Coordination chemistry (Inorganic semester 2)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the Hard Soft Acid Base (HSAB) theory?
When hard acids prefer to associate with hard bases
Soft acids prefer to associate with soft bases
What are some properties of hard acids (metals) and provide examples
Small, highly charged metal cations
Low polarisability
Good sigma-acids
High oxidation states
Examples = H+, Li+, Na+ ,CO3+, Cr3+, Sc3+
What are the properties of hard bases (ligands) and provide examples
High electronegativity
Low polarizability
Poor pi acids (No vacant pi-acceptor orbitals) so often pi-bases
Not easily oxidised
Examples = Amines and ammonia, O- donors (H2O,OH-)
F-
What are the properties of soft acids (metals) and provide examples
Large, zero or low charge metal atoms or cations
High polarizability
Good sigma-bases
Examples = Ru, Os, Rh, Pd, Hg
What are the properties of soft bases (ligands) and provide examples
Low electronegativity
High polarizability
Good pi-acids of d-electrons
Easily oxidised
Examples = Phosphine (P), As, S, Se, Alkyls,alkenes, CO, and Se donors
How can hard-soft characters be thought of?
In terms of molecular or atomic polarisabilities
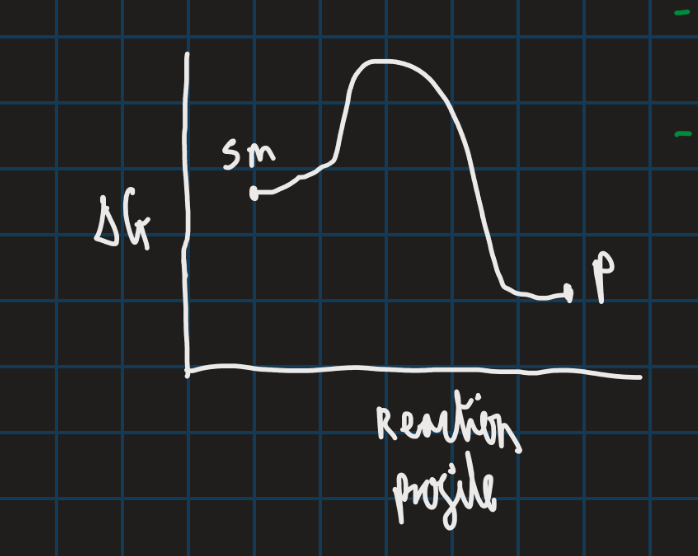
What is the equation for working out induced dipole moment (mu)?
Mu = Induced dipole moment
E = Electric field strength
Alpha = Polarisability
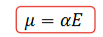
What are the units for polarisability?
J-1 C2 m2
Do soft donors / acceptors have high polarizability (alpha) values?
Yes e.g = S, PbII
Do hard donor / acceptors have high polarizability (alpha) values?
No, have low values e.g = F- and Co3+
How is sulfur have a high polarizability value?
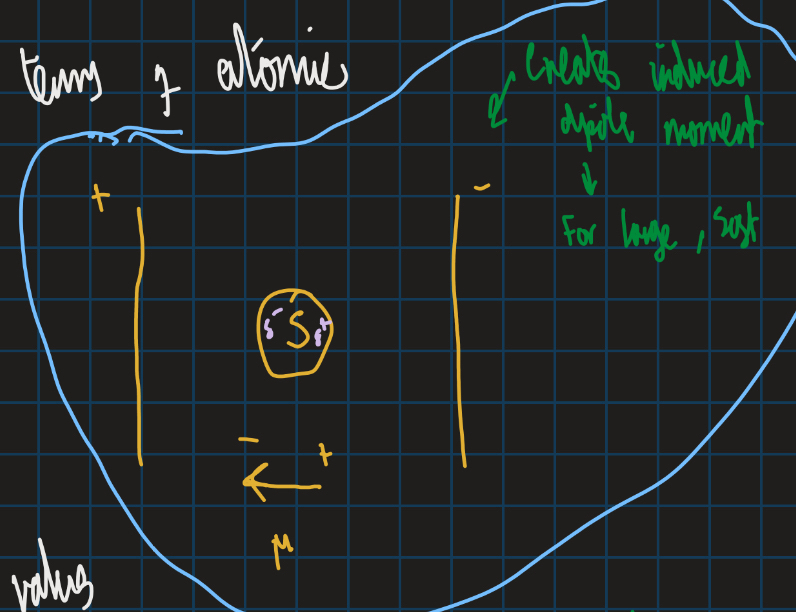
How does fluorine have a low polarizability value?
What’s the difference between thermodynamics and kinetics?
Kinetics focuses on rate of reaction and factors that influence it like temp, conc and catalysts
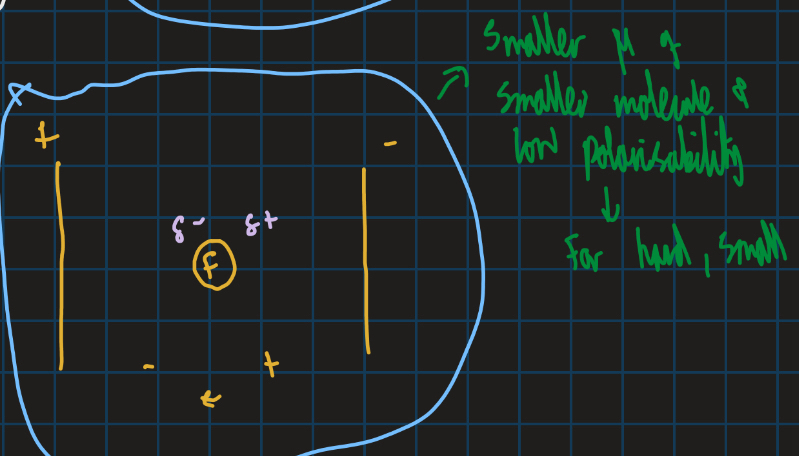
Thermodynamics deals with energy changes that occur during a reaction and the equilibrium state it reaches (diagram below shows reaction profile of thermodynamics)
How is thermodynamics represented as a letter?
K (UPPER CASE)
How is kinetics represented as a letter?
k (lower case)
What are labile complexes?
Complexes that exchanges ligands rapidly
What are inert complexes?
Complexes that exchanges ligands slowly
Do labile complexes have high or low LFSE values?
Low LFSE values
Do inter complexes have high or low LFSE values?
High LFSE values
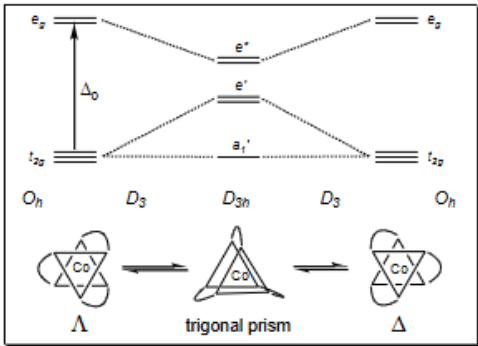
What is the Ballar twist mechanism?
Shows changes in configuration (e.g COIII has been resolved into optical isomers)
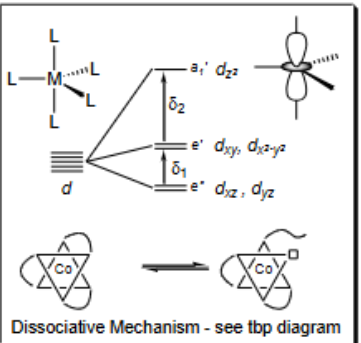
What is the dissociative mechanism?
Bond breaks to change configuration
What’s the term when metal ions are solvated in solution meaning complex formation occurs?
Ligand substitution reactions

How do you find the final thermodynamics constant Kf of this reaction (use an equation)
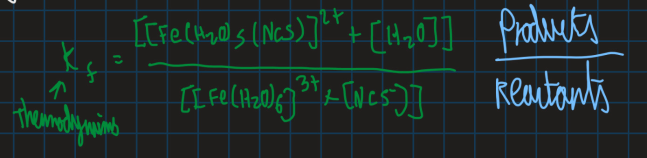
What happens if Kf > 1?
Ligand is more strongly bound than H2O
What happens if Kf < 1?
Ligand is more weakly bounded than H2O
What’s the general formula to finding thermodynamics constant if more than 1 ligand is replaced?
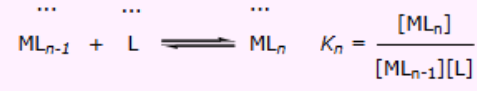
What is the thermodynamics equation to finding K1?

What is the thermodynamics equation to finding K2?
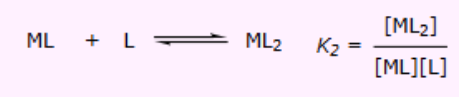
What is the thermodynamics equation to finding K3?
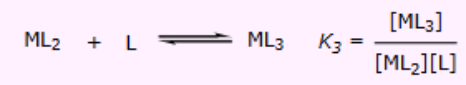
What are the stepwise formation constants?
K1 , K2 and K3 etc…
What do stepwise formation constant range up to?
~1057
What is the [H2O] value for reactions in water? (reaction of concentration of water in water)?
[H2O] remains constant ~55.5M assuming 1L of water and density of water being 1 (Use moles = mass/mr and density = mass/volume)
How do you work out overall formation constant? (use general formula)

How do you work out overall formation constant of K1 and K2?
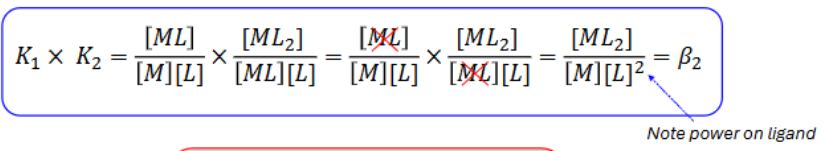
What’s the largest to smallest formation constant assuming metal ligand bond energies don’t change very much along the series? (using K1, K2, K3)?
K1 > K2 > K3 etc…
How can positions of equilibria be shifted?
Using concentration effects such as Le Chatelier’s principle and solubility effects