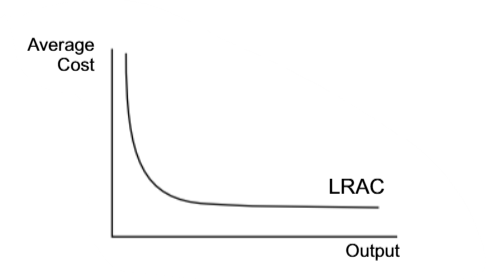

Why is it sometimes believed that the diseconomies of scale do not arise in the firm?
Because, as soon, as AC curve stops falling, the continuous technical economies of scale do not let it rise
Increasing returns to scale

Constant returns to scale

Decreasing returns to scale

Increasing returns to scale contribute to
Economies of scale
Decreasing returns to scale contribute to
Diseconomies of scale
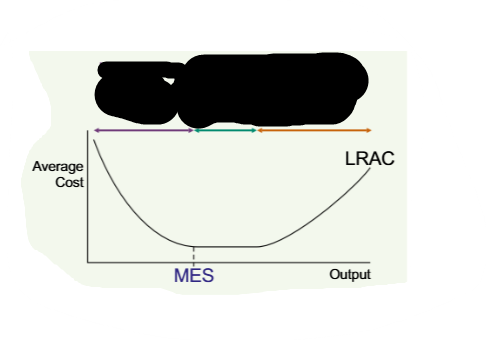
Economies of scale - Increasing returns to scale; Flat - constant returns to scale; Diseconomies of scale - decreasing returns to scale
Minimum Efficient Scale of Production means
The lowest point of output, at which the lowest average cost is possible
MES might be the
Optimal level of production
What industries have large MES
Industries with high fixed costs
Why do industries with high fixed costs have large MES

Marginal revenue MR
Extra revenue, obtained via producing the final unit of good
Firms revenue determines how revenue relates to
The output
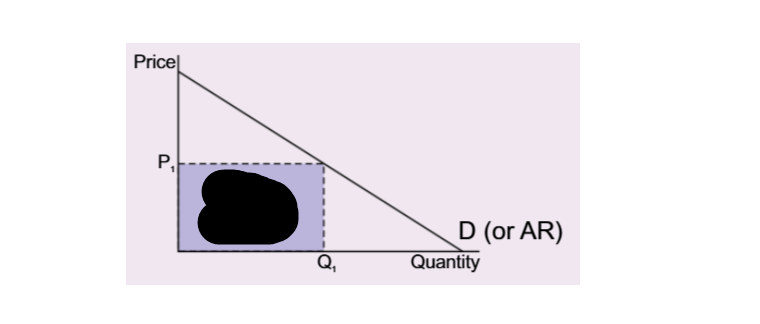
What is illustrated by the square
Total revenue
What type is price-taking firm’s AR curve look like
The perfectly elastic one
When the demand curve is perfectly elastic, then
AR=MR
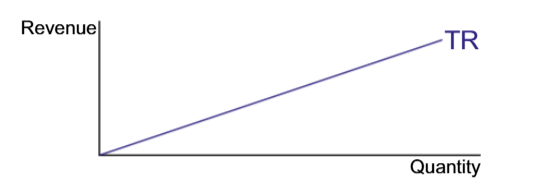
What makes the TR grow proportionally
The constant AR
The price-making firm’s Demand curve is sloping, because
It needs to decrease the price to increase demand
When the firm is a price maker, with a downward sloping Demand(AR) curve, the profit is maximized at
PED=-1; at the middle of the graph
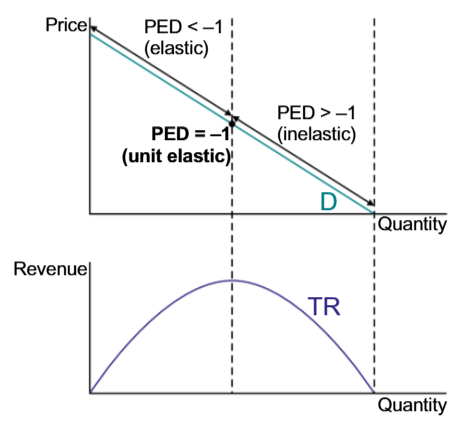
TR is at its maximum, when
MR=0
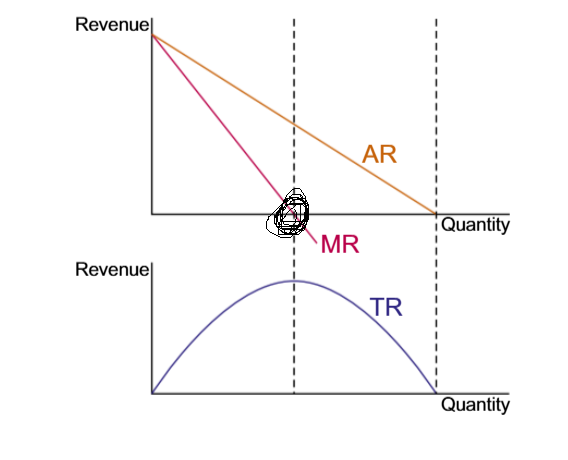
The AR slope downward, because
the firm is facing a downward sloping demand curve, because it needs to lower the price, in order to sell more output
The MR slopes downward, because
Lowering the price to sell more output reduces the revenue
Normal profit occurs when
TR=TC
Supernormal profit occurs when
TR>TC
What is the key reason for a firm to continue operating in the long run?
Making normal profit
A loos-making firm might not close immediately, because
Its average costs might not be as bad in comparison to revenue