Anatomy Lecture - CH6: Axial Division of the Skeletal System
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
function of axial skeleton
framework that supports/protects organs in the dorsal & ventral body cavities
cranial cavity
aka the cranium; a fluid-filled chamber that supports/protects the brain
the bilateral lobes (2)
parietal & temporal
sagittal suture
separates the left & right parietal bones
lamboid suture
separates the parietal & occipital bones
coronal suture
separates the parietal & frontal bones
squamous suture
separates the parietal & temporal bones
bone area of supra-orbital foramen
frontal bone
bone area of lacrimal groove
lacrimal bone
bone area of the infra-orbital foramen
maxilla
bone area of the mental foramen, mental protuberance, coronoid process
mandible
bone area of the external acoustic meatus, mastoid & styloid process
temporal bone
bone area of the superior & inferior temporal line
parietal bone
make-up of the zygomatic arch
temporal / zygomatic process of zygomatic bone
bone area of the optic canal, superior & inferior orbital fissure
sphenoid bone
bone area of the zygomaticofacial foramen
zygomatic bone
bone area of the crista galli, cribiform plate
ethmoid bone
bone area of the optic canal/nerve, foramen rotundum, lacerum, ovale, spinosum
sphenoid bone
bone area of the internal acoustic meatus
temporal bone
bone area of the hypoglossal canal
occipital bone
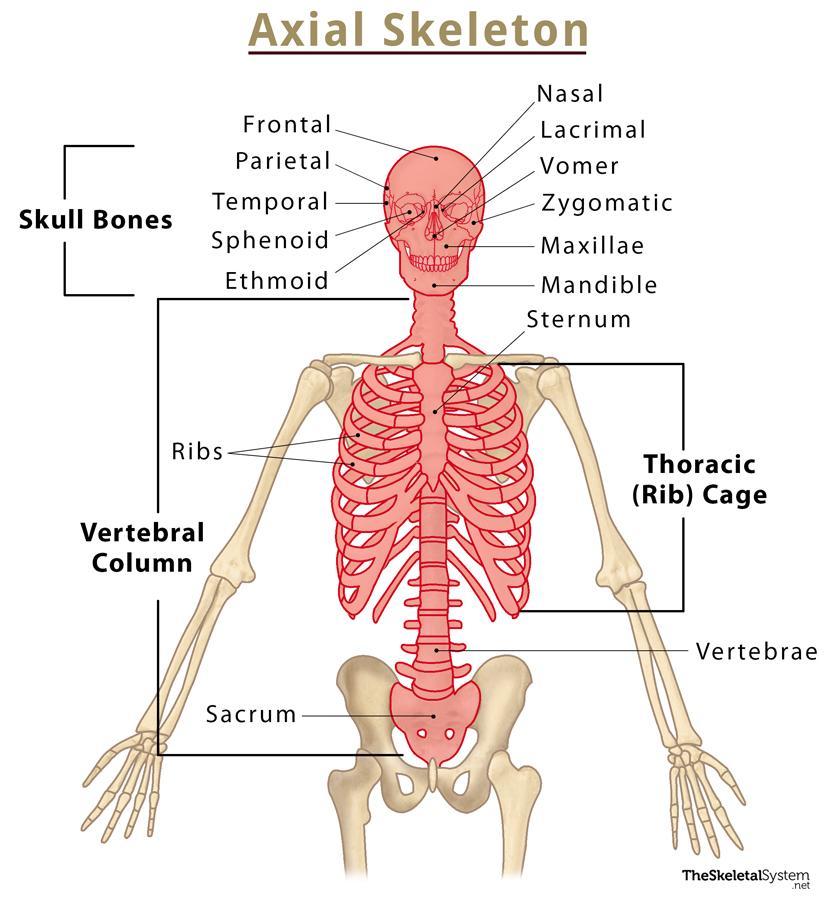
composition of the axial skeleton
bones of the skull, thorax, & vertebral column
number/percentage of bones in the axial skeleton
80 bones / 40% of bones in the body
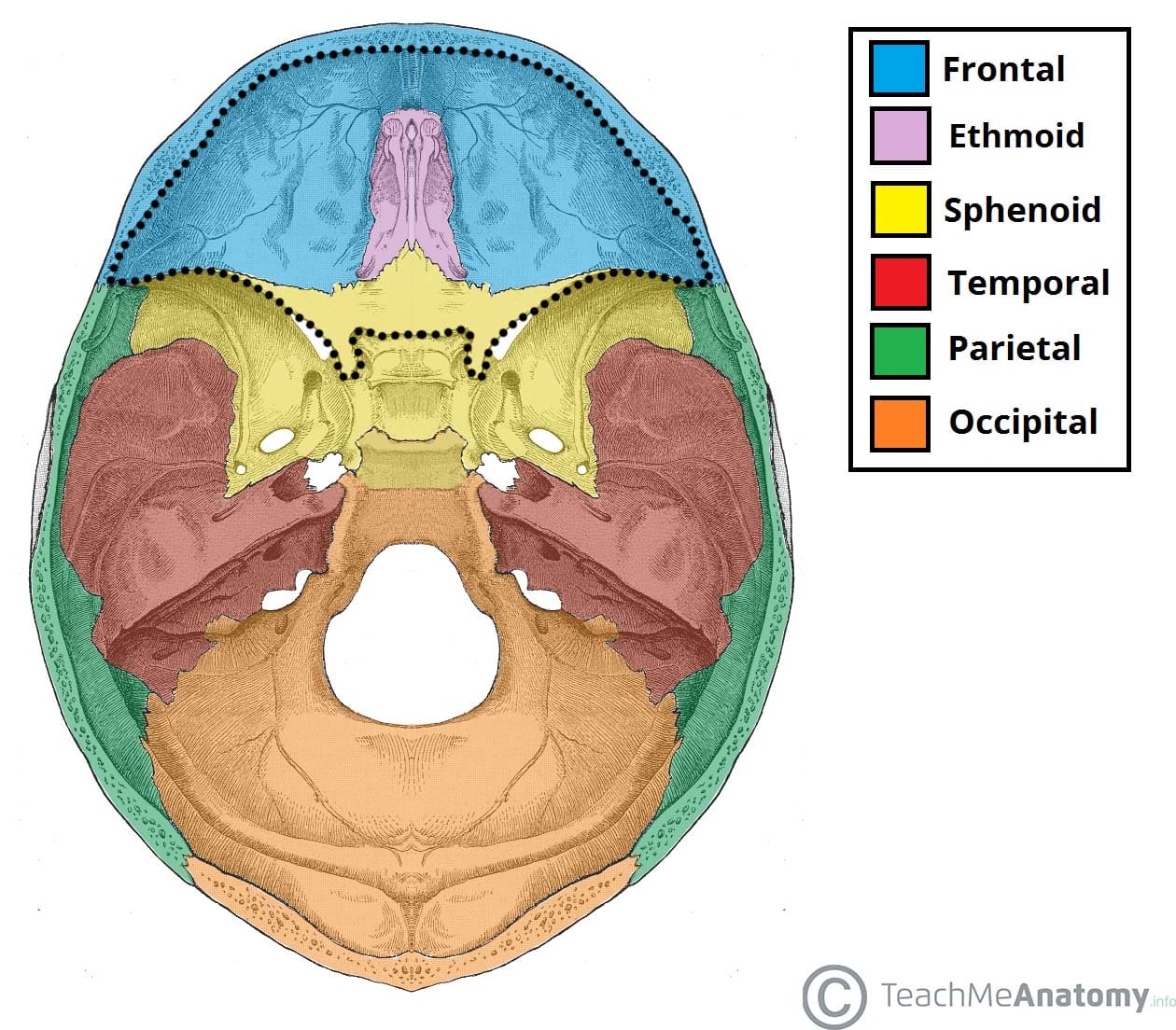
composition of the cranial cavity/cranium
occipital, frontal (2), temporal (2), parietal, sphenoid, & ethmoid
composition of the facial complex
vomer, conchae, nasal, maxilla, mandible, palatine, zygomatic, lacrimal (Van Can Not Make My Pet Zebra Laugh)
the only single bones of the face
vomer & mandible
composition of the ethmoid
cribiform plate, ethmoidal labryinth, & perpendicular plate
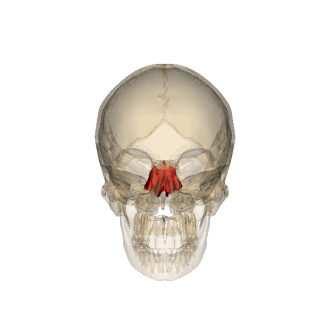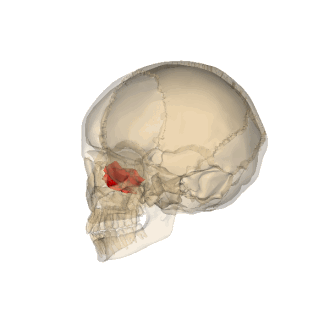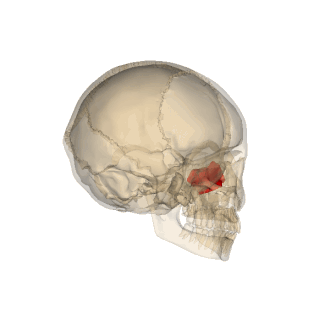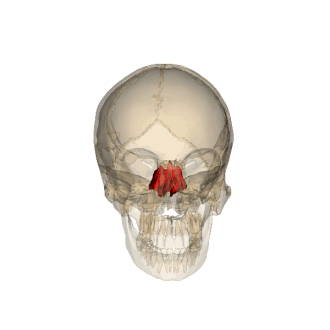
the cavity/part that the ethmoid is involved
nasal cavity/nasal septum
paranasal sinuses
interconnected air-filled pockets; ex. frontal, maxillary, sphenoid sinuses, & ethmoidal air cells
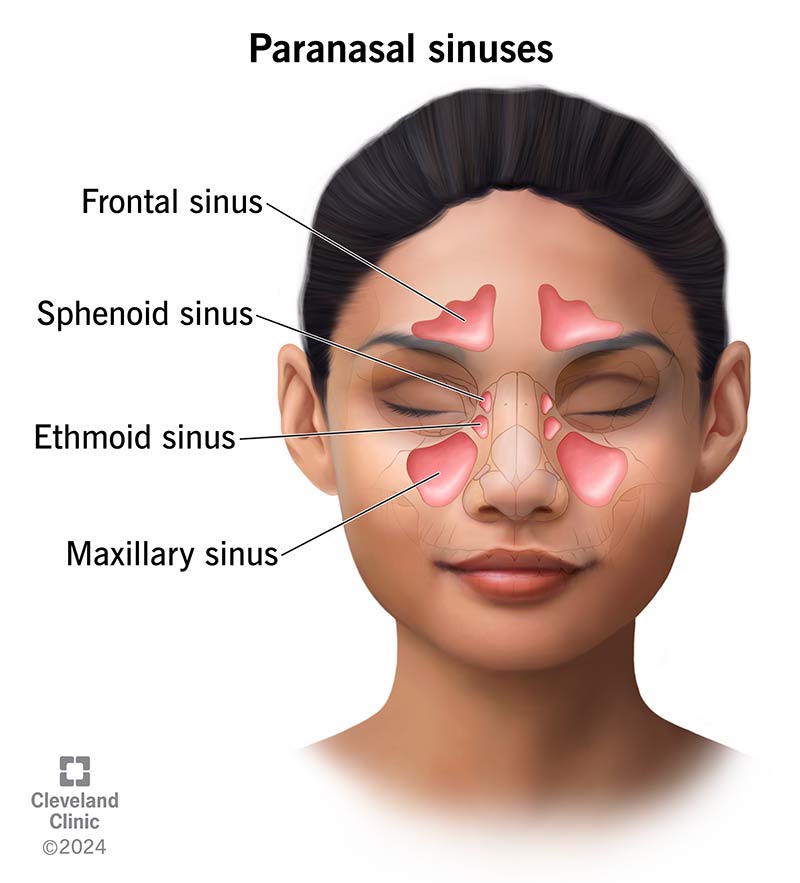
functions of paranasal sinuses
make the skull lighter; produce mucus; resonate air for voice production
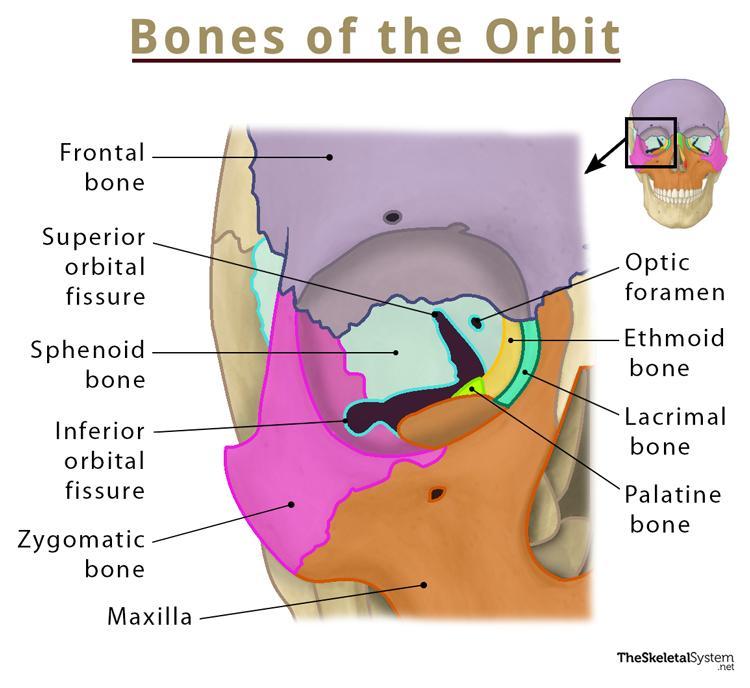
orbital complex
super orbital fissure, inferior orbital fissure, & optic foramen/canal
the base for muscles that move the tongue & larynx
hyoid bone
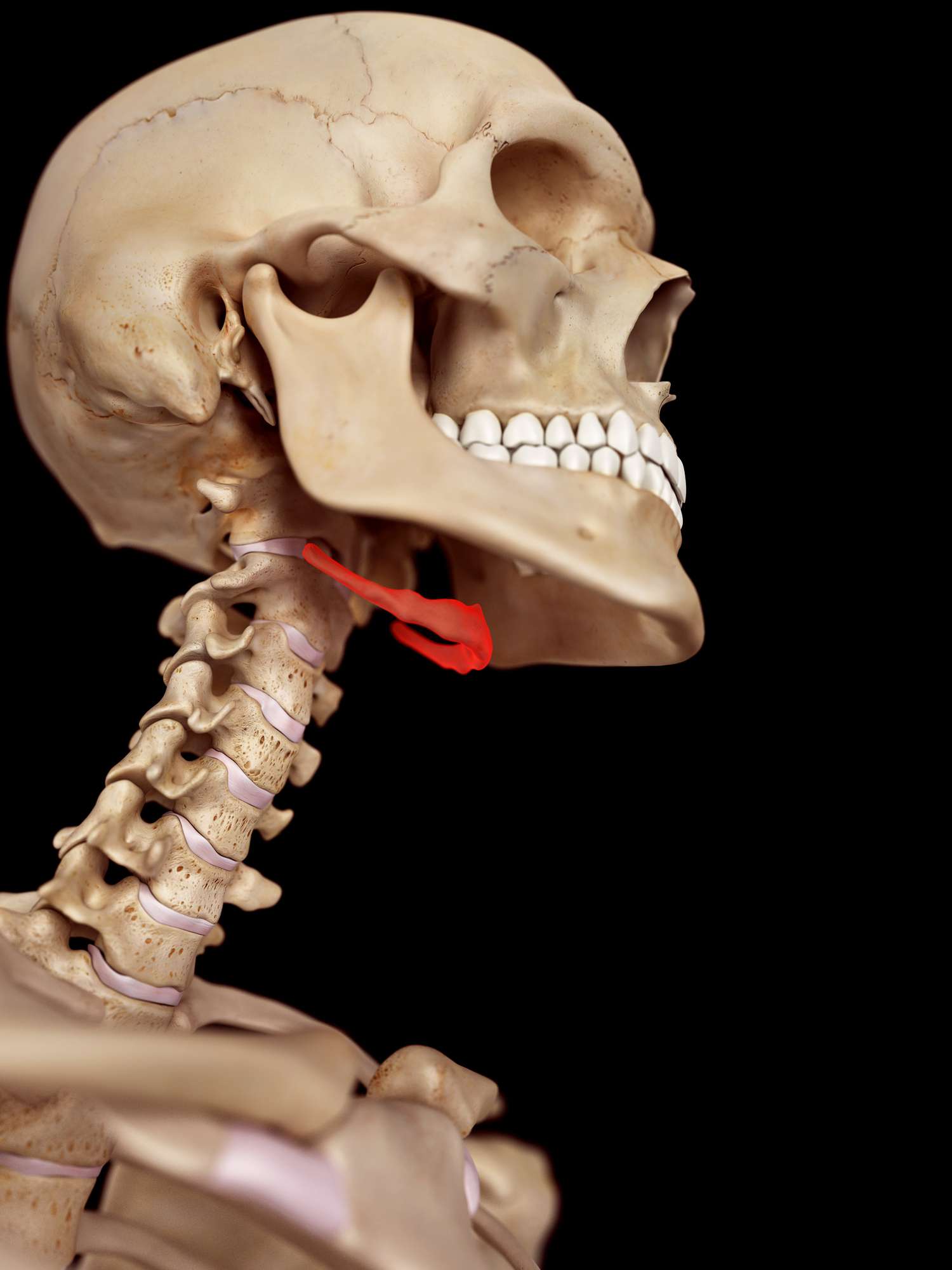
how the hyoid is held in place
suspension by stylohyoid ligaments; only bone to not be attached to another bone
fontanelles
areas of incomplete ossification (in babies); fuse later w/ development
composition of vertebral column
26 bones: 24 vertebra, 1 sacrum, 1 coccyx
regions of vertebral column (superior to inferior)
cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5)
primary (spinal) curves
curves developed before birth; posteriorly sweeping curves of thoracic & sacral regions; allows the abdominopelvic viscera more room
secondary (spinal) curves
curves developed after birth as infant learns to hold up head (cervical) & begins to walk (lumbar); anteriorly sweeping curves of cervical & lumbar regions
intervertebral disc
pads of fibrous cartilage
vertebral arch
sides & back of vertebral foramen that surround part of the spinal cord
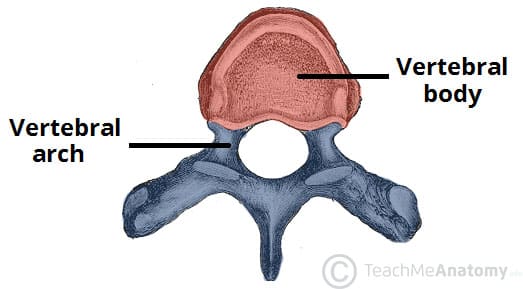
walls of the vertebral foramen
pedicles
roof of the vertebral foramen
lamina
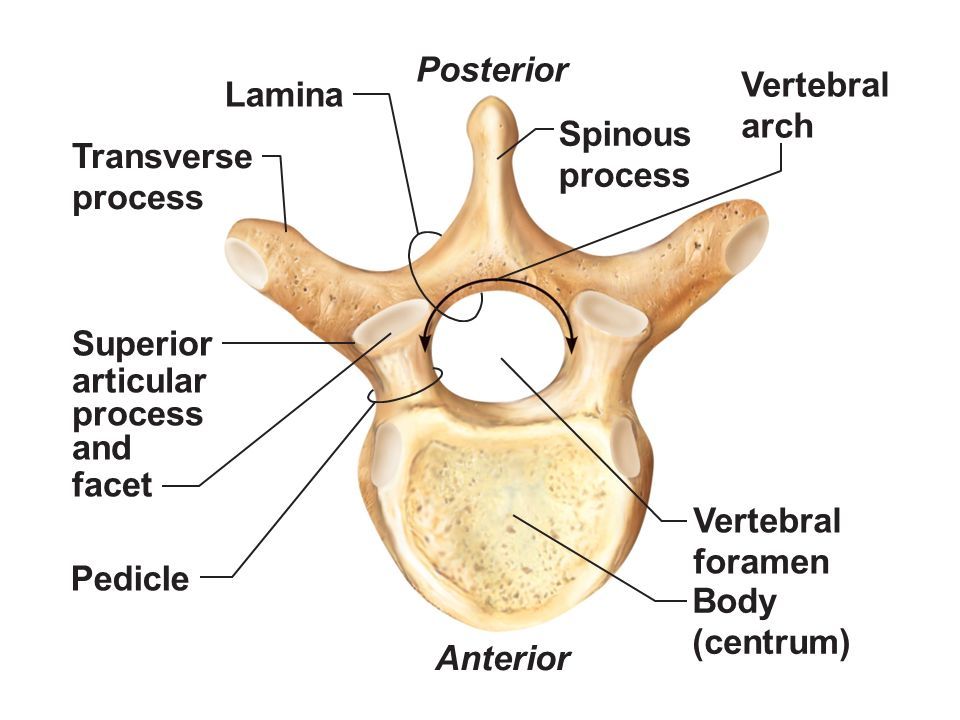
junctions between the pedicles & laminae
articular process
space formed from the vertebral foramina & column; the long tunnel that the spinal cord goes through
vertebral canal
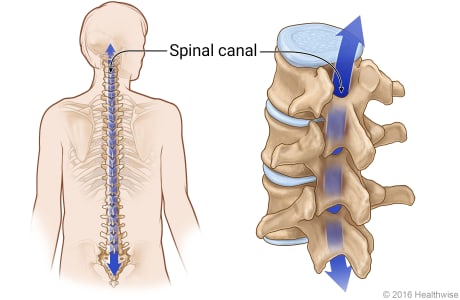
side openings between 2 vertebrae; holes for spinal nerves
intervertebral foramen
the cervical vertebrae’s notched spinous processes
bifid process
extra extensions of bone from the vertebral body that attach to the transverse processes
costal processes
hole between the costal & transverse processes
transverse foramina
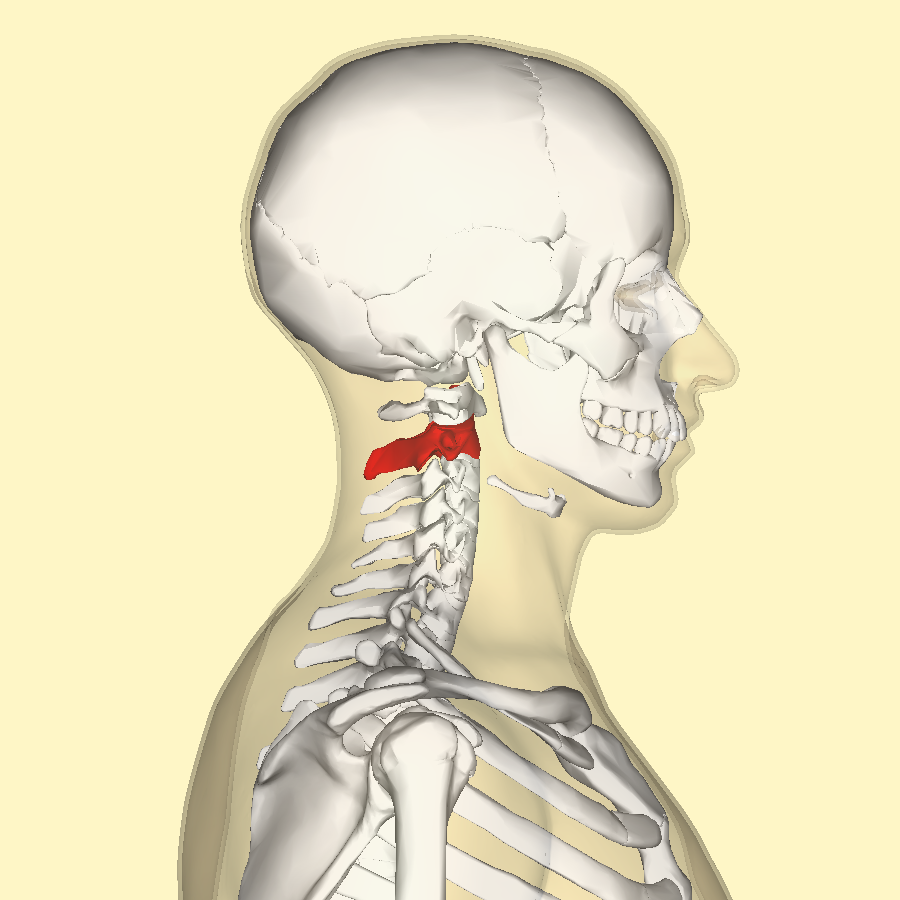
the atlas
C1; has no body; articulates cranially w/ occipital condyles; allows us to nod yes; fuses w/ body of C2→forms dens
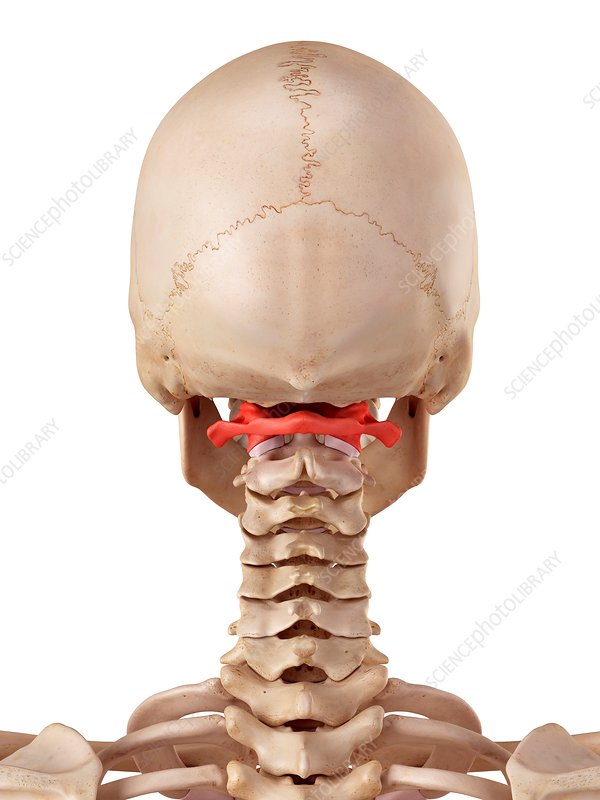
the dens formed by the atlas C1 & axis C2
odontoid processes
the axis
C2; no intervetrbal discs; allows us to shake no
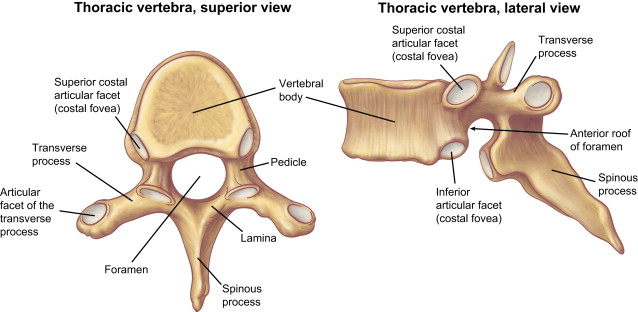
thoracic vertebrae
T1-T12; looks like a giraffe; associated w/ ribs; ribs articulate at the costal/demifacets
lumbar vertebrae
L1-L5; looks like a moose; vertebral bodies here take up the most body weight
thoracic cage
refers to the 12 ribs; can be 13 from L1
functions of thoracic cage
protects its structures; attachment site for the muscles that help w/ respiration, positioning vertebral column, & movement of the pectoral girdle & upper limb
true ribs
ribs 1-7; articulate directly w/ body of sternum
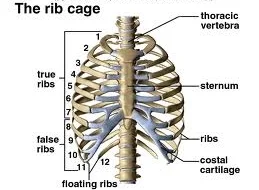
false ribs
ribs 8-12
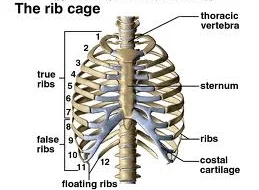
floating ribs
ribs 11-12
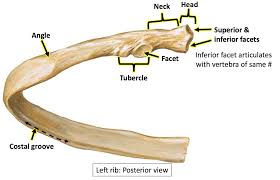
difference between human & non-human ribs
non-human ribs are missing the subcostal groove
most superior part of the sternum
manubrium
middle part of the sternum
the body
most inferior & smallest part of the sternum
xiphoid process