Scioly 26' - Nervous System
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
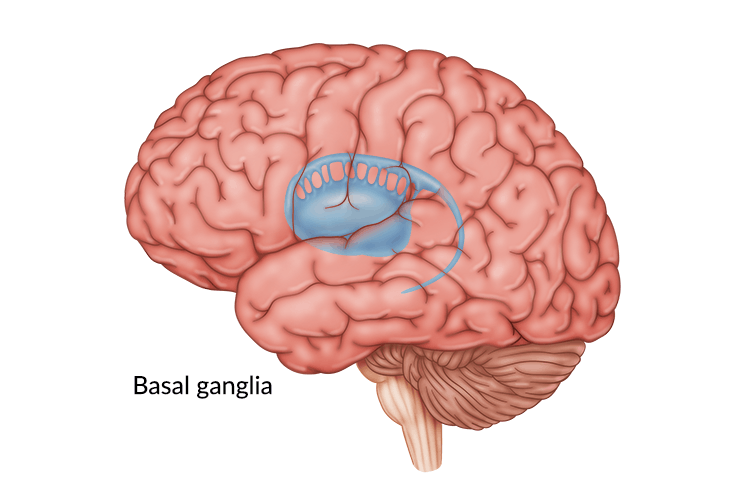
What structure lies deep to the cerebral cortex and is involved in voluntary motor control and habit learning?
Basal ganglia (includes caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, and subthalamic nucleus).
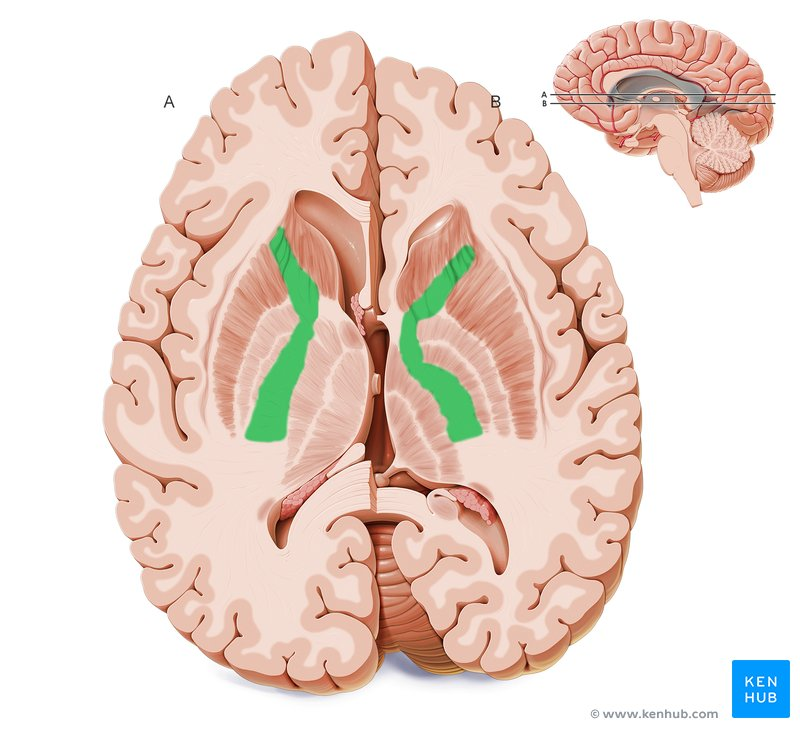
What structure lies between the putamen and thalamus and routes information through the globus pallidus to the thalamus?
Internal capsule (contains corticospinal and corticobulbar fibers).
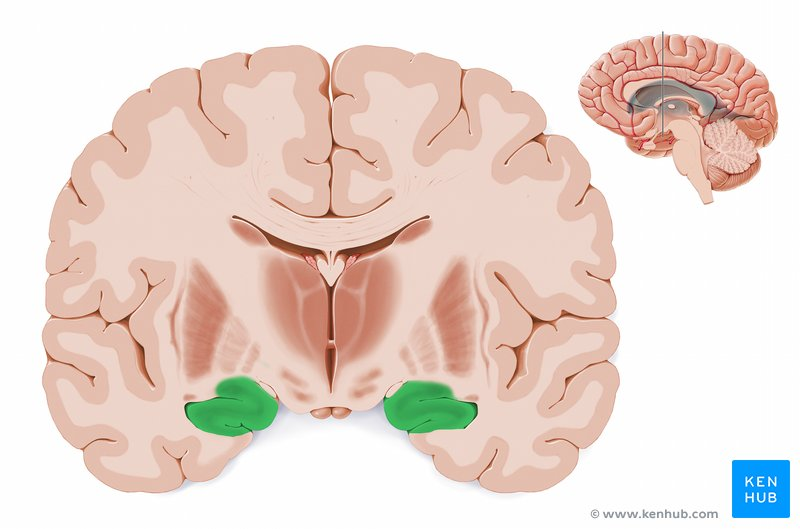
What is the function of the hippocampus and where is it located?
Memory consolidation, located in the medial temporal lobe, forming part of the limbic system.
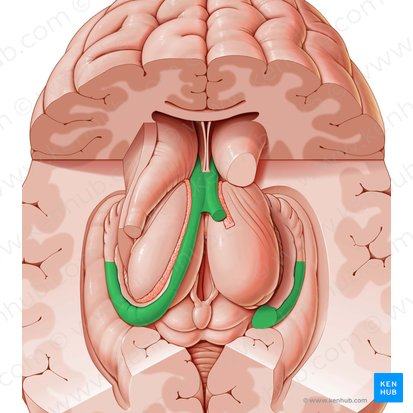
What C-shaped structure is located in the medial cerebrum, involved in memory, and part of the limbic system's circuit of Papez?
Fornix (connects hippocampus to mammillary bodies).
What white matter tract connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland?
Pituitary stalk (infundibulum).
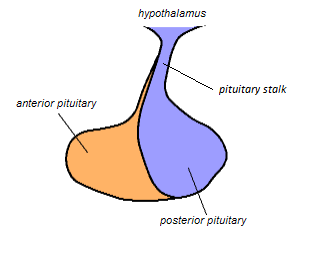
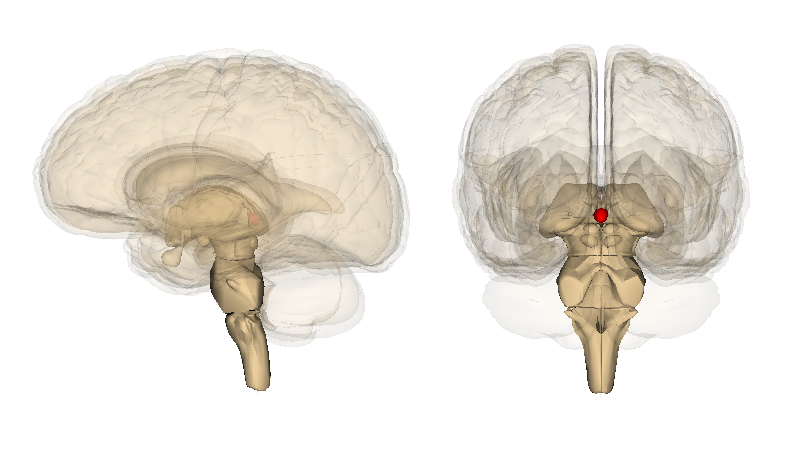
What structure forms the roof of the third ventricle and is involved in circadian regulation?
Pineal gland, part of the epithalamus.
What thalamic nuclei project visual and auditory information to the cortex?
LGN (lateral geniculate nucleus) for vision and MGN (medial geniculate nucleus) for hearing.
Where is the subthalamic nucleus located and what is its functional role?
In the diencephalon, it modulates basal ganglia circuits and inhibition dysfunction produces hemiballismus.
What midbrain tract connects the cerebral cortex to the pons and cerebellum?
Corticopontine tract, part of the corticopontocerebellar pathway.
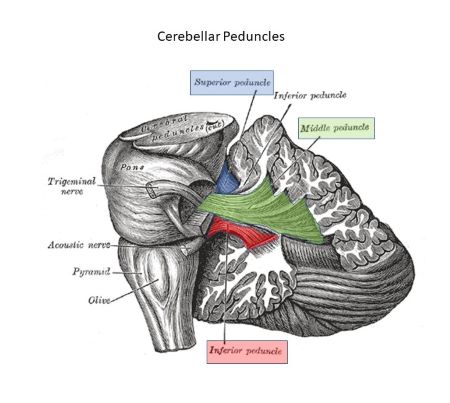
What brainstem structure connects the pons and cerebellum?
Middle cerebellar peduncle.
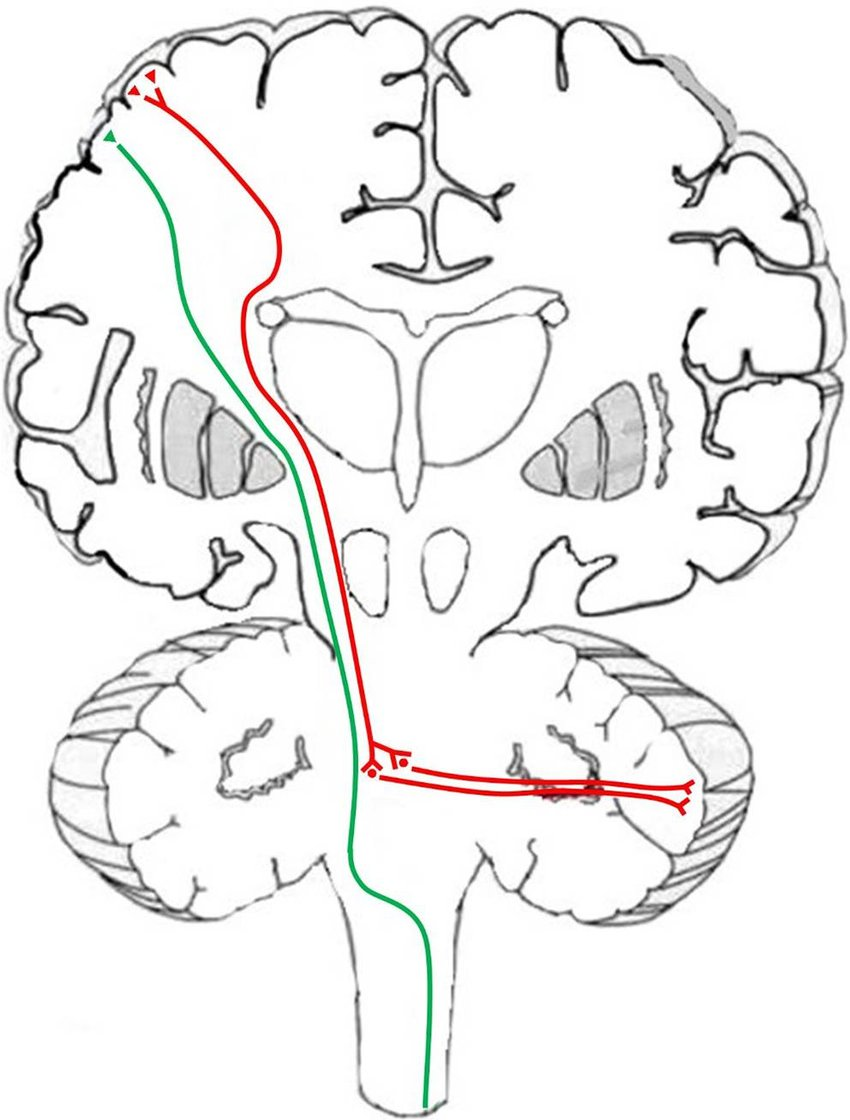
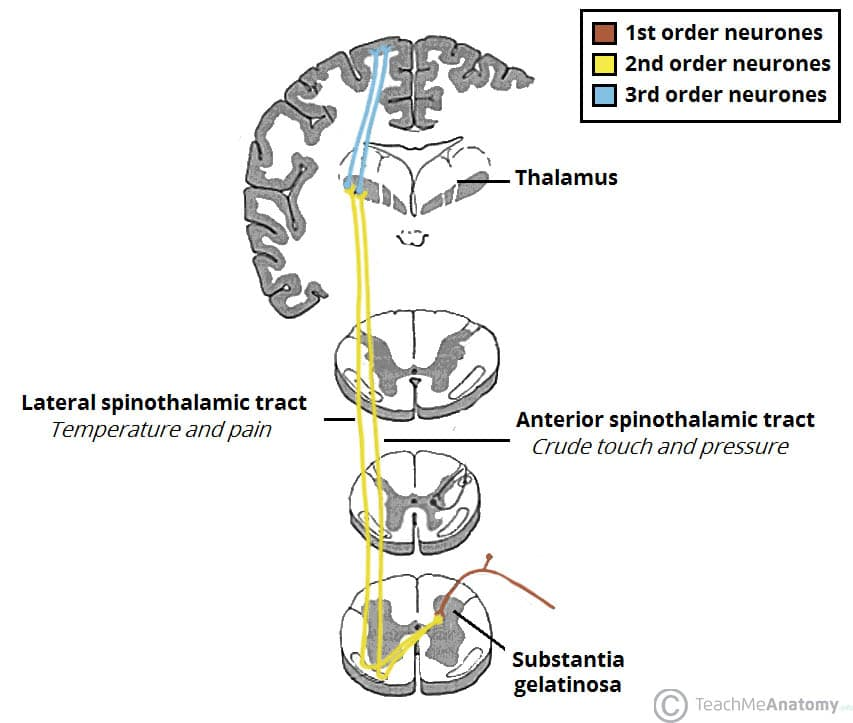
Name the brainstem tract responsible for pain and temperature transmission from the body.
Spinothalamic (anterolateral) tract, running in the brainstem before reaching the VPL thalamus.
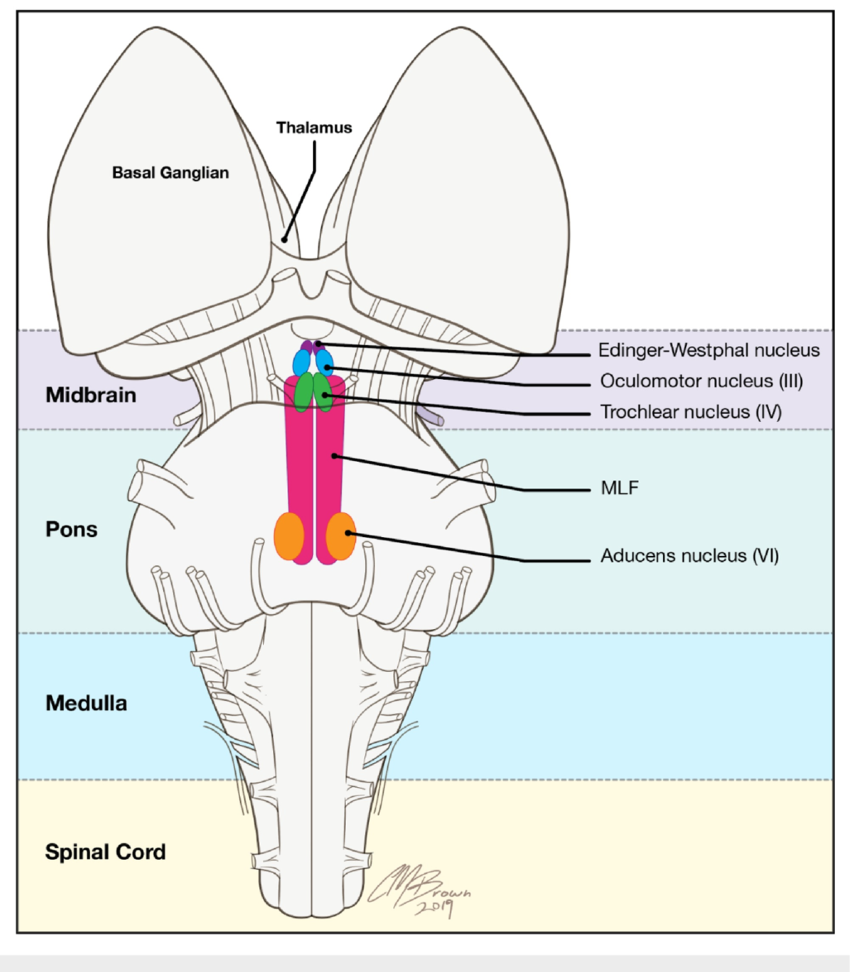
What structure allows eye movement coordination between abducens nucleus and cranial nerve III?
Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF).
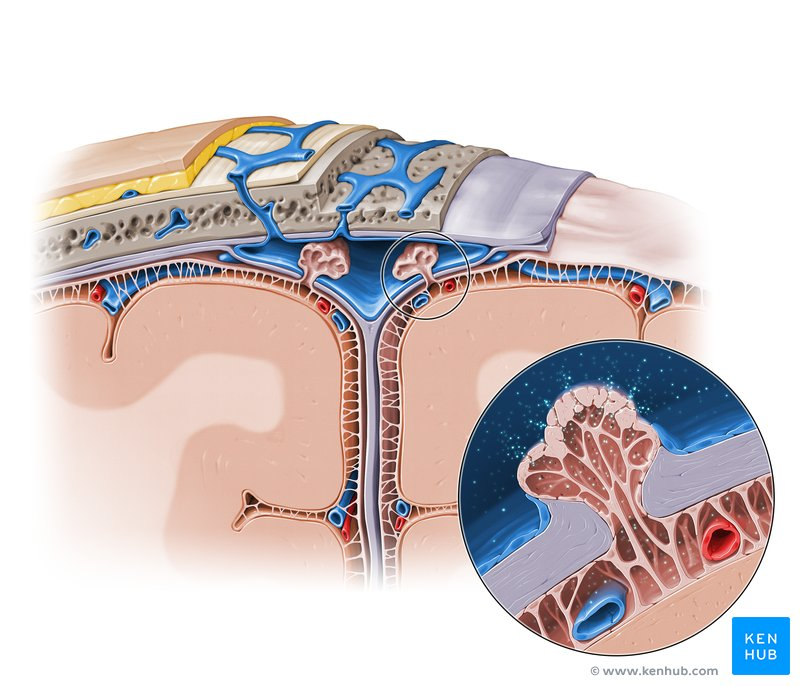
What ventricle is located within the cerebral hemispheres?
Lateral ventricles, one in each hemisphere.
How does cerebrospinal fluid flow from the lateral ventricles to the fourth ventricle?
Through the foramen of Monro to the third ventricle, then via the cerebral aqueduct.
Where is the fourth ventricle located and how does CSF leave it?
Under the cerebellum in the brainstem, draining via the foramina of Luschka and Magendie into the subarachnoid space.
What structure protrudes into the superior sagittal sinus to reabsorb CSF?
Arachnoid granulations (villi).
Which cerebellar peduncle carries input from the spinal cord?
Inferior cerebellar peduncle (restiform body).
Which peduncles connect the cerebellum with the pons and midbrain?
Middle peduncle to pons, superior peduncle to midbrain.
Where is the flocculonodular lobe located and what is its primary function?
In the cerebellar vermis, involved in balance and vestibular coordination.
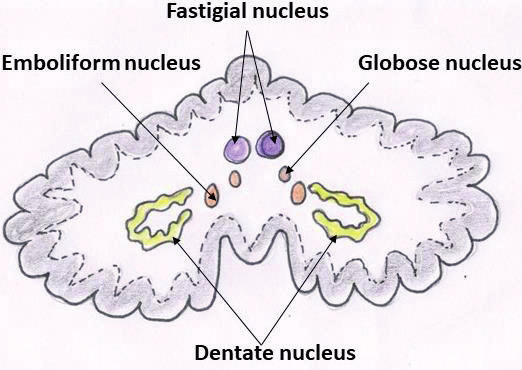
Name the deep cerebellar nuclei from lateral to medial.
Dentate, emboliform, globose, and fastigial (“Do Every Good Farmer”).
Which nucleus in the midbrain is responsible for pupillary constriction?
Edinger-Westphal nucleus (parasympathetic fibers of CN III).
What nucleus in the pons is the principal sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve?
Principal (chief) trigeminal nucleus
What nucleus controls facial expression?
Facial nucleus in the pons (motor component of CN VII).
Which nuclei are found in the medulla and are involved with autonomic control of heart and lungs?
Nucleus ambiguus, dorsal motor nucleus of Vagus, and respiratory centers.
What voltage threshold typically initiates an action potential in a neuron?
Approximately –55 mV at the axon hillock.