Anatomy Lab
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
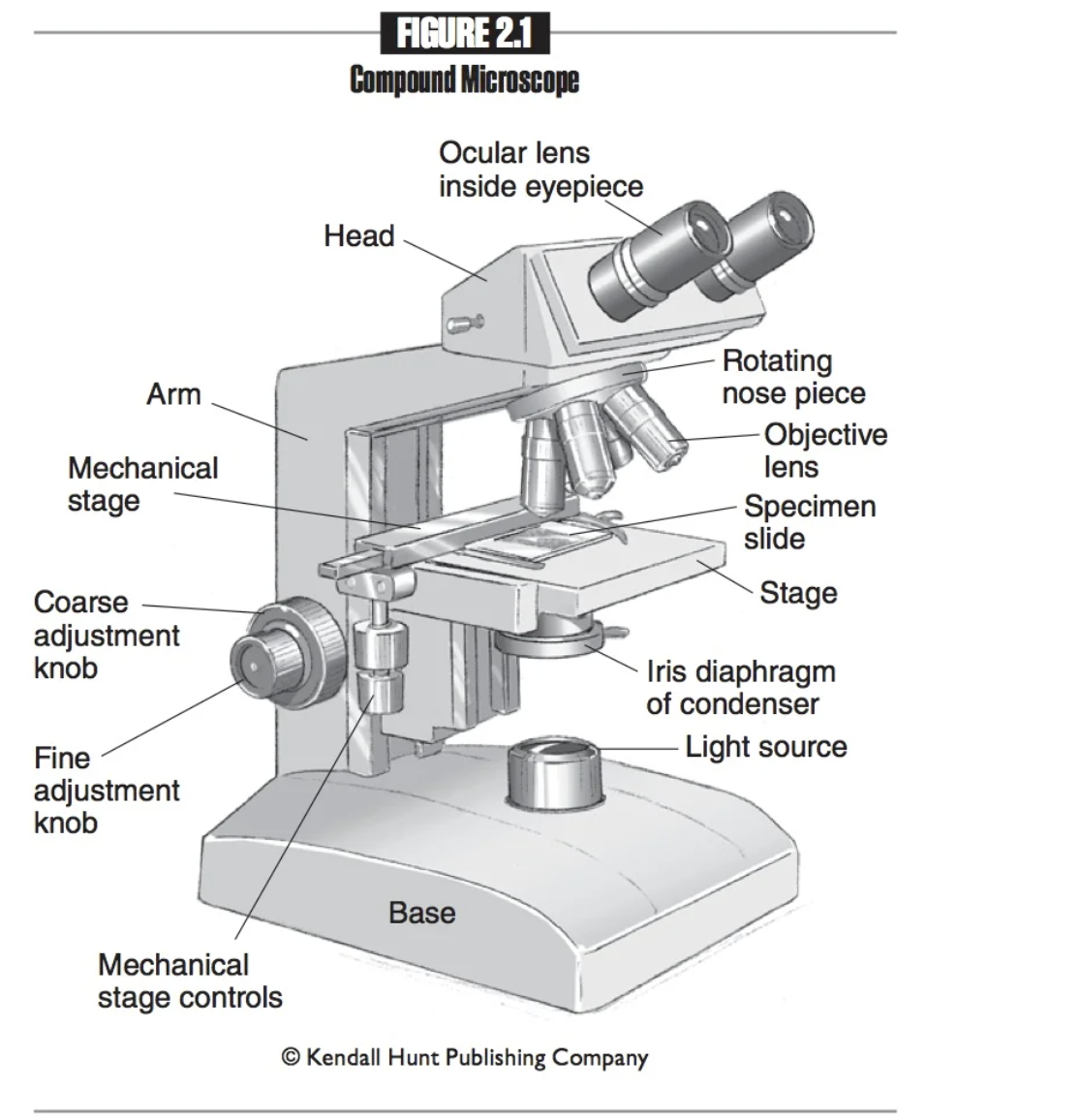
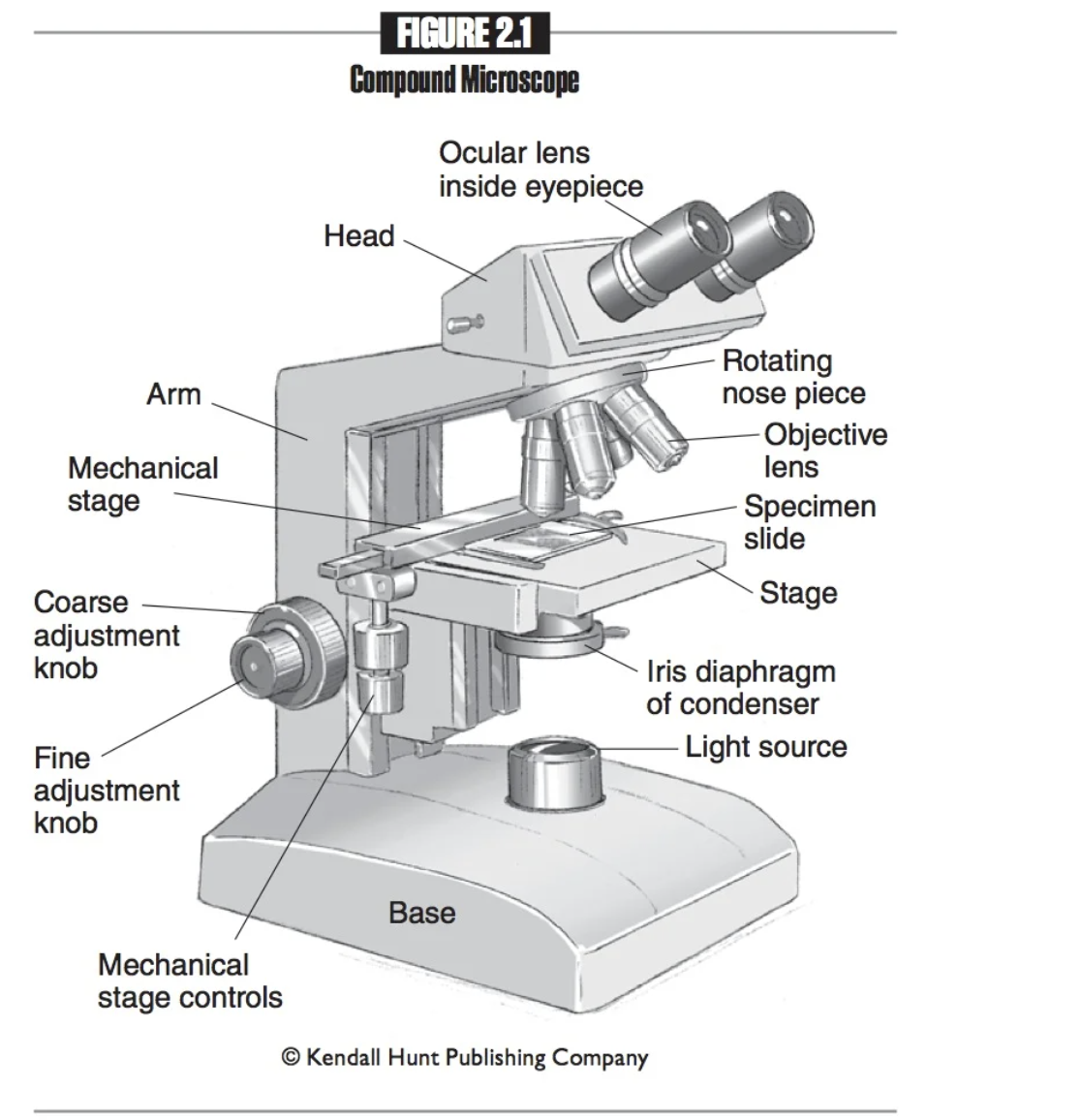
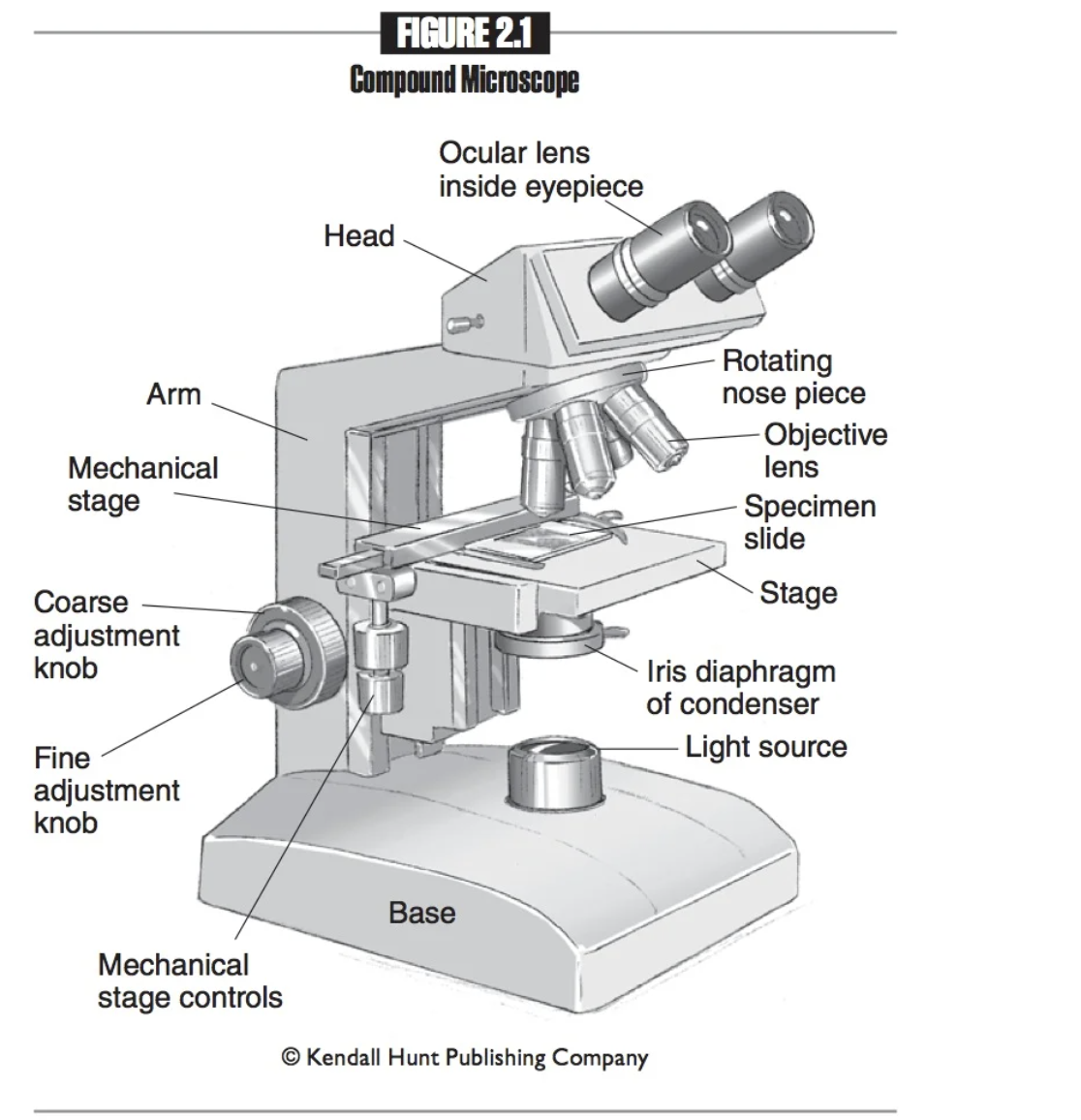
Arm
Attaches the head, nosepiece, and base. When transporting the microscope, grip the arm with one hand.
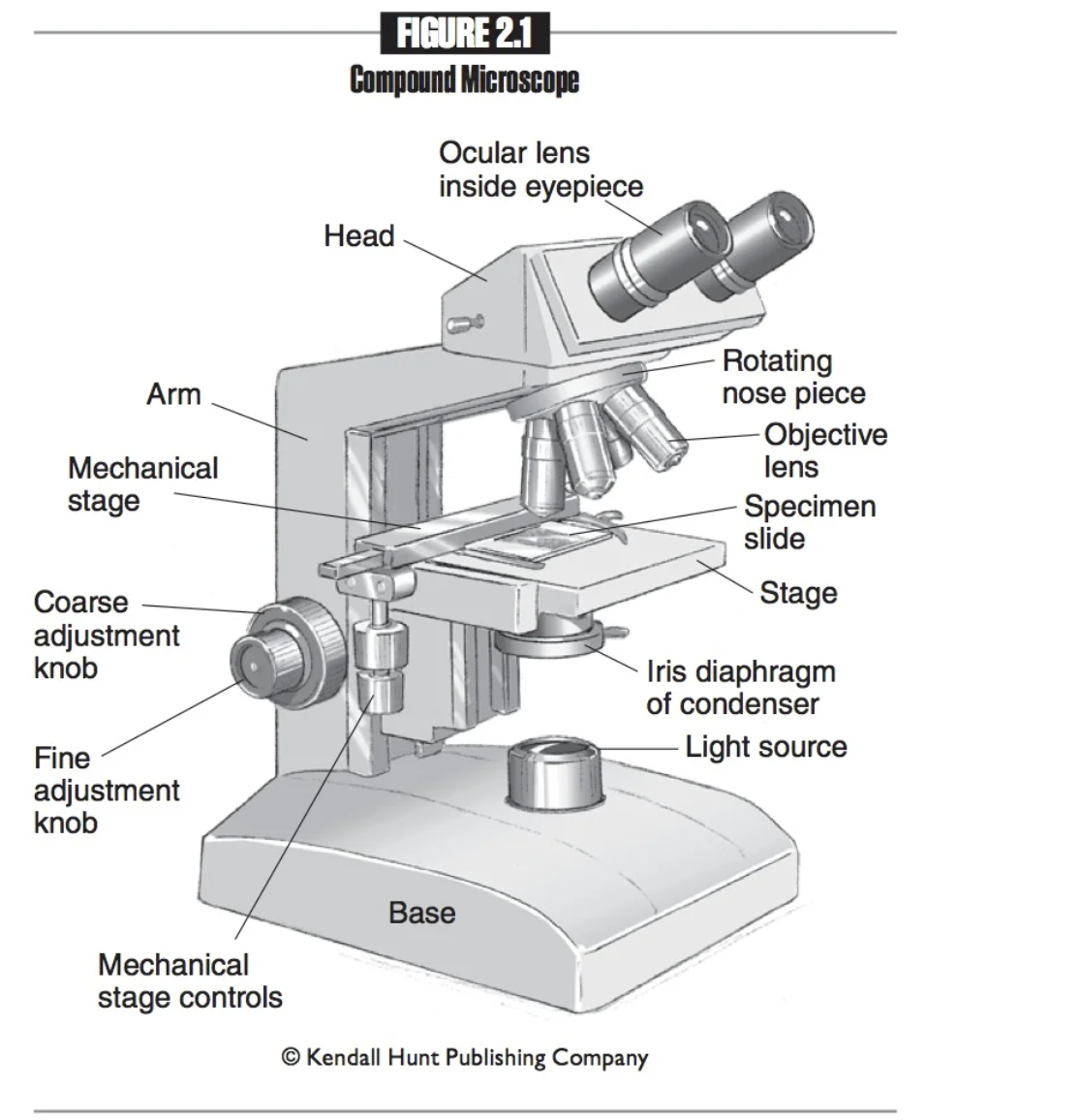
Base
The bottom part of the microscope. When transporting the microscope, place one hand under the base for support.
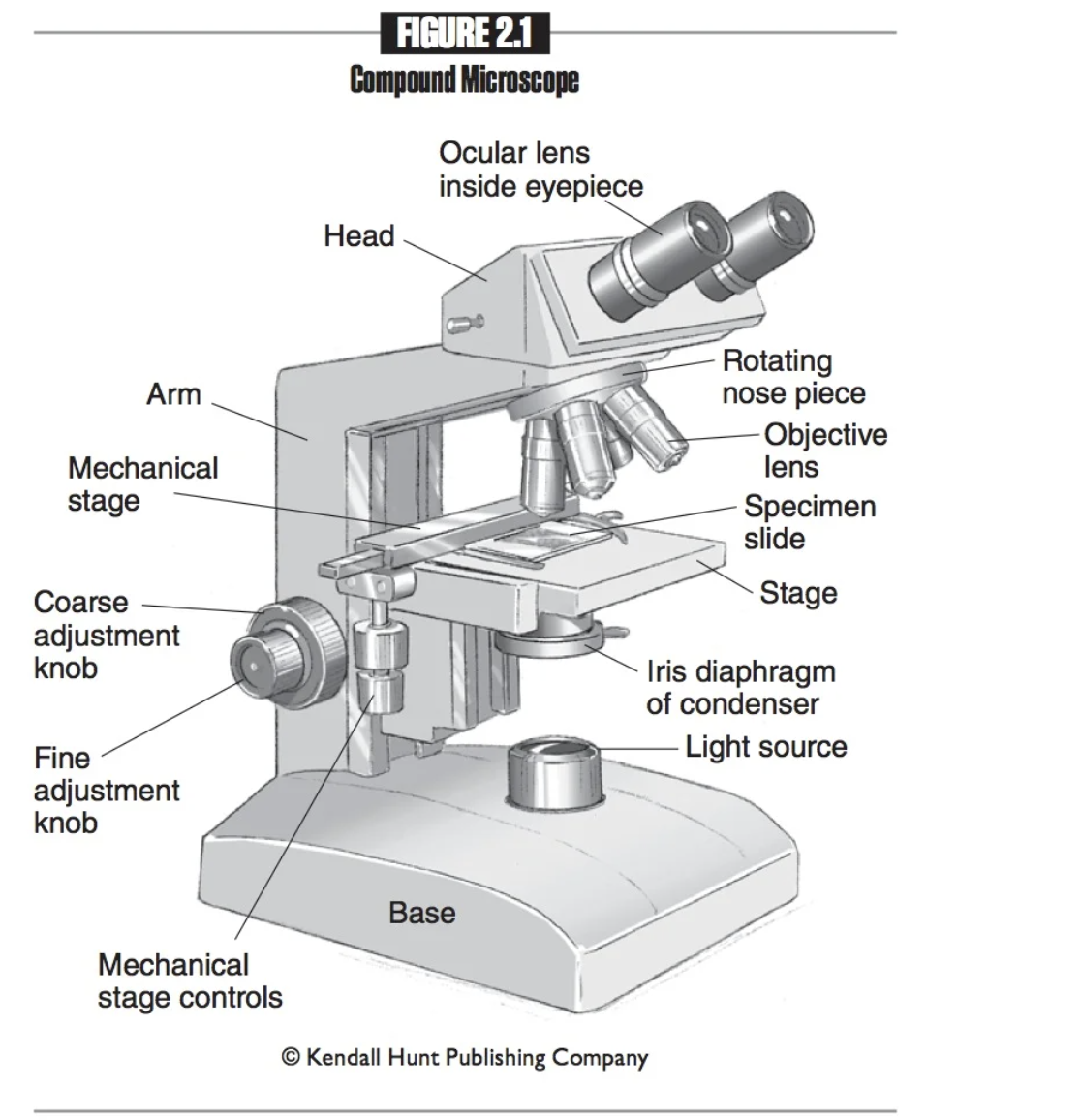
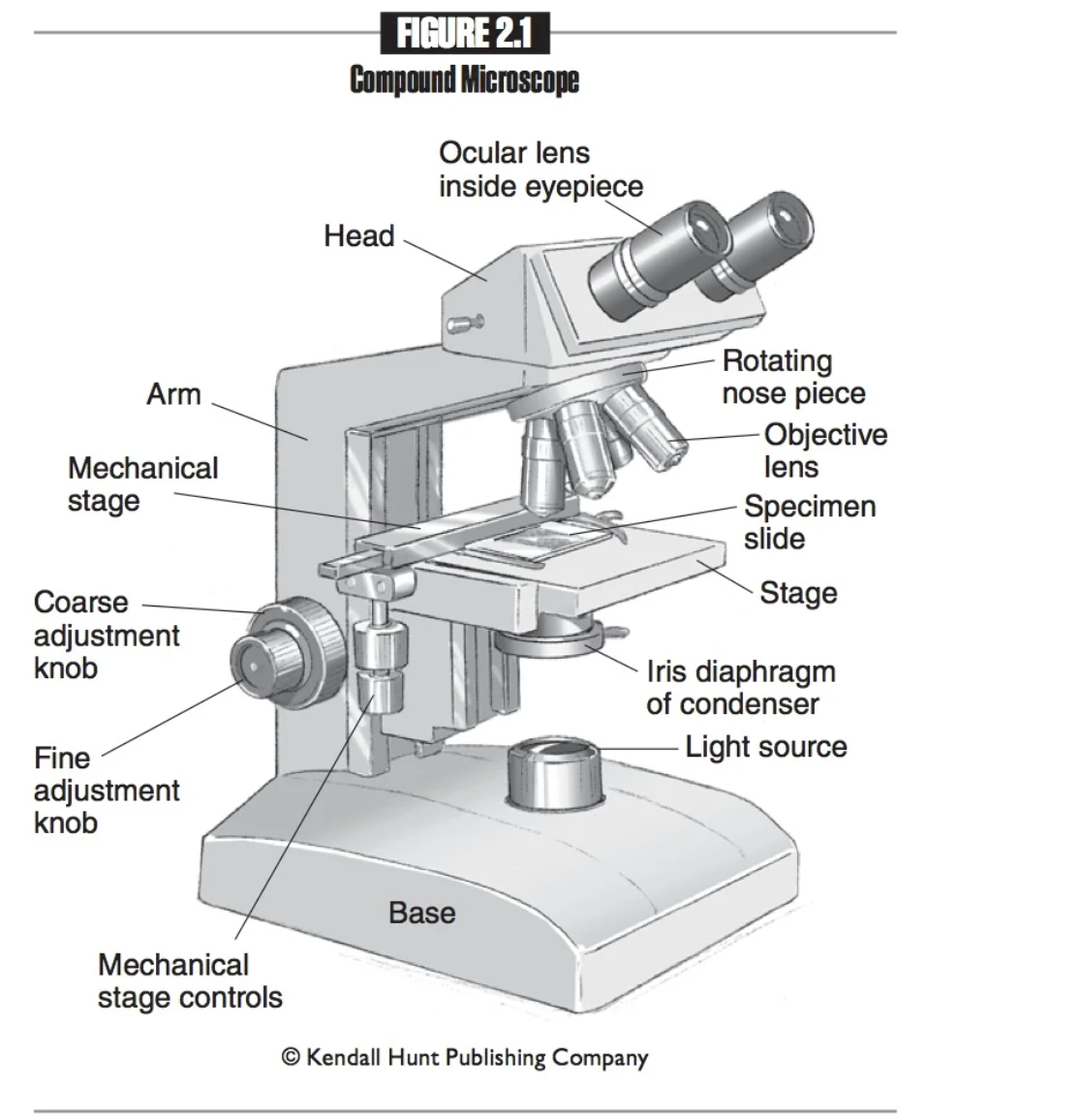
Iris Diaphragm
A lens system that focuses light onto the specimen, enhancing visibility and detail during microscopy examinations.
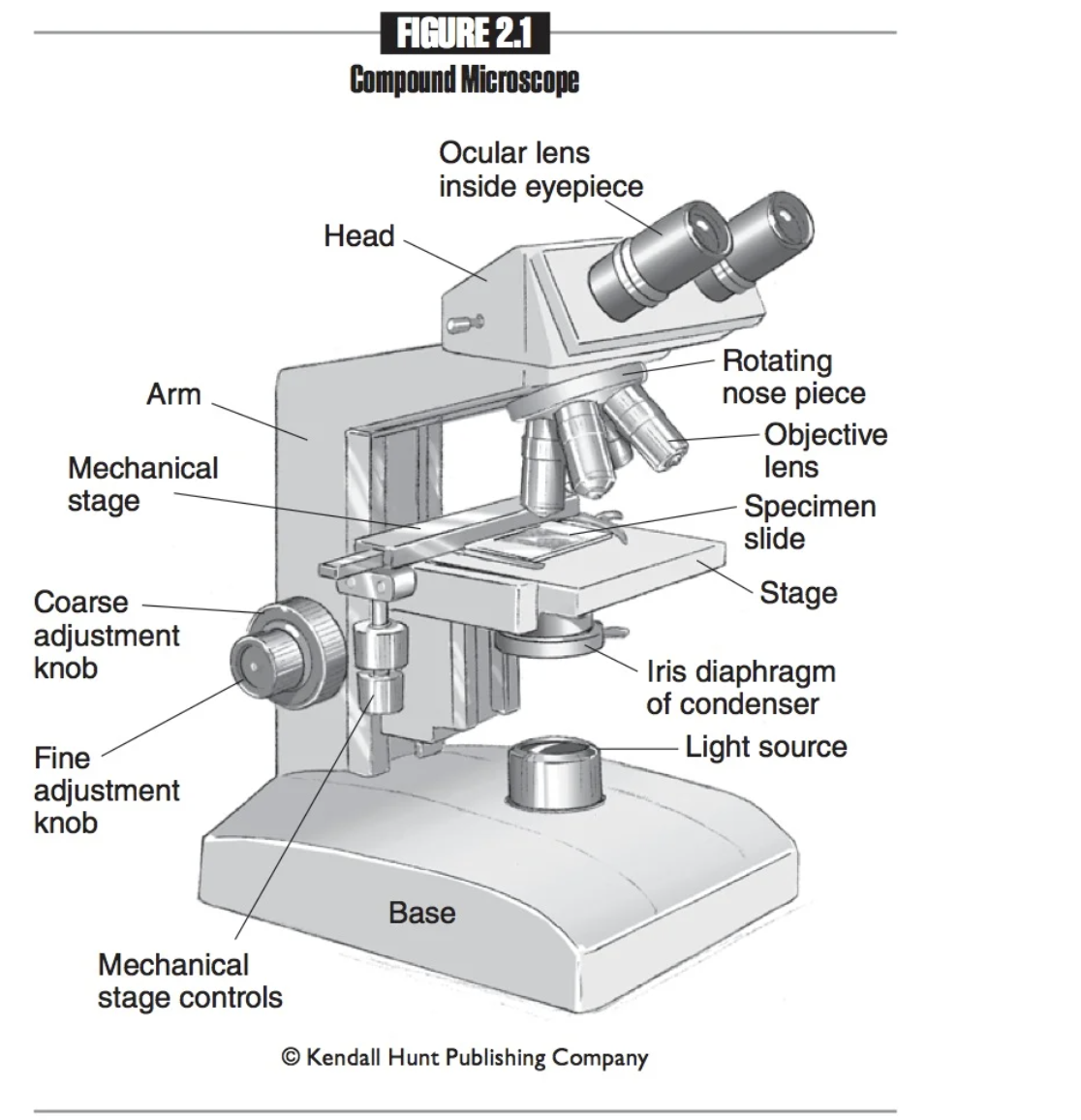
Coarse adjustment knob
A large knob on a microscope used to make significant changes in focus, allowing for initial alignment and focusing of the specimen.
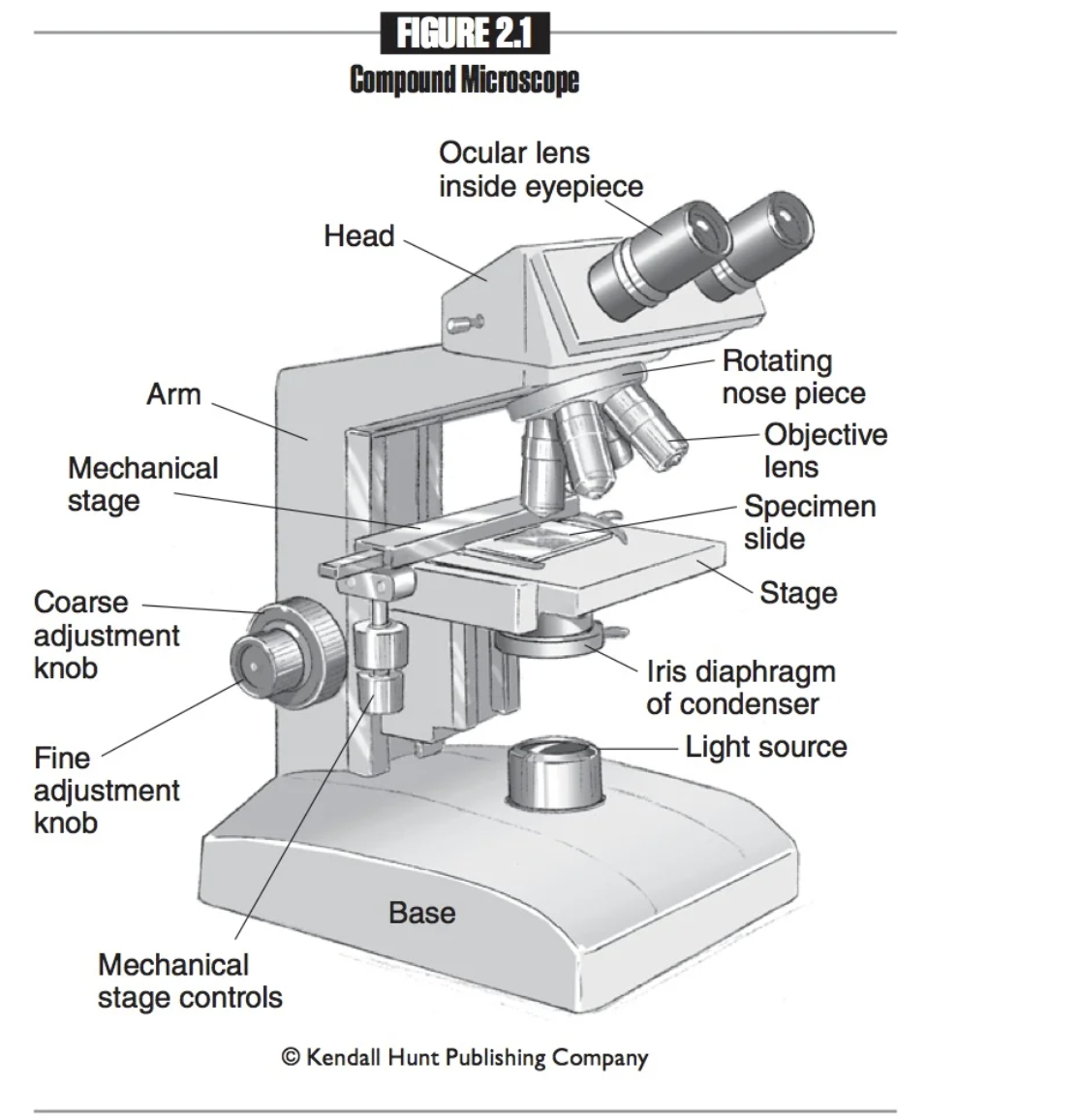
Fine adjustment knob
A smaller knob on a microscope that allows for precise focusing adjustments, enhancing the clarity and detail of the specimen.
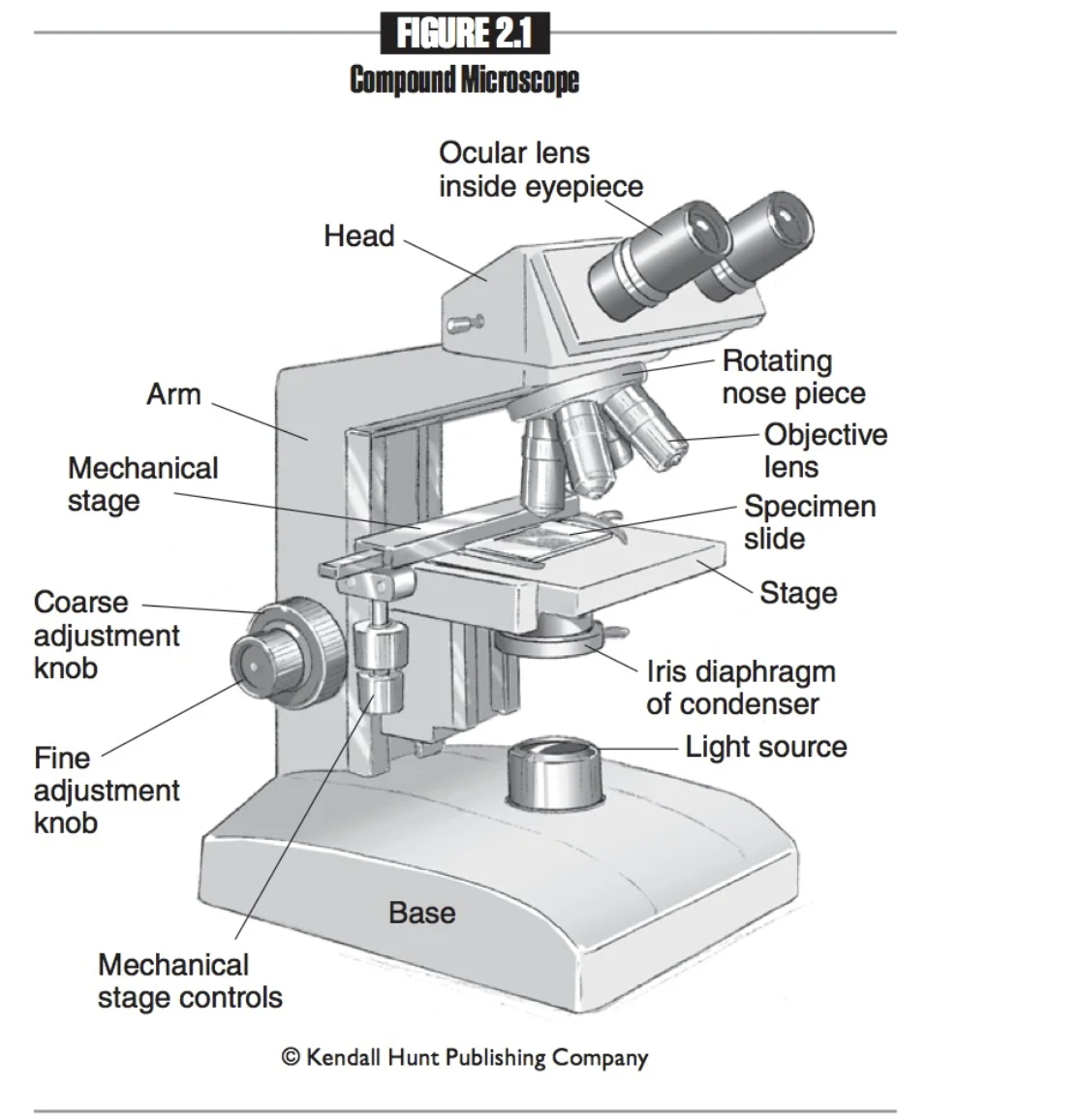
Eyepieces
The part of the microscope that you look into.
Ocular lenses
Another name for eyepieces, which magnify the specimen for viewing. 10x normal size
Head
The part of the microscope that provides attachment points for the ocular and objective lenses.
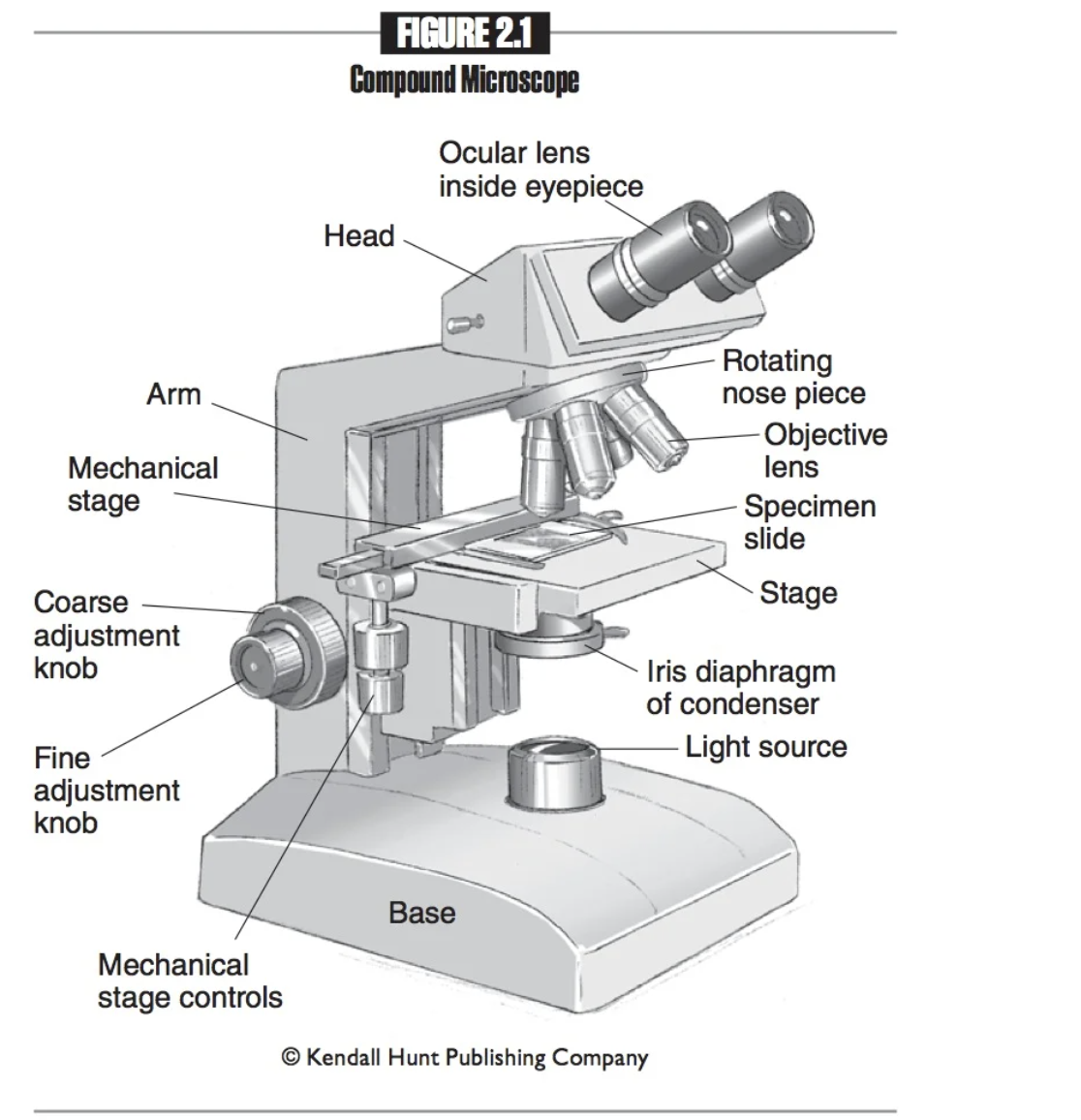
Mechanical stage
Platform that holds the slide in place.
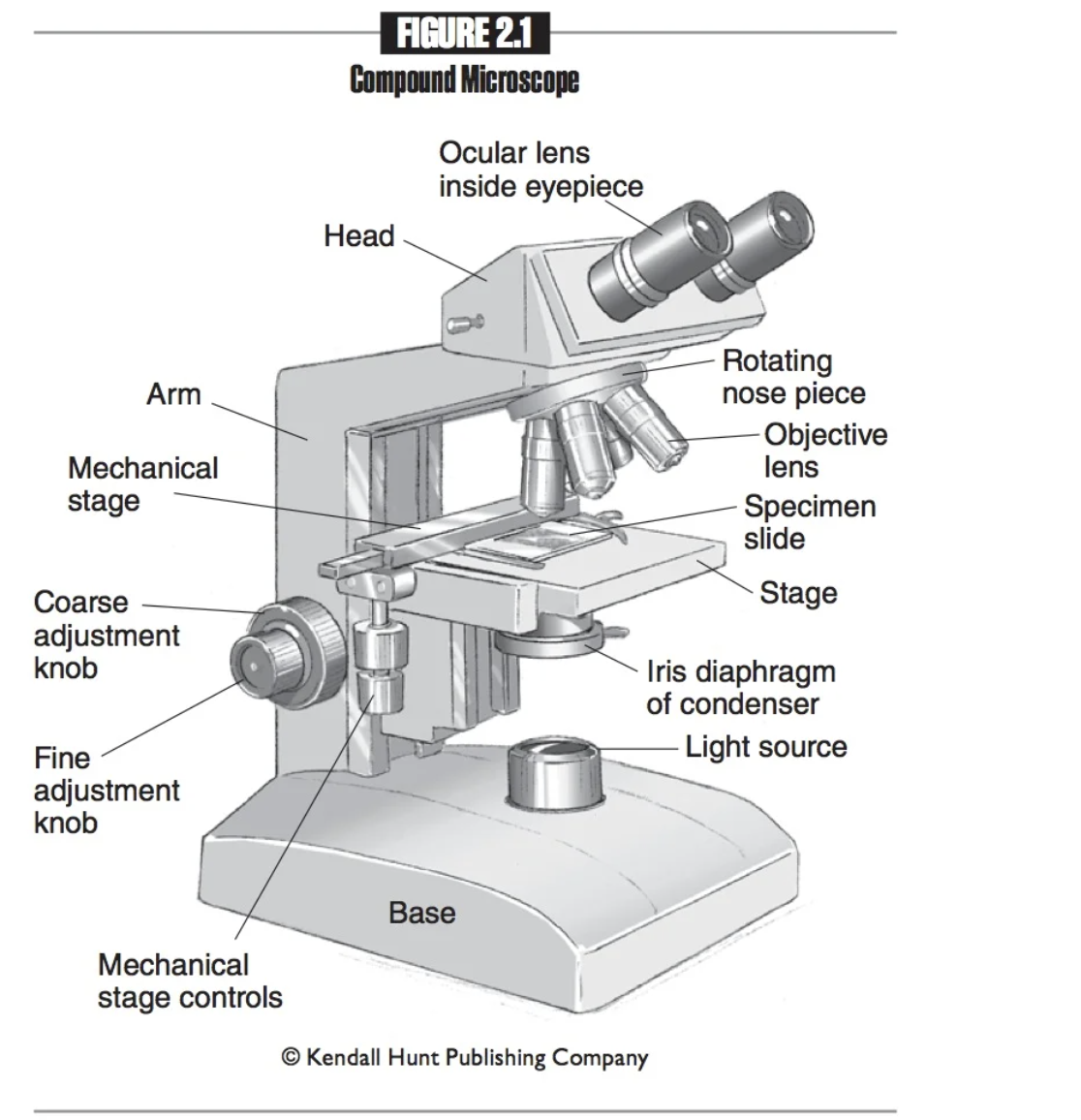
Mechanical stage controls
Knobs used to move the mechanical stage left and right or up and down.
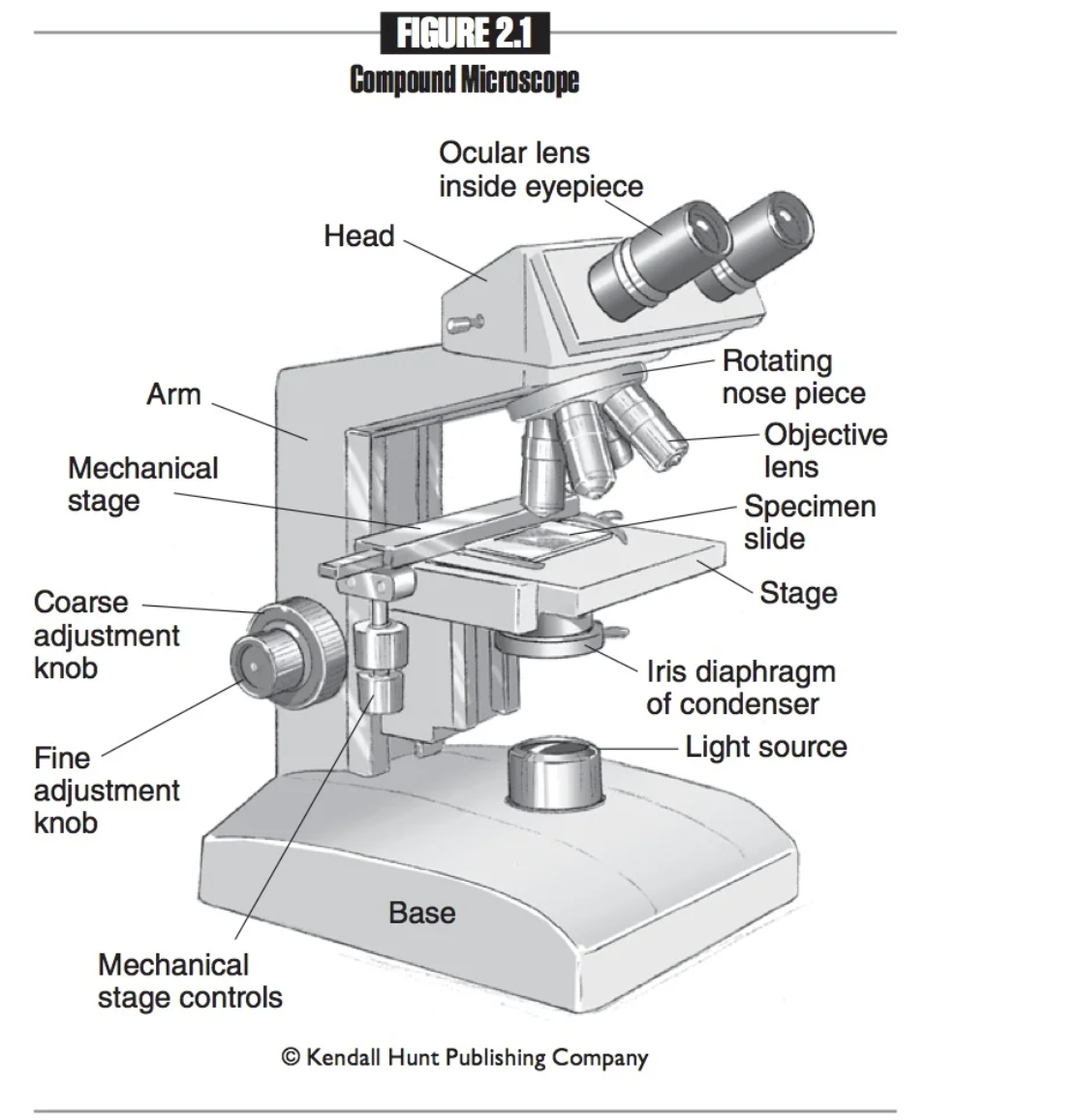
Nosepiece
Connects the objective lenses to the head, and rotates to change the objective lenses.
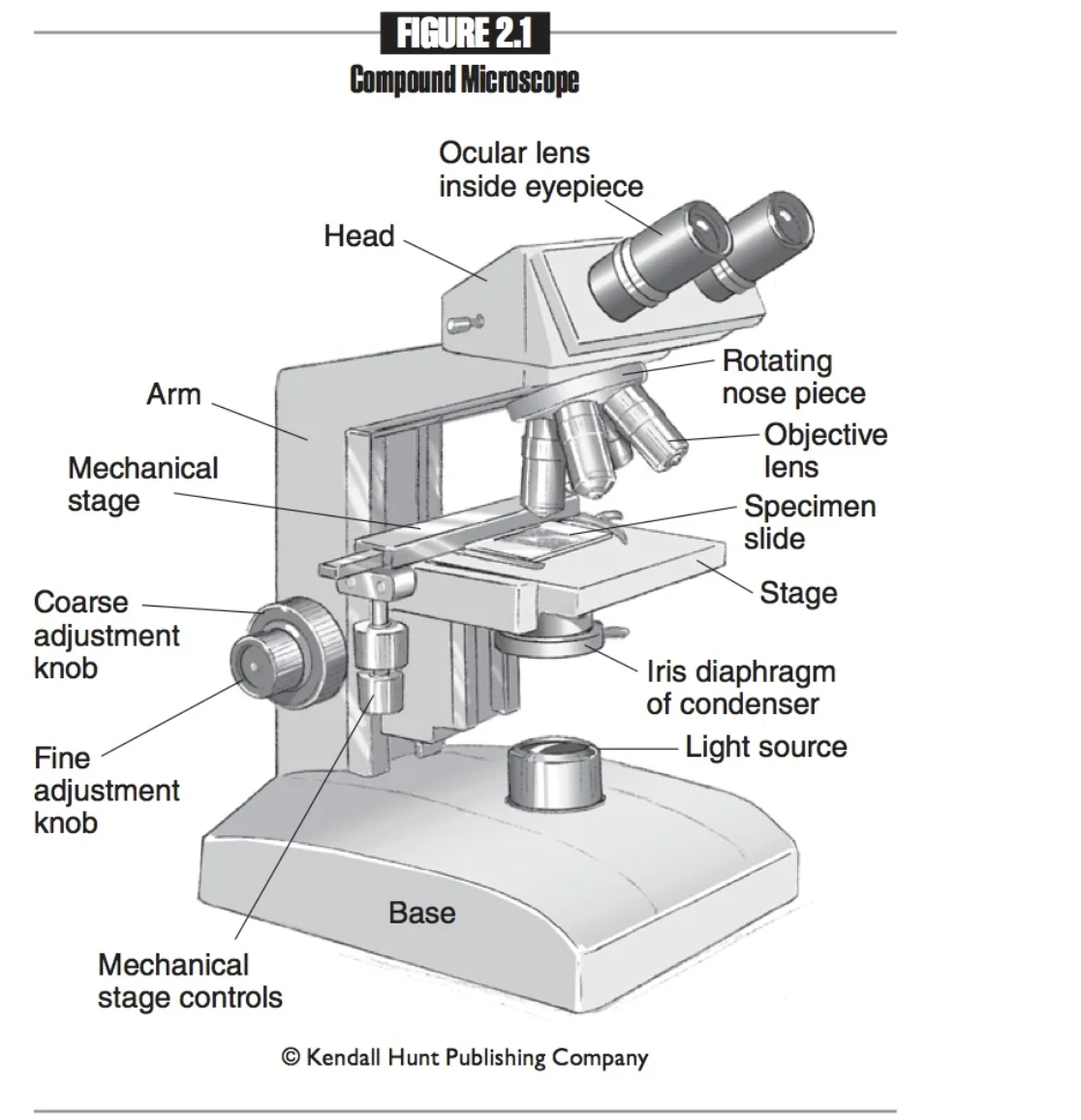
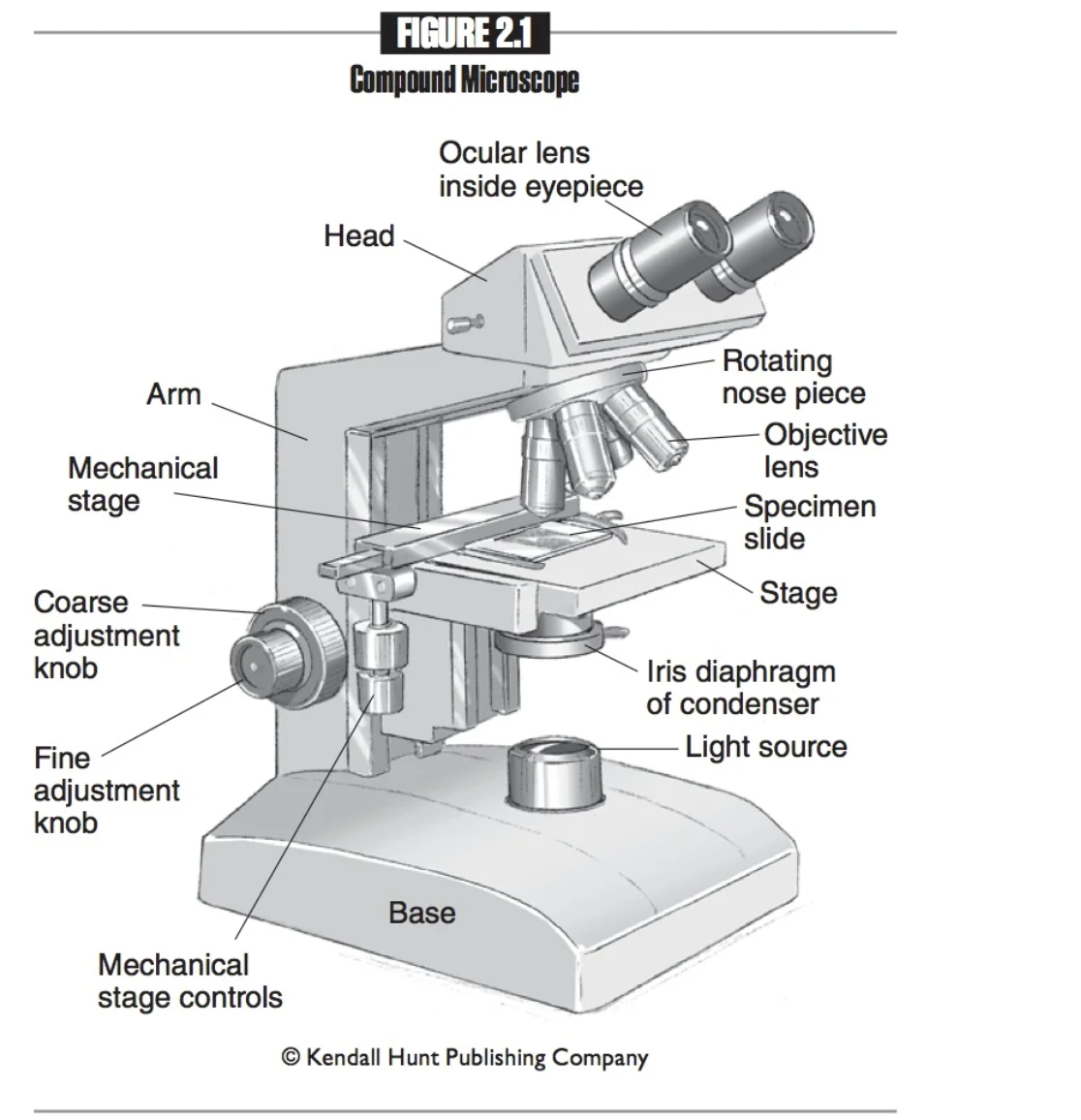
Scanning objective lens
Shortest objective lens. Magnifies 4x; has the greatest field of view and the deepest depth of field. Marked with a red band.
Low power objective lens
Second shortest objective lens. Magnifies 10x and marked with a yellow band.
High power objective lens
Second largest objective lens. Magnifies 40x and marked with a blue band.
Total magnification of scanning objective lens
40x
Total magnifcation of low power objective lens
100x
Total Magnification of high power objective lens
400x
total magnification of oil immerson lens
1,000x
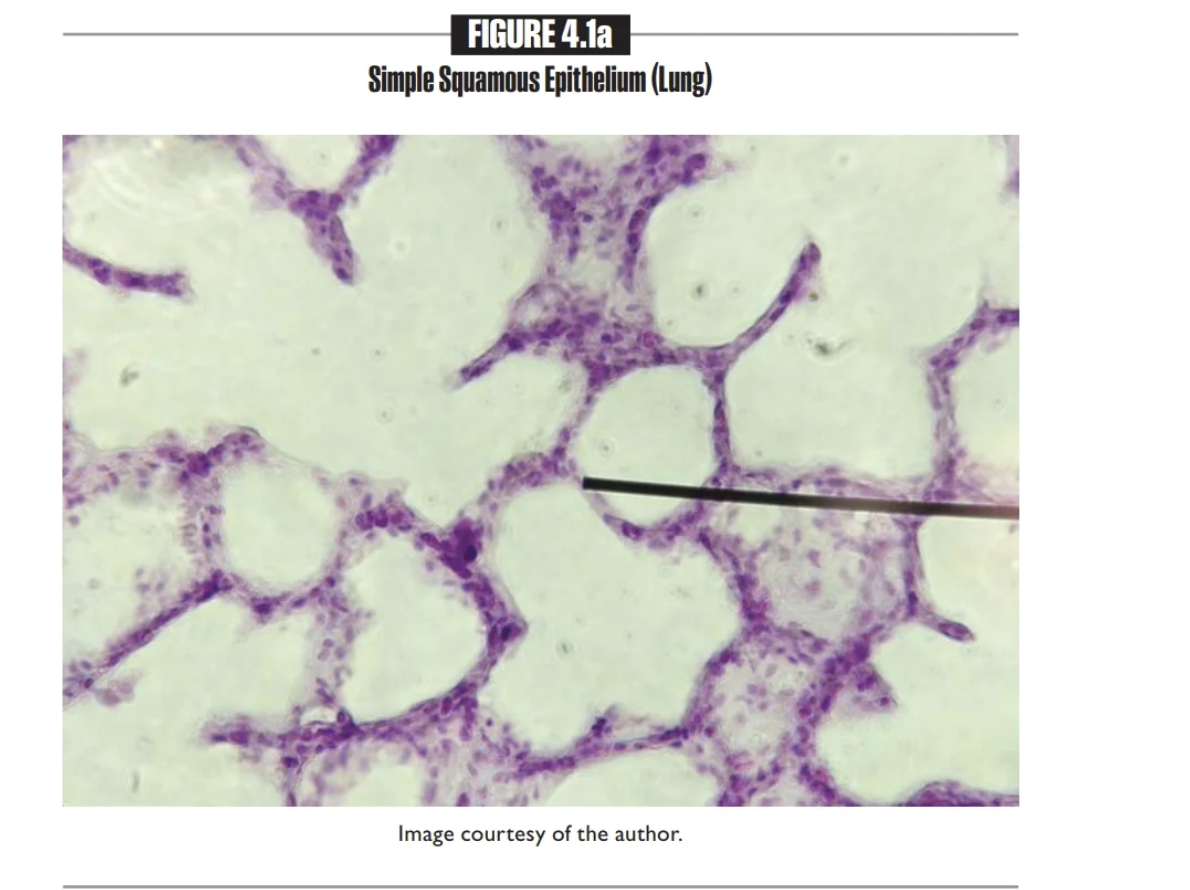
Simple Squamous Epithelium
single layer of flat cells
Found in the Alveoli(air sacs) of the lungs and the Endothelium
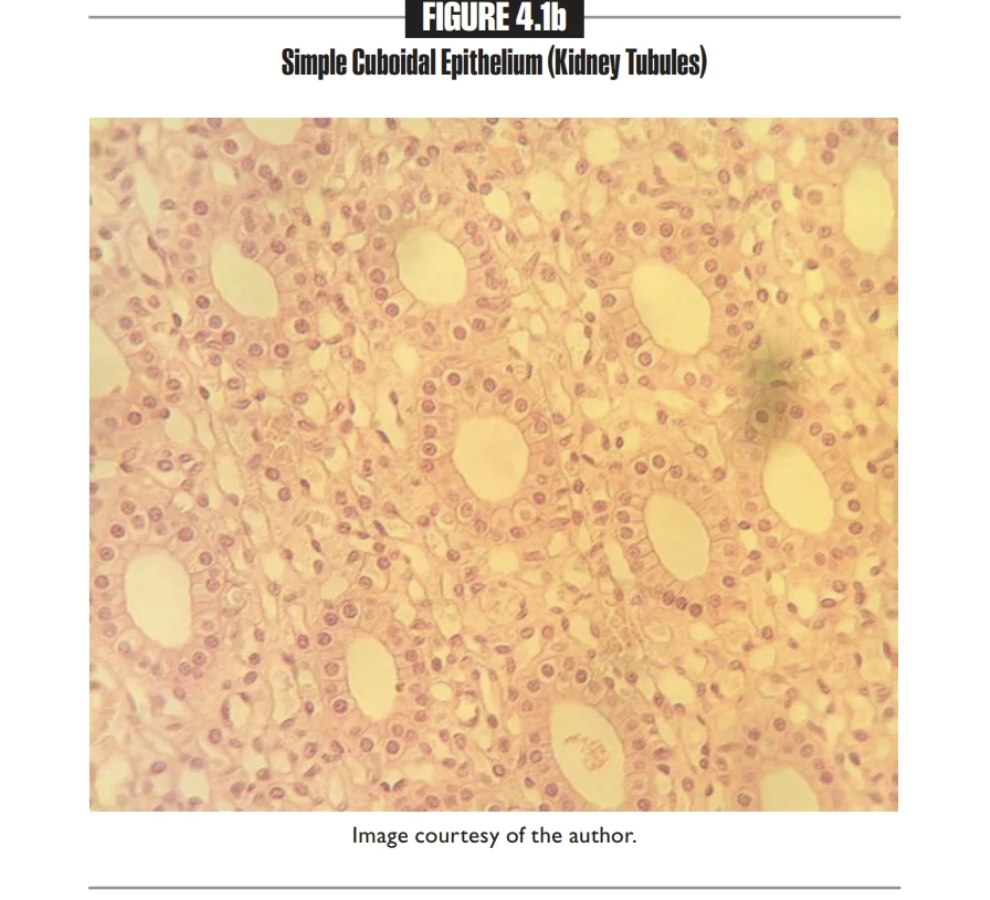
Simple cuboidal epithelium
A single layer of cube-shaped cells
Found in the kidney tubules & ovary surface
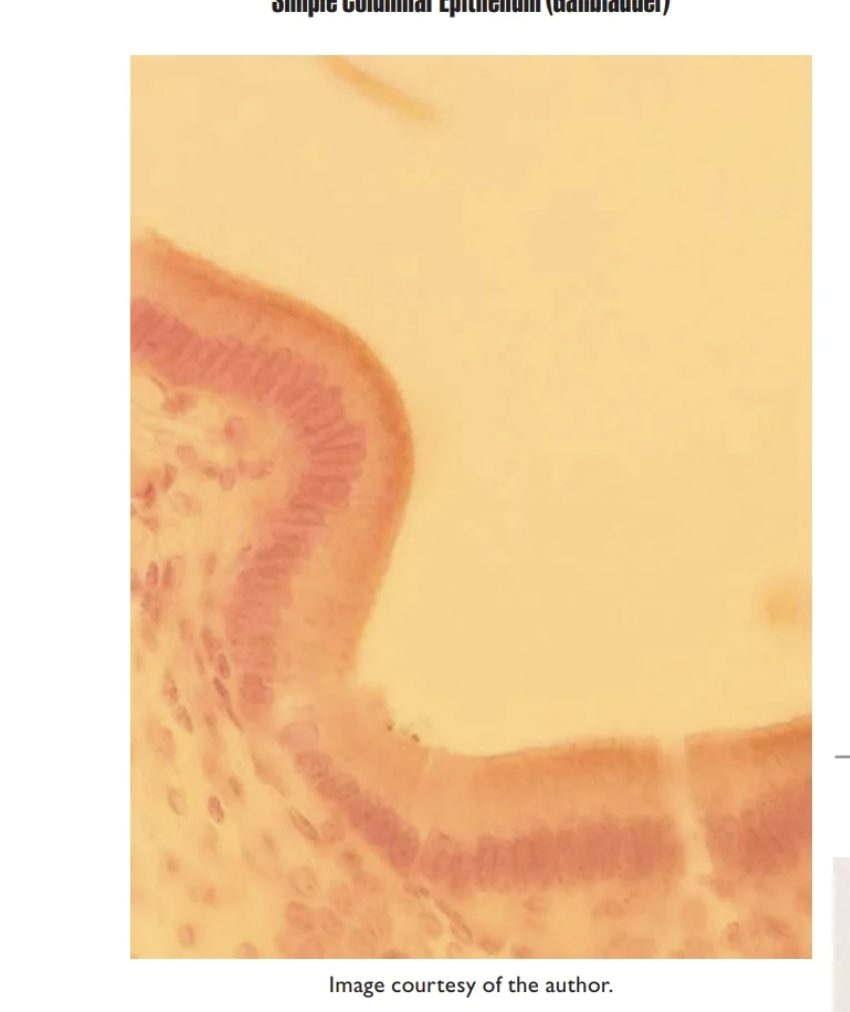
Simple columbar epithelium
Single-layer or column-shaped cells
Found in the small/large intestine, stomach, gallbladder, and lines the uterus
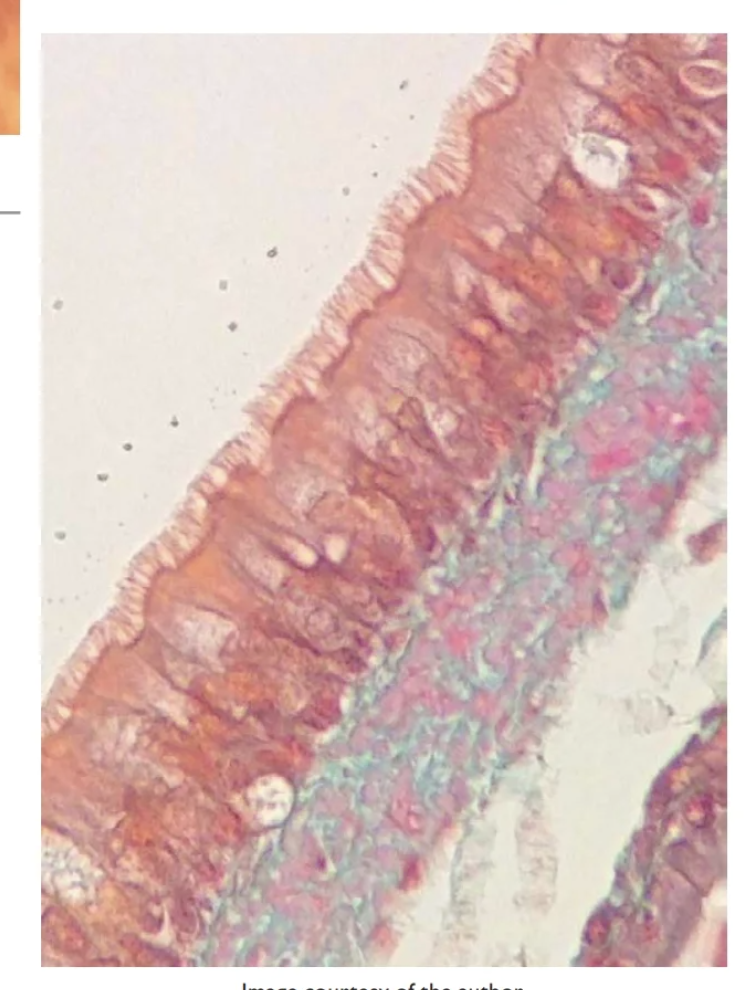
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Single layer of columnar cells, but not all reach the apical surface; cells on the apical surface may be ciliated
Ciliated version is found in the trachea; non-ciliated version lines the epididymis
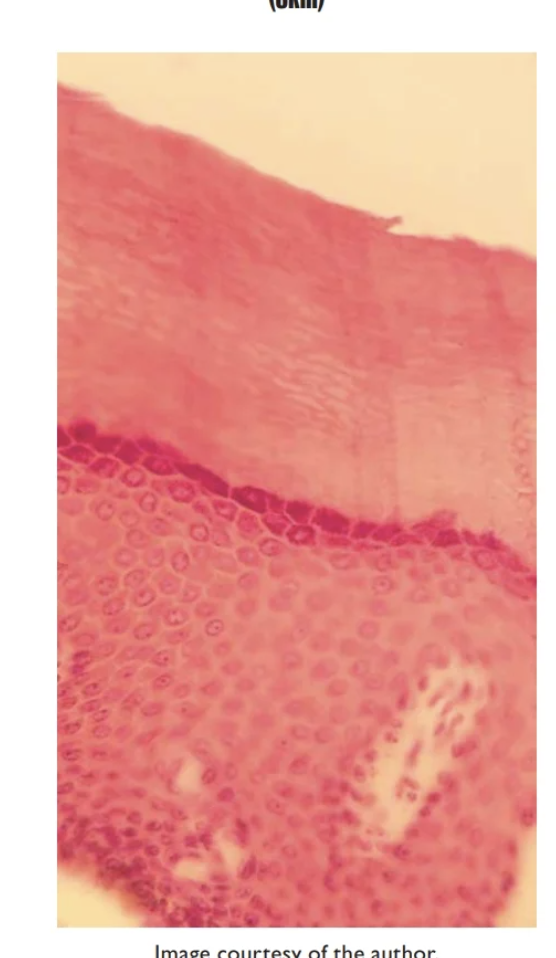
Stratified squamous epithelium- Keratinized
contain layer of dead squamous cells
Found on epidermis of skin
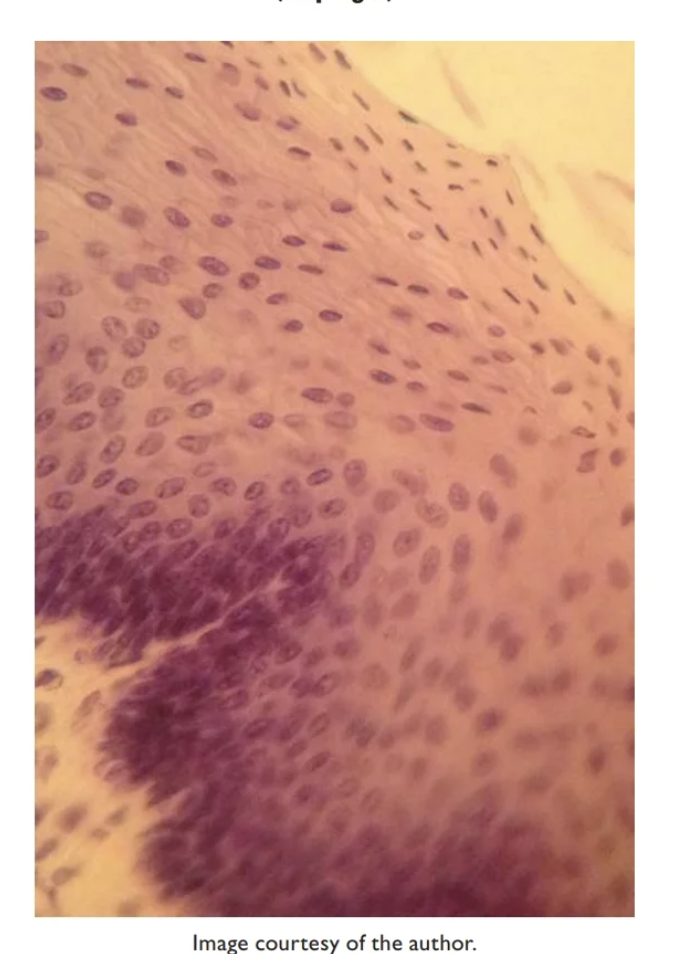
Stratified squamous epithelium- Non-Keratinized
Multiple layers of flat apical cells
forms inner lining of mouth, esophagus, and vagina
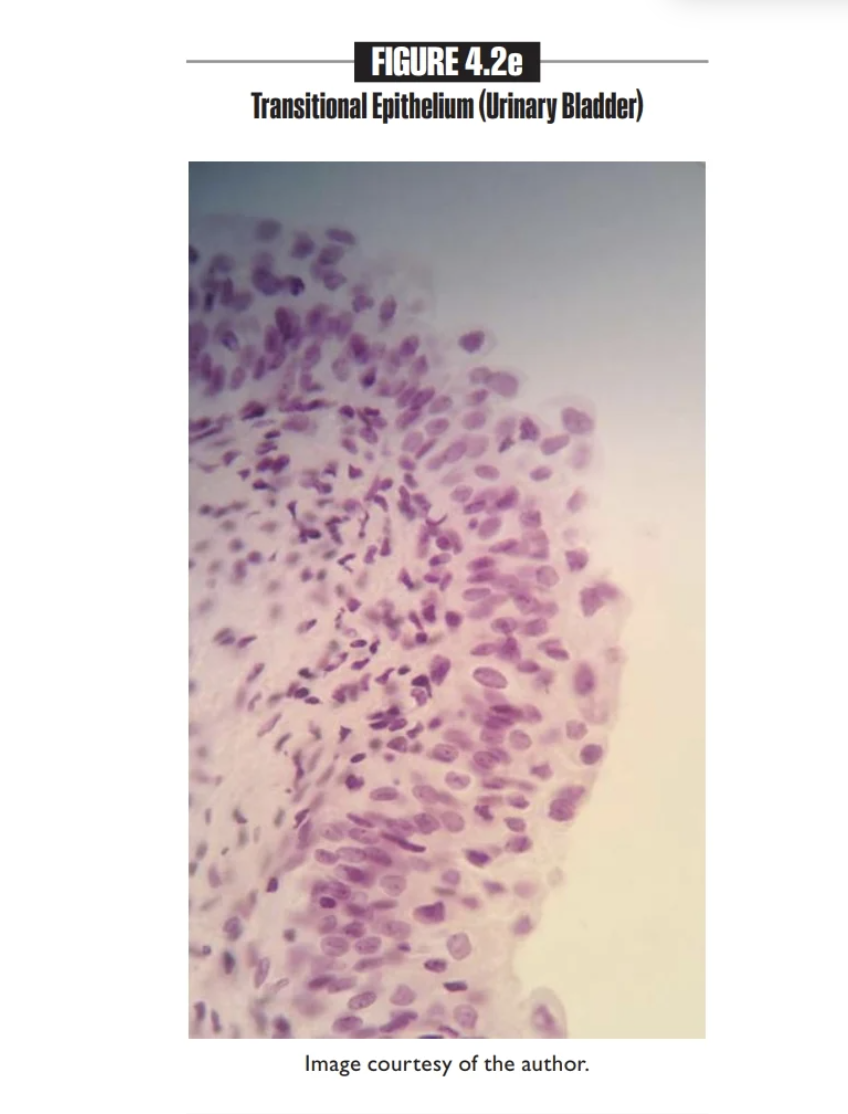
Transitional epithelium
Multiple layers of changing apical cells
Lining the ureters, the urinary bladder, and part of urethra
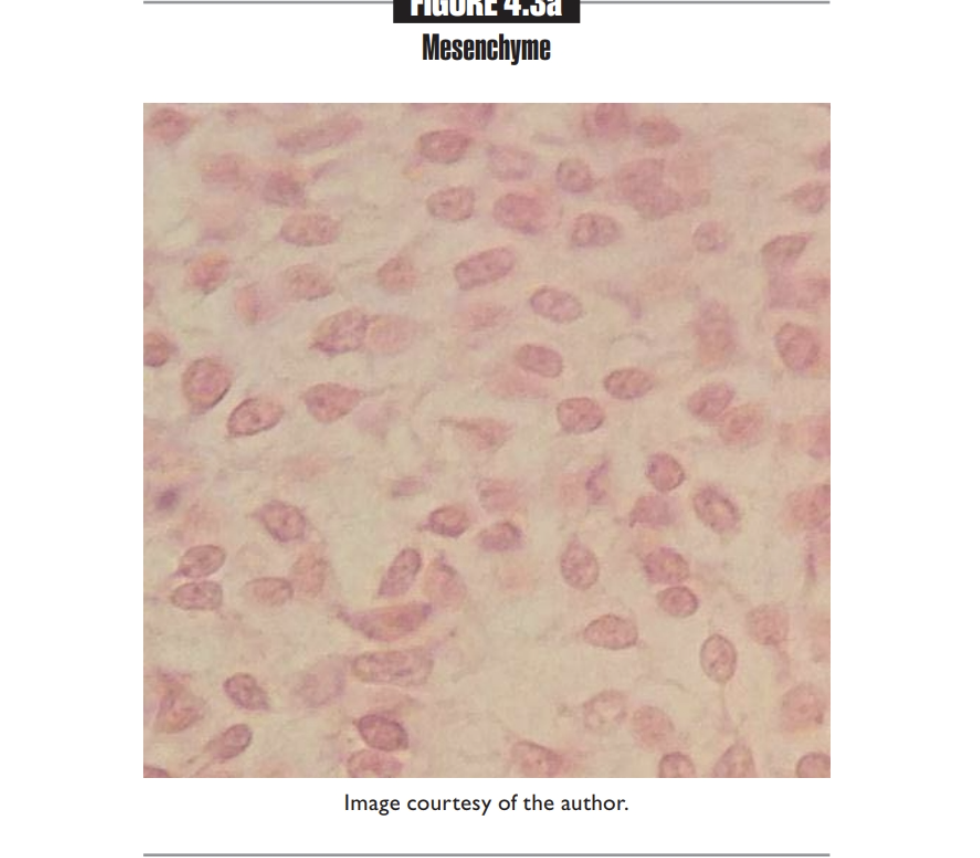
Mesenchyme
Primarily found in embryo
Mesenchymal cells
Connective Tissue
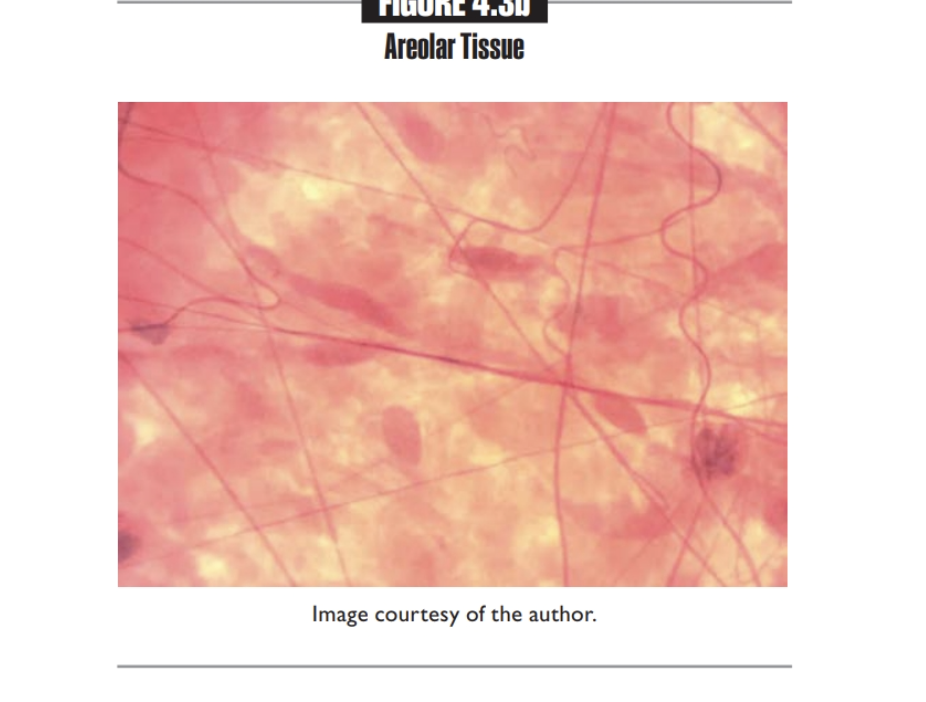
Areolar tissue
Cushions organs, plays role in inflammation, holds tissue fluid
found Below the skin and surrounding organs
Fibroblasts, macrophages, and white blood cells
Connective Tissue
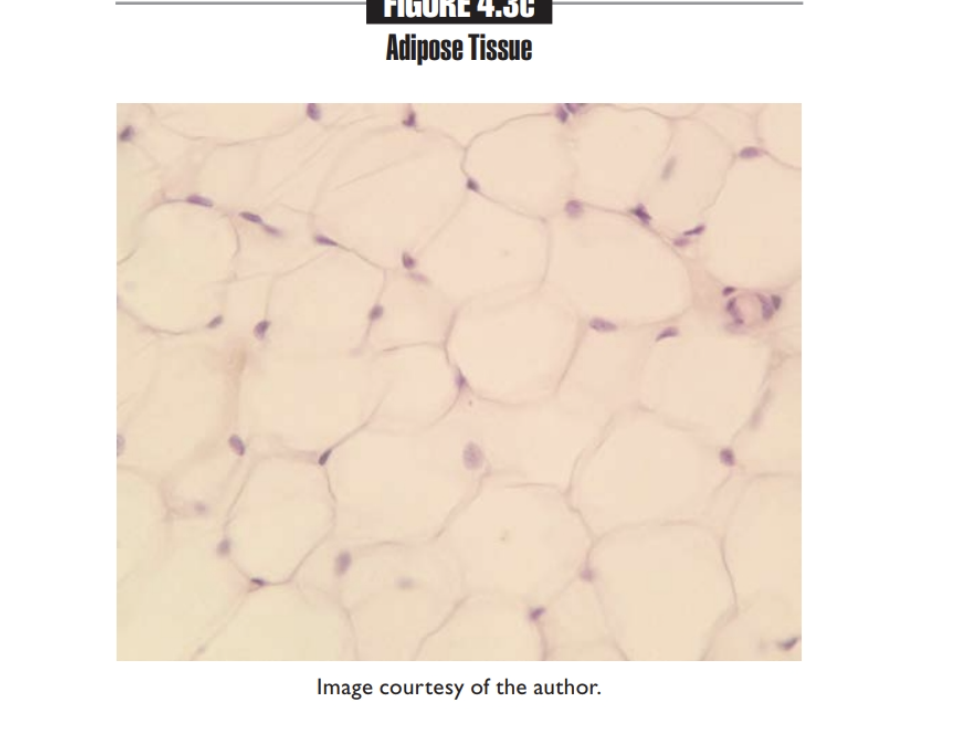
Adipose tissue
Insulates body, supports and protects organs
Found Under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen and breasts
Adipocytes
CONNECTIVE
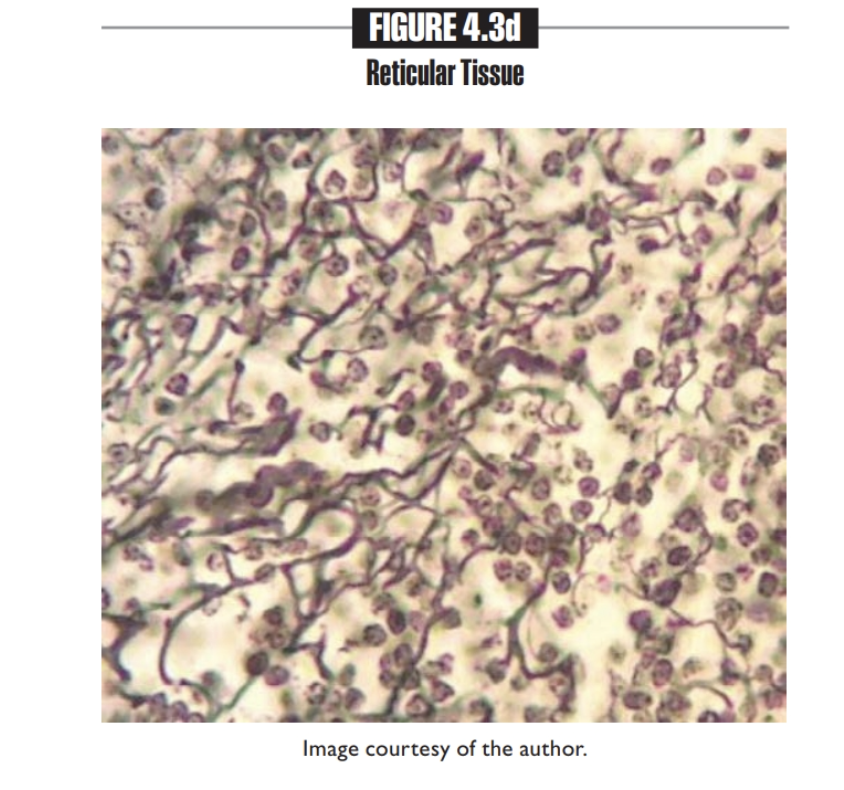
Reticular tissue
LOOKS LIKE A GRAPE VINE
- Found in Lymph nodes, bone marrow, liver, spleen
Fibroblast, white blood cells, and macrophages
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
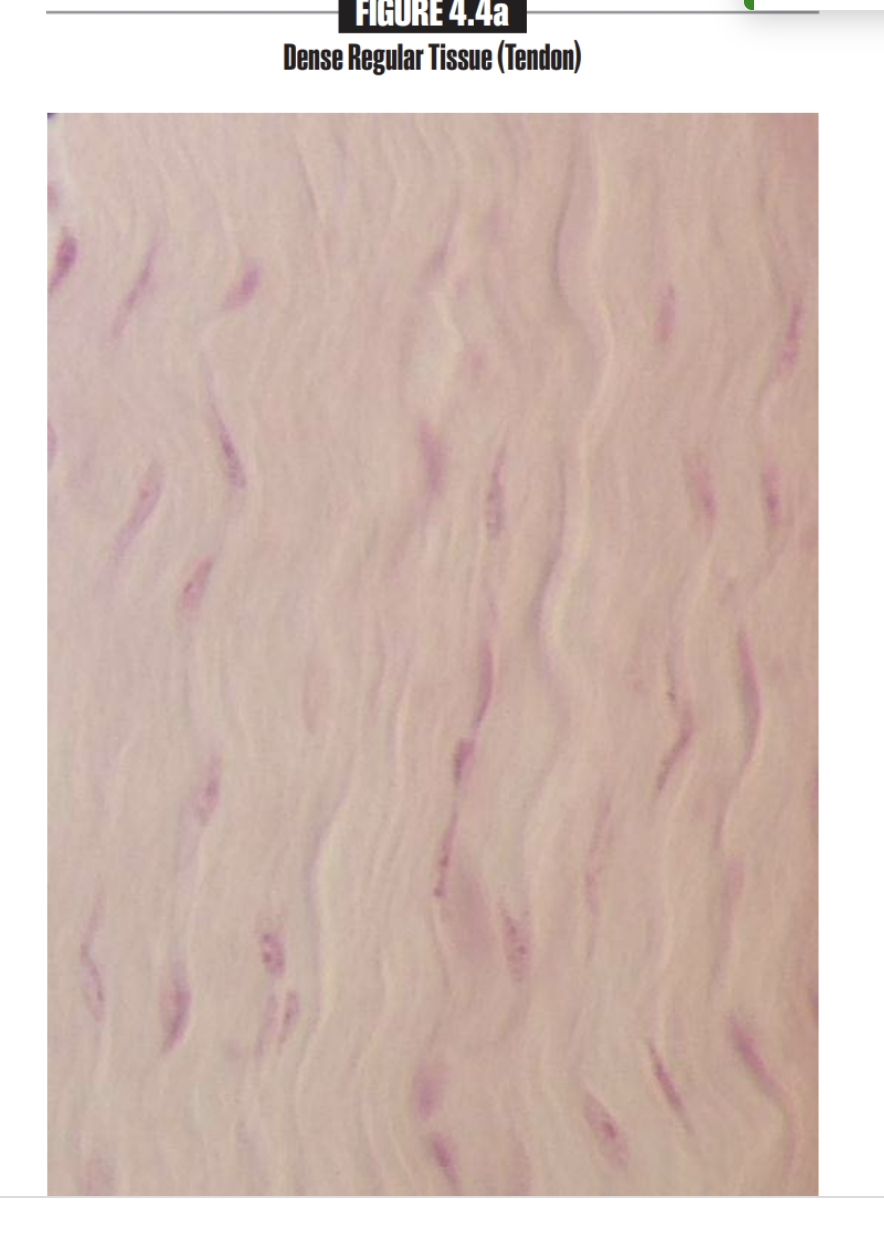

Dense regular tissue
Attaches muscle and bone in various way
Found in Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
contain Fibroblasts
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
In order or a pattern
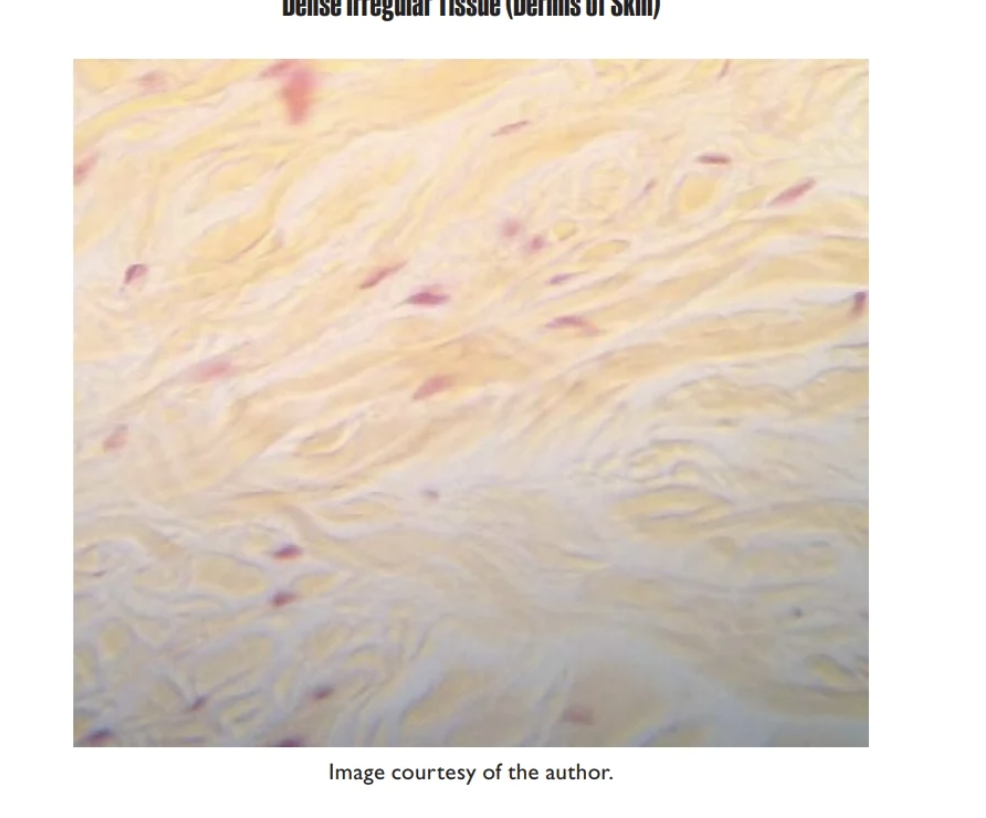
Dense Irregular Tissue
found in Dermis of skin, submucosa of digestive tract
contains Fibroblast
Connective Tissue
NOT in a pattern or order

Elastic tissue
Found in Walls of large arteries; walls of bronchial tubes
contains fibroblast
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
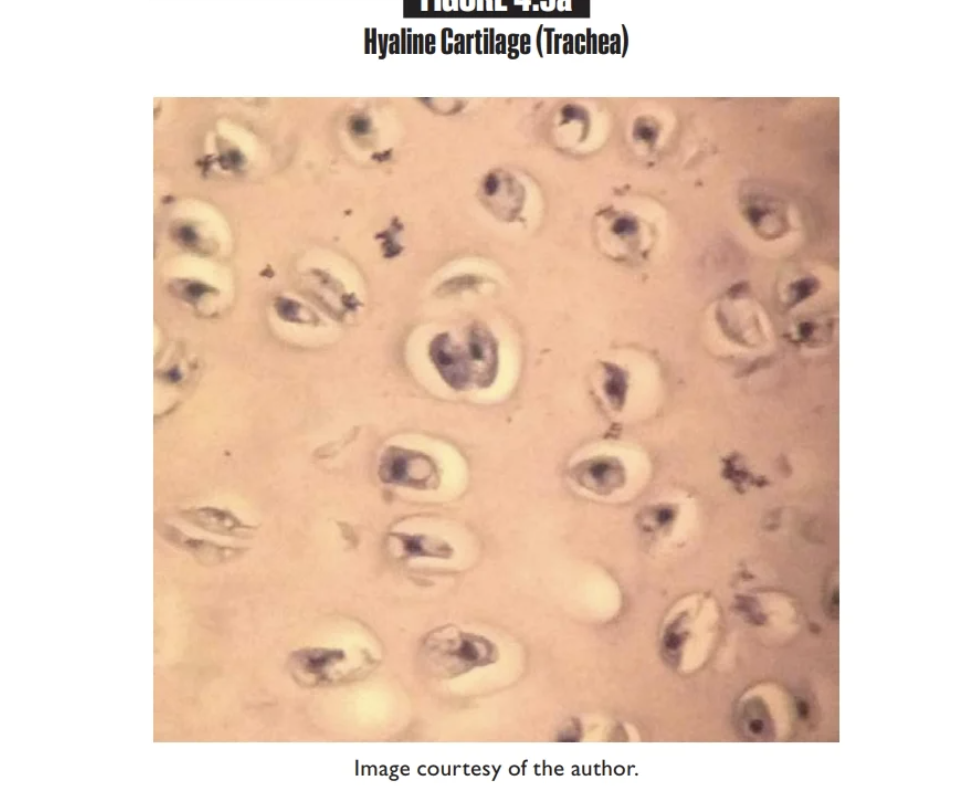
Hyaline Cartilage
Found inNasal septum, trachea, larynx, costal cartilage, ends of long bones
Chondrocytes (contained in a
lacuna)
Looks like beans
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
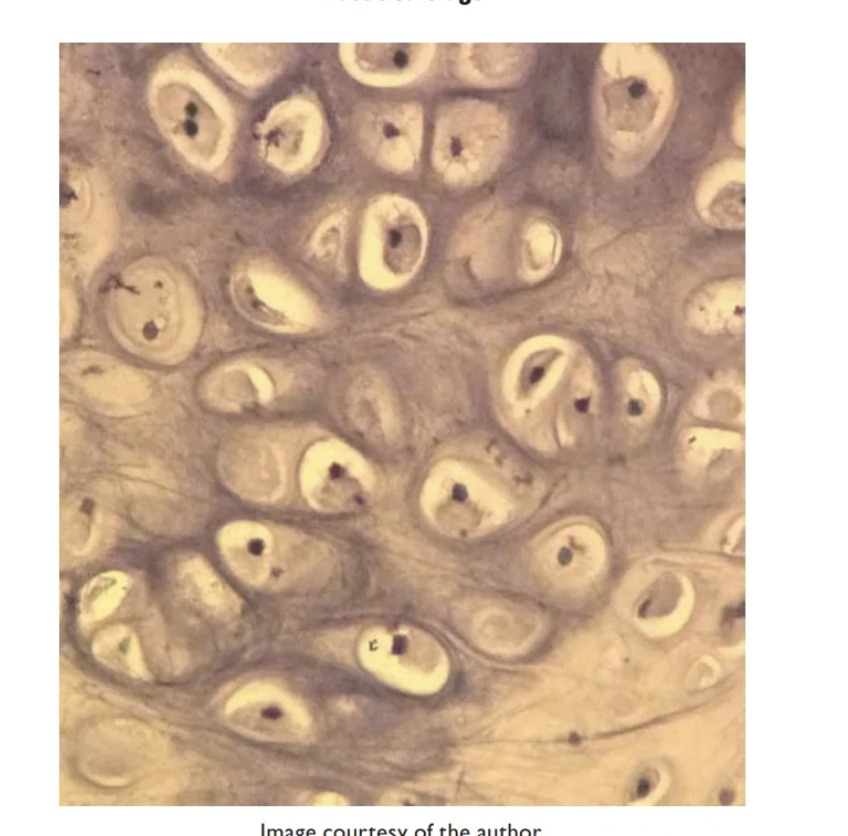
Elastic cartilage
Maintains shape while allowing flexibility
Found in External ear, epiglottis
Contains Chondrocytes (contained in a
lacuna)
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
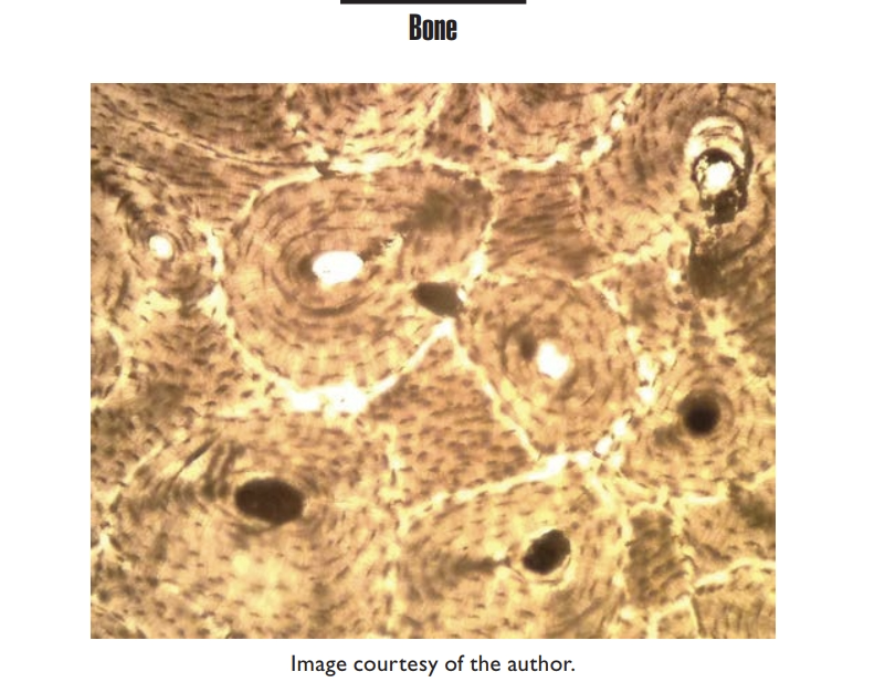
Bone
Supports and protects
Osteocytes (contained in a
lacuna
CONNECTIVE
is brown
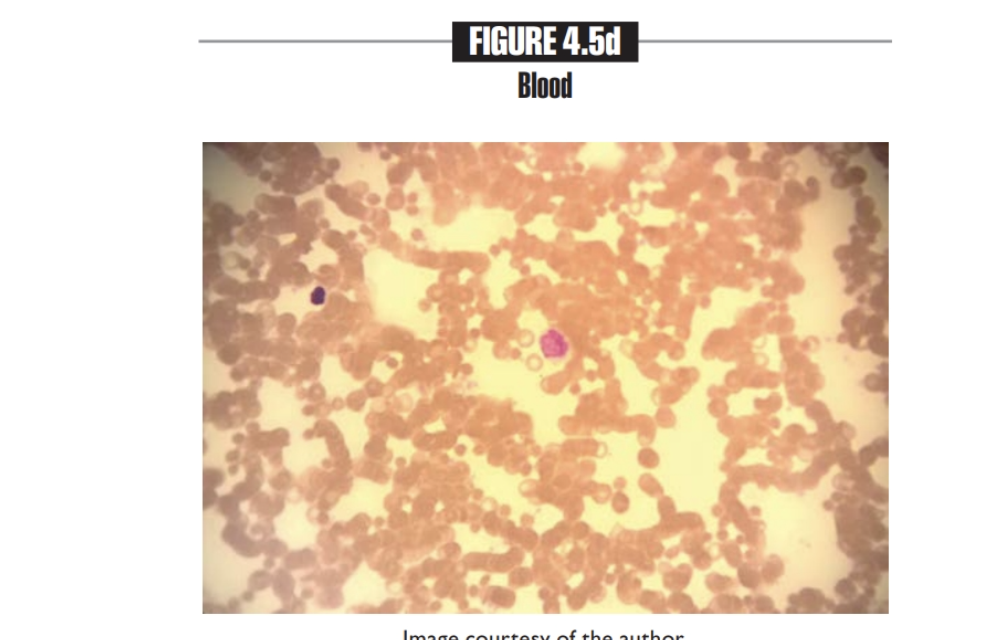
Blood
Found in Contained within blood vessels
contains Erythrocytes, leukocytes
Connective
looks like: a bunch of tiny red dots

Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Provides voluntary movements.
Location: Skeletal muscle attached to bones
Contains; Skeletal muscle fiber or cells
MUSCLE TISSUE
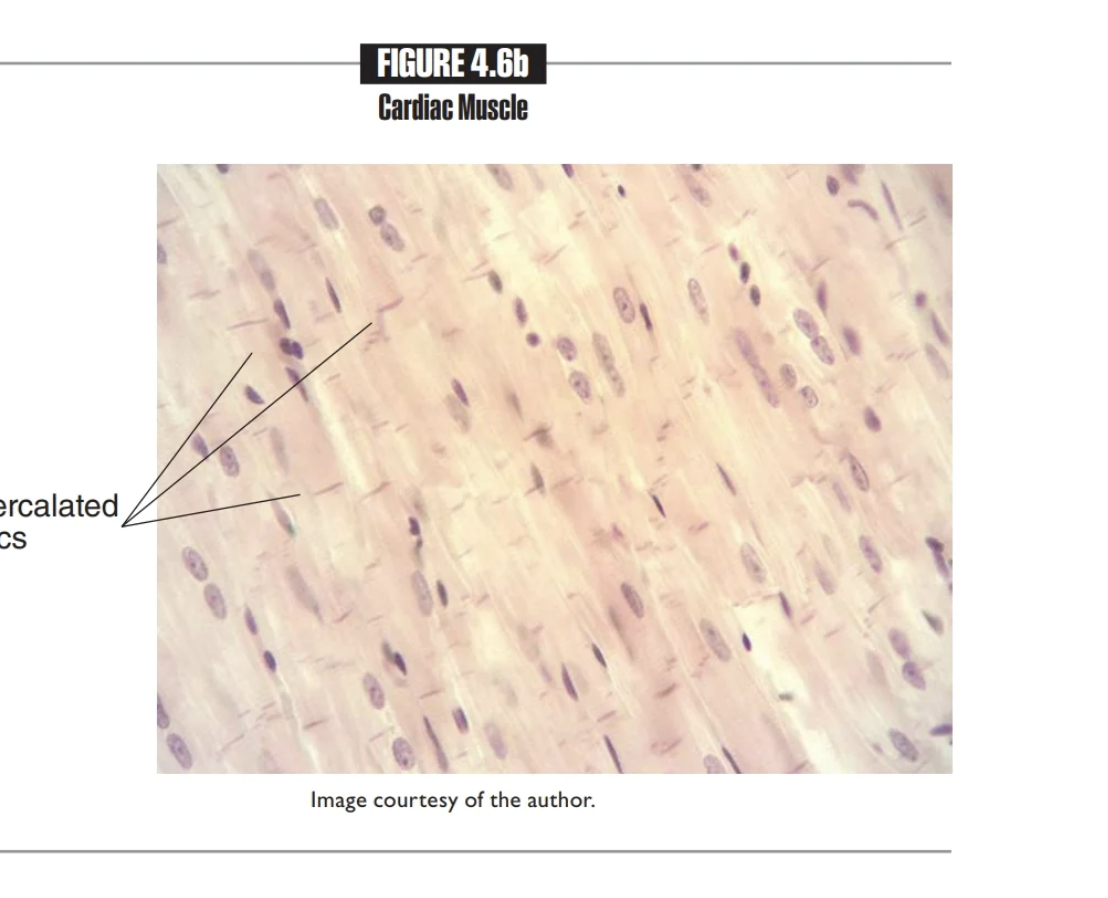
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary pumping of the heart
Found in Walls of the heart
Contains Cardiac muscle cells
MUSCLE TISSUE
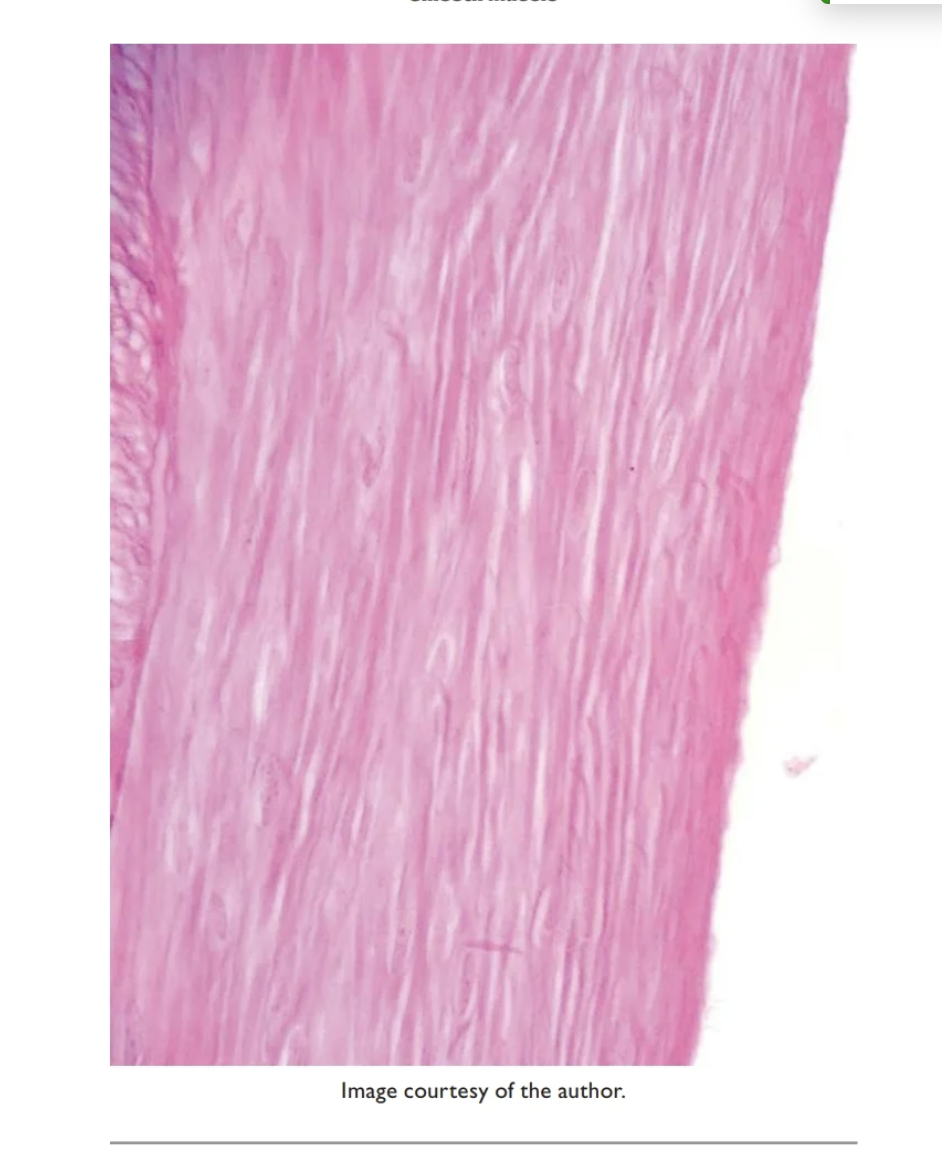
Smooth Muscle
Location: Walls of intestines, bladder, uterus, stomach, and blood vessels
Contains:Smooth muscle cells
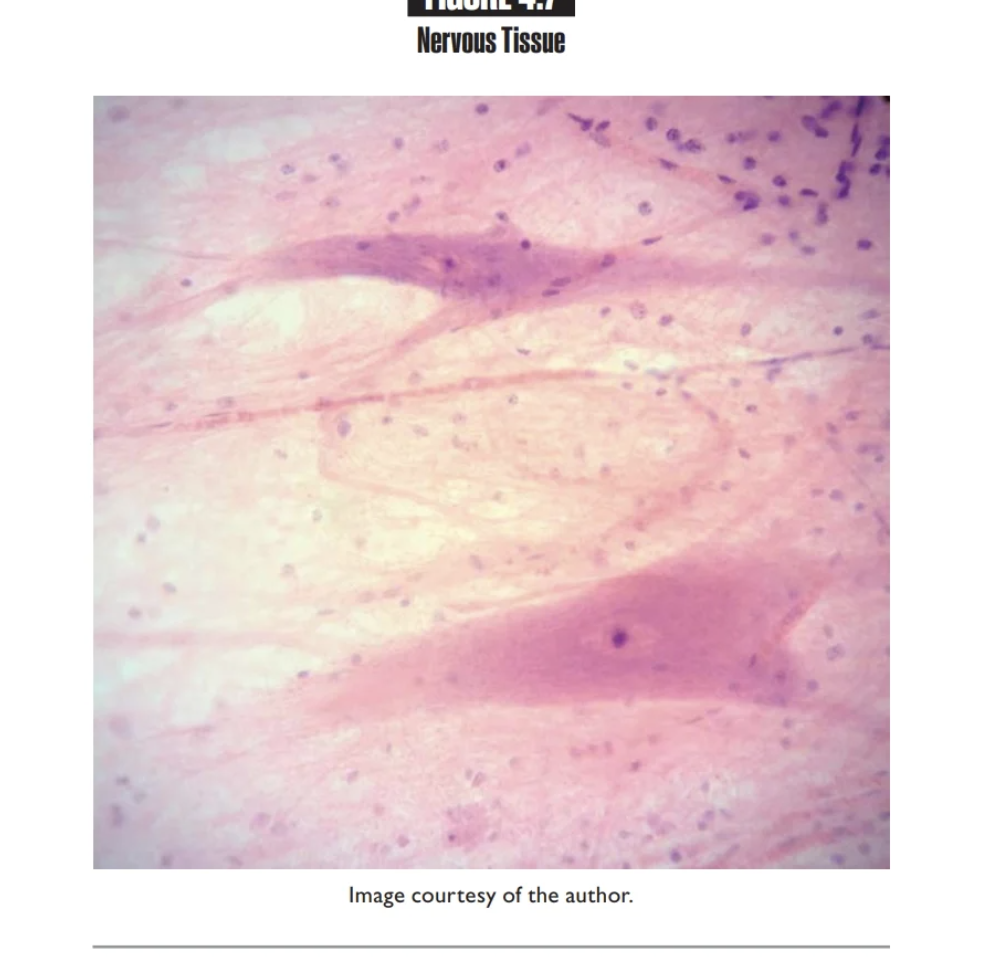
Nervous Tissue
Neurons are excitable cells that send and receive electrical signals called impulses
Contains Neuroglia cells
Found in brain, spinal cord, and nerves
NERVOUS TISSUE
Anterior
Toward the front of the body
Example: The heart is anterior to the spine.
Posterior
Toward the back of the body
Example: The spinal cord is posterior to the lungs.
Superior
Above; closer to the head
Example: The lungs are superior to the stomach.
Inferior
Below; closer to the feet
Example: The liver is inferior to the heart
Medial
Middle
The little finger is medial to the thumb.
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
The spleen is lateral to the pancreas
Superficial
Toward the surface of the body
The skin is superficial to the muscles
Deep
Beneath the surface of the body
Ex: The bones are deep to the skin.
Proximal
Closer to the trunk of the body
ex: The shoulder is proximal to the elbow
Distal
Farther from the trunk of the body
Ex: The wrist is distal to the elbow.
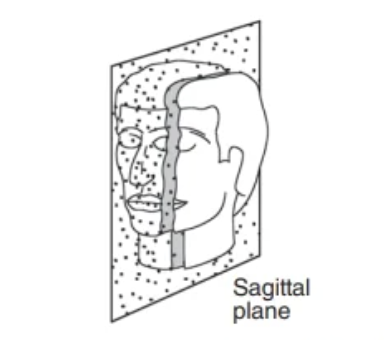
Sagittal Plane
Right/ left
Deep
Beneath surface of body
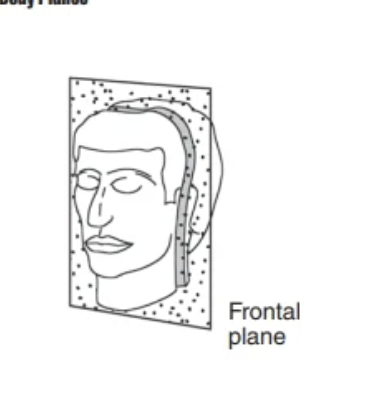
Frontal Plane
Seperates body into anterior/posteror portions
runs vertically
Ventral
Front
Dorsal
BackCr
Cranial (cephalad)
closer to head
Caudal
Closer to tail
Coronal (crown)
front/back
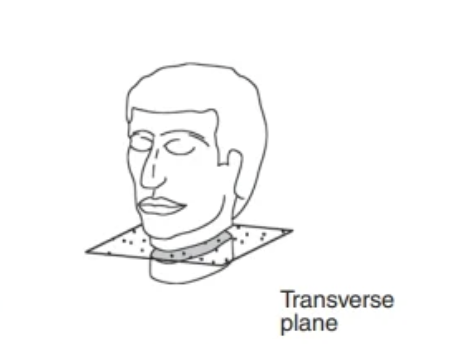
Transverse Plane
Superiori/inferior
Oblique plane
Runs at an angle to all main planes
Midsagittal Plane
Seperates body into EQUAL right & left portions
runs vertically
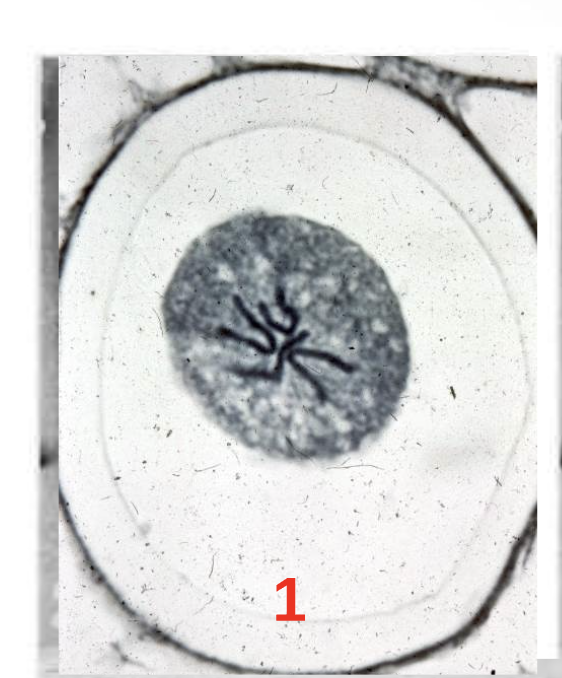
Step 1.) Prophase
Chromatin condenses forming chromosomes
Unorganized clumped in middle
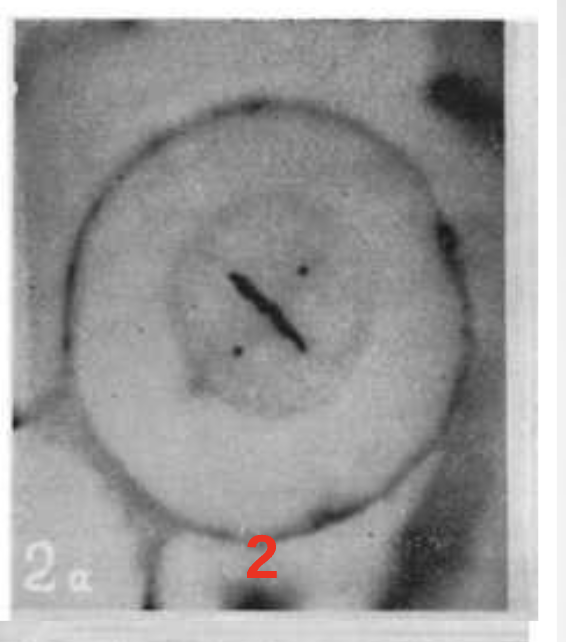
Step 2.) Metaphase
Chromosomes move/cluster to middle of the cell
Chromosomes MET in the middle
together skinny line in middle
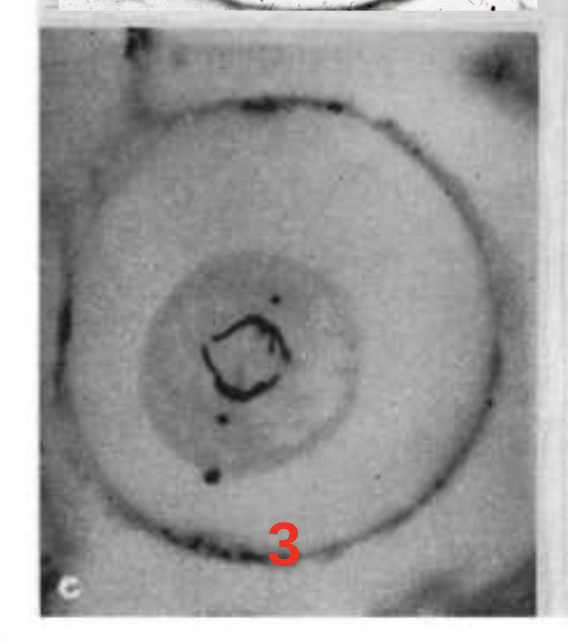
Step 3.) Anaphase
Ripping Chromosomes in half
(Ripping Ana in half)
opposite ends of cell
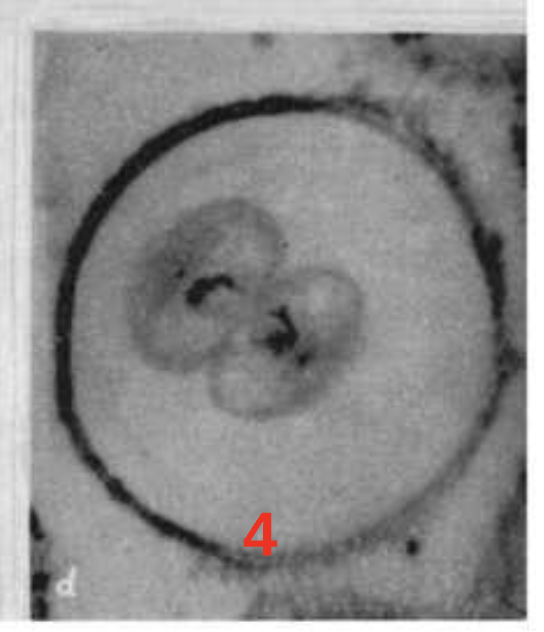
Step 4.) Telophase
Identical pairs of chromosomes are at opposite ends of cell & begin to uncoil
kinda look like 2 diff cells…. far away from each other
Pleural Cavity
Protected by the Pleura
Parietal Pleura
Lines the pleural cavity wall
Visceral Pleura
Covers the surface of the lungs
Pericardial Cavity
Protected by the pericardium
Parietal Pericardium
Covers the Pericardial cavity wall
Visceral Pericardium
Covers the surface of the heart
Abdominopelvic cavity
protected by the peritoneum
Parietal peritoneum
Covers the adbominopelvic cavity wall
Visceral Peritoneum
covers the majority of the abdominal organs
Integumentary organs
skin, hair, nails
Skeletal Organs
Bones, Ligaments, Cartilage
Muscular Organs
Muscles and Tendons
Endocrine Organs
Thyroid Gland, Adrenal Gland, Pancreas, Ovaries
Cardiovascular Organs
Heart & Blood Vessels
Lymphatic Organs
Spleen, Thymus, Tonsils, and Lymph Nodes
Respiratory Organs
Nasal cavity, Larynx, trachea, & Lungs
Digestive Organs
teeth, Tongue, Esophagus, Stomach, Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas, Small & Large Intestine
urinary organs
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
Nervous organs
brain, spinal cord, nerves
Reproductive system
Male- Penis, scrotum,testes
Female- Ovaries, uterus, vagina, uterine tubes
Stomach Regions right IN ORDER from top to bottom
Right hydochondriac region
Right Lumbar Region
Right Iliac Region
Stomach regions in order MIDDLE
Epigastric
Umbillical
Hypogastric
Stomach Regions IN ORDER LEFT- TOP TO BOTTOM
Left Hypochondriac Region
Left Lumbar Region
Left iliac Region