Physics Gcse Aqa Higher
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Energy unit
Joules (J)
Weight unit
Newtons (N)
Gravitational field strength (on Earth)
9.8 N/kg
Energy stores
thermal, kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, electrostatic, magnetic, nuclear, chemical
Energy transfers
heat, mechanical, electrical, light (radiation), sound (radiation)
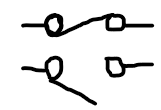
switch
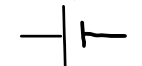
cell
converts chemical energy into electrical energy to provide power for the circuit
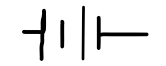
battery
two or more cells joined together that provide energy for the circuit
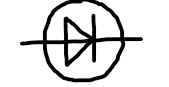
diode
allows current to flow one direction, but not the other

resistor
increases the resistance of a circuit
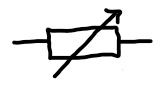
variable resistor
allows you to adjust the resistance of a circuit
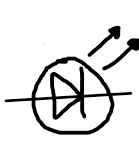
LED
a diode that converts electrical energy into light
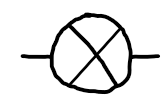
lamp
converts electrical energy into light and heat

fuse
breaks the circuit when current becomes too high, for safety reasons

voltmeter
measures the potential difference

ammeter
measures the current
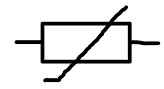
thermistor
a resistor that changes its resistance based on the temperature
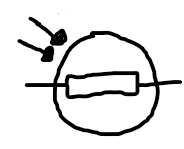
LDR
a resistor that increases its resistance as light intensity decreases, and vice versa
charge
the electrical property of everything
charge can be positive if there are more protons, or negative if there are more electrons
the greater the difference between the number of protons and electrons, the greater the charge
coulombs
current
the flow of electric charge (usually carried by free electrons)
amperes (how many coulombs of charge pass through a specific point every second)
potential difference
the difference between the electrical potential energy of two points in a circuit
pushes the current along the circuit
volts (joules per coulomb)
resistance
opposition to the electric current
added by every component of a circuit
ohms
series circuit
current is the same everywhere
potential difference is different in each component, depending on the resistance of the component
the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances of each component
parallel circuit
the total current is the sum of the individual currents of each branch
the potential difference is the same across different branches
the total resistance is always less than the resistance of the branch with the least resistance
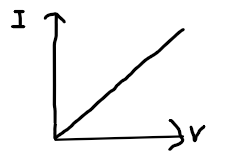
resistor

filament bulb
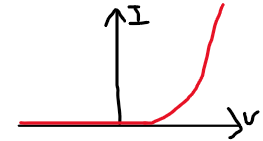
Diode & LED
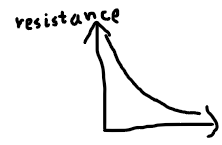
LDR (x axis light intensity)
thermistor (x axis temperature)
power unit
Watts