Hemodialysis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
chronic kidney disease (CKD)
defined as either kidney damage or glomerular filtration rate (GFR) <60 for >3 months
end-stage renal disease (ESRD)
Treatment for __________
1. kidney transplant (ideal)
2. Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT)
3. Hospice/palliative care (end-of-life care)
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
measure how much blood passes through the glomeruli each minute
end-stage renal disease (ESRD)
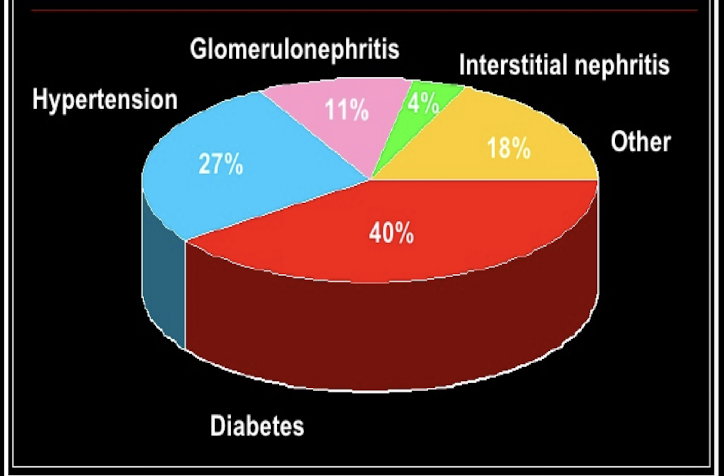
Etiology of _________
1. Diabetes
2. Hypertension
3. Glomerulonephritis (infection, autoimmune disease, minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
4. Interstitial Nephritis (infections/chronic disease, Wegener’s granulomatosis)
5. Autoimmune (IgA nephropathy, lupus nephritis, Anti-GBM -Goodpasture syndrome)
-polycystic kidney
- Alport syndrome
- benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH)
-amyloidosis/multiple myeloma
stage 3a
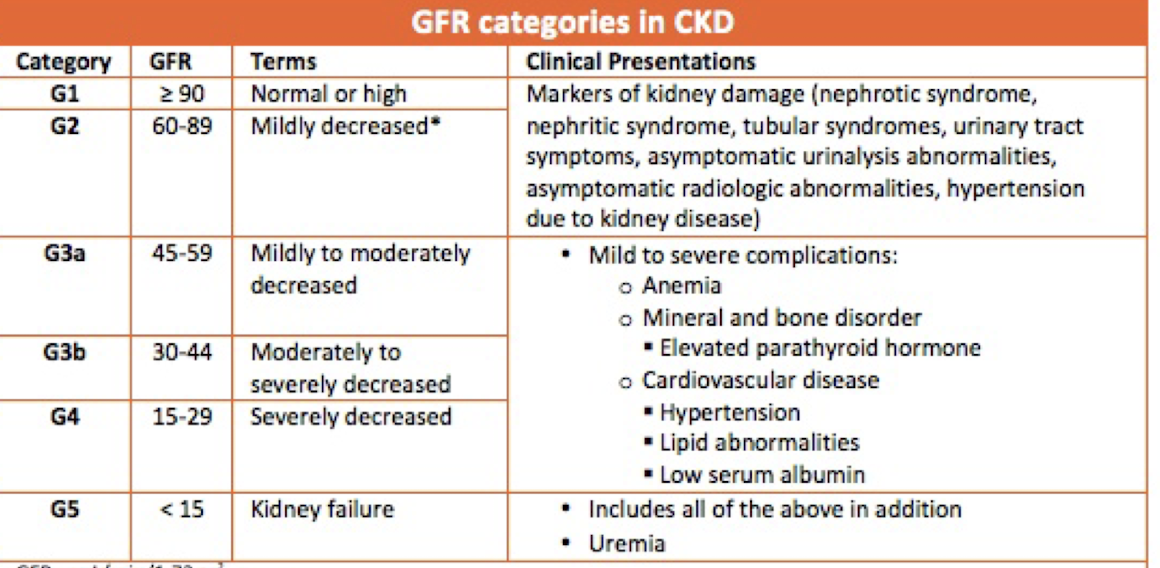
When to refer to nephrology for chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients?
→ nephrology manages transition through end-stage renal disease (stages 3b-5)
labs
renal panel
-BUN, Creatinine, GFR, potassium/electrolytes
-albumin
-CBC, iron studies (Hgb, HCT, ferritin)
-”spot" urine specimen (morning)
AKI: 24 hour creatinine clearance (CrCl)
ESRD
-renal panel: electrolytes, albumin, calcium/phosphate
-CBC, iron studies, HGB, Tsat, ferritin
-iPTH, vitamin D
_____ for managing chronic kidney disease (CKD)
→ most tests completed monthly
central venous catheter (CVC)
Which dialysis access type has the biggest risk for infection?
central venous catheter (CVC)
Which dialysis access type can be used the soonest?
dialysis access
All forms of renal replacement therapy (RRT) need a _______
Types
1. Hemodialysis
- uses a vascular access to clean the body via blood
-maximum age 75
2. Peritoneal Dialysis
- uses a peritoneal catheter and the peritoneum to clean the body
→can be done at home, rural locations
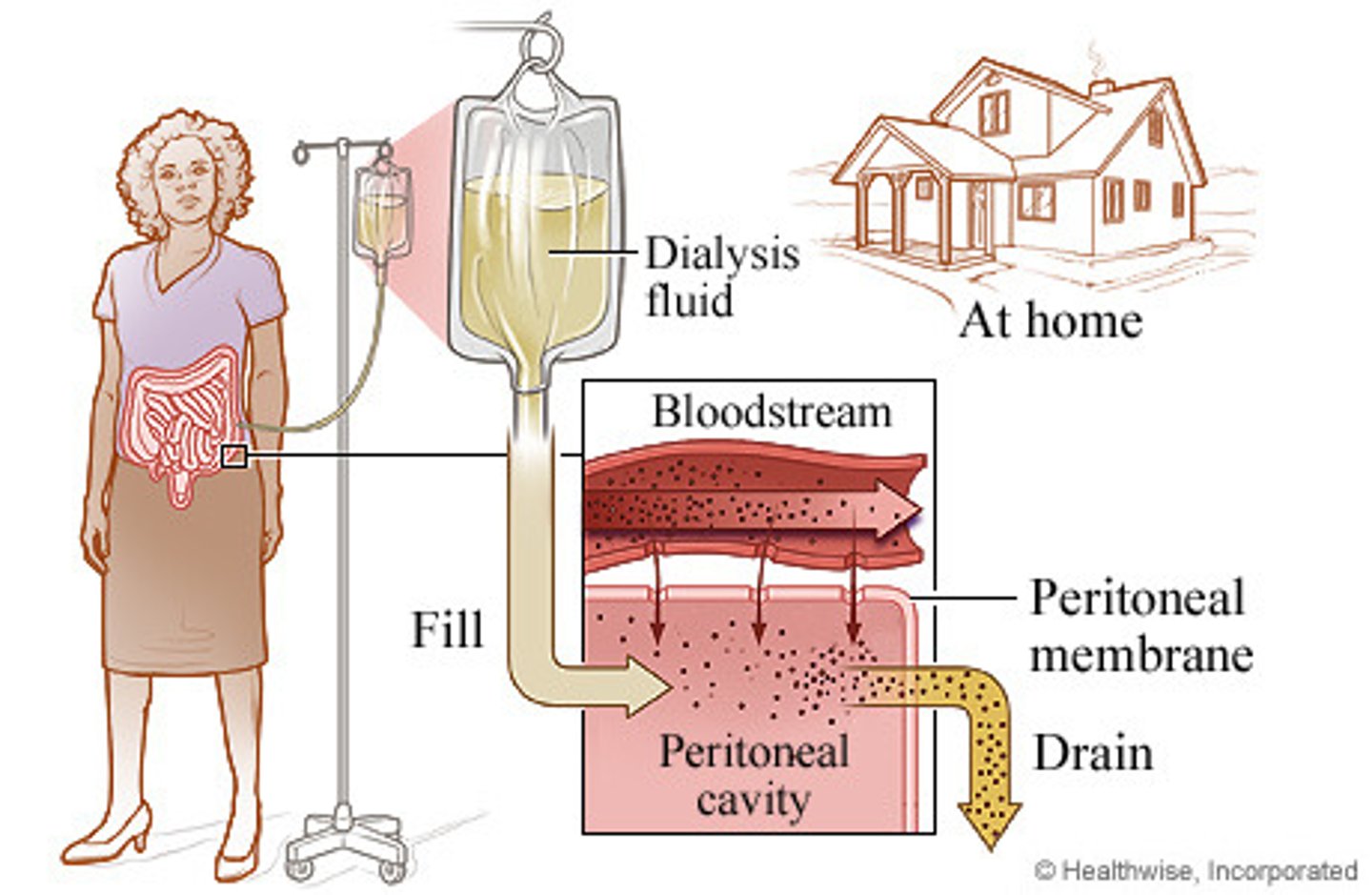
peritoneal dialysis
involves instillation of a hypertonic solution into the peritoneal cavity
→dialysate solution fills the peritoneal cavity, coming into contact with capillaries in peritoneum and viscera
→peritoneum serves as the filtration membrane, diffuses toxins and excess fluid from the blood
→toxins and excess fluid cross the membrane into the dialysis solution, are drained out of the body
peritoneal dialysis
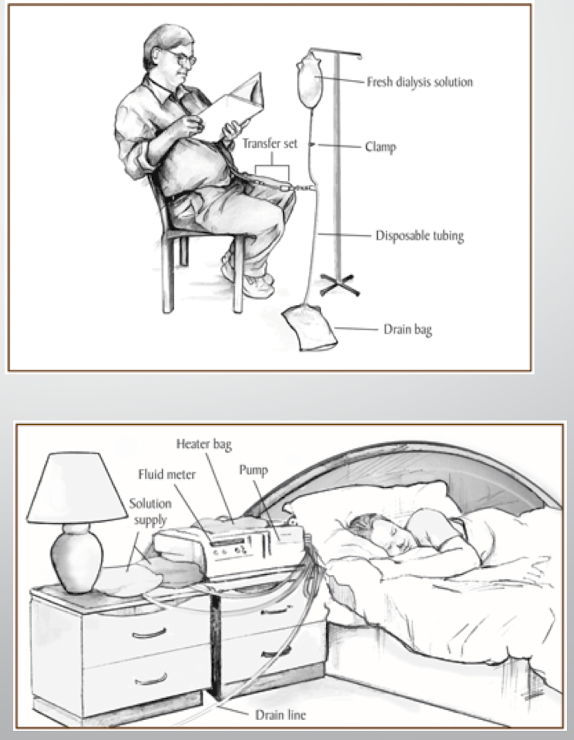
1. CAPD (Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis) - Daytime
- Frequent passive exchanges using gravity
2. CCPD (Continuous Cycle Peritoneal Dialysis) - Nighttime
- Overnight exchanges with use of an automated machine
Limitations: often daily treatments, done at home, no swimming/submerge in water, infection is highest failure risk
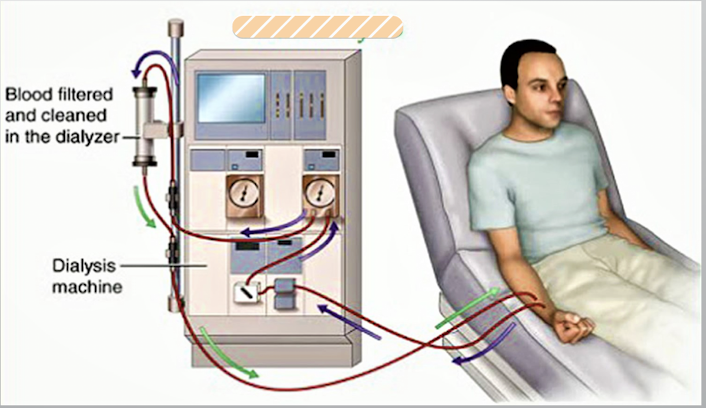
hemodialysis
Cleans the blood of waste products and controls fluids by passing the blood through an artificial kidney, called a dialyzer
→Patients must have a vascular access (AV fistula, AV graft, tunnel direct catheter)
→can be done in a dialysis center or at home (3x week schedule)
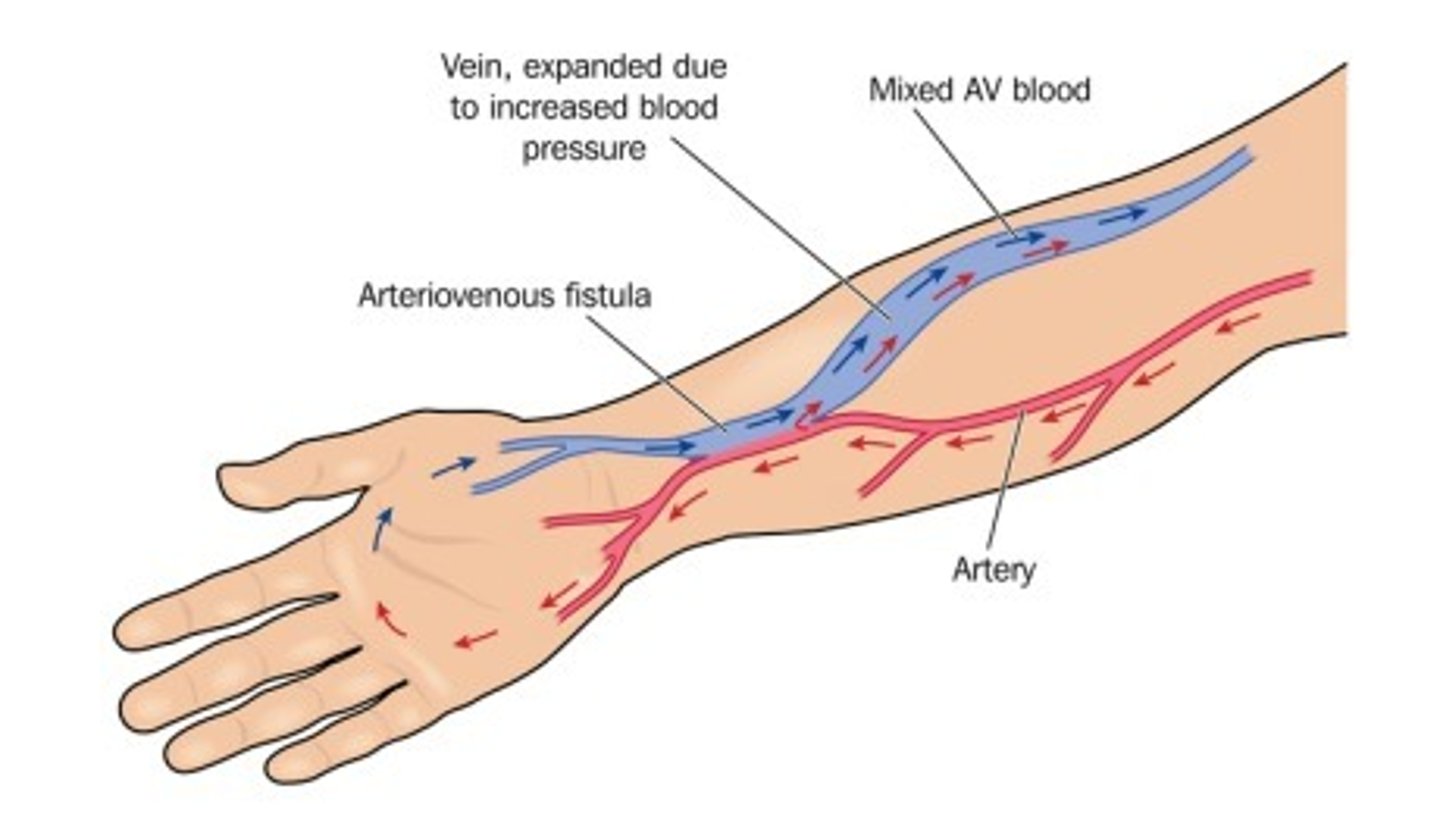
arteriovenous fistula (AVF)
surgical connection or “anastomosis” between an artery and a vein
→connection causes turbulence and vein wall to thicken
→providing a spot that can be punctured repeatedly with dialysis needles + rapid blood flow rate
Limitations:
-minimum 6 weeks maturation period before use
-Requires good vessels
Advantages:
-native vessel, no reaction to synthetic material
-Long life
-Low risk of thrombosis
-low infection risk
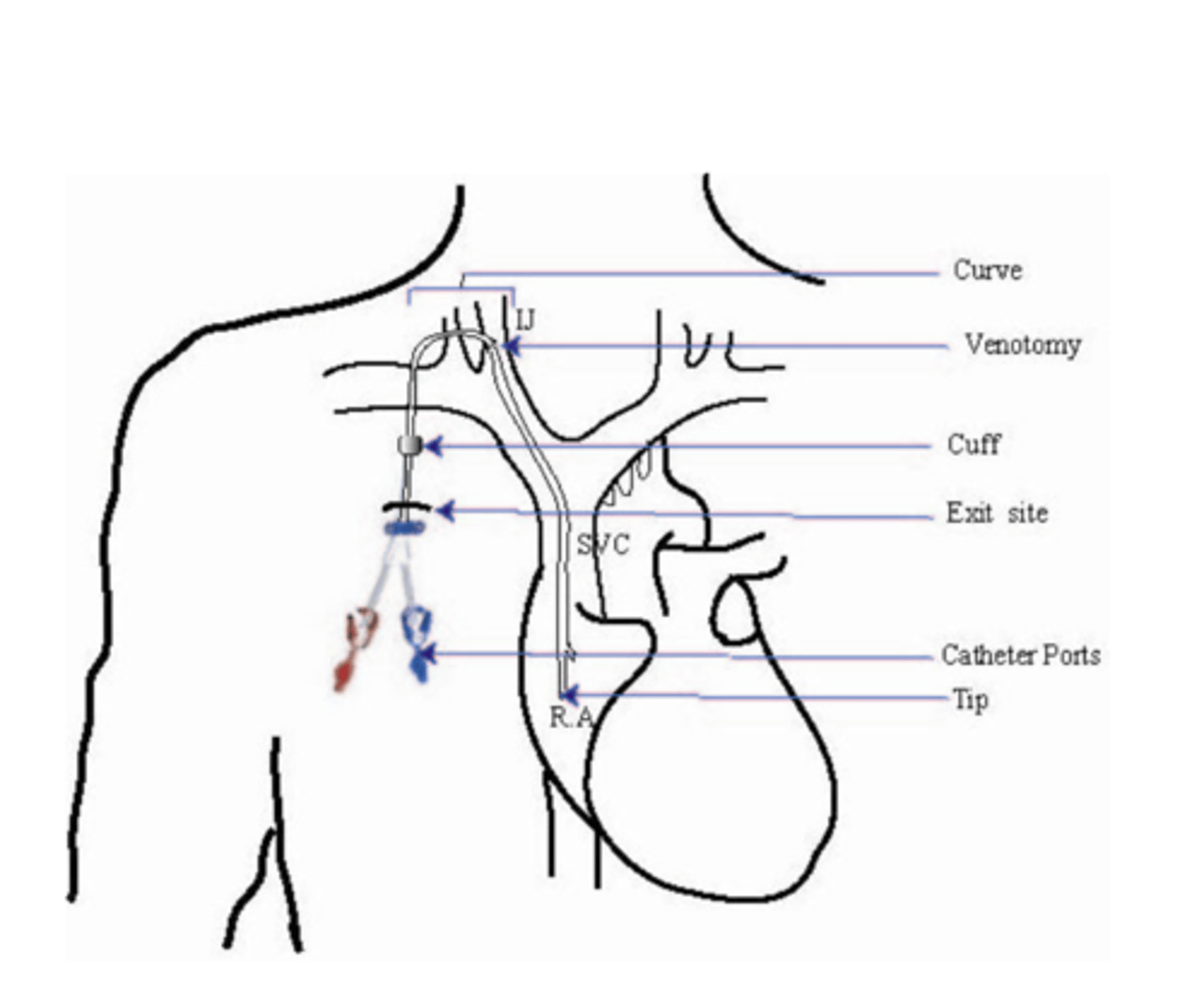
central venous catheter (CVC)
direct access to heart "central line"
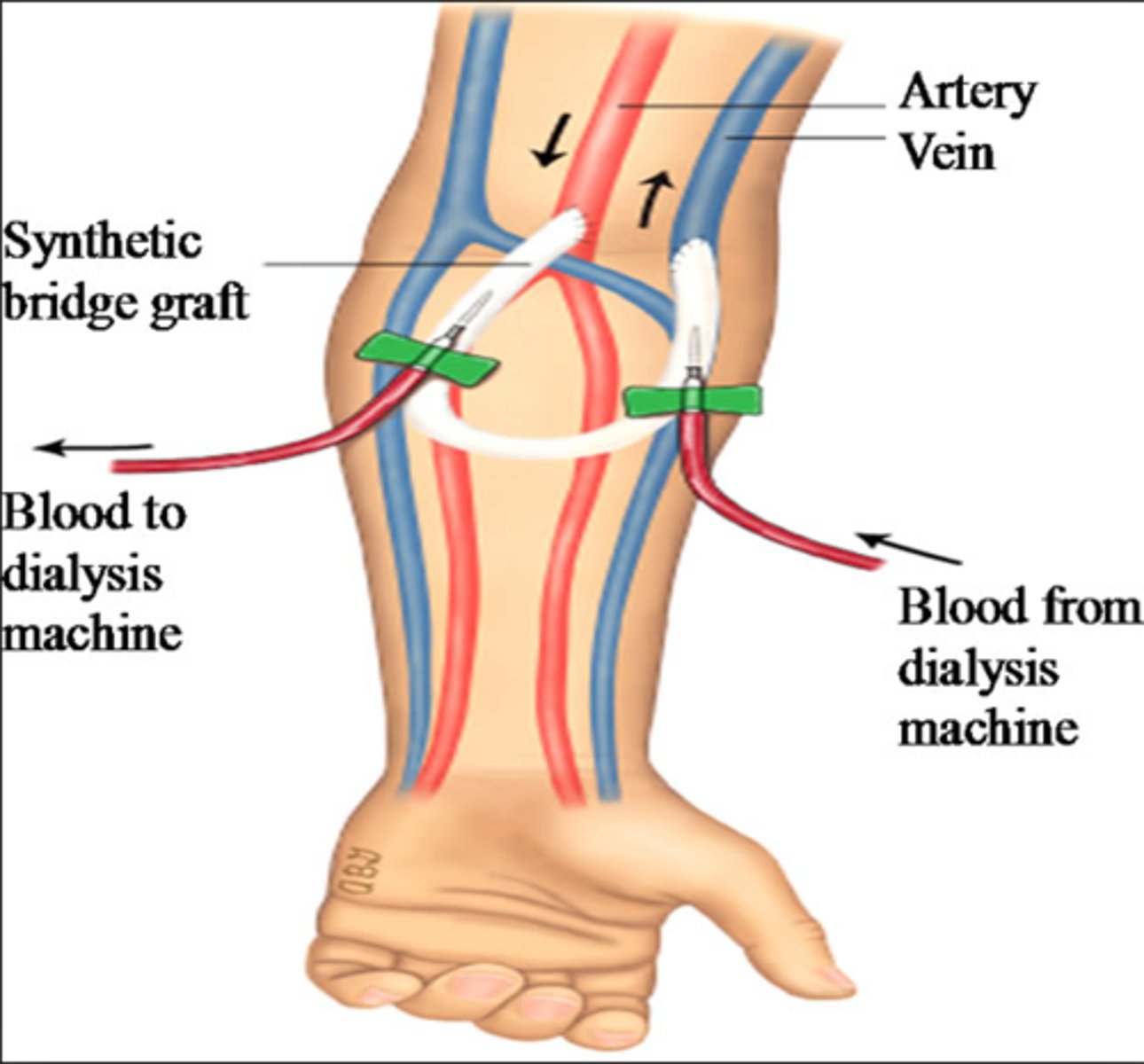
arteriovenous graft (AVG)
a piece of artificial vessel created as an access; one end is connected to an artery and the other to a vein
Limitations:
- shorter lifespan (<5 years)
- HIGH thrombosis rate
- HIGH infection rate
Advantages:
-short maturation period (2 weeks)
-easier cannulation
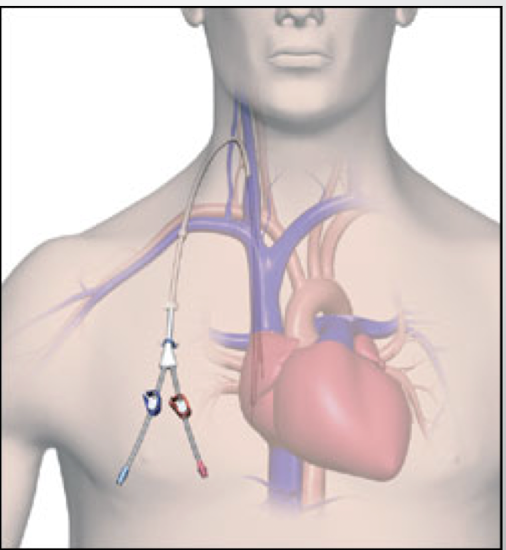
central venous catheter (CVC)
Placed as temporary (non-cuffed - lasts days) or long-term (cuffed, tunnel direct catheter - lasts weeks-months)
→typically older patients, last resort option
Location:
- internal jugular vein is preferred site (over subclavian vein)
Limitations
- HIGH risk thrombosis
- HIGH risk for infection (serious heart)
-recirculation
-decreased flow rate on hemodialysis
-no showers (sponge bath only)
Advantages:
- hemodialysis can be initiated immediately
choice
_____ of vascular access
1. Demographics/co-morbidities
2. Time of need (emergent vs planned)
3. Surgeon preference
4. Vein mapping / vessel quality
complications
______ of vascular access
1. Thrombosis
2. Stenosis
3. Infection
4. Aneurysm/Pseudoaneurysm
5. Primary non-function (fail for fistula to mature)
cardiovascular disease
What is the most common complication of CKD?
*coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular diagnosis, peripheral vascular diagnosis, CHF
Other Complications
- Anemia
- Fluid overload
- Bone ds, altered mineral metabolism
- Neuropathy
- hypertension
- Malnutrition
anemia
______ is present in the majority of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients
Causes
→insufficient production of erythropoietin (EPO) by the kidneys
→iron deficiency, blood loss & chronic inflammation
bone mineral disease (BMD)
occurs when kidneys damaged by CKD cannot filter blood and regulate hormones (calcium/phosphorus) appropriately
→hormone levels and levels of minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus become imbalanced, leading to damage
→Abnormal calcium-phosphorus metabolism may also lead to calciphylaxis or extraosseous calcification of soft tissue & vascular tissue
calcitriol
active form of vitamin D (normally converted by kidneys)
→controls calcium absorption in the gut, decreased PTH synthesis, aids in calcification of osteoid tissue (bone formation)
bone mineral disease
Hyperphosphatemia/Hypocalcemia
1. Dietary phosphate restriction
2. Phosphate Binders
- Tums
- Phoslo
- Velphoro
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
1. Vitamin D analogs (Calcitriol)
2. Calcinmimetics
Calciphylaxis (extraosseous calcification of soft tissue which leads to skin necrosis)
diet restrictions
Dialysis patient _______:
- Potassium (fruits & veggies)
- Phosphorus (dairy, nuts, processed foods)
- Sodium (meats, fast food, processed foods)
- Fluids (limit to 1L/day)
Recommendation
- Protein (to maintain albumin levels): 60-80g/day, protein drinks and bars